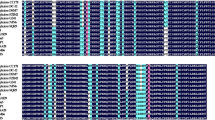
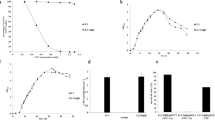
Abstract
Aside from applications in the production of commercial enzymes and metabolites, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is also an important group of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that supports plant growth and suppresses phytopathogens. A host-genotype-independent counter-selectable marker would enable rapid genetic manipulation and metabolic engineering, accelerating the study of B. amyloliquefaciens and its development as both a microbial cell factory and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Here, a host-genotype-independent counter-selectable marker pheS * was constructed through a point mutation of the gene pheS, which encodes the α-subunit of phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase in Bacillus subtilis strain 168. In the presence of 5 mM p-chloro-phenylalanine, 100 % of B. amyloliquefaciens strain SQR9 cells carrying pheS * were killed, whereas the wild-type strain SQR9 showed resistance to p-chloro-phenylalanine. A simple pheS * and overlap-PCR-based strategy was developed to create the marker-free deletion of the amyE gene as well as a 37-kb bmy cluster in B. amyloliquefaciens SQR9. The effectiveness of pheS * as a counter-selectable marker in B. amyloliquefaciens was further confirmed through the deletion of amyE genes in strains B. amyloliquefaciens FZB42 and NJN-6. In addition, the potential use of pheS * in other Bacillus species was preliminarily assessed. The expression of PheS* in B. subtilis strain 168 and B. cereus strain ATCC 14579 caused pronounced sensitivity of both hosts to p-chloro-phenylalanine, indicating that pheS * could be used as a counter-selectable marker (CSM) in these strains.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostopoulos C, Spizizen J (1961) Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 81:741–746
Barrett AR, Kang Y, Inamasu KS, Son MS, Vukovich JM, Hoang TT (2008) Genetic tools for allelic replacement in Burkholderia species. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4498–4508. doi:10.1128/AEM.00531-08
Blom J, Rückert C, Niu B, Wang Q, Borriss R (2012) The complete genome of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum CAU B946 contains a gene cluster for nonribosomal synthesis of iturin a. J Bacteriol 194:1845–1846. doi:10.1128/JB.06762-11
Brans A, Filée P, Chevigné A, Claessens A, Joris B (2004) New integrative method to generate Bacillus subtilis recombinant strains free of selection markers. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7241–7250. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.12.7241-7250.2004
Brown BJ, Carlton BC (1980) Plasmid-mediated transformation in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol 142:508–512
Carr JF, Danziger ME, Huang AL, Dahlberg AE, Gregory ST (2015) Engineering the genome of Thermus thermophilus using a counterselectable marker. J Bacteriol 197:1135–1144. doi:10.1128/JB.02384-14
Chen XH, Koumoutsi A, Scholz R, Eisenreich A, Schneider K, Heinemeyer I, Morgenstern B, Voss B, Hess WR, Reva O, Junge H, Voigt B, Jungblut PR, Vater J, Süssmuth R, Liesegang H, Strittmatter A, Gottschalk G, Borriss R (2007) Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequence of the plant growth-promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Nat Biotechnol 25:1007–1014. doi:10.1038/nbt1325
Chen XH, Koumoutsi A, Scholz R, Schneider K, Vater J, Süssmuth R, Piel J, Borriss R (2009) Genome analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 reveals its potential for biocontrol of plant pathogens. J Biotechnol 140:27–37. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.10.011
Chen XT, Ji JB, Liu YC, Ye B, Zhou CY, Yan X (2016) Artificial induction of genetic competence in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolates. Biotechnol Lett. doi:10.1007/s10529-016-2194-0
Chowdhury SP, Hartmann A, Gao X, Borriss R (2015) Biocontrol mechanism by root-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42—a review. Front Microbiol 6:780. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00780
Fabret C, Ehrlich SD, Noirot P (2002) A new mutation delivery system for genome-scale approaches in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 46:25–36. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03140.x
Geng WT, Cao MF, Song CJ, Xie H, Liu L, Yang C, Feng J, Zhang W, Jin YH, Du Y, Wang SF (2011) Complete genome sequence of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LL3, which exhibits glutamic acid-independent production of poly-γ-glutamic acid. J Bacteriol 193:3393–3394. doi:10.1128/JB.05058-11
