Abstract
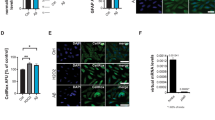
Acrylamide, a soft electrophile, is widely used in the industry and laboratories, and also contaminates certain foods. Neurotoxicity and neurodegenerative effects of acrylamide have been reported in humans and experimental animals, although the underlying mechanism remains obscure. Activation of microglia and neuroinflammation has been demonstrated in various neurodegenerative diseases as well as other pathologies of the brain. The present study aimed to investigate the role of microglial activation and neuroinflammation in acrylamide neurotoxicity. Male 10-week-old Wistar rats were exposed to acrylamide by gavage at 0, 0.2, 2, or 20 mg/kg BW, once per day for 5 weeks. The results showed that 5-week exposure to acrylamide induced inflammatory responses in the cerebral cortex, evident by upregulated mRNA and protein expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-18. Acrylamide also induced activation of microglia, indicated by increased expression of microglial markers, CD11b and CD40, and increased CD11b/c-positive microglial area and microglial process length. In vitro studies using BV-2 microglial cells confirmed microglial inflammatory response, as evident by time- (0–36 h; 50 μM) and dose- (0–500 μM; 24 h) dependent increase in mRNA expression of IL-1β and IL-18, as well as the inflammatory marker iNOS. Furthermore, acrylamide-induced upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines was mediated through the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway, as evident by increased expression of NLRP3, caspase 1, and ASC in the rat cerebral cortex, and by the inhibitory effects of NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor on the acrylamide-induced upregulation of NLRP3, caspase 1, IL-1β, and IL-18 in BV-2 microglia.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramsson-Zetterberg L, Wong J, Ilbäck NG (2005) Acrylamide tissue distribution and genotoxic effects in a common viral infection in mice. Toxicology 211:70–76
Allan SM, Rothwell NJ (2001) Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:734–744
ATSDR (Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry) (2012) Toxicological profile for acrylamide. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Public Health Service. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp203.pdf. Accessed 9 May 2019
Basu A, Krady JK, Levison SW (2004) Interleukin-1: a master regulator of neuroinflammation. J Neurosci Res 78:151–156
Block ML, Hong JS (2005) Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol 76:77–98
Block ML, Hong JS (2007) Chronic microglial activation and progressive dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1127–1132
Blum-Degen D, Müller T, Kuhn W et al (1995) Interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-6 are elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s and de novo Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurosci Lett 202:17–20
Brown GC, Neher JJ (2010) Inflammatory neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons. Mol Neurobiol 41:242–247
Campbell IL (2005) Cytokine-mediated inflammation, tumorigenesis, and disease-associated JAK/STAT/SOCS signaling circuits in the CNS. Brain Res Rev 48:166–177
Campbell IL, Abraham CR, Masliah E et al (1993) Neurologic disease induced in transgenic mice by cerebral overexpression of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:10061–10065
Chen JH, Chou CC (2015) Acrylamide inhibits cellular differentiation of human neuroblastoma and glioblastoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol 82:27–35
Chen K, Huang J, Gong W et al (2006) CD40/CD40L dyad in the inflammatory and immune responses in the central nervous system. Cell Mol Immunol 3:163–169
Coll RC, Robertson AAB, Chae JJ et al (2015) A small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Nat Med 21:248–255
Deng H, He F, Zhang S et al (1993) Quantitative measurements of vibration threshold in healthy adults and acrylamide workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 65:53–56
Doerge DR, Young JF, McDaniel LP, Twaddle NC, Churchwell MI (2005) Toxicokinetics of acrylamide and glycidamide in Fischer 344 rats. Toxicol Appl Pharm 208:199–209
Erkekoglu P, Baydar T (2014) Acrylamide neurotoxicity. Nutr Neurosci 17:49–57
Felderhoff-Mueser U, Sifringer M, Polley O et al (2005) Caspase-1-processed interleukins in hyperoxia-induced cell death in the developing brain. Ann Neurol 57:50–59
Freeman LC, Ting JPY (2016) The pathogenic role of the inflammasome in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 136:29–38
Garland TO, Patterson MWH (1967) Six cases of acrylamide poisoning. BMJ 4:134–138
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B et al (2010) Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140:918–934
Griffin WS, Stanley LC, Ling C et al (1989) Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7611–7615
He FS, Zhang SL, Wang HL et al (1989) Neurological and electroneuromyographic assessment of the adverse effects of acrylamide on occupationally exposed workers. Scand J Work Environ Health 15:125–129
Heneka MT, McManus RM, Latz E (2018) Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 19:610–621
Henn A, Lund S, Hedtjärn M et al (2009) The suitability of BV2 cells as alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for animal experiments examining brain inflammation. Altex 26:83–94
Hennig P, Garstkiewicz M, Grossi S et al (2018) The crosstalk between Nrf2 and inflammasomes. Int J Mol Sci 19:1–19
Jin X, Yamashita T (2016) Microglia in central nervous system repair after injury. J Biochem 159:491–496
Kraft AD, Harry GJ (2011) Features of microglia and neuroinflammation relevant to environmental exposure and neurotoxicity. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:2980–3018
Kumagai Y, Abiko Y (2017) Environmental electrophiles: protein adducts, modulation of redox signaling, and interaction with persulfides/polysulfides. Chem Res Toxicol 30:203–219
