Abstract
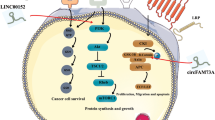
Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) have gained widespread interest and attention as vital regulators in cancer occurrence and development. Nonetheless, the functions and mechanisms of lncRNAs involved in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) are largely unknown. By analysing the data from GSE61218, we identified a novel lncRNA LINC01515 which is altered in NPC. A series of experiments were performed to examine the exact roles of LINC01515 as well as the molecular mechanisms by which LINC01515 acted in NPC. LINC01515 expression was increased in NPC and that high LINC01515 expression was associated with a worse prognosis. Functionally, depletion of LINC01515 resulted in an inhibition of cell proliferation, migration and invasion, while apoptosis was promoted. Mechanistically, LINC01515 facilitated cell division cycle associated 5 (CDCA5) expression via serving as a sponge for miR-325. And more notably, miR-325 suppressed NPC progression in vitro by targeting CDCA5. Furthermore, the anti-tumor property induced by LINC01515 knockdown was partially reversed due to the overexpression of CDCA5. Taken together, LINC01515 exerted the carcinogenic effect in NPC through regulating miR-325/CDCA5 pathway. Our findings shed light on the possibility of exploiting LINC01515 as a prognostic biomarker or therapeutic target in NPC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Balas MM, Johnson AM (2018) Exploring the mechanisms behind long noncoding RNAs and cancer. Noncoding RNA Res 3:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncrna.2018.03.001
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun Y, Ma J (2019) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 394:64–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30956-0
Chen S, Lv L, Zhan Z, Wang X, You Z, Luo X, You H (2020) Silencing of long noncoding RNA SRRM2-AS exerts suppressive effects on angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via activating MYLK-mediated cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 235:7757–7768. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29382
Dai W, Zheng H, Cheung AK, Lung ML (2016) Genetic and epigenetic landscape of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin Clin Oncol 5:16. https://doi.org/10.21037/cco.2016.03.06
Fu G, Xu Z, Chen X, Pan H, Wang Y, Jin B (2020) CDCA5 functions as a tumor promoter in bladder cancer by dysregulating mitochondria-mediated apoptosis, cell cycle regulation and PI3k/AKT/mTOR pathway activation. J Cancer 11:2408–2420. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.35372
He SW, Xu C, Li YQ, Li YQ, Zhao Y (2020) AR-induced long non-coding RNA LINC01503 facilitates proliferation and metastasis via the SFPQ-FOSL1 axis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene 39:5616–5632. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-01388-8
Lee HM, Okuda KS, González FE, Patel V (2019) Current perspectives on nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Adv Exp Med Biol 1164:11–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22254-3_2
Lin T, Zhou S, Gao H, Li Y, Sun L (2018) MicroRNA-325 is a potential biomarker and tumor regulator in human bladder cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat 17:1533033818790536. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533033818790536
Noh JH, Kim KM, McClusky WG, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2018) Cytoplasmic functions of long noncoding RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 9:e1471. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1471
Paul P, Deka H, Malakar AK, Halder B, Chakraborty S (2018) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: understanding its molecular biology at a fine scale. Eur J Cancer Prev 27:33–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000314
Rashid F, Shah A, Shan G (2016) Long non-coding RNAs in the cytoplasm. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform 14:73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2016.03.005
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y (2018) Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci 109:2093–2100. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13642
Shen A, Liu L, Chen H, Qi F, Huang Y, Lin J, Sferra TJ, Sankararaman S, Wei L, Chu J et al (2019) Cell division cycle associated 5 promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating the ERK signaling pathway. Oncogenesis 8:19. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-019-0123-5
Tang T, Yang L, Cao Y, Wang M, Zhang S, Gong Z, Xiong F, He Y, Zhou Y, Liao Q et al (2020) LncRNA AATBC regulates Pinin to promote metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Oncol 14:2251–2270. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12703
Wei KR, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Liang ZH, Li ZM, Chen WQ (2017) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China, 2013. Chin J Cancer 36:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40880-017-0257-9
Wu J, Hann SS (2018) Functions and roles of long-non-coding RNAs in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem 45:1191–1204. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487451
Xu J, Zhu C, Yu Y, Wu W, Cao J, Li Z, Dai J, Wang C, Tang Y, Zhu Q et al (2019) Systematic cancer-testis gene expression analysis identified CDCA5 as a potential therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine 46:54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.030
Zhang Z, Shen M, Zhou G (2018) Upregulation of CDCA5 promotes gastric cancer malignant progression via influencing cyclin E1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 496:482–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.046
Zhang L, Chen H, Song Y, Gu Q, Zhang L, Xie Q, Xu J, Zhang M (2020) MiR-325 promotes oxaliplatin-induced cytotoxicity against colorectal cancer through the HSPA12B/PI3K/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway. Dig Dis Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06579-7
Zheng ZQ, Li ZX, Zhou GQ, Lin L, Zhang LL, Lv JW, Huang XD (2019) Long noncoding RNA FAM225A promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma tumorigenesis and metastasis by acting as ceRNA to sponge miR-590-3p/miR-1275 and upregulate ITGB3. Cancer Res 79:4612–4626. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0799
Zheng ZQ, Li ZX, Guan JL, Liu X, Li JY, Chen Y (2020) Long non-coding RNA TINCR-mediated regulation of acetyl-CoA metabolism promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and chemoresistance. Cancer Res 80:5174–5188. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3626
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HG designed and supervised the study. DL conducted the experiments and drafted the manuscript. ZZT and SMC were responsible for collecting and analyzing the data. YGK and BKX contributed to the methodology and operated the software. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Huangshi Central Hospital and complied with the guidelines set by Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Gong, H., Tao, Z. et al. LINC01515 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression by serving as a sponge for miR-325 to up-regulate CDCA5. J Mol Histol 52, 577–587 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09969-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-09969-x