Abstract
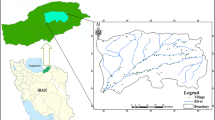
Musa Bay, the largest wetland in Iran and one of the most important Hg-polluted media, plays a significant role in the ecosystem of the area and supports many forms of life. Mercury pollution has detrimental effects on the human body and at high levels leads to the loss of microorganisms in marine ecosystems. Hence, a comprehensive assessment for selecting an effective and sustainable remediation method is crucial to restoring the ecosystem promptly. The determination of a proper and practical treatment method not only is a case-based approach, but could be challenging due to its multi-criteria decision-making nature. Considering preferred crucial factors involved in the effectiveness of remedial actions, in this study a questionnaire is designed to assess the opinion of environmental experts, stakeholders, and some occupants of the area on remedial actions based on the importance weights of criteria. Subsequently, practical remediation and management strategies ranked by hybrid FVIKOR as a multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) method. Ranking results show that dredging and stabilization could offer a promising solution for the remediation of the case study. The results of the study demonstrate that the development of MCDM methods along with effective criteria and considering the analysis of the questionnaires, could offer the best remediation strategy for a specific contaminated site.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afolayan, A. H., Ojokoh, B. A., & Adetunmbi, A. O. (2020). Performance analysis of fuzzy analytic hierarchy process multi-criteria decision support models for contractor selection. Scientific African, 9, e00471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00471
Aghabaki aloughareh, S., Betaleblouei, S., Amanipour, H., & Gerayesh, K. (2019). The investigation of Hg concentration in Musa bay sediment. Journal of Aquatic Ecology, 3(9), 143–153.
Ahmad, N., Zhu, Y., Shao, J., & Lin, H. (2020). Stakeholders’ perspective on strategies to promote contaminated site remediation and brownfield redevelopment in developing countries: Empirical evidence from Pakistan. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(13), 14614–14633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07990-3
Akcil, A., Erust, C., Ozdemiroglu, S., Fonti, V., & Beolchini, F. (2015). A review of approaches and techniques used in aquatic contaminated sediments: Metal removal and stabilization by chemical and biotechnological processes. Journal of Cleaner Production, 86, 24–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.08.009
Alsalem, M. A., Zaidan, A. A., Zaidan, B. B., Hashim, M., Albahri, O. S., Albahri, A. S., Hadi, A., & Mohammed, K. I. (2018). Systematic review of an automated multiclass detection and classification system for Acute Leukaemia in terms of evaluation and benchmarking, open challenges, issues and methodological aspects. Journal of Medical Systems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-1064-9
Alvarez-guerra, M., Canis, L., Voulvoulis, N., Viguri, J. R., & Linkov, I. (2010). Science of the Total Environment Prioritization of sediment management alternatives using stochastic multicriteria acceptability analysis. Science of the Total Environment, the, 408(20), 4354–4367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.07.016
Ayhan, M. B. (2013). A fuzzy Ahp approach for supplier selection problem: A case study in a gearmotor company. International Journal of Managing Value and Supply Chains, 4(3), 11–23. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijmvsc.2013.4302
Babadi, S., Safahieh, A., Nabavi, S. M. B., Ghanemi, K., & Taghi Ronagh, M. (2015). Assessment of mercury concentration in the water of Musa Estuary in Khuzestan Province. Iranian Water Research, 10(1), 175–179.
Balali-Mood, M., Naseri, K., Tahergorabi, Z., Khazdair, M. R., & Sadeghi, M. (2021). Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: Mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.643972
Bates, M. E., Sparrevik, M., Lichy, N. De, & Linkov, I. (2014). The Value of Information for Managing Contaminated Sediments.