Lawson LJ, Perry VH, Dri P, Gordon S (1990) Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience 39:151–170
Li S, Cui N, Zhang C et al (2006) Effect of subchronic exposure to acrylamide induced on the expression of bcl-2, bax and caspase-3 in the rat nervous system. Toxicology 217:46–53
LoPachin RM (2004) The changing view of acrylamide neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 25:617–630
LoPachin RM, Barber DS (2006) Synaptic cysteine sulfhydryl groups as targets of electrophilic neurotoxicants. Toxicol Sci 94:240–255
LoPachin RM, Gavin T (2008) Acrylamide-induced nerve terminal damage: relevance to neurotoxic and neurodegenerative mechanisms. J Agric Food Chem 56:5994–6003
LoPachin RM, Gavin T (2012) Molecular mechanism of acrylamide neurotoxicity: lessons learned from organic chemistry. Environ Health Perspect 120:1650–1657
LoPachin RM, Ross JF, Reid ML et al (2002) Neurological evaluation of toxic axonopathies in rats: acrylamide and 2,5-hexanedione. Neurotoxicology 23:95–110
LoPachin RM, Gavin T, Decaprio A, Barber DS (2012) Application of the hard and soft, acids and bases (HSAB) theory to toxicant–target interactions. Chem Res Toxicol 25:239–251
Marlowe C, Clark MJ, Mast RW et al (1986) The distribution of [14C]acrylamide in male and pregnant Swiss-Webster mice studied by whole-body autoradiography. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 86:457–465
Na KS, Jung HY, Kim YK (2014) The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the neuroinflammation and neurogenesis of schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 48:277–286
O’Sullivan JB, Ryan KM, Curtin NM et al (2009) Noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors limit neuroinflammation in rat cortex following a systemic inflammatory challenge: implications for depression and neurodegeneration. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:687–699
Oono M, Okado-Matsumoto A, Shodai A et al (2014) Transglutaminase 2 accelerates neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis through interaction with misfolded superoxide dismutase 1. J Neurochem 128:403–418
Owens T, Babcock AA, Millward JM, Toft-Hansen H (2005) Cytokine and chemokine inter-regulation in the inflamed or injured CNS. Brain Res Rev 48:178–184
Pennisi M, Malaguarnera G, Puglisi V et al (2013) Neurotoxicity of acrylamide in exposed workers. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:3843–3854
Perry VH, Teeling J (2013) Microglia and macrophages of the central nervous system: the contribution of microglia priming and systemic inflammation to chronic neurodegeneration. Semin Immunopathol 35:601–612
Ramsey JC, Young JD, Gorzinsky SJ (1984) Acrylamide: toxicodynamics in rats. Submitted to the US Environmental Protection Agency under TSCA Section 4. OTS0507270. [Unpublished study for peer review]
Reinoso RF, Telfer BA, Rowland M (1997) Tissue water content in rats measured by desiccation. J Pharm Toxicol Methods 38:87–92
Rotshenker S (2003) Microglia and macrophage activation and the regulation of complement-receptor-3 (CR46/MAC-1)-mediated myelin phagocytosis in injury and disease. J Mol Neurosci 21:65–72
Schroder K, Tschopp J (2010) The inflammasomes. Cell 140:821–832
Song L, Pei L, Yao S et al (2017) NLRP3 inflammasome in neurological diseases, from functions to therapies. Front Cell Neurosci 11:1–17
Stansley B, Post J, Hensley K (2012) A comparative review of cell culture systems for the study of microglial biology in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflamm 9:577
Stow JL, Murray RZ (2013) Intracellular trafficking and secretion of inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 24:227–239
Streit WJ, Mrak RE, Griffin WST (2004) Microglia and neuroinflammation: a pathological perspective. J Neuroinflamm 1:1–4
Subramanian K, Mohideen SS, Suzumura A et al (2012) Exposure to 1-bromopropane induces microglial changes and oxidative stress in the rat cerebellum. Toxicology 302:18–24
Tareke E, Rydberg P, Karlsson P et al (2000) Acrylamide: a cooking carcinogen? Chem Res Toxicol 13:517–522
Tareke E, Rydberg P, Karlsson P et al (2002) Analysis of acrylamide, a carcinogen formed in heated foodstuffs. J Agric Food Chem 50:4998–5006
Urban M, Kavvadias D, Riedel K et al (2006) Urinary mercapturic acids and a hemoglobin adduct for the dosimetry of acrylamide exposure in smokers and nonsmokers. Inhal Toxicol 18:831–839
Van Everbroeck B, Dewulf E, Pals P et al (2002) The role of cytokines, astrocytes, microglia and apoptosis in Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Neurobiol Aging 23:59–64
Virk-Baker MK, Nagy TR, Barnes S, Groopman J (2014) Dietary acrylamide and human cancer: a systematic review of literature. Nutr Cancer 66:774–790
Wang W, Tan M, Yu J, Tan L (2015) Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Transl Med 3:1–15
Yang TT, Lin C, Hsu CT et al (2013) Differential distribution and activation of microglia in the brain of male C57BL/6J mice. Brain Struct Funct 218:1051–1060
Zhang L, Geohagen BC, Gavin T, LoPachin RM (2016) Joint toxic effects of the type-2 alkene electrophiles. Chem Biol Interact 254:198–206
Zhao M, Lewis Wang FS, Hu X et al (2017) Acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity in primary astrocytes and microglia: roles of the Nrf2-ARE and NF-κB pathways. Food Chem Toxicol 106:25–35
Zhou K, Shi L, Wang Y et al (2016) Recent advances of the nLRP3 inflammasome in central nervous system disorders. J Immunol Res 2016:1–9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (#17H06396) and for Scientific Research (B) (#16H02965), Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. The authors would like to thank Ms. Satoko Arai for the excellent secretarial supports.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zong, C., Hasegawa, R., Urushitani, M. et al. Role of microglial activation and neuroinflammation in neurotoxicity of acrylamide in vivo and in vitro. Arch Toxicol 93, 2007–2019 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02471-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02471-0