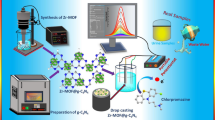
Abstract
Nitrogen doped carbon dots (NCDs) were synthesized using a low temperature approach and used to modify a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) via dipping. The oxygen groups on the surface of the NCDs, and the charge delocalization of the NCDs warrant an excellent electrocatalytic activity of the GCE toward oxidation of paracetamol (PA) and reduction of H2O2. PA and H2O2 were detected at 0.34 V and −0.4 V (both vs. Ag/AgCl) using differential pulse voltammetry and amperometric I-T measurement, respectively. The modified GCE has a linear response to PA in the 0.5 to 600 μM concentration range, and to H2O2 in the 0.05 μM to 2.25 mM concentration range. The detection limits are 157 nM and 41 nM, respectively. In our perception, the modified GCE holds promise for stable, selective and sensitive determination of PA and H2O2 in pharmaceutical analysis.

Nitrogen doped carbon dots (NCDs) were synthesized and used to modify a glassy carbon electrode. Surface functional groups on NCDs can trigger electrocatalytic reactions toward paracetamol oxidation and H2O2 reduction with high sensitivities.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 June 2019
The authors of “A glassy carbon electrode modified with N-doped carbon dots for improved detection of hydrogen peroxide and paracetamol (Microchimica Acta 185, no. 2 (2018): 87)” wish to replace the incorrect images of Fig. 1C, 1D shown below.
References
Zhu S, Song Y, Zhao X, Shao J, Zhang J, Yang B (2015) The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots, and polymer dots): current state and future perspective. Nano Res 8(2):355–381
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Lu Y, Wu A, Cai C, Lin H (2015) Red, green, and blue luminescence by carbon dots: full-color emission tuning and multicolor cellular imaging. Angew Chem Int Edit 54(18):5360–5363
Georgakilas V, Perman JA, Tucek J, Zboril R (2015) Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem Rev 115(11):4744–4822
Zhang L, Han Y, Zhu J, Zhai Y, Dong S (2015) Simple and sensitive fluorescent and electrochemical trinitrotoluene sensors based on aqueous carbon dots. Anal Chem 87(4):2033–2036
Yu L, Yue X, Yang R, Jing S, Qu L (2016) A sensitive and low toxicity electrochemical sensor for 2, 4-dichlorophenol based on the nanocomposite of carbon dots, hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium bromide and chitosan. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 224:241–247
Huang Q, Lin X, Zhu JJ, Tong QX (2017) Pd-Au@ carbon dots nanocomposite: Facile synthesis and application as an ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for determination of colitoxin DNA in human serum. Biosens Bioelectron 94:507–512
Guo W, Pi F, Zhang H, Sun J, Zhang Y, Sun X (2017) A novel molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor modified with carbon dots, chitosan, gold nanoparticles for the determination of Patulin. Biosens Bioelectron 98:299–304
Huang Q, Lin X, Lin C, Zhang Y, Hu S, Wei C (2015) A high performance electrochemical biosensor based on Cu2O–carbon dots for selective and sensitive determination of dopamine in human serum. RSC Adv 5(67):54102–54108
Wei C, Huang Q, Hu S, Zhang H, Zhang W, Wang Z, Zhu M, Dai P, Huang L (2014) Simultaneous electrochemical determination of hydroquinone, catechol and resorcinol at Nafion/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/carbon dots/multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. Electrochim Acta 149:237–244
Jiang G, Jiang T, Zhou H, Yao J, Kong X (2015) Preparation of N-doped carbon quantum dots for highly sensitive detection of dopamine by an electrochemical method. RSC Adv 5(12):9064–9068
Li Q, Xu Z, Tang W, Wu Y (2015) Determination of Dopamine with a Modified Carbon Dot Electrode. Anal Lett 48(13):2040–2050
Yuan YH, Liu ZX, Li RS, Zou HY, Lin M, Liu H, Huang CZ (2016) Synthesis of nitrogen-doping carbon dots with different photoluminescence properties by controlling the surface states. Nano 8(12):6770–6776
Guo Q, Zhang M, Zhou G, Zhu L, Feng Y, Wang H, Zhong B, Hou H (2016) Highly sensitive simultaneous electrochemical detection of hydroquinone and catechol with three-dimensional N-doping carbon nanotube film electrode. J Electroanal Chem 760:15–23
Xu G, Han J, Ding B, Nie P, Pan J, Dou H, Li H, Zhang X (2015) Biomass-derived porous carbon materials with sulfur and nitrogen dual-doping for energy storage. Green Chem 17(3):1668–1674
Sharma D, Jaggi N (2017) Co-doping as a tool for tuning the optical properties of singlewalled carbon nanotubes: A first principles study. Phys E 91:93–100
Chen X, Wu G, Cai Z, Oyama M, Chen X (2014) Advances in enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 181(7–8):689–705
