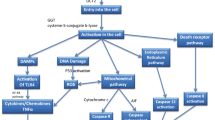
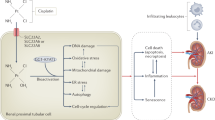
Abstract
Cisplatin (CP) is a chemotherapy drug widely prescribed to treat various neoplasms. Although fundamental for the therapeutic action of the drug, its cytotoxic mechanisms trigger adverse effects in several tissues, such as the kidney, liver, and heart, which limit its clinical use. In this sense, studies point to an essential role of damage to nuclear and mitochondrial DNA associated with oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in the pathophysiology of tissue injuries. Due to the limitation of effective preventive and therapeutic measures against CP-induced toxicity, new strategies with potential cytoprotective effects have been studied. Therefore, this article is timely in reviewing the characteristics and main molecular mechanisms common to renal, hepatic, and cardiac toxicity previously described, in addition to addressing the main validated strategies for the current management of these adverse events in clinical practice. We also handle the main promising antioxidant substances recently presented in the literature to encourage the development of new research that consolidates their potential preventive and therapeutic effects against CP-induced cytotoxicity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hussein A, Ahmed AAE, Shouman SA, Sharawy S. Ameliorating effect of DL-α-lipoic acid against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and cardiotoxicity in experimental animals. Drug Discov Ther. 2012;6(3):147–56.
Miyagi MYS, Latancia MT, Testagrossa LA, de Andrade-Oliveira V, Pereira WO, Hiyane MI, et al. Physical exercise contributes to cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity protection with decreased CD4+ T cells activation. Mol Immunol. 2018;101:507–13.
Aldossary SA. Review on pharmacology of cisplatin: clinical use, toxicity and mechanism of resistance of cisplatin. Biomed Pharmacol J. 2019;12(1):7–15.
Rocha CRR, Silva MM, Quinet A, Cabral-Neto JB, Menck CFM. DNA repair pathways and cisplatin resistance: an intimate relationship. Clin Sao Paulo Braz. 2018;73(Suppl 1):e478s.
Oun R, Moussa YE, Wheate NJ. The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: a review for chemists. Dalton Trans Camb Engl 2003. 2018;47(19):6645–53.
de Jongh FE, van Veen RN, Veltman SJ, de Wit R, van der Burg MEL, van den Bent MJ, et al. Weekly high-dose cisplatin is a feasible treatment option: analysis on prognostic factors for toxicity in 400 patients. Br J Cancer. 2003;88(8):1199–206.
Uehara T, Yamate J, Torii M, Maruyama T. Comparative nephrotoxicity of cisplatin and nedaplatin: mechanisms and histopathological characteristics. J Toxicol Pathol. 2011;24(2):87–94.
Ozkok A, Edelstein CL. Pathophysiology of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. BioMed Res Int. 2014;2014: 967826.
Xing JJ, Hou JG, Liu Y, Zhang RB, Jiang S, Ren S, et al. Supplementation of Saponins from leaves of Panax quinquefolius mitigates cisplatin-evoked cardiotoxicity via inhibiting oxidative stress-associated inflammation and apoptosis in mice. Antioxid Basel Switz. 2019;8(9):347.
Peres LAB, da Cunha AD. Acute nephrotoxicity of cisplatin: molecular mechanisms. J Bras Nefrol. 2013;35(4):332–40.
Oh GS, Kim HJ, Shen A, Lee SB, Khadka D, Pandit A, et al. Cisplatin-induced kidney dysfunction and perspectives on improving treatment strategies. Electrolytes Blood Press E BP. 2014;12(2):55–65.
Ma X, Yan L, Zhu Q, Shao F. Puerarin attenuates cisplatin-induced rat nephrotoxicity: the involvement of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(2): e0171612.
Almutairi MM, Alanazi WA, Alshammari MA, Alotaibi MR, Alhoshani AR, Al-Rejaie SS, et al. Neuro-protective effect of rutin against cisplatin-induced neurotoxic rat model. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):472.
Qi L, Luo Q, Zhang Y, Jia F, Zhao Y, Wang F. Advances in toxicological research of the anticancer drug cisplatin. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(8):1469–86.
Gu J, Wang X, Chen Y, Xu K, Yu D, Wu H. An enhanced antioxidant strategy of astaxanthin encapsulated in ROS-responsive nanoparticles for combating cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. J Nanobiotechnol. 2022;20(1):268.
Li W, Sun Y, Chen J, Jiang Z, Yang J. PEGylated cisplatin nanoparticles for treating colorectal cancer in a pH-responsive manner. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:8023915.
Holditch SJ, Brown CN, Lombardi AM, Nguyen KN, Edelstein CL. Recent advances in models, mechanisms, biomarkers, and interventions in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):3011.
Volarevic V, Djokovic B, Jankovic MG, Harrell CR, Fellabaum C, Djonov V, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity: a balance on the knife edge between renoprotection and tumor toxicity. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26(1):25.
