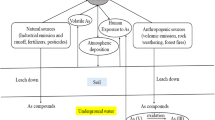
Abstract
Mercury (Hg) is a pollutant that poses a global threat, and it was listed as one of the ten leading ‘chemicals of concern’ by the World Health Organization in 2017. The review aims to summarize the sources of Hg, its combined effects on the ecosystem, and its remediation in the environment. The flow of Hg from coal to fly ash (FA), soil, and plants has become a serious concern. Hg chemically binds to sulphur-containing components in coal during coal formation. Coal combustion in thermal power plants is the major anthropogenic source of Hg in the environment. Hg is taken up by plant roots from contaminated soil and transferred to the stem and aerial parts. Through bioaccumulation in the plant system, Hg moves into the food chain, resulting in potential health and ecological risks. The world average Hg concentrations reported in coal and FA are 0.01–1 and 0.62 mg/kg, respectively. The mass of Hg accumulated globally in the soil is estimated to be 250–1000 Gg. Several techniques have been applied to remove or minimize elevated levels of Hg from FA, soil, and water (soil washing, selective catalytic reduction, wet flue gas desulphurization, stabilization, adsorption, thermal treatment, electro-remediation, and phytoremediation). Adsorbents such as activated carbon and carbon nanotubes have been used for Hg removal. The application of phytoremediation techniques has been proven as a promising approach in the removal of Hg from contaminated soil. Plant species such as Brassica juncea are potential candidates for Hg removal from soil.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, P., Mittal, A., Kumar, M., & Tripathi, S. K. (2008). Mercury exposure in Indian environment due to coal fired thermal power plants and existing legislations. International Journal of Forensic Medicine and Pathology, 1, 41.
Ali, M. H., & Al-Qahtani, K. M. (2012). Assessment of some heavy metals in vegetables, cereals and fruits in Saudi Arabian markets. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research, 38, 31–37.
Alloway, B. J. (2013). Heavy metals in soils: trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability, vol 22. Dordrecht: Springer.
Anbia, M., & Dehghan, R. (2014). Functionalized CMK-3 mesoporous carbon with 2-amino-5-mercapto-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole for Hg (II) removal from aqueous media. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 26, 1541–1548.
Ansari, F. A., Gupta, A. K., & Yunus, M. (2011). Fly-ash from coal-fed thermal power plants: Bulk utilization in horticulture–a long-term risk management option. International Journal of Environmental Research, 5, 101–108.
Arbestain, M. C., Rodriguez-Lado, L., Bao, M., & Macias, F. (2009). Assessment of mercury-polluted soils adjacent to an old mercury-fulminate production plant. Applied and Environmental Soil Science. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/387419.
ASTM (2006). ASTM D6414: standard test methods for total mercury in coal and coal combustion residues by acid extraction or wet oxidation/cold vapour atomic absorption.
ATSDR. (1999). Toxicological Profile for mercury. Atlanta: US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
Azevedo, R., & Rodriguez, E. (2012). Phytotoxicity of mercury in plants: a review. Journal of Botany, 2012, 1–6.
Bai, X., Li, W., Wang, Y., & Ding, H. (2017). The distribution and occurrence of mercury in Chinese coals. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 4, 172–182.
Bailey, E. A., Gray, J. E., & Theodorakos, P. M. (2002). Mercury in vegetation and soils at abandoned mercury mines in southwestern Alaska, USA. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2, 275–285.
Bailon, M. X., David, A. S., Park, Y., Kim, E., & Hong, Y. (2018). Total mercury, methyl mercury, and heavy metal concentrations in Hyeongsan River and its tributaries in Pohang city, South Korea. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 274.
Beckers, F., & Rinklebe, J. (2017). Cycling of mercury in the environment: Sources, fate, and human health implications: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 47, 693–794.
Belkin, H. E., Tewalt, S. J., Hower, J. C., Stucker, J. D., & O'Keefe, J. M. K. (2009). Geochemistry and petrology of selected coal samples from Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, and Papua, Indonesia. International Journal of Coal Geology, 77, 260–268.
Biester, H., Müller, G., & Schöler, H. F. (2002). Binding and mobility of mercury in soils contaminated by emissions from chlor-alkali plants. Science of the Total Environment, 284, 191–203.
Boszke, L., Kowalski, A., Astel, A., Barański, A., Gworek, B., & Siepak, J. (2008). Mercury mobility and bioavailability in soil from contaminated area. Environmental Geology, 55, 1075–1087.
Bradley, M., Barst, B., & Basu, N. (2017). A review of mercury bioavailability in humans and fish. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14, 169.
Brigden, K., & Santillo, D. (2002). Heavy metal and metalloid content of fly ash collected from the Sual, Mauban and Masinloc coal-fired power plants in the Philippines, 2002. Greenpeace Araştırma Laboratuarı Teknik Notu, 7, 2002.
