Abstract
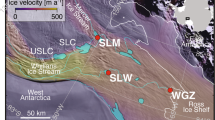
Microorganisms inhabiting stream sediments mediate biogeochemical processes of importance to both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. In deserts, the lateral margins of ephemeral stream channels (parafluvial sediments) are dried and rewetted, creating periodically wet conditions that typically enhance microbial activity. However, the influence of water content on microbial community composition and diversity in desert stream sediments is unclear. We sampled stream margins along gradients of wet to dry sediments, measuring geochemistry and bacterial 16S rRNA gene composition, at streams in both a cold (McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica) and hot (Chihuahuan Desert, New Mexico, USA) desert. Across the gradients, sediment water content spanned a wide range (1.6–37.9% w/w), and conductivity was highly variable (12.3–1,380 μS cm−2). Bacterial diversity (at 97% sequence similarity) was high and variable, but did not differ significantly between the hot and cold desert and was not correlated with sediment water content. Instead, conductivity was most strongly related to diversity. Water content was strongly related to bacterial 16S rRNA gene community composition, though samples were distributed in wet and dry clusters rather than as assemblages shifting along a gradient. Phylogenetic analyses showed that many taxa from wet sediments at the hot and cold desert site were related to, respectively, halotolerant Gammaproteobacteria, and one family within the Sphingobacteriales (Bacteroidetes), while dry sediments at both sites contained a high proportion of taxa related to the Acidobacteria. These results suggest that bacterial diversity and composition in desert stream sediments is more strongly affected by hydrology and conductivity than temperature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aislabie JM, Chhour KL, Saul DJ, Miyauchi S, Ayton J, Paetzold RF, Balks MR (2006) Dominant bacteria in soils of Marble Point and Wright Valley, Victoria Land, Antarctica. Soil Biol Biochem 38:3041–3056
Allen AP, Brown JH, Gillooly JF (2002) Global biodiversity, biochemical kinetics, and the energetic-equivalence rule. Science 297:1545–1548
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in-situ detection of individual microbial-cells without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Atmar W, Patterson BD (1993) The measure of order and disorder in the distribution of species in fragmented habitat. Oecologia 96:373–382
Bardgett RD, Anderson JM, Behan-Pelletier V, Brussaard L, Coleman DC, Ettema C, Moldenke A, Schimel JP, Wall DH (2001) The influence of soil biodiversity on hydrological pathways and the transfer of materials between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 4:421–429
Barns SM, Cain EC, Sommerville L, Kuske CR (2007) Acidobacteria phylum sequences in uranium-contaminated subsurface sediments greatly expand the known diversity within the phylum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3113–3116
Barns SM, Takala SL, Kuske CR (1999) Wide distribution and diversity of members of the bacterial kingdom Acidobacterium in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1731–1737
Barrett JE, Gooseff MN, Takacs-Vesbach C (2009) Spatial variation in soil active-layer geochemistry across hydrologic margins in polar desert ecosystems. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discussion 6:3725–3751
Barrett JE, Virginia RA, Wall DH, Doran PT, Fountain AG, Welch KA, Lyons WB (2008) Persistent effects of a discrete warming event on a polar desert ecosystem. Glob Chang Biol 14:2249–2261
Battin TJ, Wille A, Sattler B, Psenner R (2001) Phylogenetic and functional heterogeneity of sediment biofilms along environmental gradients in a glacial stream. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:799–807
Belnap J, Welter JR, Grimm NB, Barger N, Ludwig JA (2005) Linkages between microbial and hydrologic processes in arid and semiarid watersheds. Ecology 86:298–307
Benlloch S, Lopez-Lopez A, Casamayor EO, Ovreas L, Goddard V, Daae FL, Smerdon G, Massana R, Joint I, Thingstad F, Pedros-Alio C, Rodriguez-Valera F (2002) Prokaryotic genetic diversity throughout the salinity gradient of a coastal solar saltern. Environ Microbiol 4:349–360
Bernhard AE, Donn T, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2005) Loss of diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria correlates with increasing salinity in an estuary system. Environ Microbiol 7:1289–1297
Bobb M (2005) Spatial patterns of bacterial diversity in cold desert riparian zones. M.S. Thesis. Department of Biology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, USA