Kumar P, Sulakhiya K, Barua CC, Mundhe N. TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 expressions, responsible for disparity in action of curcumin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017;431(1–2):113–22.
Meng H, Fu G, Shen J, Shen K, Xu Z, Wang Y, et al. Ameliorative effect of daidzein on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice via modulation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and cell death. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3140680.
Francescato HDC, Coimbra TM, Costa RS, Bianchi M de LP. Protective effect of quercetin on the evolution of cisplatin-induced acute tubular necrosis. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2004;27(3):148–58.
Francescato HDC, Almeida LF, Reis NG, Faleiros CM, Papoti M, Costa RS, et al. Previous exercise effects in cisplatin-induced renal lesions in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2018;43(2):582–93.
Wei Q, Dong Z. Mouse model of ischemic acute kidney injury: technical notes and tricks. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012;303(11):F1487-1494.
Wang JN, Liu MM, Wang F, Wei B, Yang Q, Cai YT, et al. RIPK1 inhibitor Cpd-71 attenuates renal dysfunction in cisplatin-treated mice via attenuating necroptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress. Clin Sci Lond Engl 1979. 2019;133(14):1609–27.
Yuluğ E, Türedi S, Yıldırım Ö, Yenilmez E, Aliyazıcıoğlu Y, Demir S, et al. Biochemical and morphological evaluation of the effects of propolis on cisplatin induced kidney damage in rats. Biotech Histochem. 2019;94(3):204–13.
Leite AB, Lima HN, Flores C de O, Oliveira CA, Cunha LEC, Neves JL, et al. High-intensity interval training is more effective than continuous training to reduce inflammation markers in female rats with cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Life Sci. 2021;266:118880.
Aljuhani N, Ismail RS, El-Awady MS, Hassan MH. Modulatory effects of perindopril on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice: Implication of inflammatory cytokines and caspase-3 mediated apoptosis. Acta Pharm Zagreb Croat. 2020;70(4):515–25.
Ugur S, Ulu R, Dogukan A, Gurel A, Yigit IP, Gozel N, et al. The renoprotective effect of curcumin in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Ren Fail. 2015;37(2):332–6.
Malik S, Bhatia J, Suchal K, Gamad N, Dinda AK, Gupta YK, et al. Nobiletin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury due to its anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2015;67(7–8):427–33.
Oliveira CA, Mercês ÉAB, Portela FS, De Benedictis JM, De Benedictis LM, da Silva AVB, et al. Benefits of high-intensity interval training compared to continuous training to reduce apoptotic markers in female rats with cisplatin nephrotoxicity – possible modulatory role of IL-11. Apoptosis Int J Program Cell Death. 2023;28(3–4):566–75.
Winston JA, Safirstein R. Reduced renal blood flow in early cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1985;249(4 Pt 2):F490-496.
Robbins ME, Campling D, Whitehouse E, Hopewell JW, Michalowski A. Cisplatin-induced reductions in renal functional reserve uncovered by unilateral nephrectomy: an experimental study in the pig. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1990;27(3):211–8.
Germani G, Battistella S, Ulinici D, Zanetto A, Shalaby S, Pellone M, et al. Drug induced liver injury: from pathogenesis to liver transplantation. Minerva Gastroenterol. 2021;67(1):50–64.
Cersosimo RJ. Hepatotoxicity associated with cisplatin chemotherapy. Ann Pharmacother. 1993;27(4):438–41.
Ateyya H, Yosef H, Nader MA. Ameliorative effect of trimetazidine on cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;94(2):225–30.
Karale S, Kamath JV. Effect of daidzein on cisplatin-induced hematotoxicity and hepatotoxicity in experimental rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2017;49(1):49–54.
Martins NM, Santos N a. G, Curti C, Bianchi MLP, Santos AC. Cisplatin induces mitochondrial oxidative stress with resultant energetic metabolism impairment, membrane rigidification and apoptosis in rat liver. J Appl Toxicol JAT. 2008;28(3):337–44.
Paunović MG, Matić MM, Stanković VD, Milošević MD, Jevtić VV, Trifunović SR, et al. Evaluation of toxic effects of novel platinum (IV) complexes in female rat liver: potential protective role of resveratrol. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021;79(1):141–52.
Abd Rashid N, Hussan F, Hamid A, Adib Ridzuan NR, Halim SASA, Abdul Jalil NA, et al. Polygonum minus essential oil modulates cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity through inflammatory and apoptotic pathways. EXCLI J. 2020;19:1246–65.
Un H, Ugan RA, Kose D, Bayir Y, Cadirci E, Selli J, et al. A novel effect of Aprepitant: protection for cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxicity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;880: 173168.
Bano N, Najam R. Histopathological and biochemical assessment of liver damage in albino Wistar rats treated with cytotoxic platinum compounds in combination with 5-fluorouracil. Arch Med Sci AMS. 2019;15(4):1092–103.