Burmistrz, P., Kogut, K., Marczak, M., & Zwoździak, J. (2016). Lignites and subbituminous coals combustion in Polish power plants as a source of anthropogenic mercury emission. Fuel Processing Technology, 152, 250–258.
Cassina, L., Tassi, E., Pedron, F., Petruzzelli, G., Ambrosini, P., & Barbafieri, M. (2012). Using a plant hormone and a thioligand to improve phytoremediation of Hg-contaminated soil from a petrochemical plant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 231, 36–42.
Chen, X., Xia, X., Wu, S., Wang, F., & Guo, X. (2010). Mercury in urban soils with various types of land use in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution, 158, 48–54.
Cheng, Z., Wang, H. S., Du, J., Sthiannopkao, S., Xing, G. H., Kim, K. W., Yasin, M. S. M., Hashim, J. H., & Wong, M. H. (2013). Dietary exposure and risk assessment of mercury via total diet study in Cambodia. Chemosphere, 92, 143–149.
Csuros, M., & Csuros, C. (2016). Environmental sampling and analysis for metals. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420032345.
Dabrowski, J. M., Ashton, P. J., Murray, K., Leaner, J. J., & Mason, R. P. (2008). Anthropogenic mercury emissions in South Africa: Coal combustion in power plants. Atmospheric Environment, 42, 6620–6626.
Dahl, O., Pöykiö, R., & Nurmesniemi, H. (2008). Concentrations of heavy metals in fly ash from a coal-fired power plant with respect to the new Finnish limit values. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 10, 87–92.
Dai, S., Ren, D., Chou, C. L., Finkelman, R. B., Seredin, V. V., & Zhou, Y. (2012). Geochemistry of trace elements in Chinese coals: a review of abundances, genetic types, impacts on human health, and industrial utilization. International Journal of Coal Geology, 94, 3–21.
Deng, S., Zhang, C., Liu, Y., Cao, Q., Xu, Y. Y., Wang, H. L., & Zhang, F. (2014). A full-scale field study on chlorine emission of pulverized coal-fired power plants in China. Research of Environmental Sciences, 27, 127–133.
Dermont, G., Bergeron, M., Mercier, G., & Richer-Laflèche, M. (2008). Soil washing for metal removal: a review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 152, 1–31.
Dołęgowska, S., & Michalik, A. (2019). The use of a geostatistical model supported by multivariate analysis to assess the spatial distribution of mercury in soils from historical mining areas: Karczówka Mt., Miedzianka Mt., and Rudki (south-central Poland). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 302.
Donatello, S., Fernández-Jiménez, A., & Palomo, A. (2012). An assessment of Mercury immobilisation in alkali activated fly ash (AAFA) cements. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 213, 207–215.
Dragović, S., Ćujić, M., Slavković-Beškoski, L., Gajić, B., Bajat, B., Kilibarda, M., & Onjia, A. (2013). Trace element distribution in surface soils from a coal burning power production area: A case study from the largest power plant site in Serbia. Catena, 104, 288–296.
Dziok, T., Strugała, A., Rozwadowski, A., & Macherzyński, M. (2015). Studies of the correlation between mercury content and the content of various forms of sulfur in Polish hard coals. Fuel, 159, 206–213.
EA. (2009). Contaminants in soil: updated collation of toxicological data and intake values for humans. Mercury. Science Report SC050021/SR TOX7. Bristol: Environment Agency.
El Mahmoud-Hamed, M. S., Montesdeoca-Esponda, S., Santana-Del Pino, A., Zamel, M. L., Brahim, M., T’feil, H., Santana-Rodiguez, J. J., Sidoumou, Z., & Sidi’Ahmed-Kankou, M. (2019). Distribution and health risk assessment of cadmium, lead, and mercury in freshwater fish from the right bank of Senegal River in Mauritania. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 493.
Fernández-Martínez, R., Loredo, J., Ordóñez, A., & Rucandio, M. I. (2005). Distribution and mobility of mercury in soils from an old mining area in Mieres, Asturias (Spain). Science of The Total Environment, 346, 200–212.
Fernández-Martínez, R., Larios, R., Gómez-Pinilla, I., Gómez-Mancebo, B., López-Andrés, S., Loredo, J., Ordóñez, A., & Rucandio, I. (2015). Mercury accumulation and speciation in plants and soils from abandoned cinnabar mines. Geoderma, 253, 30–38.
Figueira, P., Lopes, C. B., Daniel-da-Silva, A. L., Pereira, E., Duarte, A. C., & Trindade, T. (2011). Removal of mercury (II) by dithiocarbamate surface functionalized magnetite particles: application to synthetic and natural spiked waters. Water Research, 45, 5773–5784.
Font, O., Córdoba, P., Leiva, C., Romeo, L. M., Bolea, I., Guedea, I., Moreno, N., Querol, X., Fernandez, C., & Díez, L. I. (2012). Fate and abatement of mercury and other trace elements in a coal fluidised bed oxy combustion pilot plant. Fuel, 95, 272–281.
