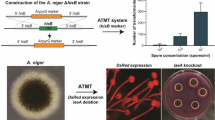
Abstract
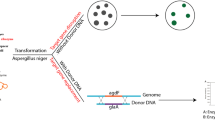
The filamentous fungus Aspergillus niger is widely used in the biotechnology industry for the production of chemicals and enzymes. Engineering of this valuable organism to improve its productivity is currently hampered by the lack of efficient genetic tools. Here, a Cre-loxP-based system for gene editing in A. niger was developed and its application in construction of A. niger cell factories to produce various organic acids was explored. Two established inducible systems, the xylanase A gene promoter Pxln and Tet-on system, were examined for driving cre expression and thus selection marker hyh deletion. Under inducing conditions, the efficiency of loxP site-specific recombination in the strain with cre driven by Pxln is about 2%, while cre driven by Tet-on system is about 34% which was used as the platform strain for further genetic engineering. As a proof of application of this system, strains containing different copies of oxaloacetate acetylhydrolase–encoding gene (oahA) were constructed, and the resultant strain S428 showed as high as 3.1-fold increase in oxalic acid production. Furthermore, an efficient malate-producing strain was generated through four-step genetic manipulation (oahA deletion, pyc, mdh3 and C4-dicarboxylate transporter gene c4t318 insertion). The resultant strain S575 achieved a titer 120.38 g/L malic acid with the flask culture, and a titer 201.24 g/L malic acid in fed-batch fermentation. These results demonstrated that this modified Cre-loxP system is a powerful tool for genetic engineering in A. niger, which has the potential to be genetically modified as a viable aciduric platform strain to produce high levels of various organic acids.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe S, Furuya A, Saito T, Takayama K (1962) Method of producing L-malic acid by fermentation. U.S. patent 3,063,910
Abremski K, Hoess R (1984) Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. Purification and properties of the Cre recombinase protein. J Biol Chem 259:1509–1514. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(84)90154-2
Andersen MR, Nielsen ML, Nielsen J (2008) Metabolic model integration of the bibliome, genome, metabolome and reactome of Aspergillus niger. Mol Syst Biol 4:178. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2008.12
Andersen MR, Lehmann L, Nielsen J (2009) Systemic analysis of the response of Aspergillus niger to ambient pH. Genome Biol 10:R47. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2009-10-5-r47
Boecker S, Grätz S, Kerwat D, Adam L, Schirmer D, Richter L, Schütze T, Petras D, Süssmuth RD, Meyer V (2018) Aspergillus niger is a superior expression host for the production of bioactive fungal cyclodepsipeptides. Fungal Biol Biotechnol 5:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40694-018-0048-3
Brown SH, Bashkirova L, Berka R, Chandler T, Doty T, McCall K, McCulloch M, McFarland S, Thompson S, Yaver D, Berry A (2013) Metabolic engineering of Aspergillus oryzae NRRL 3488 for increased production of L-malic acid. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:8903–8912. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5132-2
Campo N, Daveranmingot ML, Leenhouts K, Ritzenthaler P, Le BP (2002) Cre-loxP recombination system for large genome rearrangements in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2359–2367. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.5.2359-2367.2002
Chen M, Wolfe A, Wang X, Chang C, Yeh S, Radovick S (2009) Generation and characterization of a complete null estrogen receptor α mouse using Cre/LoxP technology. Mol Cell Biochem 321:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-008-9928-9
Chen H, He X, Geng H, Liu H (2014) Physiological characterization of ATP-citrate lyase in Aspergillus niger. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:721–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1418-3
Dai Z, Mao X, JK M, LL L (2004) Identification of genes associated with morphology in Aspergillus niger by using suppression subtractive hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2474–2485. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.4.2474-2485.2004
De Buck S, Peck I, De Wilde C, Marjanac G, Nolf J, De Paepe A, Depicker A (2007) Generation of single-copy T-DNA transformants in Arabidopsis by the CRE/loxP recombination-mediated resolution system. Plant Physiol 145:1171–1182. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.104067
Engels B, Dahm P, Jennewein S (2008) Metabolic engineering of taxadiene biosynthesis in yeast as a first step towards Taxol (Paclitaxel) production. Metab Eng 10:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2008.03.001
Forment JV, Ramón D, MacCabe AP (2006) Consecutive gene deletions in Aspergillus nidulans: application of the Cre/loxP system. Curr Genet 50:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-006-0081-2
Jantama K, Haupt MJ, Svoronos SA, Zhang X, Moore JC, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (2008) Combining metabolic engineering and metabolic evolution to develop nonrecombinant strains of Escherichia coli C that produce succinate and malate. Biotechnol Bioeng 99:1140–1153. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.21694
Jiang B, Zhang R, Dan F, Wang F, Liu K, Yi J, Niu K, Yuan Q, Wang M, Wang H (2016) A Tet-on and Cre-loxP based genetic engineering system for convenient recycling of selection markers in Penicillium oxalicum. Front Microbiol 7:485. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00485
Karaffa L, Kubicek CP (2003) Aspergillus niger citric acid accumulation: do we understand this well working black box? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1201-7
Kobayashi K, Hattori T, Honda Y (2014) Oxalic acid production by citric acid-producing Aspergillus niger overexpressing the oxaloacetate hydrolase gene oahA. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41:749–756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1419-2