Abdel-Gayoum AA, Ahmida MHS. Changes in the serum, liver, and renal cortical lipids and electrolytes in rabbits with cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Turk J Med Sci. 2017;47(3):1019–27.
Afsar T, Razak S, Almajwal A, Rashid Khan M. Modulatory influence of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker ethyl acetate extract against cisplatin inveigled hepatic injury and dyslipidemia in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):307.
Tlili N, Feriani A, Saadoui E, Nasri N, Khaldi A. Capparis spinosa leaves extract: source of bioantioxidants with nephroprotective and hepatoprotective effects. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedicine Pharmacother. 2017;87:171–9.
El-Gizawy MM, Hosny EN, Mourad HH, Abd-El Razik AN. Curcumin nanoparticles ameliorate hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(10):1941–53.
Daher IN, Yeh ETH. Vascular complications of selected cancer therapies. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2008;5(12):797–805.
Afsar T, Razak S, Almajwal A, Shabbir M, Khan MR. Evaluating the protective potency of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker on histological and biochemical changes induced by Cisplatin in the cardiac tissue of rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):182.
Herradón E, González C, Uranga JA, Abalo R, Martín MI, López-Miranda V. Characterization of cardiovascular alterations induced by different chronic cisplatin treatments. Front Pharmacol [Internet]. 2017 [citado 2 de fevereiro de 2024];8. Disponível em: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2017.00196
Saleh R, Awadin W, Elseady Y, Waheish FE. Renal and cardiovascular damage induced by Cisplatin in rats. Life Sci J. 2014;11:191–203.
Topal İ, Bilgin AÖ, Çimen FK, Kurt N, Süleyman Z, Bilgin Y, et al. The effect of rutin on cisplatin-induced oxidative cardiac damage in rats. Anatol J Cardiol. 2018;20(3):136–42.
Dugbartey GJ, Peppone LJ, de Graaf IAM. An integrative view of cisplatin-induced renal and cardiac toxicities: molecular mechanisms, current treatment challenges and potential protective measures. Toxicology. 2016;371:58–66.
El-Awady ESE, Moustafa YM, Abo-Elmatty DM, Radwan A. Cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: mechanisms and cardioprotective strategies. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;650(1):335–41.
Chowdhury S, Sinha K, Banerjee S, Sil PC. Taurine protects cisplatin induced cardiotoxicity by modulating inflammatory and endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. BioFactors Oxf Engl. 2016;42(6):647–64.
Saleh DO, Mansour DF, Mostafa RE. Rosuvastatin and simvastatin attenuate cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity via disruption of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptotic death in rats: targeting ER-Chaperone GRP78 and Calpain-1 pathways. Toxicol Rep. 2020;7:1178–86.
Soliman AF, Anees LM, Ibrahim DM. Cardioprotective effect of zingerone against oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis induced by cisplatin or gamma radiation in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018;391(8):819–32.
Quintanilha JCF, de Sousa VM, Visacri MB, Amaral LS, Santos RMM, Zambrano T, et al. Involvement of cytochrome P450 in cisplatin treatment: implications for toxicity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017;80(2):223–33.
More SS, Akil O, Ianculescu AG, Geier EG, Lustig LR, Giacomini KM. Role of the copper transporter, CTR1, in platinum-induced ototoxicity. J Neurosci. 2010;30(28):9500–9.
Manohar S, Leung N. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review of the literature. J Nephrol. 2018;31(1):15–25.
Ciarimboli G, Deuster D, Knief A, Sperling M, Holtkamp M, Edemir B, et al. Organic cation transporter 2 mediates cisplatin-induced oto- and nephrotoxicity and is a target for protective interventions. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(3):1169–80.
Yokoo S, Yonezawa A, Masuda S, Fukatsu A, Katsura T, Inui KI. Differential contribution of organic cation transporters, OCT2 and MATE1, in platinum agent-induced nephrotoxicity. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;74(3):477–87.
Pabla N, Murphy RF, Liu K, Dong Z. The copper transporter Ctr1 contributes to cisplatin uptake by renal tubular cells during cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009;296(3):F505-511.
Koepsell H. Organic cation transporters in intestine, kidney, liver, and brain. Annu Rev Physiol. 1998;60:243–66.
Sugawara-Yokoo M, Urakami Y, Koyama H, Fujikura K, Masuda S, Saito H, et al. Differential localization of organic cation transporters rOCT1 and rOCT2 in the basolateral membrane of rat kidney proximal tubules. Histochem Cell Biol. 2000;114(3):175–80.
Zatulovskiy EA, Skvortsov AN, Rusconi P, Ilyechova EY, Babich PS, Tsymbalenko NV, et al. Serum depletion of holo-ceruloplasmin induced by silver ions in vivo reduces uptake of cisplatin. J Inorg Biochem. 2012;116:88–96.