Fthenakis, V. M., Lipfert, F. W., Moskowitz, P. D., & Saroff, L. (1995). An assessment of mercury emissions and health risks from a coal-fired power plant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 44, 267–283.
Gall, J. E., Boyd, R. S., & Rajakaruna, N. (2015). Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: a review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 201.
Genthe, B., Kapwata, T., Le Roux, W., Chamier, J., & Wright, C. Y. (2018). The reach of human health risks associated with metals/metalloids in water and vegetables along a contaminated river catchment: South Africa and Mozambique. Chemosphere, 199, 1–9.
Ghosh, S. B., Das, M. C., Ghosh, B., Roy, R. R. P., & Banerjee, N. N. (1994). Mercury in Indian coals. Journal of Chemical Technology, 1, 237-240.
Gil, C., Ramos-Miras, J., Roca-Pérez, L., & Boluda, R. (2010). Determination and assessment of mercury content in calcareous soils. Chemosphere, 78, 409–415.
Gnamuš, A., Byrne, A. R., & Horvat, M. (2000). Mercury in the soil-plant-deer-predator food chain of a temperate forest in Slovenia. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 3337–3345.
Gomes, M. V. T., de Souza, R. R., Teles, V. S., & Mendes, É. A. (2014). Phytoremediation of water contaminated with mercury using Typha domingensis in constructed wetland. Chemosphere, 103, 228–233.
Goodarzi, F. (2006). Characteristics and composition of fly ash from Canadian coal-fired power plants. Fuel, 85, 1418–1427.
Gosar, M., Šajn, R., & Biester, H. (2006). Binding of mercury in soils and attic dust in the Idrija mercury mine area (Slovenia). Science of The Total Environment, 369, 150–162.
Gustin, M. S. (2003). Are mercury emissions from geologic sources significant? A status report. Science of the Total Environment, 304, 153–167.
Ha, E., Basu, N., Bose-O’Reilly, S., Dorea, J. G., McSorley, E., Sakamoto, M., & Chan, H. M. (2016). Current progress on understanding the impact of mercury on human health. Environmental Research, 152, 419–433.
Habuda-Stanić, M., & Nujić, M. (2015). Arsenic removal by nanoparticles: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 8094–8123.
Halbach, K., Mikkelsen, Ø., Berg, T., & Steinnes, E. (2017). The presence of mercury and other trace metals in surface soils in the Norwegian Arctic. Chemosphere, 188, 567–574.
Han, Y., Kingston, H. M., Boylan, H. M., Rahman, G. M., Shah, S., Richter, R. C., et al. (2003). Speciation of mercury in soil and sediment by selective solvent and acid extraction. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 375, 428–436.
Hansen, H. K., Ottosen, L. M., Kliem, B. K., & Villumsen, A. (1997). Electrodialytic remediation of soils polluted with Cu, Cr, Hg, Pb and Zn. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology: International Research in Process, Environmental and Clean Technology, 70, 67–73.
Henriques, B., Rocha, L. S., Lopes, C. B., Figueira, P., Monteiro, R. J., Duarte, A. C., Pardal, M. A., & Pereira, E. (2015). Study on bioaccumulation and biosorption of mercury by living marine macroalgae: prospecting for a new remediation biotechnology applied to saline waters. Chemical Engineering Journal, 281, 759–770.
Hossain, M. N., Paul, S. K., & Hasan, M. M. (2015). Environmental impacts of coal mine and thermal power plant to the surroundings of Barapukuria, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 202.
Hower, J. C., Senior, C. L., Suuberg, E. M., Hurt, R. H., Wilcox, J. L., & Olson, E. S. (2010). Mercury capture by native fly ash carbons in coal-fired power plants. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 36, 510–529.
Hower, J. C., Clack, H. L., Hood, M. M., Hopps, S. G., & Thomas, G. H. (2017). Impact of coal source changes on mercury content in fly ash: Examples from a Kentucky power plant. International Journal of Coal Geology, 170, 2–6.
Hu, Y., & Cheng, H. (2016). Control of mercury emissions from stationary coal combustion sources in China: Current status and recommendations. Environmental Pollution, 218, 1209–1221.
Hu, W., Huang, B., Tian, K., Holm, P. E., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Heavy metals in intensive greenhouse vegetable production systems along Yellow Sea of China: Levels, transfer and health risk. Chemosphere, 167, 82–90.
Huang, X., Hu, J., Qin, F., Quan, W., Cao, R., Fan, M., & Wu, X. (2017). Heavy metal pollution and ecological assessment around the Jinsha Coal-Fired Power Plant (China). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14, 1589.
Hussein, H. S., Ruiz, O. N., Terry, N., & Daniell, H. (2007). Phytoremediation of mercury and organomercurials in chloroplast transgenic plants: enhanced root uptake, translocation to shoots, and volatilization. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 8439–8446.
Isaksson, R., Balogh, S. J., & Farris, M. A. (2007). Accumulation of mercury by the aquatic plant Lemna minor. International Journal of Environmental Studies, 64, 189–194.