He PF, Hao K, Blom J, Rückert C, Vater J, Mao Z, Wu Y, Hou M, He PB, He YQ, Borriss R (2012) Genome sequence of the plant growth promoting strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum B9601-Y2 and expression of mersacidin and other secondary metabolites. J Biotechnol 164:281–291. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.12.014
Hoang TT, Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Kutchma AJ, Schweizer HP (1998) A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212:77–86. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00130-9
Huang Y, Sun L, Zhao JS, Huang R, Li R, Shen QR (2015) Utilization of different waste proteins to create a novel PGPR-containing bio-organic fertilizer. Sci Rep 5:7766 . doi:10.1038/Srep07766Artn 7766
Kaczmarczyk A, Vorholt JA, Francez-Charlot A (2012) Markerless gene deletion system for sphingomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:3774–3777. doi:10.1128/AEM.07347-11
Kast P (1994) pKSS—a second-generation general purpose cloning vector for efficient positive selection of recombinant clones. Gene 138:109–114. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90790-0
Kast P, Hennecke H (1991) Amino acid substrate specificity of Escherichia coli phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase altered by distinct mutations. J Mol Biol 222:99–124. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(91)90740-W
Kristich CJ, Chandler JR, Dunny GM (2007) Development of a host-genotype-independent counterselectable marker and a high-frequency conjugative delivery system and their use in genetic analysis of Enterococcus faecalis. Plasmid 57:131–144. doi:10.1016/j.plasmid.2006.08.003
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948 . doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404ARTN e19
Li B, Li Q, Xu ZH, Zhang N, Shen QR, Zhang RF (2014) Responses of beneficial Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 to different soilborne fungal pathogens through the alteration of antifungal compounds production. Front Microbiol 5:636. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00636
Liu S, Endo K, Ara K, Ozaki K, Ogasawara N (2008) Introduction of marker-free deletions in Bacillus subtilis using the AraR repressor and the ara promoter. Microbiol 154:2562–2570. doi:10.1099/mic.0.2008/016881-0
Malten M, Nahrstedt H, Meinhardt F, Jahn D (2005) Coexpression of the type I signal peptidase gene sipM increases recombinant protein production and export in Bacillus megaterium MS941. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:616–621. doi:10.1002/bit.20523
Peng D, Luo Y, Guo S, Zeng H, Ju S, Yu Z, Sun M (2009) Elaboration of an electroporation protocol for large plasmids and wild-type strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Appl Microbiol 106:1849–1858. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04151.x
Rückert C, Blom J, Chen X, Reva O, Borriss R (2011) Genome sequence of B. amyloliquefaciens type strain DSM7(T) reveals differences to plant-associated B. amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J Biotechnol 155:78–85. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.01.006
Shao JH, Li SQ, Zhang N, Cui X, Zhou X, Zhang GS, Shen QR, Zhang RF (2015) Analysis and cloning of the synthetic pathway of the phytohormone indole-3-acetic acid in the plant-beneficial Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Microb Cell Fact 14:130. doi:10.1186/s12934-015-0323-4
Shevchuk NA, Bryksin AV, Nusinovich YA, Cabello FC, Sutherland M, Ladisch S (2004) Construction of long DNA molecules using long PCR-based fusion of several fragments simultaneously. Nucl Acids Res 32:e19. doi:10.1093/nar/gnh014
Turgeon N, Laflamme C, Ho J, Duchaine C (2006) Elaboration of an electroporation protocol for Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579. J Microbiol Meth 67:543–548. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2006.05.005
Ueki T, Inouye S, Inouye M (1996) Positive-negative KG cassettes for construction of multi-gene deletions using a single drug marker. Gene 183:153–157. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(96)00546-X
Waschkau B, Waldeck J, Wieland S, Eichstӓdt R, Meinhardt F (2008) Generation of readily transformable Bacillus licheniformis mutants. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:181–188. doi:10.1007/s00253-007-1278-0