Kim BE, Turski ML, Nose Y, Casad M, Rockman HA, Thiele DJ. Cardiac copper deficiency activates a systemic signaling mechanism that communicates with the copper acquisition and storage organs. Cell Metab. 2010;11(5):353–63.
Barabas K, Milner R, Lurie D, Adin C. Cisplatin: a review of toxicities and therapeutic applications. Vet Comp Oncol. 2008;6(1):1–18.
Galluzzi L, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Michels J, Martins I, Kepp O, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene. 2012;31(15):1869–83.
Townsend DM, Tew KD, He L, King JB, Hanigan MH. Role of glutathione S-transferase Pi in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedicine Pharmacother. 2009;63(2):79–85.
Shahid F, Farooqui Z, Alam T, Abidi S, Parwez I, Khan F. Thymoquinone supplementation ameliorates cisplatin-induced hepatic pathophysiology. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021;40(10):1673–84.
Zhang J, Ye Z wei, Tew KD, Townsend DM. Cisplatin chemotherapy and renal function. Adv Cancer Res. 2021;152:305–27.
Hanigan MH, Devarajan P. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: molecular mechanisms. Cancer Ther. 2003;1:47–61.
Ali R, Aouida M, Alhaj Sulaiman A, Madhusudan S, Ramotar D. Can cisplatin therapy be improved? Pathways that can be targeted. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7241.
Townsend DM, Hanigan MH. Inhibition of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase or cysteine S-conjugate beta-lyase activity blocks the nephrotoxicity of cisplatin in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;300(1):142–8.
Amable L. Cisplatin resistance and opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacol Res. 2016;106:27–36.
Johnstone TC, Suntharalingam K, Lippard SJ. The next generation of platinum drugs: targeted Pt(II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt(IV) prodrugs. Chem Rev. 2016;116(5):3436–86.
El-Sawalhi MM, Ahmed LA. Exploring the protective role of apocynin, a specific NADPH oxidase inhibitor, in cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2014;207:58–66.
Adalı F, Gonul Y, Kocak A, Yuksel Y, Ozkececi G, Ozdemir C, et al. Effects of thymoquinone against cisplatin-induced cardiac injury in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2016;31(4):271–7.
Yang Z, Schumaker LM, Egorin MJ, Zuhowski EG, Guo Z, Cullen KJ. Cisplatin preferentially binds mitochondrial DNA and voltage-dependent anion channel protein in the mitochondrial membrane of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: possible role in apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(19):5817–25.
Hu Y, Yang C, Amorim T, Maqbool M, Lin J, Li C, et al. Cisplatin-mediated upregulation of APE2 binding to MYH9 provokes mitochondrial fragmentation and acute kidney injury. Cancer Res. 2021;81(3):713–23.
Cocetta V, Ragazzi E, Montopoli M. Mitochondrial involvement in cisplatin resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(14):3384.
Mapuskar KA, Steinbach EJ, Zaher A, Riley DP, Beardsley RA, Keene JL, et al. Mitochondrial superoxide dismutase in cisplatin-induced kidney injury. Antioxid Basel Switz. 2021;10(9):1329.
Huang G, Zhang Q, Xu C, Chen L, Zhang H. Mechanism of kidney injury induced by cisplatin. Toxicol Res. 2022;11(3):385–90.
Cullen KJ, Yang Z, Schumaker L, Guo Z. Mitochondria as a critical target of the chemotheraputic agent cisplatin in head and neck cancer. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2007;39(1):43–50.
Qian W, Nishikawa M, Haque AM, Hirose M, Mashimo M, Sato E, et al. Mitochondrial density determines the cellular sensitivity to cisplatin-induced cell death. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289(6):C1466-1475.
Jiang M, Wang CY, Huang S, Yang T, Dong Z. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in p53-deficient renal cells via the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Am J Physiol – Ren Physiol. 2009;296(5):F983–93.
Desoize B. Cancer and metals and metal compounds: part I–carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2002;42(1):1–3.
Siddik ZH. Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22(47):7265–79.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Li B, Ding P, Jin D, Hou S, et al. The effect of monotropein on alleviating cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting oxidative damage, inflammation and apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedicine Pharmacother. 2020;129: 110408.
Noori S, Mahboob T. Antioxidant effect of carnosine pretreatment on cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress in rats. Indian J Clin Biochem IJCB. 2010;25(1):86–91.
Al Fayi M, Otifi H, Alshyarba M, Dera AA, Rajagopalan P. Thymoquinone and curcumin combination protects cisplatin-induced kidney injury, nephrotoxicity by attenuating NFκB, KIM-1 and ameliorating Nrf2/HO-1 signalling. J Drug Target. 2020;28(9):913–22.
Aboraya DM, El Baz A, Risha EF, Abdelhamid FM. Hesperidin ameliorates cisplatin induced hepatotoxicity and attenuates oxidative damage, cell apoptosis, and inflammation in rats. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022;29(5):3157–66.