Li A, Punt PJ (2013) Industrial production of organic acids by fungi: state of the art and opportunities. In: Maria G. Tuohy (ed) Industrial production of organic acids by fungi, applications of microbial engineering, 2rd edn. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC, pp 52–74
Liu H, Suresh A, Willard FS, Siderovski DP, Lu S, Naqvi NI (2007) Rgs1 regulates multiple Gα subunits in Magnaporthe pathogenesis, asexual growth and thigmotropism. EMBO J 26:690–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601536
Meijer S, Otero J, Olivares R, Andersen MR, Olsson L, Nielsen J (2009) Overexpression of isocitrate lyase-glyoxylate bypass influence on metabolism in Aspergillus niger. Metab Eng 11:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2008.12.002
Meyer V (2008) Genetic engineering of filamentous fungi-progress, obstacles and future trends. Biotechnol Adv 26:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2007.12.001
Meyer V, Wanka F, Van Gent J, Arentshorst M, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Ram AFJ (2011a) Fungal gene expression on demand: an inducible, tunable, and metabolism-independent expression system for Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2975–2983. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02740-10
Meyer V, Wu B, Ram AF (2011b) Aspergillus as a multi-purpose cell factory: current status and perspectives. Biotechnol Lett 33:469–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0473-8
Michielse CB, Hooykaas PJJ, van den Hondel CAMJJ, Ram AFJ (2005) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation as a tool for functional genomics in fungi. Curr Genet 48:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0578-0
Mizutani O, Masaki K, Gomi K, Iefuji H (2012) Modified cre-loxp recombination in Aspergillus oryzae by direct introduction of Cre recombinase for marker gene rescue. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:4126–4133. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00080-12
Niu J, Arentshorst M, Nair PD, Dai Z, Baker SE, Frisvad JC, Nielsen KF, Punt PJ, Ram AF (2016) Identification of a classical mutant in the industrial host Aspergillus niger by systems genetics: LaeA is required for citric acid production and regulates the formation of some secondary metabolites. G3 Genesgenetics 6:193–204. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.115.024067
Pel HJ, de Winde JH, Archer DB, Dyer PS, Hofmann G, Schaap PJ (2007) Genome sequencing and analysis of the versatile cell factory Aspergillus niger CBS 513.88. Nat Biotechnol 25:221–231. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1282
Shi TQ, Liu GN, Ji RY, Shi K, Song P, Ren LJ, Huang H, Ji XJ (2017) CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing of the filamentous fungi: the state of the art. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:7435–7443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8497-9
Smith AJ, De Sousa MA, Kwabi-Addo B, Heppell-Parton A, Impey H, Rabbitts P (1995) A site-directed chromosomal translocation induced in embryonic stem cells by Cre-loxP recombination. Nat Genet 9:376–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0495-376
Steiger MG, Vitikainen M, Uskonen P, Brunner K, Adam G, Pakula T, Penttilä M, Saloheimo M, Mach RL, Mach-Aigner AR (2011) Transformation system for Hypocrea jecorina (Trichoderma reesei) that favors homologous integration and employs reusable bidirectionally selectable markers. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02100-10
Stephanopoulos G, Aristidou A, Nielsen J (1998) Metabolic engineering: principles and methodologies. Academic, San Diego, pp 115–146
Sternberg N, Hamilton D, Austin S, Yarmolinsky M, Hoess R (1981) Site-specific recombination and its role in the life cycle of bacteriophage P1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 45:297–309. https://doi.org/10.1101/SQB.1981.045.01.042
Yang L, Christakou E, Vang J, Lübeck M, Lübeck PS (2017) Overexpression of a C4-dicarboxylate transporter is the key for rerouting citric acid to C4-dicarboxylic acid production in Aspergillus carbonarius. Microb Cell Factories 16:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-017-0660-6
Zelle RM, de Hulster E, van Winden WA, de Waard P, Dijkema C, Winkler AA, Geertman J-MA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT, van Maris AJA (2008) Malic acid production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: engineering of pyruvate carboxylation, oxaloacetate reduction, and malate export. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2766–2777. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02591-07
Zhang X, Wang X, Shanmugam KT, Ingram LO (2011) L-malate production by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:427–434. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01971-10
Zhang X-H, Tee LY, Wang X-G, Huang Q-S, Yang S-H (2015) Off-target effects in CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome engineering. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 4:e264. https://doi.org/10.1038/mtna.2015.37
Zheng X, Zheng P, Zhang K, Cairns TC, Meyer V, Sun J, Ma Y (2018) 5S rRNA promoter for guide RNA expression enabled highly efficient CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing in Aspergillus niger. ACS Synth Biol 8:1568–1574. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00456
Funding
Funding for this research was provided by Tianjin Science and Technology Committee (18YFZCSY01360), the program of Distinguished Professor of Tianjin 2015 and Industrial Microbial Strain Selection and Fermentation Technology Public Service Platform Project (17PTGCCX00190).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the author.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 293 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Shan, L., Zhou, Y. et al. Development of a Cre-loxP-based genetic system in Aspergillus niger ATCC1015 and its application to construction of efficient organic acid-producing cell factories. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103, 8105–8114 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10054-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10054-3