Jagtap, R., & Maher, W. (2015). Measurement of mercury species in sediments and soils by HPLC–ICPMS. Microchemical Journal, 121, 65–98.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2010). Trace elements in soils and plants. Washington DC: CRC Press.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Mukherjee, A. B. (2007). Trace elements from soil to human. Springer Science & Business Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-32714-1.
Kolker, A., Panov, B. S., Panov, Y. B., Landa, E. R., Conko, K. M., Korchemagin, V. A., Shendrik, T., & McCord, J. D. (2009). Mercury and trace element contents of Donbas coals and associated mine water in the vicinity of Donetsk, Ukraine. International Journal of Coal Geology, 79, 83–91.
Kostova, I., Vassileva, C., Dai, S., Hower, J. C., & Apostolova, D. (2013). Influence of surface area properties on mercury capture behaviour of coal fly ashes from some Bulgarian power plants. International Journal of Coal Geology, 116, 227–235.
Lafabrie, C., Major, K. M., Major, C. S., & Cebrián, J. (2011). Arsenic and mercury bioaccumulation in the aquatic plant, Vallisneria neotropicalis. Chemosphere, 82, 1393–1400.
Li, Y., Yang, L., Ji, Y., Sun, H., & Wang, W. (2009). Quantification and fractionation of mercury in soils from the Chatian mercury mining deposit, southwestern China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31, 617–628.
Li, Z., Wu, L., Liu, H., Lan, H., & Qu, J. (2013). Improvement of aqueous mercury adsorption on activated coke by thiol-functionalization. Chemical Engineering Journal, 228, 925–934.
Li, R., Wu, H., Ding, J., Fu, W., Gan, L., & Li, Y. (2017). Mercury pollution in vegetables, grains and soils from areas surrounding coal-fired power plants. Scientific Reports, 7, 46545.
Liang, Y., Dongxing, Y. U. A. N., Min, L. U., Zhenbin, G. O. N. G., Xiyao, L. I. U., & Zhang, Z. (2009). Distribution characteristics of total mercury and methylmercury in the topsoil and dust of Xiamen, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 21, 1400–1408.
Lim, J. M., Salido, A. L., & Butcher, D. J. (2004). Phytoremediation of lead using Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) with EDTA and electrodics. Microchemical Journal, 76, 3–9.
Lin, C. J., Gustin, M. S., Singhasuk, P., Eckley, C., & Miller, M. (2010). Empirical models for estimating mercury flux from soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 8522–8528.
Liu, Z., Wang, L. A., Xu, J., Ding, S., Feng, X., & Xiao, H. (2017). Effects of different concentrations of mercury on accumulation of mercury by five plant species. Ecological Engineering, 106, 273–278.
Lomonte, C., Gregory, D., Baker, A. J., & Kolev, S. D. (2008). Comparative study of hotplate wet digestion methods for the determination of mercury in biosolids. Chemosphere, 72, 1420–1424.
Lu, X., Jiang, J., Sun, K., Wang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2014). Influence of the pore structure and surface chemical properties of activated carbon on the adsorption of mercury from aqueous solutions. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 78, 69–76.
Luo, W., Lu, Y., Wang, B., Tong, X., Wang, G., Shi, Y., Wang, T., & Giesy, J. P. (2009). Distribution and sources of mercury in soils from former industrialized urban areas of Beijing, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 158, 507–517.
Luo, G., Ma, J., Han, J., Yao, H., Xu, M., Zhang, C., Chen, G., Gupta, R., & Xu, Z. (2013). Hg occurrence in coal and its removal before coal utilization. Fuel, 104, 70–76.
Luo, Y., Duan, L., Wang, L., Xu, G., Wang, S., & Hao, J. (2014). Mercury concentrations in forest soils and stream waters in northeast and south China. Science of the Total Environment, 496, 714–720.
Lusilao-Makiese, J., Tessier, E., Amouroux, D., Tutu, H., Chimuka, L., & Cukrowska, E. M. (2012). Speciation of mercury in South African coals. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 94, 688–706.
Ma, F., Peng, C., Hou, D., Wu, B., Zhang, Q., Li, F., & Gu, Q. (2015). Citric acid facilitated thermal treatment: an innovative method for the remediation of mercury contaminated soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 300, 546–552.
Mahajan, V. E., Yadav, R. R., Dakshinkar, N. P., Dhoot, V. M., Bhojane, G. R., Naik, M. K., Shrivastava, P., Naoghare, P. K., & Krishnamurthi, K. (2012). Influence of mercury from fly ash on cattle reared nearby thermal power plant. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 7365–7372.
Marrugo-Negrete, J., Durango-Hernández, J., Pinedo-Hernández, J., Olivero-Verbel, J., & Díez, S. (2015). Phytoremediation of mercury-contaminated soils by Jatropha curcas. Chemosphere, 127, 58–63.
Martín, J. A. R., & Nanos, N. (2016). Soil as an archive of coal-fired power plant mercury deposition. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 308, 131-138.