Başak Türkmen N, Aşkın Özek D, Taşlıdere A, Çiftçi O, Saral Ö, Gül CC. Protective role of Diospyros lotus L. in cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: cardiac damage and oxidative stress in rats. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2022;19(2):132–7.
Karasawa T, Steyger PS. An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol Lett. 2015;237(3):219–27.
Shao YP, Zhou Q, Li YP, Zhang SC, Xu HW, Wu S, et al. Curcumin ameliorates cisplatin-induced cystopathy via activating NRF2 pathway. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018;37(8):2470–9.
Sun L, Liu J, Yuan Y, Zhang X, Dong Z. Protective effect of the BET protein inhibitor JQ1 in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol - Ren Physiol. 2018;315(3):F469–78.
Done AJ, Traustadóttir T. Nrf2 mediates redox adaptations to exercise. Redox Biol. 2016;10:191–9.
Di Meo S, Napolitano G, Venditti P. Mediators of physical activity protection against ROS-linked skeletal muscle damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):3024.
Alibakhshi T, Khodayar MJ, Khorsandi L, Rashno M, Zeidooni L. Protective effects of zingerone on oxidative stress and inflammation in cisplatin-induced rat nephrotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedicine Pharmacother. 2018;105:225–32.
Al-Malki AL, Sayed AAR. Thymoquinone attenuates cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity via nuclear factor kappa-β. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:282.
Bilgic Y, Akbulut S, Aksungur Z, Erdemli ME, Ozhan O, Parlakpinar H, et al. Protective effect of dexpanthenol against cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(5):4049–57.
Ibrahim MA, Bakhaat GA, Tammam HG, Mohamed RM, El-Naggar SA. Cardioprotective effect of green tea extract and vitamin E on Cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice: toxicological, histological and immunohistochemical studies. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedicine Pharmacother. 2019;113: 108731.
Elkomy A, Abdelhiee EY, Fadl SE, Emam MA, Gad FAM, Sallam A, et al. l-Carnitine mitigates oxidative stress and disorganization of cytoskeleton intermediate filaments in cisplatin-induced hepato-renal toxicity in rats. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11: 574441.
Sherif IO. Hepatoprotective effect of arjunolic acid against cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity: targeting oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(4): e22714.
El Shaffei I, Abdel-Latif GA, Farag DB, Schaalan M, Salama RM. Ameliorative effect of betanin on experimental cisplatin-induced liver injury; the novel impact of miRNA-34a on the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(6):1–14.
Lin Z, Bao Y, Hong B, Wang Y, Zhang X, Wu Y. Salvianolic acid B attenuated cisplatin-induced cardiac injury and oxidative stress via modulating Nrf2 signal pathway. J Toxicol Sci. 2021;46(5):199–207.
Wang SH, Tsai KL, Chou WC, Cheng HC, Huang YT, Ou HC, et al. Quercetin mitigates cisplatin-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Am J Chin Med. 2022;50(5):1281–98.
Visacri MB, Quintanilha JCF, de Sousa VM, Amaral LS, Ambrósio RdFL, Calonga L, et al. Can acetylcysteine ameliorate cisplatin‐induced toxicities and oxidative stress without decreasing antitumor efficacy? A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial involving patients with head and neck cancer. Cancer Med. 2019;8(5):2020–30.
Raja W, Mir MH, Dar I, Banday MA, Ahmad I. Cisplatin induced paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 2013;34(4):330–2.
Vickers AEM, Rose K, Fisher R, Saulnier M, Sahota P, Bentley P. Kidney slices of human and rat to characterize cisplatin-induced injury on cellular pathways and morphology. Toxicol Pathol. 2004;32(5):577–90.
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci. 2007;334(2):115–24.
Oh GS, Kim HJ, Shen A, Lee SB, Yang SH, Shim H, et al. New therapeutic concept of NAD redox balance for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. BioMed Res Int. 2016;2016:4048390.
Ma ZN, Liu Z, Wang Z, Ren S, Tang S, Wang YP, et al. Supplementation of American ginseng berry extract mitigated cisplatin-evoked nephrotoxicity by suppressing ROS-mediated activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol Int J Publ Br Ind Biol Res Assoc. 2017;110:62–73.
Li F, Yao Y, Huang H, Hao H, Ying M. Xanthohumol attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through inhibiting NF-κB and activating Nrf2 signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:277–82.
Habib SA, Suddek GM, Abdel Rahim M, Abdelrahman RS. The protective effect of protocatechuic acid on hepatotoxicity induced by cisplatin in mice. Life Sci. 2021;277: 119485.
Zhang B, Ramesh G, Norbury CC, Reeves WB. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha produced by renal parenchymal cells. Kidney Int. 2007;72(1):37–44.