Brettar I, Christen R, Hofle MG (2006) Rheinheimera perlucida sp nov., a marine bacterium of the Gammaproteobacteria isolated from surface water of the central Baltic Sea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2177–2183
Cowan DA, Tow LA (2004) Endangered Antarctic environments. Annu Rev Microbiol 58:649–690
Demergasso C, Escudero L, Casamayor EO, Chong G, Balague V, Pedros-Alio C (2008) Novelty and spatio-temporal heterogeneity in the bacterial diversity of hypersaline Lake Tebenquiche (Salar de Atacama). Extremophiles 12:491–504
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Keller K, Brodie EL, Larsen N, Piceno YM, Phan R, Andersen GL (2006) NAST: a multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W394–W399
Dillon JG, McMath LM, Trout AL (2009) Seasonal changes in bacterial diversity in the Salton Sea. Hydrobiologia 632:49–64
Doran PT, McKay CP, Clow GD, Dana GL, Fountain AG, Nylen T, Lyons WB (2002) Valley floor climate observations from the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica, 1986–2000. J Geophys Res Atmos 107:4772
Doran PT, Priscu JC, Lyons WB, Walsh JE, Fountain AG, McKnight DM, Moorhead DL, Virginia RA, Wall DH, Clow GD, Fritsen CH, McKay CP, Parsons AN (2002) Antarctic climate cooling and terrestrial ecosystem response. Nature 415:517–520
Dowd SE, Callaway TR, Wolcott RD, Sun Y, McKeehan T, Hagevoort RG, Edrington TS (2008) Evaluation of the bacterial diversity in the feces of cattle using 16S rDNA bacterial tag-encoded FLX amplicon pyrosequencing (bTEFAP). BMC Microbiol 8:125
Drees KP, Neilson JW, Betancourt JL, Quade J, Henderson DA, Pryor BM, Maier RM (2006) Bacterial community structure in the hyperarid core of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7902–7908
Eichorst SA, Breznak JA, Schmidt TM (2007) Isolation and characterization of soil bacteria that define Terriglobus gen. nov., in the phylum Acidobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2708–2717
Esposito RMM, Horn SL, McKnight DM, Cox MJ, Grant MC, Spaulding SA, Doran PT, Cozzetto KD (2006) Antarctic climate cooling and response of diatoms in glacial meltwater streams. Geophys Res Lett 33:L07406
Feris KP, Ramsey PW, Frazar C, Rillig M, Moore JN, Gannon JE, Holben WE (2004) Seasonal dynamics of shallow-hyporheic-zone microbial community structure along a heavy-metal contamination gradient. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2323–2331
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:626–631
Fritsen CH, Grue AM, Priscu JC (2000) Distribution of organic carbon and nitrogen in surface soils in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Polar Biol 23:121–128
Good IJ (1953) The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 40:237–264
Gooseff MN, McKnight DM, Doran PT, Lyons WB (2007) Trends in discharge and flow season timing of the Onyx River, Wright Valley, Antarctica since 1969. US Geological Survey and The National Academies, Short Research Paper USGS: OF-2007-1047
Gosz JR, Moore DI, Shore GA, Grover HD, Rison W, Rison C (1995) Lightning estimates of precipitation location and quantity on the Sevilleta LTER, New Mexico. Ecol Appl 5:1141–1150
Gregorich EG, Hopkins DW, Elberling B, Sparrow AD, Novis P, Greenfield LG, Rochette P (2006) Emission of CO2, CH4 and N2O from lakeshore soils in an Antarctic dry valley. Soil Biol Biochem 38:3120–3129
Heffernan JB, Sponseller RA (2004) Nutrient mobilization and processing in Sonoran desert riparian soils following artificial re-wetting. Biogeochemistry 70:117–134
Hieber M, Gessner MO (2002) Contribution of stream detritivores, fungi, and bacteria to leaf breakdown based on biomass estimates. Ecology 83:1026–1038
Hogan JF, Phillips FM, Mills SK, Hendrickx JMH, Ruiz J, Chesley JT, Asmerom Y (2007) Geologic origins of salinization in a semi-arid river: the role of sedimentary basin brines. Geology 35:1063–1066
Holmes RM, Fisher SG, Grimm NB (1994) Parafluvial nitrogen dynamics in a desert stream ecosystem. J North Am Benthol Soc 13:468–478
Holmes RM, Jones JBJ, Fisher SG, Grimm NB (1996) Denitrification in a nitrogen-limited stream ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 33:125–146
Hopkins DW, Sparrow AD, Novis PM, Grogorich EG, Elberling B, Greenfield LG (2006) Controls on the distribution of productivity and organic resources in Antarctic Dry Valley soils. Proc R Soc B 273:2687–2695
Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20:2317–2319
Hugenholtz P (2002) Exploring prokaryotic diversity in the genomic era. Genome Biol 3:1–8