Matsuyama, A., Yano, S., Taninaka, T., Kindaichi, M., Sonoda, I., Tada, A., & Akagi, H. (2018). Chemical characteristics of dissolved mercury in the pore water of Minamata Bay sediments. Marine Oollution Bulletin, 129, 503–511.
Mbanga, O., Ncube, S., Tutu, H., Chimuka, L., & Cukrowska, E. (2019). Mercury accumulation and biotransportation in wetland biota affected by gold mining. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 186.
Meng, X., Hua, Z., Dermatas, D., Wang, W., & Kuo, H. Y. (1998). Immobilization of mercury (II) in contaminated soil with used tire rubber. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 57, 231–241.
Meng, M., Li, B., Shao, J. J., Wang, T., He, B., Shi, J. B., Ye, Z. H., & Jiang, G. B. (2014). Accumulation of total mercury and methylmercury in rice plants collected from different mining areas in China. Environmental Pollution, 184, 179–186.
Millán, R., Lominchar, M. A., Rodríguez-Alonso, J., Schmid, T., & Sierra, M. J. (2014). Riparian vegetation role in mercury uptake (Valdeazogues River, Almadén, Spain). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 140, 104–110.
Mishra, V. K., Tripathi, B. D., & Kim, K. H. (2009). Removal and accumulation of mercury by aquatic macrophytes from an open cast coal mine effluent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172, 749–754.
Montoya, A. J., Lena, J. C., & Windmöller, C. C. (2019). Adsorption of gaseous elemental mercury on soils: Influence of chemical and/or mineralogical characteristics. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 170, 98–106.
Mukherjee, A. B., Zevenhoven, R., Bhattacharya, P., Sajwan, K. S., & Kikuchi, R. (2008). Mercury flow via coal and coal utilization by-products: a global perspective. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 52, 571–591.
Müller, A. K., Westergaard, K., Christensen, S., & Sørensen, S. J. (2001). The effect of long-term mercury pollution on the soil microbial community. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 36, 11–19.
Nagpal, N., Bettiol, S. S., Isham, A., Hoang, H., & Crocombe, L. A. (2017). A review of mercury exposure and health of dental personnel. Safety and Health at Work, 8, 1–10.
Noda, N., & Ito, S. (2018). Mercury Partitioning in Coal-fired Power Plants in Japan. Journal of the Japan Institute of Energy, 97, 342–347.
Obrist, D., Kirk, J. L., Zhang, L., Sunderland, E. M., Jiskra, M., & Selin, N. E. (2018). A review of global environmental mercury processes in response to human and natural perturbations: Changes of emissions, climate, and land use. Ambio, 47, 116-140.
O'Connor, D., Hou, D., Ok, Y. S., Mulder, J., Duan, L., Wu, Q., Wang, S., Tack, F. M. G., & Rinklebe, J. (2019). Mercury speciation, transformation, and transportation in soils, atmospheric flux, and implications for risk management: A critical review. Environment International, 126, 747–761.
Ohki, A., Taira, M., Hirakawa, S., Haraguchi, K., Kanechika, F., Nakajima, T., & Takanashi, H. (2014). Determination of mercury in various coals from different countries by heat-vaporization atomic absorption spectrometry: Influence of particle size distribution of coal. Microchemical Journal, 114, 119–124.
Ojea-Jiménez, I., López, X., Arbiol, J., & Puntes, V. (2012). Citrate-coated gold nanoparticles as smart scavengers for mercury (II) removal from polluted waters. ACS Nano, 6, 2253–2260.
Omine, N., Romero, C. E., Kikkawa, H., Wu, S., & Eswaran, S. (2012). Study of elemental mercury re-emission in a simulated wet scrubber. Fuel., 91, 93–101.
Ostos, C., Pérez-Rodríguez, F., Arroyo, B. M., & Moreno-Rojas, R. (2015). Study of mercury content in wild edible mushrooms and its contribution to the Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake in Spain. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 37, 136–142.
Özkul, C. (2016). Heavy metal contamination in soils around the Tunçbilek thermal power plant (Kütahya, Turkey). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 284.
Palmieri, H. E., Nalini, H. A., Jr., Leonel, L. V., Windmöller, C. C., Santos, R. C., & de Brito, W. (2006). Quantification and speciation of mercury in soils from the Tripuí Ecological Station, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Science of the Total Environment, 368, 69–78.
Pant, P., Allen, M., & Tansel, B. (2010). Mercury uptake and translocation in Impatiens walleriana plants grown in the contaminated soil from oak ridge. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 13, 168–176.
Park, K. S., Seo, Y. C., Lee, S. J., & Lee, J. H. (2008). Emission and speciation of mercury from various combustion sources. Powder Technology, 180, 151–156.
Park, C. H., Eom, Y., Lee, L. J. E., & Lee, T. G. (2013). Simple and accessible analytical methods for the determination of mercury in soil and coal samples. Chemosphere, 93, 9–13.
