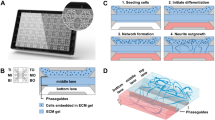
Abstract
Many cell types communicate by means of dendritic extensions via a multi-tiered set of geometric and chemical cues. Until recently, mimicking the compartmentalized in vivo cellular environment of dendrite-expressing cells such as osteocytes and motor neurons in a spatially and temporally controllable manner was limited by the challenges of in vitro device fabrication at submicron scales. Utilizing the improved resolution of current fabrication technology, we have designed a multiscale device, the Macro-micro-nano system, or Mμn, composed of two distinct cell-seeding and interrogation compartments separated by a nanochannel array. The array enables dendrite ingrowth, while providing a mechanism for fluidic sequestration and/or temporally-mediated diffusible signaling between cell populations. Modeling of the Mμn system predicted the ability to isolate diffusible signals, namely ATP. Empirical diffusion studies verified computational modeling. In addition, cell viability, dendrite interaction with the nanoarray, and cellular purinergic response to heat shock were experimentally evaluated within the device for both osteocytes and motor neurons. Our results describe a novel in vitro system in which dendrite-expressing cell types can be studied within nano-environments that mimic in vivo conditions. In particular, the Mμn system enables real-time observation of cell to cell communication between cell populations in distinct, but fluidically coupled regions.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Aarden, A.-M. Wassenaar, M.J. Alblas, P.J. Nijweide, Immunocytochemical demonstration of extracellular matrix proteins in isolated osteocytes. Histochem. Cell Biol. 106, 495–501 (1996)
H. Aldskogius, E.N. Kozlova, Central neuron–glial and glial–glial interactions following axon injury. Prog. Neurobiol. 55, 1–26 (1998)
N.J. Allen, B.A. Barres, Neuroscience: Glia—More than just brain glue. Nature 457, 675–677 (2009)
J. Banchereau, R.M. Steinman, Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392, 245–252 (1998)
S. Burra, D.P. Nicolella, W.L. Francis, C.J. Freitas, N.J. Mueschke, K. Poole, J.X. Jiang, Dendritic processes of osteocytes are mechanotransducers that induce the opening of hemichannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 13648–13653 (2010)
C.T. Culbertson, S.C. Jacobson, J. Michael Ramsey, Diffusion coefficient measurements in microfluidic devices. Talanta 56, 365–373 (2002)
R.D. Fields, G. Burnstock, Purinergic signalling in neuron–glia interactions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 423–436 (2006)
D.C. Genetos, C.J. Kephart, Y. Zhang, C.E. Yellowley, H.J. Donahue, Oscillating fluid flow activation of gap junction hemichannels induces ATP release from MLO-Y4 osteocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 212, 207–214 (2007)
A. Hoebertz, S. Mahendran, G. Burnstock, T.R. Arnett, ATP and UTP at low concentrations strongly inhibit bone formation by osteoblasts: A novel role for the P2Y2 receptor in bone remodeling. J. Cell. Biochem. 86, 413–419 (2002)
T. Kalwarczyk, M. Tabaka, R. Holyst, Biologistics—diffusion coefficients for complete proteome of Escherichia Coli. Bioinformatics 28, 2971–2978 (2012)
Y. Kato, J.J. Windle, B.A. Koop, G.R. Mundy, L.F. Bonewald, Establishment of an osteocyte-like cell line, MLO-Y4. J. Bone Miner. Res. 12, 2014–2023 (1997)
T.M. Kringelbach, D. Aslan, I. Novak, P. Schwarz, N.R. Jørgensen, UTP-induced ATP release is a fine-tuned signalling pathway in osteocytes. Purinergic Signal 10, 337–347 (2014)
D.A. Lauffenburger, A.F. Horwitz, Cell migration: A physically integrated molecular process. Cell 84, 359–369 (1996)
M.D. Levenson, N. Viswanathan, R.A. Simpson, Improving resolution in photolithography with a phase-shifting mask. Electron Devices, IEEE Transactions on 29, 1828–1836 (1982)
K. Lingenhöhl, D.M. Finch, Morphological characterization of rat entorhinal neurons in vivo: Soma-dendritic structure and axonal domains. Exp. Brain Res. 84, 57–74 (1991)
X.L. Lu, B. Huo, M. Park, X.E. Guo, Calcium response in osteocytic networks under steady and oscillatory fluid flow. Bone 51, 466–473 (2012)
M.G. Lykissas, A.K. Batistatou, K.A. Charalabopoulos, A.E. Beris, The role of neurotrophins in axonal growth, guidance, and regeneration. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 4, 143–151 (2007)
R. Malik, D. Burch, M. Bazant, G. Ceder, Particle size dependence of the ionic diffusivity. Nano Lett. 10, 4123–4127 (2010)
McCutcheon, S., Unachukwu, U., Thakur, A., Majeska, R., Redenti, S., and Vazquez, M. (2016). In vitro formation of Neuroclusters in microfluidic devices and cell migration as a function of stromal-derived growth factor 1 gradients. Cell adhesion & migration, 0
Nidadavolu, S.S. (2013). Analysis and comparison of parallel plate flow chambers to determine consistency of fluid forces on cells
A.F. Oberhauser, C. Badilla-Fernandez, M. Carrion-Vazquez, J.M. Fernandez, The mechanical hierarchies of fibronectin observed with single-molecule AFM. J. Mol. Biol. 319, 433–447 (2002)
S. Orrenius, B. Zhivotovsky, P. Nicotera, Regulation of cell death: The calcium-apoptosis link. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 552–565 (2003)