Jain SK, Rains JL, Croad JL. Effect of chromium niacinate and chromium picolinate supplementation on lipid peroxidation, TNF-alpha, IL-6, CRP, glycated hemoglobin, triglycerides, and cholesterol levels in blood of streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43(8):1124–31.
Hop HT, Reyes AWB, Huy TXN, Arayan LT, Min W, Lee HJ, et al. Activation of NF-kB-mediated TNF-induced antimicrobial immunity is required for the efficient Brucella abortus clearance in RAW 264.7 cells. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:437.
Hui D, Rui-Zhi T, Jian-Chun L, Xia Z, Dan W, Jun-Ming F, et al. Astragalus propinquus Schischkin and Panax notoginseng (A&P) compound relieved cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through inhibiting the mincle maintained macrophage inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;252: 112637.
TNF-alpha mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity – PubMed [Internet]. [citado 2 de fevereiro de 2024]. Disponível em: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12235115/
Khedr LH, Rahmo RM, Farag DB, Schaalan MF, El Magdoub HM. Crocin attenuates cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity via TLR4/NF-κBp50 signaling and BAMBI modulation of TGF-β activity: involvement of miRNA-9 and miRNA-29. Food Chem Toxicol Int J Publ Br Ind Biol Res Assoc. 2020;140: 111307.
Pabla N, Dong Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int. 2008;73(9):994–1007.
El-Hawwary AA, Omar NM. The influence of ginger administration on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity in rat: light and electron microscopic study. Acta Histochem. 2019;121(5):553–62.
Tsuruya K, Tokumoto M, Ninomiya T, Hirakawa M, Masutani K, Taniguchi M, et al. Antioxidant ameliorates cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell death through inhibition of death receptor-mediated pathways. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003;285(2):F208-218.
Kim HJ, Park DJ, Kim JH, Jeong EY, Jung MH, Kim TH, et al. Glutamine protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by decreasing cisplatin accumulation. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;127(1):117–26.
Al-Lamki RS, Mayadas TN. TNF receptors: signaling pathways and contribution to renal dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2015;87(2):281–96.
Dong Z, Atherton SS. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha in cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a homebred foe? Kidney Int. 2007;72(1):5–7.
Yang S, Wang J, Brand DD, Zheng SG. Role of TNF-TNF receptor 2 signal in regulatory T cells and its therapeutic implications. Front Immunol. 2018;9:784.
Farzanegi P, Abbaszadeh H, Farokhi F, Rahmati-Ahmadabad S, Hosseini SA, Ahmad A, et al. Attenuated renal and hepatic cells apoptosis following swimming exercise supplemented with garlic extract in old rats. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:1409–18.
Yu X, Meng X, Xu M, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Ding G, et al. Celastrol ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity by inhibiting NF-κB and improving mitochondrial function. EBioMedicine. 2018;36:266–80.
Wang S, Zheng Y, Jin S, Fu Y, Liu Y. Dioscin protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by reducing ferroptosis and apoptosis through activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Antioxidants. 2022;11(12):2443.
Targeted inhibition of CX3CL1 limits podocytes ferroptosis to ameliorate cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury – PubMed [Internet]. [citado 2 de fevereiro de 2024]. Disponível em: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37875838/
Glutathione metabolism rewiring protects renal tubule cells against cisplatin-induced apoptosis and ferroptosis – PubMed [Internet]. [citado 2 de fevereiro de 2024]. Disponível em: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36692085/
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060–72.
Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J, He D, Zhang C, Duan C, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):34.
Frontiers | VPA improves ferroptosis in tubular epithelial cells after cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury [Internet]. [citado 2 de fevereiro de 2024]. Disponível em: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2023.1147772/full
Xie LH, Fefelova N, Pamarthi SH, Gwathmey JK. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and relevance to cardiovascular disease. Cells. 2022;11(17):2726.
Fang X, Ardehali H, Min J, Wang F. The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2023;20(1):7–23.
Ikeda Y, Hamano H, Horinouchi Y, Miyamoto L, Hirayama T, Nagasawa H, et al. Role of ferroptosis in cisplatin-induced acute nephrotoxicity in mice. J Trace Elem Med Biol Organ Soc Miner Trace Elem GMS. 2021;67: 126798.
Mei H, Zhao L, Li W, Zheng Z, Tang D, Lu X, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis protects House Ear Institute-Organ of Corti 1 cells and cochlear hair cells from cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(20):12065–81.
Guo J, Yin J, Liu P, Zhang X, Wei J, Wang M, et al. Glycyrrhizin arginine salt protects against cisplation-induced acute liver injury by repressing BECN1-mediated ferroptosis. Front Pharmacol [Internet]. 2023 [citado 3 de fevereiro de 2024];14. Disponível em: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2023.1219486
Tsang RY, Al-Fayea T, Au HJ. Cisplatin overdose: toxicities and management. Drug Saf. 2009;32(12):1109–22.
Desilets A, Adam JP, Soulières D. Management of cisplatin-associated toxicities in bladder cancer patients. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2020;14(3):286–92.