Pastrana-Corral, M. A., Wakida, F. T., Temores-Peña, J., Rodriguez-Mendivil, D. D., García-Flores, E., Piñon-Colin, T. D. J., & Quiñonez-Plaza, A. (2017). Heavy metal pollution in the soil surrounding a thermal power plant in Playas de Rosarito, Mexico. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76, 583.
Patel, K. S., Sharma, R., Dahariya, N. S., Yadav, A., Blazhev, B., Matini, L., & Hoinkis, J. (2015). Heavy metal contamination of tree leaves. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 6, 687–693.
Patra, M., Bhowmik, N., Bandopadhyay, B., & Sharma, A. (2004). Comparison of mercury, lead and arsenic with respect to genotoxic effects on plant systems and the development of genetic tolerance. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 52, 199–223.
Pavlish, J. H., Sondreal, E. A., Mann, M. D., Olson, E. S., Galbreath, K. C., Laudal, D. L., & Benson, S. A. (2003). Status review of mercury control options for coal-fired power plants. Fuel Processing Technology, 82, 89–165.
Pazos, M., Rosales, E., Alcántara, T., Gómez, J., & Sanromán, M. A. (2010). Decontamination of soils containing PAHs by electroremediation: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177, 1–11.
Piao, H., & Bishop, P. L. (2006). Stabilization of mercury-containing wastes using sulfide. Environmental Pollution, 139, 498–506.
Pirrone, N., Cinnirella, S., Feng, X., Finkelman, R. B., Friedli, H. R., Leaner, J., Mason, R., Mukherjee, A. B., Stracher, G. B., Streets, D. G., & Telmer, K. (2010). Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 10, 5951–5964.
Pöykiö, R., Mäkelä, M., Watkins, G., Nurmesniemi, H., & Olli, D. A. H. L. (2016). Heavy metals leaching in bottom ash and fly ash fractions from industrial-scale BFB-boiler for environmental risks assessment. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 26, 256–264.
Pudasainee, D., Kim, J. H., & Seo, Y. C. (2009). Mercury emission trend influenced by stringent air pollutants regulation for coal-fired power plants in Korea. Atmospheric Environment, 43, 6254–6259.
Qiu, G., Feng, X., Wang, S., & Xiao, T. (2006). Mercury contaminations from historic mining to water, soil and vegetation in Lanmuchang, Guizhou, southwestern China. Science of the Total Environment, 368, 56–68.
Rahman, Z., & Singh, V. P. (2019). The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs)(arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: an overview. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 419.
Rai, V. K., Raman, N. S., & Choudhary, S. K. (2013). Mercury in thermal power plants–a case study. International Journal of Pure &Applied Bioscience, 1, 31–37.
Raj, D., & Maiti, S. K. (2019). Bioaccumulation of potentially toxic elements in tree and vegetable species with associated health and ecological risks: a case study from a thermal power plant, Chandrapura, India. Rendiconti Lincei. Scienze Fisiche e Naturali. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-019-00831-7.
Raj, D., Chowdhury, A., & Maiti, S. K. (2017). Ecological risk assessment of mercury and other heavy metals in soils of coal mining area: A case study from the eastern part of a Jharia coal field, India. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 23, 767–787.
Raju, A., Singh, A., Srivastava, N., Singh, S., Jigyasu, D. K., & Singh, M. (2019). Mapping human health risk by geostatistical method: a case study of mercury in drinking groundwater resource of the central Ganga alluvial plain, northern India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 298.
Rasulov, O., Zacharová, A., & Schwarz, M. (2017). Determination of total mercury in aluminium industrial zones and soil contaminated with red mud. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189, 388.
Reis, A. T., Rodrigues, S. M., Davidson, C. M., Pereira, E., & Duarte, A. C. (2010). Extractability and mobility of mercury from agricultural soils surrounding industrial and mining contaminated areas. Chemosphere, 81, 1369–1377.
Reis, A. T., Lopes, C. B., Davidson, C. M., Duarte, A. C., & Pereira, E. (2015). Extraction of available and labile fractions of mercury from contaminated soils: The role of operational parameters. Geoderma, 259, 213–223.
Ren, D. Y., Zhao, F. H., Dai, S. F., Zhang, J. Y., & Luo, K. L. (2006). Geochemistry of trace elements in coals (pp. 268–279). Beijing: The Science Press.
Renneberg, A. J., & Dudas, M. J. (2001). Transformations of elemental mercury to inorganic and organic forms in mercury and hydrocarbon co-contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 45, 1103–1109.
Rodriguez, L., Rincón, J., Asencio, I., & Rodríguez-Castellanos, L. (2007). Capability of selected crop plants for shoot mercury accumulation from polluted soils: phytoremediation perspectives. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 9, 1–13.
Sahi, C., Singh, A., Kumar, K., Blumwald, E., & Grover, A. (2006). Salt stress response in rice: genetics, molecular biology, and comparative genomics. Functional & Integrative Genomics, 6, 263–284.