Hullar MAJ, Kaplan LA, Stahl DA (2006) Recurring seasonal dynamics of microbial communities in stream habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:713–722
Janssen PH (2006) Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1719–1728
Jones JB, Fisher SG, Grimm NB (1995) Nitrification in the hyporheic zone of a desert stream ecosystem. J North Am Benthol Soc 14:249–258
Kennedy AD (1993) Water as a limiting factor in the Antarctic terrestrial environment—a biogeographical synthesis. Arct Alpine Res 25:308–315
Knapp CW, Dodds WK, Wilson KC, O'Brien JM, Graham DW (2009) Spatial heterogeneity of denitrification genes in a highly homogeneous urban stream. Environ Sci Technol 43:4273–4279
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/12S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrant E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, London, pp 115–175
Lozupone C, Hamady M, Knight R (2006) UniFrac—an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinform 7:371–385
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar BA, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G, Forster W, Brettske I, Gerber S, Ginhart AW, Gross O, Grumann S, Hermann S, Jost R, Konig A, Liss T, Lussmann R, May M, Nonhoff B, Reichel B, Strehlow R, Stamatakis A, Stuckmann N, Vilbig A, Lenke M, Ludwig T, Bode A, Schleifer KH (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1363–1371
Mattimore V, Battista JR (1996) Radioresistance of Deinococcus radiodurans: functions necessary to survive ionizing radiation are also necessary to survive prolonged desiccation. J Bacteriol 178:633–637
McKnight DM, Niyogi DK, Alger AS, Bomblies A, Conovitz PA, Tate CM (1999) Dry valley streams in Antarctica: ecosystems waiting for water. Bioscience 49:985–995
Mitchell KR, Takacs-Vesbach CD (2008) A comparison of methods for total community DNA preservation and extraction from various thermal environments. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1139–1147
Molles MC Jr, Dahm CN, Crocker MT (1992) Climatic variability and streams and rivers in semi-arid regions. In: Roberts RD, Bothwell ML (eds) Aquatic ecosystems in semi-arid regions: implications for resource management. The Institute, Saskatoon, pp 197–201
Moorhead DL, Barrett JE, Virginia RA, Wall DH, Proazinska D (2003) Organic matter and soil biota of upland wetlands in Taylor Valley, Antarctica. Polar Biol 26:567–576
Newell DL, Crossey LJ, Karlstrom KE, Fischer TP, Hilton DR (2005) Continental-scale links between the mantle and groundwater systems of the western United States: evidence from travertine springs and regional He isotope data. GSA Today 15:4–10
Niederberger TD, McDonald IR, Hacker AL, Soo RM, Barrett JE, Wall DH, Cary SC (2008) Microbial community composition in soils of Northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 10:1713–1724
Noguez AM, Arita HT, Escalante AE, Forney LJ, Garcia-Oliva F, Souza V (2005) Microbial macroecology: highly structured prokaryotic soil assemblages in a tropical deciduous forest. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 14:241–248
Northcott ML, Gooseff MN, Barrett JE, Zeglin LH, Takacs-Vesbach CD, Humphrey J (2009) Hydrologic characteristic of lake- and stream-side riparian wetted margins in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Hydrol Process 23:1255–1267
Noy-Meir I (1973) Desert ecosystems: environment and producers. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 4:25–51
Papke RT, Ward DM (2004) The importance of physical isolation to microbial diversification. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:293–303
Patterson BD (1999) Contingency and determinism in mammalian biogeography: the role of history. J Mammal 80:345–360
Pointing SB, Chan Y, Lacap DC, Lau MCY, Jurgens JA, Farrell RL (2010) Highly specialized microbial diversity in hyper-arid polar desert. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:1254–1254
Pointing SB, Warren-Rhodes KA, Lacap DC, Rhodes KL, McKay CP (2007) Hypolithic community shifts occur as a result of liquid water availability along environmental gradients in China's hot and cold hyperarid deserts. Environ Microbiol 9:414–424
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Prosser JI, Bohannan BJM, Curtis TP, Ellis RJ, Firestone MK, Freckleton RP, Green JL, Green LE, Killham K, Lennon JJ, Osborn AM, Solan M, van der Gast CJ, Young JPW (2007) Essay—the role of ecological theory in microbial ecology. Nat Rev Microbiol 5:384–392
Rees GN, Watson GO, Baldwin DS, Mitchell AM (2006) Variability in sediment microbial communities in a semipermanent stream: impact of drought. J North Am Benthol Soc 25:370–378
Romani AM, Fischer H, Mille-Lindbloom C, Travnik LJ (2006) Interactions of bacteria and fungi on decomposing litter: differential extracellular enzyme activities. Ecology 87:2559–2569