I.R. Orriss, G. Burnstock, T.R. Arnett, Purinergic signalling and bone remodelling. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 10, 322–330 (2010)
L.I. Plotkin, S.C. Manolagas, T. Bellido, Glucocorticoids induce osteocyte apoptosis by blocking focal adhesion kinase-mediated survival evidence for inside-out signaling leading to anoikis. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 24120–24130 (2007)
J.C.L. Plumier, D.A. Hopkins, H.A. Robertson, R.W. Currie, Constitutive expression of the 27-kDa heat shock protein (Hsp27) in sensory and motor neurons of the rat nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 384, 409–428 (1997)
J.T. Podichetty, D.V. Dhane, S.V. Madihally, Dynamics of diffusivity and pressure drop in flow-through and parallel-flow bioreactors during tissue regeneration. Biotechnol. Prog. 28, 1045–1054 (2012)
D. Rochon, I. Rousse, R. Robitaille, Synapse–glia interactions at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J. Neurosci. 21, 3819–3829 (2001)
M. Romanello, B. Pani, M. Bicego, P. D'Andrea, Mechanically induced ATP release from human osteoblastic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 289, 1275–1281 (2001)
Schaap, A., and Bellouard, Y. (2013). Fabrication of topologically-complex 3D microstructures by femtosecond laser machining and polymer molding. Paper presented at: CLEO: Applications and Technology (Optical Society of America)
M.B. Schaffler, W.-Y. Cheung, R. Majeska, O. Kennedy, Osteocytes: Master orchestrators of bone. Calcif. Tissue Int. 94, 5–24 (2014)
K.A. Schalper, H.A. Sánchez, S.C. Lee, G.A. Altenberg, M.H. Nathanson, J.C. Sáez, Connexin 43 hemichannels mediate the Ca2+ influx induced by extracellular alkalinization. Am. J. Phys. Cell Phys. 299, C1504–C1515 (2010)
Shao, P.G., van Kan, J.A., and Watt, F. (2010). Sub Micron Poly-Dimethyl Siloxane (PDMS) Replication Using Proton Beam Fabricated Nickel Moulds. Paper presented at: Key Engineering Materials (Trans Tech Publ)
E. Takai, R.L. Mauck, C.T. Hung, X.E. Guo, Osteocyte viability and regulation of osteoblast function in a 3D trabecular bone explant under dynamic hydrostatic pressure. J. Bone Miner. Res. 19, 1403–1410 (2004)
S.D. Tan, T.J. de Vries, A.M. Kuijpers-Jagtman, C.M. Semeins, V. Everts, J. Klein-Nulend, Osteocytes subjected to fluid flow inhibit osteoclast formation and bone resorption. Bone 41, 745–751 (2007)
K. Tanaka-Kamioka, H. Kamioka, H. Ris, S.S. Lim, Osteocyte shape is dependent on actin filaments and osteocyte processes are unique actin-rich projections. J. Bone Miner. Res. 13, 1555–1568 (1998)
D.T. Theodosis, D.A. Poulain, S.H.R. Oliet, Activity-dependent structural and functional plasticity of astrocyte-neuron interactions. Physiol. Rev. 88, 983–1008 (2008)
M.M. Thi, S. Islam, S.O. Suadicani, D.C. Spray, Connexin43 and pannexin1 channels in osteoblasts: Who is the "hemichannel"? J. Membr. Biol. 245, 401–409 (2012)
M.M. Thi, S.O. Suadicani, M.B. Schaffler, S. Weinbaum, D.C. Spray, Mechanosensory responses of osteocytes to physiological forces occur along processes and not cell body and require α(V)β(3) integrin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 21012–21017 (2013)
K.J. Tomaselli, C.H. Damsky, L.F. Reichardt, Interactions of a neuronal cell line (PC12) with laminin, collagen IV, and fibronectin: Identification of integrin-related glycoproteins involved in attachment and process outgrowth. J. Cell Biol. 105, 2347–2358 (1987)
M.G. Vander Heiden, L.C. Cantley, C.B. Thompson, Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 324, 1029–1033 (2009)
C. Wei, B. Fan, D. Chen, C. Liu, Y. Wei, B. Huo, L. You, J. Wang, J. Chen, Osteocyte culture in microfluidic devices. Biomicrofluidics 9, 014109 (2015)
S. Weinbaum, S.C. Cowin, Y. Zeng, A model for the excitation of osteocytes by mechanical loading-induced bone fluid shear stresses. J. Biomech. 27, 339–360 (1994)
H. Xu, S. Gu, M.A. Riquelme, S. Burra, D. Callaway, H. Cheng, T. Guda, J. Schmitz, R.J. Fajardo, S.L. Werner, et al., Connexin 43 channels are essential for normal bone structure and osteocyte viability. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 30, 436–448 (2015)
L.D. You, S. Weinbaum, S.C. Cowin, M.B. Schaffler, Ultrastructure of the osteocyte process and its pericellular matrix. Anat. Rec. A: Discov. Mol. Cell. Evol. Biol. 278, 505–513 (2004)
L. You, S. Temiyasathit, E. Tao, F. Prinz, C.R. Jacobs, 3D microfluidic approach to mechanical stimulation of osteocyte processes. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 1, 103–107 (2008)
Acknowledgements
Tanya Singh, The City College of New York
National Institutes of Health Grant #5R01AR041210-23
National Science Foundation Grant #CBET0939511
National Institutes of Health Grant #R21EY026752
CUNY Advanced Science Research Center
Wallace H. Coulter Foundation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCutcheon, S., Majeska, R., Schaffler, M. et al. A multiscale fluidic device for the study of dendrite-mediated cell to cell communication. Biomed Microdevices 19, 71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0212-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-017-0212-1