Bełdowski, J., Szubska, M., Bełdowska, M., Jankowska, K., Kotlarska, E., & Graca, B. (2018). Seasonal changes of mercury speciation in the coastal sediments. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18(12), 3424–3436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-1993-4
Bera, B., Shit, P. K., Sengupta, N., Saha, S., & Bhattacharjee, S. (2022). Susceptibility of deforestation hotspots in Terai-Dooars belt of Himalayan Foothills: A comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS models. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 34(10), 8794–8806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.10.005
Boening, D. W. (2000). Ecological effects, transport, and fate of mercury: A general review. Chemosphere, 40(12), 1335–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00283-0
Cinelli, M., Gonzalez, M. A., Ford, R., McKernan, J., Corrente, S., Kadziński, M., & Słowiński, R. (2021). Supporting contaminated sites management with multiple criteria decision analysis: Demonstration of a regulation-consistent approach. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128347
Copernicus Sentinel data. (2017). Musa Bay, Iran. https://www.google.com/search?q=esa+satellite&rlz=1C1GCEA_enIR956IR956&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjxrejXlNj3AhUN3BoKHd0OAFAQ_AUoAXoECAEQAw&biw=1242&bih=597&dpr=1.1#imgrc=F0YNOJA8k68Y7M
Cornelissen, G., Elmquist Kruså, M., Breedveld, G. D., Eek, E., Oen, A. M. P., Arp, H. P. H., Raymond, C., Samuelsson, G., Hedman, J. E., Stokland, Ø., & Gunnarsson, J. S. (2011). Remediation of contaminated marine sediment using thin-layer capping with activated carbon-A field experiment in Trondheim harbor, Norway. Environmental Science and Technology, 45(14), 6110–6116. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2011397
Cukrov, N., Doumandji, N., Garnier, C., Tucaković, I., Dang, D. H., Omanović, D., & Cukrov, N. (2020). Anthropogenic mercury contamination in sediments of Krka River estuary (Croatia). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(7), 7628–7638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07475-y
Dhamodharan, A., Abinandan, S., & Aravind, U. (2019). Distribution of metal contamination and risk indices assessment of surface sediments from Cooum River, Chennai, India. International Journal of Environmental Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00222-8
Diop, M., Net, S., Howsam, M., Lencel, P., Watier, D., Grard, T., Duflos, G., Diouf, A., & Amara, R. (2017). Concentrations and potential human health risks of trace metals (Cd, Pb, Hg) and selected organic pollutants (PAHs, PCBs) in fish and seafood from the Senegalese Coast. International Journal of Environmental Research, 11(3), 349–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0032-4
Eckley, C. S., Gilmour, C. C., Janssen, S., Luxton, T. P., Randall, P. M., Whalin, L., & Austin, C. (2020). The assessment and remediation of mercury contaminated sites: A review of current approaches. Science of the Total Environment, 707, 136031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136031
Esmaili, S., Sadeghi, M., & Emtyazjoo, M. (2022). Investigation of accumulation and pollution of heavy metals (mercury, lead, nickel and vanadium) related to oil and petrochemical industries in mud and sandy sediments in the Creek of Mahshar. Iran Biological Knowledge, 16(4), 1–14.
Faghiri, I., Mirza, R., Abouali, S., & Jafari, S. (2011). Studying the quality of Musa bay sediment for Hg toxic heayv metal. MIC, Mic.
Haghnazar, H., Hudson-Edwards, K. A., Kumar, V., Pourakbar, M., Mahdavianpour, M., & Aghayani, E. (2021). Potentially toxic elements contamination in surface sediment and indigenous aquatic macrophytes of the Bahmanshir River, Iran: Appraisal of phytoremediation capability. Chemosphere, 285, 131446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131446
Haghshenas, S. M. (2020). An exploratory view of water quality and sediment characteristics in Musa Estuary, the Persian Gulf. ArXiv.
Havranek, T. J. (2019). Multi-criteria decision analysis for environmental remediation: Benefits, challenges, and recommended practices. Remediation, 29(2), 93–108. https://doi.org/10.1002/rem.21589
Hsu-Kim, H., Eckley, C. S., Achá, D., Feng, X., Gilmour, C. C., Jonsson, S., & Mitchell, C. P. J. (2018). Challenges and opportunities for managing aquatic mercury pollution in altered landscapes. Ambio, 47(2), 141–169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13280-017-1006-7
Jersak, J., Göransson, G., Ohlsson, Y., Larsson, L., Flyhammar, P., & Lindh, P. (2016). In-situ capping of contaminated sediments. Sediment remediation technologies: A general overview.