Cornelison TL, Reed E. Nephrotoxicity and hydration management for cisplatin, carboplatin, and ormaplatin. Gynecol Oncol. 1993;50(2):147–58.
Ben Ayed W, Ben Said A, Hamdi A, Mokrani A, Masmoudi Y, Toukabri I, et al. Toxicity, risk factors and management of cisplatin-induced toxicity: a prospective study. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020;26(7):1621–9.
Tiseo M, Martelli O, Mancuso A, Sormani MP, Bruzzi P, Di Salvia R, et al. Short hydration regimen and nephrotoxicity of intermediate to high-dose cisplatin-based chemotherapy for outpatient treatment in lung cancer and mesothelioma. Tumori. 2007;93(2):138–44.
Burns CV, Edwin SB, Szpunar S, Forman J. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in an outpatient setting. Pharmacotherapy. 2021;41(2):184–90.
Crona DJ, Faso A, Nishijima TF, McGraw KA, Galsky MD, Milowsky MI. A systematic review of strategies to prevent cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Oncologist. 2017;22(5):609–19.
Ninomiya K, Hotta K, Hisamoto-Sato A, Ichihara E, Gotoda H, Morichika D, et al. Short-term low-volume hydration in cisplatin-based chemotherapy for patients with lung cancer: the second prospective feasibility study in the Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group Trial 1201. Int J Clin Oncol. 2016;21(1):81–7.
Fukushima K, Okada A, Oe H, Hirasaki M, Hamori M, Nishimura A, et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis of cisplatin with hydration and mannitol diuresis: the contribution of urine cisplatin concentration to nephrotoxicity. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018;43(2):193–203.
Ruggiero A, Ariano A, Triarico S, Capozza MA, Romano A, Maurizi P, et al. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in children: what is the best protective strategy? J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2021;27(1):180–6.
Markman M, Cleary S, Howell SB. Nephrotoxicity of high-dose intracavitary cisplatin with intravenous thiosulfate protection. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1985;21(9):1015–8.
Gandara DR, Wiebe VJ, Perez EA, Makuch RW, DeGregorio MW. Cisplatin rescue therapy: experience with sodium thiosulfate, WR2721, and diethyldithiocarbamate. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1990;10(4):353–65.
Oun R, Rowan E. Cisplatin induced arrhythmia; electrolyte imbalance or disturbance of the SA node? Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;811:125–8.
Pai VB, Nahata MC. Cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents: incidence, treatment and prevention. Drug Saf. 2000;22(4):263–302.
Zhao L. Protective effects of trimetazidine and coenzyme Q10 on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity by alleviating oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Anatol J Cardiol. 2019;22(5):232–9.
Taghizadeh F, Hosseinimehr SJ, Zargari M, Karimpour Malekshah A, Mirzaei M, Talebpour AF. Alleviation of cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity by gliclazide: involvement of oxidative stress and caspase-3 activity. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021;9(3): e00788.
El-Shitany NA, Eid B. Proanthocyanidin protects against cisplatin-induced oxidative liver damage through inhibition of inflammation and NF-κβ/TLR-4 pathway. Environ Toxicol. 2017;32(7):1952–63.
Ortega-Domínguez B, Aparicio-Trejo OE, García-Arroyo FE, León-Contreras JC, Tapia E, Molina-Jijón E, et al. Curcumin prevents cisplatin-induced renal alterations in mitochondrial bioenergetics and dynamic. Food Chem Toxicol Int J Publ Br Ind Biol Res Assoc. 2017;107(Pt A):373–85.
Waseem M, Pandey P, Tomar B, Raisuddin S, Parvez S. Ameliorative action of curcumin in cisplatin-mediated hepatotoxicity: an in vivo study in Wistar rats. Arch Med Res. 2014;45(6):462–8.
Bahadır A, Ceyhan A, Öz Gergin Ö, Yalçın B, Ülger M, Özyazgan TM, et al. Protective effects of curcumin and beta-carotene on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity: an experimental rat model. Anatol J Cardiol. 2018;19(3):213–21.
Khadrawy YA, Hosny EN, El-Gizawy MM, Sawie HG, Aboul Ezz HS. The effect of curcumin nanoparticles on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity in male Wistar Albino rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021;21(6):433–43.
Darwish MA, Abo-Youssef AM, Khalaf MM, Abo-Saif AA, Saleh IG, Abdelghany TM. Vitamin E mitigates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity due to reversal of oxidative/nitrosative stress, suppression of inflammation and reduction of total renal platinum accumulation. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2017;31(1):1–9.
Abdel-Daim MM, Aleya L, El-Bialy BE, Abushouk AI, Alkahtani S, Alarifi S, et al. The ameliorative effects of ceftriaxone and vitamin E against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26(15):15248–54.