Salt, D. E., Blaylock, M., Kumar, N. P., Dushenkov, V., Ensley, B. D., Chet, I., & Raskin, I. (1995). Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnology, 13, 468.
Sanchez-Rodas, D., Corns, W. T., Chen, B., & Stockwell, P. B. (2010). Atomic fluorescence spectrometry: a suitable detection technique in speciation studies for arsenic, selenium, antimony and mercury. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 25, 933–946.
Shiyab, S., Chen, J., Han, F. X., Monts, D. L., Matta, F. B., Gu, M., & Su, Y. (2009). Phytotoxicity of mercury in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L.). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 72, 619–625.
Sierra, C., Gallego, J. R., Afif, E., Menéndez-Aguado, J. M., & González-Coto, F. (2010). Analysis of soil washing effectiveness to remediate a brownfield polluted with pyrite ashes. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 180, 602–608.
Soares, L. C., Egreja Filho, F. B., Linhares, L. A., Windmoller, C. C., & Yoshida, M. I. (2015). Accumulation and oxidation of elemental mercury in tropical soils. Chemosphere, 134, 181–191.
Sorkhoh, N. A., Ali, N., Al-Awadhi, H., Dashti, N., Al-Mailem, D. M., Eliyas, M., & Radwan, S. S. (2010). Phytoremediation of mercury in pristine and crude oil contaminated soils: Contributions of rhizobacteria and their host plants to mercury removal. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 73, 1998–2003.
Spahić, M. P., Sakan, S., Cvetković, Ž., Tančić, P., Trifković, J., Nikić, Z., & Manojlović, D. (2018). Assessment of contamination, environmental risk, and origin of heavy metals in soils surrounding industrial facilities in Vojvodina, Serbia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 208.
Spahić, M. P., Manojlović, D., Tančić, P., Cvetković, Ž., Nikić, Z., Kovačević, R., & Sakan, S. (2019). Environmental impact of industrial and agricultural activities to the trace element content in soil of Srem (Serbia). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191, 133.
Steinnes, E. (1995). Mercury. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy Metals in Soils (2nd ed.). London: Blackie Academic & Professional..
Streets, D. G., Devane, M. K., Lu, Z., Bond, T. C., Sunderland, E. M., & Jacob, D. J. (2011). All-time releases of mercury to the atmosphere from human activities. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 10485–10491.
Streets, D. G., Lu, Z., Levin, L., ter Schure, A. F., & Sunderland, E. M. (2018). Historical releases of mercury to air, land, and water from coal combustion. Science of the Total Environment, 615, 131-140.
Su, Y., Han, F. X., Chen, J., Sridhar, B. M., & Monts, D. L. (2008). Phytoextraction and accumulation of mercury in three plant species: Indian mustard (Brassica juncea), beard grass (Polypogon monospeliensis), and Chinese brake fern (Pteris vittata). International Journal of Phytoremediation, 10, 547–560.
Subirés-Muñoz, J. D., García-Rubio, A., Vereda-Alonso, C., Gómez-Lahoz, C., Rodríguez-Maroto, J. M., García-Herruzo, F., & Paz-Garcia, J. M. (2011). Feasibility study of the use of different extractant agents in the remediation of a mercury contaminated soil from Almaden. Separation and Purification Technology, 79, 151–156.
Tan, Y., Mortazavi, R., Dureau, B., & Douglas, M. A. (2004). An investigation of mercury distribution and speciation during coal combustion. Fuel, 83, 2229–2236.
Tang, X. Y., & Huang, W. H. (2004). Trace elements in Chinese coal. Beijing: The commercial press (In Chinese).
Tomašević, M., Rajšić, S., Đorđević, D., Tasić, M., Krstić, J., & Novaković, V. (2004). Heavy metals accumulation in tree leaves from urban areas. Environmental Chemistry Letters., 2, 151–154.
Toole-O'Neil, B., Tewalt, S. J., Finkelman, R. B., & Akers, D. J. (1999). Mercury concentration in coal—unraveling the puzzle. Fuel, 78, 47–54.
UN. (1997). Glossary of environment statistics, studies in methods. NY: United Nations New York.
UNEP. (2013). Global Mercury Assessment 2013: Sources, Emissions, Releases and Environmental Transport. Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme.
UNEP. (2014). Assessment of the Mercury Content in Coal fed to Power Plant and study of Mercury Emissions from the Sector in India. UNEP Chemicals Branch, Geneva, Switzerland. http://www.unep.org/chemicalsandwaste/Portals/9/Mercury/REPORT%20FINAL%2019%20March%202014.pdf. Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
USEPA. (1991). Determination of Mercury in Tissues by Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Cincinnati, Ohio. 906R1102, Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
USEPA. (2002). Control of Mercury Emissions From Coal-fired Electric Utility Boilers, Interim Report Including Errata Data, 3-21-02, EPA-600/R-01-109, Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
USEPA. (2007). Treatment technologies for mercury in soil, waste, and water. US EPA, Office of Superfund Remediation and Technology Innovation Washington, DC 20460, EPA-542-R-07-003. Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
USEPA. (2007a). Method 7471B, Mercury in Solid or Semisolid Waste (Manual Cold Vapor Technique), revision 2. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/7471b.pdf. Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
Virkutyte, J., Sillanpää, M., & Latostenmaa, P. (2002). Electrokinetic soil remediation—critical overview. Science of the Total Environment, 289, 97–121.