Wemhoff S, Meinhardt F (2013) Generation of biologically contained, readily transformable, and genetically manageable mutants of the biotechnologically important Bacillus pumilus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7805–7819. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-4935-5
Wu SS, Kaiser D (1996) Markerless deletions of pil genes in Myxococcus xanthus generated by counterselection with the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene. J Bacteriol 178:5817–5821
Wu L, Wu H, Chen L, Lin L, Borriss R, Gao X (2015) Bacilysin overproduction in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 markerless derivative strains FZBREP and FZBSPA enhances antibacterial activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:4255–4263. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-6251-0
Xie ZJ, Okinaga T, Qi F, Zhang ZJ, Merritt J (2011) Cloning-independent and counterselectable markerless mutagenesis system in Streptococcus mutans. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:8025–8033. doi:10.1128/AEM.06362-11
Xu ZH, Shao JH, Li B, Yan X, Shen QR, Zhang RF (2013) Contribution of bacillomycin D in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 to antifungal activity and biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:808–815. doi:10.1128/AEM.02645-12
Yan X, Yu HJ, Hong Q, Li SP (2008) Cre/lox system and PCR-based genome engineering in Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:5556–5562. doi:10.1128/AEM.01156-08
Yuan J, Zhang N, Huang QW, Raza W, Li R, Vivanco JM, Shen QR (2015) Organic acids from root exudates of banana help root colonization of PGPR strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens NJN-6. Sci Rep 5:13438. doi:10.1038/srep13438
Zakataeva NP, Nikitina OV, Gronskiy SV, Romanenkov DV, Livshits VA (2010) A simple method to introduce marker-free genetic modifications into the chromosome of naturally nontransformable Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1201–1209. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-2276-1
Zhang XZ, Yan X, Cui ZL, Hong Q, Li SP (2006) mazF, a novel counter-selectable marker for unmarked chromosomal manipulation in Bacillus subtilis. Nucl Acids Res 34:e71. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl358
Zhang C, Zhang XH, Yao ZY, Lu YP, Lu FX, Lu ZX (2011a) A new method for multiple gene inactivations in Bacillus subtilis 168, producing a strain free of selectable markers. Can J Microbiol 57:427–436. doi:10.1139/W11-035
Zhang GQ, Bao P, Zhang Y, Deng AH, Chen N, Wen TY (2011b) Enhancing electro-transformation competency of recalcitrant Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by combining cell-wall weakening and cell-membrane fluidity disturbing. Anal Biochem 409:130–137. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2010.10.013
Zhang W, Gao WX, Feng J, Zhang C, He YL, Cao MF, Li Q, Sun Y, Yang C, Song CJ, Wang SF (2014) A markerless gene replacement method for B. amyloliquefaciens LL3 and its use in genome reduction and improvement of poly-γ-glutamic acid production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8963–8973. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5824-2
Zhang N, Yang D, Wang D, Miao YZ, Shao JH, Zhou X, Xu ZH, Li Q, Feng HC, Li SQ, Shen QR, Zhang RF (2015) Whole transcriptomic analysis of the plant-beneficial rhizobacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9 during enhanced biofilm formation regulated by maize root exudates. BMC Genomics 16:685. doi:10.1186/s12864-015-1825-5
Zhou P, Li X, Qi F (2015) Establishment of a counter-selectable markerless mutagenesis system in Veillonella atypica. J Microbiol Meth 112:70–72. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2015.03.010
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Natalia P. Zakataeva from the Ajinomoto-Genetika Research Institute for providing the plasmid pNZT1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors would like to express their thanks for financial support from the 863 Plan (2014AA020543), the 973 Plan (2015CB150505) and the National Natural Science Foundation (31300099 and 31470225) of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 437 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Shi, L., Ye, B. et al. pheS *, an effective host-genotype-independent counter-selectable marker for marker-free chromosome deletion in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 217–227 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7906-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7906-9