Jersak, J., Göransson, G., Ohlsson, Y., Larsson, L., Flyhammar, P., & Lindh, P. (2018). In-situ capping of contaminated sediments. In Swedish Geotechnical Institute.
Kiker, G. A., & Seager, T. P. (2004). Multi-criteria decision analysis: A framework for managing contaminated sediments. Strategic Management of Marine Ecosystems. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3198-X_15
Kim, J. H., & Ahn, B. S. (2019). Extended VIKOR method using incomplete criteria weights. Expert Systems with Applications, 126, 124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.02.019
Knox, A. S., & Paller, M. H. (2013). Contaminants in sediments - Remediation and management. E3S Web of Conferences, 1, 3–6. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/201301002003
Kumar, S., & Gopal, A. (2021). Fuzzy TOPSIS and fuzzy VIKOR in selecting green suppliers for sponge iron and steel manufacturing. Soft Computing, 25(8), 6505–6525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-05644-1
Kumari, S., Amit, Jamwal, R., Mishra, N., & Singh, D. K. (2020). Recent developments in environmental mercury bioremediation and its toxicity: A review. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 13, 100283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100283
Kwasigroch, U., Bełdowska, M., Jędruch, A., & Łukawska-Matuszewska, K. (2021). Distribution and bioavailability of mercury in the surface sediments of the Baltic Sea. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(27), 35690–35708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13023-4
Labianca, C., De Gisi, S., Todaro, F., Notarnicola, M., & Bortone, I. (2022). A review of the in-situ capping amendments and modeling approaches for the remediation of contaminated marine sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 806, 151257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151257
de Lacerda, L. D., & Malm, O. (2008). Mercury Contamination in aquatic ecosystems : an analysis of the Critical areas. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:111379617
Lee, G., Suonan, Z., Kim, S. H., Hwang, D. W., & Lee, K. S. (2019). Heavy metal accumulation and phytoremediation potential by transplants of the seagrass Zostera marina in the polluted bay systems. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 149, 110509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110509
Li, Y. (2013). Environmental contamination and risk assessment of mercury from a historic mercury mine located in southwestern China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 35(1), 27–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-012-9470-2
Libralato, G., Minetto, D., Lofrano, G., Guida, M., Carotenuto, M., Aliberti, F., Conte, B., & Notarnicola, M. (2018). Toxicity assessment within the application of in situ contaminated sediment remediation technologies: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 621, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.229
Linkov, I., Satterstrom, F. K., Kiker, G., Seager, T. P., Bridges, T., Gardner, K. H., Rogers, S. H., Belluck, D. A., & Meyer, A. (2006). Multicriteria decision analysis: A comprehensive decision approach for management of contaminated sediments. Risk Analysis, 26(1), 61–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2006.00713.x
Liu, Q., Sheng, Y., & Liu, X. (2021). Efficacy of in situ active capping Cd highly contaminated sediments with nano-Fe2O3 modified biochar. Environmental Pollution, 290, 118134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118134
Liu, Yan, Eckert, C. M., & Earl, C. (2020a). A review of fuzzy AHP methods for decision-making with subjective judgements. In Expert Systems with Applications (Vol. 161). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113738
Liu, Y., Tang, Y., Zhong, G., & Zeng, H. (2019). A comparison study on heavy metal/metalloid stabilization in Maozhou River sediment by five types of amendments. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(12), 3922–3933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02310-w
Liu, Z., Chen, B., Wang, L., Urbanovich, O., Nagorskaya, L., Li, X., & Tang, L. (2020b). A review on phytoremediation of mercury contaminated soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 400, 123138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123138
