Abstract
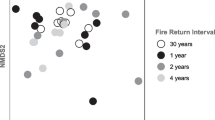
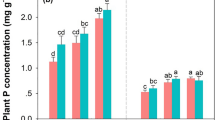
Plant nutrient concentrations and stoichiometry drive fundamental ecosystem processes, with important implications for primary production, diversity, and ecosystem sustainability. While a range of evidence exists regarding how plant nutrients vary across spatial scales, our understanding of their temporal variation remains less well understood. Nevertheless, we know nutrients regulate plant function across time, and that important temporal controls could strongly interact with environmental change. Here, we report results from a 3-year assessment of inter-annual changes of foliar nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) concentrations and stoichiometry in three dominant grasses in response to N deposition and prescribed fire in a temperate steppe of northern China. Foliar N and P concentrations and their ratios varied greatly among years, with this temporal variation strongly related to inter-annual variation in precipitation. Nitrogen deposition significantly increased foliar N concentrations and N:P ratios in all species, while fire significantly altered foliar N and P concentrations but had no significant impacts on N:P ratios. Generally, N addition enhanced the temporal stability of foliar N and decreased that of foliar P and of N:P ratios. Our results indicate that plant nutrient status and response to environmental change are temporally dynamic and that there are differential effects on the interactions between environmental change drivers and timing for different nutrients. These responses have important implications for consideration of global change effects on plant community structure and function, management strategies, and the modeling of biogeochemical cycles under global change scenarios.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R, Chapin FS (2000) The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and patterns. Adv Ecol Res 30:1–67
Agren GI (2008) Stoichiometry and nutrition of plant growth in natural communities. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 39:153–170
Agren GI, Wetterstedt JAM, Billberger MFK (2012) Nutrient limitation on terrestrial plant growth—modeling the interaction between nitrogen and phosphorus. New Phytol 194(4):953–960
Ahlstrom A, Raupach MR, Schurgers G, Smith B, Arneth A, Jung M, Reichstein M, Canadell JG, Friedlingstein P, Jain AK, Kato E, Poulter B, Sitch S, Stocker BD, Viovy N, Wang YP, Wiltshire A, Zaehle S, Zeng N (2015) The dominant role of semi-arid ecosystems in the trend and variability of the land CO2 sink. Science 348(6237):895–899
Alvarez-Clare S, Mack MC (2015) Do foliar, litter, and root nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations reflect nutrient limitation in a lowland tropical wet forest? PLoS ONE 10(4):e0123796
Austin AT, Zanne AE (2015) Whether in life or in death: fresh perspectives on how plants affect biogeochemical cycling. J Ecol 103(6):1367–1371
Bardgett RD, Wardle DA, Yeates GW (1998) Linking above-ground and below-ground interactions: how plant responses to foliar herbivory influence soil organisms. Soil Biol Biochem 30(14):1867–1878
Bennett LT, Judd TS, Adams MA (2002) Growth and nutrient content of perennial grasslands following burning in semi-arid, sub-tropical Australia. Plant Ecol 164:185–199
Binzer A, Guill C, Rall BC, Brose U (2016) Interactive effects of warming, eutrophication and size structure: impacts on biodiversity and food-web structure. Glob Chang Biol 22(1):220–227
Blair JM (1997) Fire, N availability, and plant response in grasslands: a test of the transient maxima hypothesis. Ecology 78(8):2359–2368
Cease AJ, Fay M, Elser JJ, Harrison JF (2016) Dietary phosphate affects food selection, post-ingestive phosphorus fate, and performance of a polyphagous herbivore. J Exp Biol 219(1):64–72
Cui QA, Lu XT, Wang QB, Han XG (2010) Nitrogen fertilization and fire act independently on foliar stoichiometry in a temperate steppe. Plant Soil 334(1–2):209–219
Declerck SAJ, Malo AR, Diehl S, Waasdorp D, Lemmen KD, Proios K, Papakostas S (2015) Rapid adaptation of herbivore consumers to nutrient limitation: eco-evolutionary feedbacks to population demography and resource control. Ecol Lett 18(6):553–562
Dijkstra FA, Augustine DJ, Brewer P, von Fischer JC (2012) Nitrogen cycling and water pulses in semiarid grasslands: are microbial and plant processes temporally asynchronous? Oecologia 170(3):799–808
Elser JJ, Fagan WF, Denno RF, Dobberfuhl DR, Folarin A, Huberty A, Interlandi S, Kilham SS, McCauley E, Schulz KL, Siemann EH, Sterner RW (2000) Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 408(6812):578–580
Elser JJ, Bracken ME, Cleland EE, Gruner DS, Harpole WS, Hillebrand H, Ngai JT, Seabloom EW, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2007) Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 10(12):1135–1142