Hepatoprotective effect of curcumin and alpha-tocopherol against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress | BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies | Full Text [Internet]. [citado 3 de fevereiro de 2024]. Disponível em: https://bmccomplementmedtherapies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6882-14-111
Rosic G, Selakovic D, Joksimovic J, Srejovic I, Zivkovic V, Tatalović N, et al. The effects of N-acetylcysteine on cisplatin-induced changes of cardiodynamic parameters within coronary autoregulation range in isolated rat hearts. Toxicol Lett. 2016;242:34–46.
Gunturk EE, Yucel B, Gunturk I, Yazici C, Yay A, Kose K. The effects of N-acetylcysteine on cisplatin induced cardiotoxicity. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2019;120(6):423–8.
Abdel-Wahab WM, Moussa FI, Saad NA. Synergistic protective effect of N-acetylcysteine and taurine against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017;11:901–8.
Elsayed A, Elkomy A, Elkammar R, Youssef G, Abdelhiee EY, Abdo W, et al. Synergistic protective effects of lycopene and N-acetylcysteine against cisplatin-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):13979.
Huang S, You J, Wang K, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wei H, et al. N-acetylcysteine attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting the C5a receptor. BioMed Res Int. 2019;2019:4805853.
Kandemir FM, Yildirim S, Caglayan C, Kucukler S, Eser G. Protective effects of zingerone on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in female rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26(22):22562–74.
Gwon MG, Gu H, Leem J, Park KK. Protective effects of 6-Shogaol, an active compound of ginger, in a murine model of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Mol Basel Switz. 2021;26(19):5931.
Mohamed HE, Badawy MMM. Modulatory effect of zingerone against cisplatin or γ-irradiation induced hepatotoxicity by molecular targeting regulation. Appl Radiat Isot Data Instrum Methods Use Agric Ind Med. 2019;154: 108891.
Moradi M, Goodarzi N, Faramarzi A, Cheraghi H, Hashemian AH, Jalili C. Melatonin protects rats testes against bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin-induced toxicity via mitigating nitro-oxidative stress and apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedecine Pharmacother. 2021;138: 111481.
Zhuo X, Jiang H. Protective effects of melatonin in cisplatin-induced cardiac toxicity: possible role of BDNF-TNF-α signaling pathway. Acta Cirúrgica Bras. 2022;37: e370208.
Yilmaz I, Demiryilmaz I, Turan MI, Suleyman B, Turan IS, Altuner D, et al. The protective effect of melatonin and agomelatin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in the rat kidney. Lat Am J Pharm. 2013;32:1231.
Ko JW, Shin NR, Jung TY, Shin IS, Moon C, Kim SH, et al. Melatonin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats via induction of anti-aging protein, Klotho. Food Chem Toxicol Int J Publ Br Ind Biol Res Assoc. 2019;129:201–10.
Ali BH, Abdelrahman A, Al Suleimani Y, Manoj P, Ali H, Nemmar A, et al. Effect of concomitant treatment of curcumin and melatonin on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biomed Pharmacother Biomedecine Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110761.
Soetikno V, Sari SDP, Ul Maknun L, Sumbung NK, Rahmi DNI, Pandhita BAW, et al. Pre-treatment with curcumin ameliorates cisplatin-induced kidney damage by suppressing kidney inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Drug Res. 2019;69(2):75–82.
Abd El-Kader M, Taha RI. Comparative nephroprotective effects of curcumin and etoricoxib against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Acta Histochem. 2020;122(4): 151534.
Abo-Elmaaty AMA, Behairy A, El-Naseery NI, Abdel-Daim MM. The protective efficacy of vitamin E and cod liver oil against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020;27(35):44412–26.
Rosic G, Srejovic I, Zivkovic V, Selakovic D, Joksimovic J, Jakovljevic V. The effects of N-acetylcysteine on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity on isolated rat hearts after short-term global ischemia. Toxicol Rep. 2015;2:996–1006.
Coşkun Ö, Öztopuz Ö, Büyük B. Possible protective activity of n-acetyl cysteine against cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(1):637–44.
Bishr A, Sallam N, Nour El-Din M, Awad AS, Kenawy SA. Ambroxol attenuates cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity via inhibition of p-JNK/p-ERK. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;97(1):55–64.
Ali DA, Abdeen AM, Ismail MF, Mostafa MA. Histological, ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies on the protective effect of ginger extract against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in male rats. Toxicol Ind Health. 2015;31(10):869–80.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado da Bahia (FAPESB), grant number: BOL0472/2021 and BOL0766/2023 and Institutional Program of Scientific Initiation Scholarship (PIBIC) from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), grant number: 01/2023 and Universidade Federal da Bahia (UFBA), grand number: 01/2022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors have read the journal's authorship agreement and policy and declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, C.A., Mercês, É.A.B., Portela, F.S. et al. An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity: characteristics, common molecular mechanisms, and current clinical management. Clin Exp Nephrol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-024-02490-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-024-02490-x