Lofrano, G., Libralato, G., Minetto, D., De Gisi, S., Todaro, F., Conte, B., Calabrò, D., Quatraro, L., & Notarnicola, M. (2017). In situ remediation of contaminated marinesediment: An overview. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(6), 5189–5206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8281-x
Maghsoudi Moud, F., Abbaszadeh Shahri, A., van Ruitenbeek, F., Hewson, R., & van der Meijde, M. (2022). Evaluation of the modified AHP-VIKOR for mapping and ranking copper mineralized areas, a case study from the Kerman metallogenic belt, SE Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-022-10913-w
Manap, N., & Voulvoulis, N. (2014). Risk-based decision-making framework for the selection of sediment dredging option. Science of the Total Environment, 496, 607–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.009
Marcomini, A., W. Suter, G., & Critto, A. (2009). Decision Support Systems for Risk-Based Management of Contaminated Sites. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-09722-0.pdf?pdf=button
Mardani, A., Zavadskas, E. K., Govindan, K., Senin, A. A., & Jusoh, A. (2016). VIKOR technique: A systematic review of the state of the art literature on methodologies and applications. Sustainability (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010037
McNally, A. D., Fitzpatrick, A. G., Harrison, D., Busey, A., & Apitz, S. E. (2020). Tiered approach to sustainability analysis in sediment remediation decision making. Remediation, 31(1), 29–44. https://doi.org/10.1002/rem.21661
McNally, A. D., Fitzpatrick, A. G., Mirchandani, S., Salmon, M., & Edwards, D. A. (2018). CERCLA-linked environmental impact and benefit analysis: Evaluating remedial alternatives for the Portland Harbor Superfund Site, Portland, Oregon, USA. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 14(1), 22–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.2000
Micheline, G., Rachida, C., Céline, M., Gaby, K., Rachid, A., & Petru, J. (2019). Levels of Pb, Cd, Hg and As in fishery products from the Eastern Mediterranean and human health risk assessment due to their consumption. International Journal of Environmental Research, 13(3), 443–455. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00185-w
Nabavi, S. M. B., Parsa, Y., Hosseini, M., & Nabavi, S. N. (2015). Heavy metal concentration in sediment from North of Persian Gulf. World Applied Sciences Journal, 29(6), 792–795. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2014.29.06.2074
NAVFAC. (2015). Technical Report TR-NAVFAC EXWC-EV-1515- Sustainable Sediment Remediation. In Naval facilities engineering commands (Issue September).
Nenad, M., & Zoran, A. (2017). Multi-Criteria Decision Making Methods: Comparative Analysis of PROMETHEE and VIKOR. October, 284–287. http://www.iim.ftn.uns.ac.rs/is17IS’17
Nishimura, H., & Kumagai, M. (1983). Mercury pollution of fishes in Minamata Bay and surrounding water: Analysis of pathway of mercury. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 20(4), 401–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208514
Niu, Z., Cao, Y., Zhao, W., & Li, R. (2019). Distribution and assessment of mercury (Hg) in surface sediments of Futian mangrove forest, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41(1), 125–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0151-7
O’Brien, R. M., Phelan, T. J., Smith, N. M., & Smits, K. M. (2021). Remediation in developing countries: A review of previously implemented projects and analysis of stakeholder participation efforts. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 51(12), 1259–1280. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1755203
Opricovic, S. (2004). Compromise solution by MCDM methods : A comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. 156, 445–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(03)00020-1
Public Services and Procurement Canada. (2016). Fact sheet: Dredging and Off-site Disposal (Ex situ)— Sediments. https://gost.tpsgc-pwgsc.gc.ca/tfs.aspx?ID=68&lang=eng
Putra, M. S. D., Andryana, S., Fauziah, & Gunaryati, A. (2018). Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process Method to Determine the Quality of Gemstones. Advances in Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 9094380. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9094380
Quintana, G., Mirlean, N., Costa, L., & Johannesson, K. (2020). Mercury distributions in sediments of an estuary subject to anthropogenic hydrodynamic alterations (Patos Estuary, Southern Brazil). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8232-3