Elser JJ, Fagan WF, Kerkhoff AJ, Swenson NG, Enquist BJ (2010) Biological stoichiometry of plant production: metabolism, scaling and ecological response to global change. New Phytol 186(3):593–608
Finzi AC (2009) Decades of atmospheric deposition have not resulted in widespread phosphorus limitation or saturation of tree demand for nitrogen in southern New England. Biogeochemistry 92(3):217–229
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai ZC, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320(5878):889–892
Guiz J, Hillebrand H, Borer ET, Abbas M, Ebeling A, Weigelt A, Oelmann Y, Fornara D, Wilcke W, Temperton VM, Weisser WW (2016) Long-term effects of plant diversity and composition on plant stoichiometry. Oikos 125(5):613–621
Han WX, Fang JY, Reich PB, Woodward FI, Wang ZH (2011) Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol Lett 14(8):788–796
Harpole WS, Ngai JT, Cleland EE, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Bracken MES, Elser JJ, Gruner DS, Hillebrand H, Shurin JB, Smith JE (2011) Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities. Ecol Lett 14(9):852–862
Hautier Y, Tilman D, Isbell F, Seabloom EW, Borer ET, Reich PB (2015) Anthropogenic environmental changes affect ecosystem stability via biodiversity. Science 348(6232):336–340
Heisler JL, Briggs JM, Knapp AK, Blair JM, Seery A (2004) Direct and indirect effects of fire on shrub density and aboveground productivity in a mesic grassland. Ecology 85(8):2245–2257
Henry HAL, Chiariello NR, Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Field CB (2006) Interactive effects of fire, elevated carbon dioxide, nitrogen deposition, and precipitation on a California annual grassland. Ecosystems 9(7):1066–1075
Hobbie SE (2015) Plant species effects on nutrient cycling: revisiting litter feedbacks. Trends Ecol Evol 30(6):357–363
Hooper DU, Johnson L (1999) Nitrogen limitation in dryland ecosystems: responses to geographical and temporal variation in precipitation. Biogeochemistry 46(1–3):247–293
IPCC (2013) In: Stocker TF, Qing D, Plattner G-K, Tingor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group 1 to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
John R, Chen JQ, Ou-Yang ZT, Xiao JF, Becker R, Samanta A, Ganguly S, Yuan WP, Batkhishig O (2013) Vegetation response to extreme climate events on the Mongolian Plateau from 2000 to 2010. Environ Res Lett 8:035033
Koerselman W, Meuleman AFM (1996) The vegetation N: P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J Appl Ecol 33(6):1441–1450
Lu XT, Kong DL, Pan QM, Simmons ME, Han XG (2012) Nitrogen and water availability interact to affect leaf stoichiometry in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia 168(2):301–310
Lu XT, Reed S, Yu Q, He NP, Wang ZW, Han XG (2013) Convergent responses of nitrogen and phosphorus resorption to nitrogen inputs in a semiarid grassland. Glob Chang Biol 19(9):2775–2784
Marklein AR, Houlton BZ (2012) Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol 193(3):696–704
Mattson WJ (1980) Herbivory in relation to plant nitrogen-content. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 11:119–161
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. Circular no. 939. USDA, Washington, DC
Ostertag R (2010) Foliar nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation responses after fertilization: an example from nutrient-limited Hawaiian forests. Plant Soil 334(1–2):85–98
Pellegrini AFA, Hedin LO, Staver AC, Govender N (2015) Fire alters ecosystem carbon and nutrients but not plant nutrient stoichiometry or composition in tropical savanna. Ecology 96(5):1275–1285
Penuelas J, Poulter B, Sardans J, Ciais P, van der Velde M, Bopp L, Boucher O, Godderis Y, Hinsinger P, Llusia J, Nardin E, Vicca S, Obersteiner M, Janssens IA (2013) Human-induced nitrogen-phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nat Commun 4:2934
Perring MP, Hedin LO, Levin SA, McGroddy M, de Mazancourt C (2008) Increased plant growth from nitrogen addition should conserve phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(6):1971–1976
Poulter B, Frank D, Ciais P, Myneni RB, Andela N, Bi J, Broquet G, Canadell JG, Chevallier F, Liu YY, Running SW, Sitch S, van der Werf GR (2014) Contribution of semi-arid ecosystems to interannual variability of the global carbon cycle. Nature 509(7502):600–603
Rau BM, Blank RR, Chambers JC, Johnson DW (2007) Prescribed fire in a Great Basin sagebrush ecosystem: dynamics of soil extractable nitrogen and phosphorus. J Arid Environ 71(4):362–375
Reed SC, Townsend AR, Davidson EA, Cleveland CC (2012) Stoichiometric patterns in foliar nutrient resorption across multiple scales. New Phytol 196(1):173–180
Reich PB, Oleksyn J (2004) Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. P Natl Acad Sci USA 101(30):11001–11006