Gatselou VA, Giokas DL, Vlessidis AG, Prodromidis MI (2015) Rhodium nanoparticle-modified screen-printed graphite electrodes for the determination of hydrogen peroxide in tea extracts in the presence of oxygen. Talanta 134:482–487
Barman MK, Jana B, Bhattacharyya S, Patra A (2014) Photophysical properties of doped carbon dots (N, P, and B) and their influence on electron/hole transfer in carbon dots–nickel (II) phthalocyanine conjugates. J Phys Chem C 118(34):20034–20041
Li L, Liu D, Wang K, Mao H, You T (2017) Quantitative detection of nitrite with N-doped graphene quantum dots decorated N-doped carbon nanofibers composite-based electrochemical sensor. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 252:17–23
Li Y, Zhong Y, Zhang Y, Weng W, Li S (2015) Carbon quantum dots/octahedral Cu2O nanocomposites for non-enzymatic glucose and hydrogen peroxide amperometric sensor. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 206:735–743
Hsu SC, Cheng HT, PX W, Weng CJ, Santiago KS, Yeh JM (2017) Electrochemical sensor constructed using a carbon paste electrode modified with mesoporous silica encapsulating pani chains decorated with gnps for detection of ascorbic acid. Electrochim Acta 238:246–256
Liu X, Li L, Meng C, Han Y (2012) Palladium nanoparticles/defective graphene composites as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts: a first-principles study. J Phys Chem C 116(4):2710–2719
Stergiou DV, Diamanti EK, Gournis D, Prodromidis MI (2010) Comparative study of different types of graphenes as electrocatalysts for ascorbic acid. Electrochem Commun 12(10):1307–1309
Chen CW, Liu ZT, Zhang YZ, Ye JS, Lee CL (2015) Sonoelectrochemical intercalation and exfoliation for the preparation of defective graphene sheets and their application as nonenzymatic H2O2 sensors and oxygen reduction catalysts. RSC Adv 5(28):21988–21998
Pumera M (2009) Electrochemistry of graphene: new horizons for sensing and energy storage. Chem Rec 9(4):211–223
Luque G, Rojas M, Rivas G, Leiva E (2010) The origin of the catalysis of hydrogen peroxide reduction by functionalized graphene surfaces: A density functional theory study. Electrochim Acta 56(1):523–530
Wang Y, Shao Y, Matson DW, Li J, Lin Y (2010) Nitrogen-doped graphene and its application in electrochemical biosensing. ACS Nano 4(4):1790–1798
Fu L, Lai G, Yu A (2015) Preparation of β-cyclodextrin functionalized reduced graphene oxide: application for electrochemical determination of paracetamol. RSC Adv 5(94):76973–76978
Hassan SS, Panhwar S, Nafady A, Al-Enizi AM, Sherazi STH, Kalhoro MS, Arain M, Shah MR, Talpur MY (2017) Fabrication of highly sensitive and selective electrochemical sensors for detection of paracetamol by using piroxicam stabilized gold nanoparticles. J Electrochem Soc 164(9):B427–B434
Currie LA (1999) Detection and quantification limits: origins and historical overview. Anal Chim Acta 391(2):127–134
Huang Y, Cheng C, Tian X, Zheng B, Li Y, Yuan H, Xiao D, Choi MMF (2013) Low-potential amperometric detection of dopamine based on MnO2 nanowires/chitosan modified gold electrode. Electrochim Acta 89:832–839
Chen PY, Vittal R, Nien PC, Ho KC (2009) Enhancing dopamine detection using a glassy carbon electrode modified with MWCNTs, quercetin, and Nafion®. Biosens Bioelectron 24(12):3504–3509
He G, Jiang J, Wu D, You Y, Yang X, Wu F, Hu Y (2016) A novel nonenzymatic hydrogen peroxide electrochemical sensor based on facile synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles dopping into graphene sheets@ cerium oxide nanocomposites sensitized screen printed electrode. Int J Electrochem Sc 11(10):8486–8498
Li SJ, Xing Y, Yang HY, Huang JY, Wang WT, Liu RT (2017) Electrochemical Synthesis of a Binary Mn-Co Oxides Decorated Graphene Nanocomposites for Application in Nonenzymatic H2O2 Sensing. Int J Electrochem Sc 12:6566–6576
Ni Y, Liao Y, Zheng M, Shao S (2017) In-situ growth of Co3O4 nanoparticles on mesoporous carbon nanofibers: a new nanocomposite for nonenzymatic amperometric sensing of H2O2. Microchimi Acta 184(10):3689–3695
Acknowledgements
This work has been financially supported by Research Foundation from Hangzhou Dianzi University (KYS205617071) and Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation of China (LQ18E010001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 261 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, L., Wang, A., Lai, G. et al. A glassy carbon electrode modified with N-doped carbon dots for improved detection of hydrogen peroxide and paracetamol. Microchim Acta 185, 87 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2646-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2646-9