Raj, D., & Maiti, S. K. (2019). Sources, toxicity, and remediation of mercury: An essence review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7743-2
Rezania, S., Park, J., Rupani, P. F., Darajeh, N., Xu, X., & Shahrokhishahraki, R. (2019). Phytoremediation potential and control of Phragmites australis as a green phytomass: An overview. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(8), 7428–7441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04300-4
Salimi, A. H., Noori, A., Bonakdari, H., Samakosh, J. M., Sharifi, E., Hassanvand, M., Gharabaghi, B., & Agharazi, M. (2020). Exploring the role of advertising types on improving the water consumption behavior: An application of integrated fuzzy AHP and fuzzy VIKOR method. Sustainability (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12031232
Salmak, S., Alishirazi, M., & Shahriari, T. (2022). Offering the best remediation method for cadmium contaminated sediment using hybrid FAHP and FVIKOR models. Journal of Environmental Studies, 48(3), 419–437. https://doi.org/10.22059/JES.2022.348087.1008355
Sarasiab, A. R., Hosseini, M., & Tadi Beni, F. (2014). Mercury and methyl mercury concentration in sediment, benthic, Barbus Grypus and pelagic, Barbus esocinus fish species, from Musa estuary, Iran. International Aquatic Research, 6(3), 147–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40071-014-0075-5
Sarkar, B., Tsang, D. C. W., Song, H., Ding, S., & Vithanage, M. (2019). Technological innovation for soil/sediment remediation. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(12), 3881–3882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-019-02503-3
Seelen, E. A., Massey, G. M., & Mason, R. P. (2018). Role of sediment resuspension on estuarine suspended particulate mercury dynamics. Environmental Science and Technology, 52(14), 7736–7744. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01920
Smolders, A. J. P., Lock, R. A. C., Van der Velde, G., Medina Hoyos, R. I., & Roelofs, J. G. M. (2003). Effects of mining activities on heavy metal concentrations in water, sediment, and macroinvertebrates in different reaches of the Pilcomayo River, South America. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 44(3), 314–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-002-2042-1
Soltanian, M., Gitipour, S., & Baghdadi, M. (2022). Ecological and human health risk assessment of sites with heavy metal contaminated soils in Isfahan metropolitan. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 19(12), 12357–12368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04481-5
Song, B., Zeng, G., Gong, J., Liang, J., Xu, P., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Cheng, M., Liu, Y., Ye, S., Yi, H., & Ren, X. (2017). Evaluation methods for assessing effectiveness of in situ remediation of soil and sediment contaminated with organic pollutants and heavy metals. Environment International, 105(May), 43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2017.05.001
Sparrevik, M., Barton, D. N., Bates, M. E., & Linkov, I. (2012). Use of stochastic multi-criteria decision analysis to support sustainable management of contaminated sediments.
Sun, W., Cheng, K., Sun, K. Y., & Ma, X. (2021). Microbially mediated remediation of contaminated sediments by heavy metals: A critical review. Current Pollution Reports, 7(2), 201–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40726-021-00175-7
Taherdoost, H., & Madanchian, M. (2023). Multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) methods and concepts. Encyclopedia, 3(1), 77–87. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia3010006
Ayağ, Z., & Özdem[idot]r, R. G. (2007). An analytic network process-based approach to concept evaluation in a new product development environment. Journal of Engineering Design, 18(3), 209–226. https://doi.org/10.1080/09544820600752740
Tehrani, G. M., Hashim, R., Sulaiman, A. H., Sany, B. T., Salleh, A., Jazani, R. K., Savari, A., & Barandoust, R. F. (2013). Distribution of total petroleum hydrocarbons and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in musa bay sediments (Northwest of the Persian Gulf). Environment Protection Engineering, 39(1), 115–128. https://doi.org/10.5277/EPE130109
Tehrani, M. G., Hshim, R., Sulaiman, A. H., Belin, S., Sany, T., Jazani, R. K., & Tehrani, Z. M. (2012). Assessment of contamination by petroleum hydrocarbons in sediments of Musa Bay, Northwest of the Persian Gulf-Iran. International Conference on Environment, Energy and Biotechnology IPCBEE, 33, 75–80.