Reich PB, Walters MB, Tjoelker MG, Vanderklein D, Buschena C (1998) Photosynthesis and respiration rates depend on leaf and root morphology and nitrogen concentration in nine boreal tree species differing in relative growth rate. Funct Ecol 12(3):395–405
Reich PB, Oleksyn J, Wright IJ (2009) Leaf phosphorus influences the photosynthesis-nitrogen relation: a cross-biome analysis of 314 species. Oecologia 160(2):207–212
Sardans J, Rivas-Ubach A, Penuelas J (2012) The C:N: P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect Plant Ecol 14(1):33–47
Schaller J, Tischer A, Struyf E, Bremer M, Belmonte DU, Potthast K (2015) Fire enhances phosphorus availability in topsoils depending on binding properties. Ecology 96(6):1598–1606
Schlesinger WH, Cole JJ, Finzi AC, Holland EA (2011) Introduction to coupled biogeochemical cycles. Front Ecol Environ 9(1):5–8
Smith MD (2011) An ecological perspective on extreme climatic events: a synthetic definition and framework to guide future research. J Ecol 99(3):656–663
Soong JL, Cotrufo MF (2015) Annual burning of a tallgrass prairie inhibits C and N cycling in soil, increasing recalcitrant pyrogenic organic matter storage while reducing N availability. Glob Chang Biol 21(6):2321–2333
Tessier JT, Raynal DJ (2003) Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J Appl Ecol 40(3):523–534
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature 441(7093):629–632
Treydte AC, van Beeck FAL, Ludwig F, Heitkoenig IMA (2008) Improved quality of beneath-canopy grass in South African savannas: local and seasonal variation. J Veg Sci 19(5):663–670
Van de Vijver CADM, Poot P, Prins HHT (1999) Causes of increased nutrient concentrations in post-fire regrowth in an East African savanna. Plant Soil 214(1–2):173–185
Vitousek PM, Porder S, Houlton BZ, Chadwick OA (2010) Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen-phosphorus interactions. Ecol Appl 20(1):5–15
Walker AP, Beckerman AP, Gu LH, Kattge J, Cernusak LA, Domingues TF, Scales JC, Wohlfahrt G, Wullschleger SD, Woodward FI (2014) The relationship of leaf photosynthetic traits—V-cmax and J(max)—to leaf nitrogen, leaf phosphorus, and specific leaf area: a meta-analysis and modeling study. Ecol Evol 4(16):3218–3235
Wan SQ, Hui DF, Luo YQ (2001) Fire effects on nitrogen pools and dynamics in terrestrial ecosystems: a meta-analysis. Ecol Appl 11(5):1349–1365
Wang C, Wang XB, Liu DW, Wu HH, Lu XT, Fang YT, Cheng WX, Luo WT, Jiang P, Shi JS, Yin HQ, Zhou JZ, Han XG, Bai E (2014) Aridity threshold in controlling ecosystem nitrogen cycling in arid and semi-arid grasslands. Nat Commun 5:4799
Wang RZ, Creamer CA, Wang X, He P, Xu ZW, Jiang Y (2016) The effects of a 9-year nitrogen and water addition on soil aggregate phosphorus and sulfur availability in a semi-arid grassland. Ecol Indic 61:806–814
Wright IJ, Reich PB, Westoby M, Ackerly DD, Baruch Z, Bongers F, Cavender-Bares J, Chapin T, Cornelissen JHC, Diemer M, Flexas J, Garnier E, Groom PK, Gulias J, Hikosaka K, Lamont BB, Lee T, Lee W, Lusk C, Midgley JJ, Navas ML, Niinemets U, Oleksyn J, Osada N, Poorter H, Poot P, Prior L, Pyankov VI, Roumet C, Thomas SC, Tjoelker MG, Veneklaas EJ, Villar R (2004) The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 428(6985):821–827
Zhou LS, Huang JH, Lu FM, Han XG (2009) Effects of prescribed burning and seasonal and interannual climate variation on nitrogen mineralization in a typical steppe in Inner Mongolia. Soil Biol Biochem 41(4):796–803
Zhu JX, He NP, Wang QF, Yuan GF, Wen D, Yu GR, Jia YL (2015) The composition, spatial patterns, and influencing factors of atmospheric wet nitrogen deposition in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 511:777–785
Acknowledgements
We thank the Inner Mongolia Grassland Ecosystem Research Station for logistical support. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31470505), National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFC0500601 and 2015CB150802), Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB15010403), Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2014174), and the Key Research Program from CAS (QYZDB-SSW-DQC006 and KFZD-SW-305-002). Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the US Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XTL and XGH designed this research, XTL, SLH, YYH, HWW, FML, QC carried out the experiment and collected data, XTL and SCR analyzed and interpreted the data, all authors contributed to drafting the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Harrison.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lü, XT., Reed, S., Hou, SL. et al. Temporal variability of foliar nutrients: responses to nitrogen deposition and prescribed fire in a temperate steppe. Biogeochemistry 133, 295–305 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-017-0333-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-017-0333-x