Rutz BA, Kieft TL (2004) Phylogenetic characterization of dwarf archaea and bacteria from a semiarid soil. Soil Biol Biochem 36:825–833
Schade JD, Marti E, Welter JR, Fisher SG, Grimm NB (2002) Sources of nitrogen to the riparian zone of a desert stream: implications for riparian vegetation and nitrogen retention. Ecosystems 5:68–79
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducting DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501–1506
Schwinning S, Sala OE (2004) Hierarchy of responses to resource pulses in arid and semi-arid ecosystems. Oecologia 141:221–220
Smith JJ, Tow LA, Stafford W, Cary C, Cowan DA (2006) Bacterial diversity in three different Antarctic cold desert mineral soils. Microb Ecol 51:413–421
Souza V, Espinosa-Asuar L, Escalante AE, Eguiarte LE, Farmer J, Forney L, Lloret L, Rodriguez-Martinez JM, Soberon X, Dirzo R, Elser JJ (2006) An endangered oasis of aquatic microbial biodiversity in the Chihuahuan desert. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:6565–6570
Swofford DL (2003) Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony. Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Takacs-Vesbach C, Zeglin LH, Barrett JE, Gooseff MN, Priscu JC (2010) Factors promoting microbial diversity in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. In: Doran PT, Lyons WB, McKnight DM (eds) Life in antarctic deserts and other cold dry environments. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Treonis AM, Wall DH, Virginia RA (1999) Invertebrate biodiversity in Antarctic Dry Valley soils and sediments. Ecosystems 2:482–492
Vincent WF, Howard-Williams C (1986) Antarctic stream ecosystems: physiological ecology of a blue-green algal epilithon. Freshw Biol 16:219–233
Walsh DA, Papke RT, Doolittle WF (2005) Archaeal diversity along a soil salinity gradient prone to disturbance. Environ Microbiol 7:1655–1666
Whitaker RJ (2006) Allopatric origins of microbial species. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361:1975–1984
Xie CH, Yokota A (2006) Reclassification of Flavobacterium ferrugineum as Terrimonas ferruginea gen. nov., comb. nov., and description of Terrimonas lutea sp nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1117–1121
Yergeau E, Kowalchuk GA (2008) Responses of Antarctic soil microbial communities and associated functions to temperature and freeze-thaw cycle frequency. Environ Microbiol 10:2223–2235
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Lee CH, Oh TK (2005) Marinicola seohaensis gen. nov., sp nov., isolated from sea water of the Yellow Sea, Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:859–863
Yoon MH, Im WT (2007) Flavisolibacter ginsengiterrae gen. nov., sp nov and Flavisolibacter ginsengisoli sp nov., isolated from ginseng cultivating soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1834–1839
Zeglin LH (2008) Microbial diversity and function at aquatic-terrestrial interfaces in desert ecosystems. Ph.D. Dissertation. Department of Biology, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM, USA
Zeglin LH, Sinsabaugh RL, Barrett JE, Gooseff MN, Takacs-Vesbach CD (2009) Landscape distribution of microbial activity in the McMurdo Dry Valleys: linked biotic processes, hydrology and geochemistry in a cold desert ecosystem. Ecosystems 12:562–573
Zhou J, Xia B, Treves DS, Wu L-Y, Marsh TL, O'Neill RV, Palumbo AV, Tiedje JM (2002) Spatial and resource factors influencing high microbial diversity in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:326–334
Acknowledgments
We offer many thanks to the personnel of the Long Term Ecological Research (LTER) programs of both the Sevilleta and McMurdo Dry Valleys. We also thank Raytheon Polar Services and Petroleum Helicopters, Inc. for logistical support in Antarctica. Field team members included D. Bradley Bate, Mike Bobb, Chelsea Crenshaw, Kenneth Hill, and Melissa Northcott. Laboratory team members included Nathan Daves-Brody, Kendra Mitchell, and Kris Mossberg. This work was funded by NSF OPP-0338267 to CTV, MNG, and JEB; NSF Freshwater Sciences Interdisciplinary Doctoral Program IGERT (DGE-9972810) to CND; a Sevilleta LTER (DEB-0620482) graduate student grant; and an NSF Graduate Research Fellowship to LHZ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeglin, L.H., Dahm, C.N., Barrett, J.E. et al. Bacterial Community Structure Along Moisture Gradients in the Parafluvial Sediments of Two Ephemeral Desert Streams. Microb Ecol 61, 543–556 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9782-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-010-9782-7