The Interstate Technology & Regulatory Council, C. S. T. (2014). Contaminated Sediments Remediation (Issue August).
Thomé, A., Reginatto, C., Vanzetto, G., & Braun, A. B. (2019). Remediation technologies applied in polluted soils: New perspectives in this field. Environmental Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-2221-1_11
Ting, Y., & Hsi, H. (2019). Iron sulfide minerals as potential active capping materials for mercury-contaminated sediment remediation : A minireview. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061747
Tiodar, E. D., Văcar, C. L., & Podar, D. (2021). Phytoremediation and microorganisms-assisted phytoremediation of mercury-contaminated soils: Challenges and perspectives. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(5), 1–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052435
Todaro, F., Barjoveanu, G., Gisi, S. D., Teodosiu, C., & Notarnicola, M. (2020). Sustainability assessment of reactive capping alternatives for the remediation of contaminated marine sediments. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124946
U.S. EPA. (2006). 1996 Protocol to the convention on the prevention of marine pollution by dumping of wastes and other matter, 1972 (Vol. 1972).
U.S. EPA. (2021). Health Effects of Exposures to Mercury.
Wang, C. N., Nguyen, N. A. T., Dang, T. T., & Lu, C. M. (2021). A compromised decision-making approach to third-party logistics selection in sustainable supply chain using fuzzy ahp and fuzzy vikor methods. Mathematics. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9080886
Wang, T. (2006). Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis by Using Fuzzy VIKOR.
Who. (2017). Mercury and health.
Wibawa, A. P., Fauzi, J. A., Isbiyantoro, S., Irsyada, R., & Hernández, L. (2019). VIKOR multi-criteria decision making with AHP reliable weighting for article acceptance recommendation. International Journal of Advances in Intelligent Informatics, 5(2), 160–168. https://doi.org/10.26555/ijain.v5i2.172
Wood, J. L., Tang, C., & Franks, A. E. (2016). Microbial associated plant growth and heavy metal accumulation to improve phytoextraction of contaminated soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 103, 131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.08.021
Xu, Q., Wu, B., & Chai, X. (2022). In situ remediation technology for heavy metal contaminated sediment: A review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416767
Xue, W., Cao, S., Zhu, J., Li, W., Li, J., Huang, D., Wang, R., & Gao, Y. (2022). Stabilization of cadmium in contaminated sediment based on a nanoremediation strategy: Environmental impacts and mechanisms. Chemosphere, 287, 132363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132363
Zhang, C., Zhu, M., Zeng, G., Yu, Z., Cui, F., Yang, Z., & Shen, L. (2016). Active capping technology: a new environmental remediation of contaminated sediment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(5), 4370–4386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6076-8
Zhang, M., Wang, X., Yang, L., & Chu, Y. (2019). Research on progress in combined remediation technologies of heavy metal polluted sediment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16245098
Zhang, Y., Labianca, C., Chen, L., De Gisi, S., Notarnicola, M., Guo, B., Sun, J., Ding, S., & Wang, L. (2021). Sustainable ex-situ remediation of contaminated sediment: A review. Environmental Pollution, 287, 117333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117333
Zheng, Z. J., Lin, M. Y., Chiueh, P. T., & Lo, S. L. (2019). Framework for determining optimal strategy for sustainable remediation of contaminated sediment: A case study in Northern Taiwan. Science of the Total Environment, 654, 822–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.152
Zoveidadianpour, Z., Doustshenas, B., Alava, J. J., Savari, A., & Karimi Organi, F. (2023). Environmental and human health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Musa estuary (northwest of Persian Gulf), Iran. Journal of Sea Research. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2023.102335
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by MA, and SS. The original draft of the manuscript was written by SS and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alishirazi, M., Salmak, S. & Gitipour, S. A comprehensive assessment to offer optimized remediation method for mercury contamination in Musa Bay by using hybrid Fuzzy AHP-VIKOR approach. Environ Geochem Health 45, 8685–8707 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01745-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01745-y