Wang, S., & Luo, K. (2017). Atmospheric emission of mercury due to combustion of steam coal and domestic coal in China. Atmospheric Environment, 162, 45–54.
Wang, D., Shi, X., & Wei, S. (2003). Accumulation and transformation of atmospheric mercury in soil. Science of the Total Environment, 304, 209–214.
Wang, J., Feng, X., Anderson, C. W., Xing, Y., & Shang, L. (2012). Remediation of mercury contaminated sites–a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 221, 1–18.
Wang, X., Liu, X., Han, Z., Zhou, J., Xu, S., Zhang, Q., Chen, H., Bo, W., & Xia, X. (2015). Concentration and distribution of mercury in drainage catchment sediment and alluvial soil of China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 154, 32–48.
Wang, S., Zhong, T., Chen, D., & Zhang, X. (2016). Spatial distribution of mercury (Hg) concentration in agricultural soil and its risk assessment on food safety in China. Sustainability, 8, 795.
WHO (1993). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Vol. 1: Recommendations. 2d ed. Geneva. Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
WHO (2003). Elemental Mercury and Inorganic Mercury Compounds: Human Health Aspects. http://www.who.int/ipcs/publications/cicad/en/cicad50.pdf. Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
WHO (2004). Guidelines for drinking-water quality (Vol. 1). World Health Organization. Accessed 11 Feb 2019.
Xinmin, Z., Kunli, L., Xinzhang, S., Jian'an, T., & Yilun, L. (2006). Mercury in the topsoil and dust of Beijing City. Science of the Total Environment, 368, 713–722.
Xu, J., Bravo, A. G., Lagerkvist, A., Bertilsson, S., Sjöblom, R., & Kumpiene, J. (2015). Sources and remediation techniques for mercury contaminated soil. Environment International, 74, 42–53.
Xun, Y., Feng, L., Li, Y., & Dong, H. (2017). Mercury accumulation plant Cyrtomium macrophyllum and its potential for phytoremediation of mercury polluted sites. Chemosphere, 189, 161–170.
Yao, D. X., Meng, J., & Zhang, Z. G. (2010). Heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risk in reclaimed soils in Huainan mining area. Journal of Coal Science and Engineering (China), 16, 316-319.
Yin, Y., Allen, H. E., Li, Y., Huang, C. P., & Sanders, P. F. (1996). Adsorption of mercury (II) by soil: effects of pH, chloride, and organic matter. Journal of Environmental Quality, 25, 837–844.
Yu, J. G., Yue, B. Y., Wu, X. W., Liu, Q., Jiao, F. P., Jiang, X. Y., & Chen, X. Q. (2016). Removal of mercury by adsorption: a review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 5056–5076.
Yudovich, Y. E., & Ketris, M. P. (2005a). Mercury in coal: a review. Part 1. Geochemistry. International Journal of Coal Geology, 62, 107–134.
Yudovich, Y. E., & Ketris, M. P. (2005b). Mercury in coal: a review Part 2. Coal use and environmental problems. International Journal of Coal Geology, 62, 135–165.
Zalups, R. K. (2000). Molecular interactions with mercury in the kidney. Pharmacological Reviews., 52, 113–144.
Zhang, H., Chen, J., Zhu, L., Yang, G., & Li, D. (2014). Anthropogenic mercury enrichment factors and contributions in soils of Guangdong Province, South China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 144, 312–319.
Zhang, L., Wang, S., Wang, L., Wu, Y., Duan, L., Wu, Q., Wang, F., Yang, M., Yang, H., Hao, J., & Liu, X. (2015). Updated emission inventories for speciated atmospheric mercury from anthropogenic sources in China. Environmental Science & Technolog, 49, 3185–3194.
Zhao, S., Duan, Y., Yao, T., Liu, M., Lu, J., Tan, H., Wang, X., & Wu, L. (2017). Study on the mercury emission and transformation in an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant. Fuel, 199, 653–661.
Zheng, L., Liu, G., & Chou, C. L. (2007). The distribution, occurrence and environmental effect of mercury in Chinese coals. Science of the Total Environment, 384, 374–383.
Acknowledgements
The first author is grateful to the Ministry of Human Resource and Development (MHRD), Government of India, for providing scholarship. The authors also acknowledge the Indian Institute of Technology (Indian School of Mines), Dhanbad (India), for providing basic research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raj, D., Maiti, S.K. Sources, toxicity, and remediation of mercury: an essence review. Environ Monit Assess 191, 566 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7743-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7743-2