Abstract
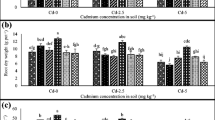
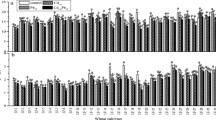
Different foliar barrier agents (FBA) were used by foliar spraying in first season field and pot experiments to compare their effects on Cadmium (Cd) reduction in wheat grains. The best two FBA (50 µM SNP and 2 mM Na2EDTA) can significantly reduce Cd concentration in wheat grains, and the filling period was the most effective period for FBA application. Compared with the control (H2O), foliar spraying 50 µM SNP or 2 mM Na2EDTA inhibited the moving of Cd from the lower tissue to upper tissue in stem and also significantly reduced the Cd accumulation in grains. Furthermore, compared with normal wheat variety (AK58), foliar spraying 50 µmol SNP or 2 mM Na2EDTA as the best two FBA significantly reduced Cd concentration in shoots of Cd low accumulation varieties (HZB and HJBY), which can be used for the safe production of wheat in Cd-contaminated farmlands.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arasimowicz M, Floryszakwieczorek J (2007) Nitric oxide as a bioactive signalling molecule in plant stress responses. Plant Sci 172:876–887
Arshad M, Iqbal M, Ashraf MY, Ali Q, Iqbal N (2019) Exogenous sodium nitroprusside increases antioxidative potential and grain yield of bread wheat exposed to cadmium. Pak J Bot 51:409–420
Chen W, Dong Y, Hu G, Bai X (2018) Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on cadmium toxicity and antioxidative system in perennial ryegrass. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 18:129–143
Cheng BB (2014) Determination of soil pH. Chem Teach Learn 4:95–97
Duan MM, Wang S, Huang DY, Zhu QH, Liu SL, Zhang Q, Zhu HH, Xu C (2018) Effectiveness of simultaneous applications of lime and zinc/iron foliar sprays to minimize cadmium accumulation in rice. Ecotox Environ Safe 165:510–515
FAO (2014) Core Production Data Base. Core Production Data Base, ProdStat
Forster SM, Rickertsen JR, Mehring GH, Ransom JK (2018) Type and placement of zinc fertilizer impacts cadmium content of harvested durum wheat grain. J Plant Nut 41:1471–1481
Fujimaki S, Suzul N, Ishloka NS, Kawachi N, Ito S, Chino M, Nakamura S (2010) Tracing cadmium from culture to spikelet: noninvasive imaging and quantitative characterization of absorption, transport, and accumulation of cadmium in an intact rice plant. Plant Physiol 152:1796–1806
Ghadakchiasl A, Mozafari AA (2017) Mitigation by sodium nitroprusside of the effects of salinity on the morpho-physiological and biochemical characteristics of Rubus idaeus under in vitro conditions Physiol. Mol Biol Plants 23:73–83
Hart JJ, Welch RM, Norvell WA, Kochian LV (2002) Transport interactions between cadmium and zinc in roots of breed and durum wheat seedlings. Physiol Plantarum 116:73–78
Hart JJ, Welch RM, Norvell WA, Clarke JM, Kochian LV (2005) Zinc effects on cadmium accumulation and partitioning in near-isogenic lines of durum wheat that differ in grain cadmium concentration. New Phytol 167:391–401
He JY, Ren YF, Chen XL, Chen H (2014) Protective roles of nitric oxide on seed germination and seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under cadmium stress. Ecotox Environ Safe 108:114–119
Huang B, Xin J, Dai H, Zhou W (2017) Effects of interaction between cadmium (Cd) and selenium (Se) on grain yield and Cd and Se accumulation in a hybrid rice (Oryza sativa) system. J Agr Food Chem 65:9537–9546
Hussain S, Khan AM, Rengel Z (2019) Zinc-biofortified wheat accumulates more cadmium in grains than standard wheat when grown on cadmium-contaminated soil regardless of soil and foliar zinc application. Sci Total Environ 654:402–408
Ismael MA, Elyamine AM, Zhao YY, Moussa MG, Rana MS, Afzal J, Imran M, Zhao XH, Hu CX (2018) An selenium and molybdenum restrain cadmium toxicity to pollen grains in Brassica napus ? Int J Mol Sci 19:2163
Jin X, Luo XG, Tang YJ (2016) Effects of exogenous boric acid on physiology and uranium enrichment of kidney bean under uranium stress. Chin Agric Sci Bull 32:175–181
Kaya C, Ashraf M, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Responses of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in regulating oxidative defence system in wheat plants grown under cadmium stress. Physiol Plantarum 168:345–360
Kotapati KV, Palaka BK, Ampasala DR (2017) Alleviation of nickel toxicity in finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.) germinating seedlings by exogenous application of salicylic acid and nitric oxide. Crop J 5:58–68
Kumari A, Sunita S, Kumari S (2011) Nitric oxide induced alleviation of toxic effects of short term and long term Cd stress on growth, oxidative metabolism and Cd accumulation in Chickpea. Braz J Plant Physiol 22:271–284
Li J (2008) Summary of soil organic matter determination methods. Analysis Laboratory 154–156
Li M, Wang G, Li J, Cao F (2016) Foliar application of betaine alleviates cadmium toxicity in maize seedlings. Acta Physiol Plant 38:1–14
Liu Y, Chen Y, Yang Y, Zhang QF, Fu BS, Cai J, Guo W, Shi L, Wu JZ, Chen YH (2020) A thorough screening based on QTLs controlling zinc and copper accumulation in the grain of different wheat genotypes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020:1–12
Marwa I, Ali E, Yuan Z, Mohamed M, Muhammad R, Javaria A, Muhammad I, Xiao HZ, Cheng XH (2018) Can selenium and molybdenum restrain cadmium toxicity to pollen grains in Brassica napus? Int J Mol Sci 19:2163
Naeem A, Saifullah, Ghafoor A, Farooq M (2015) Suppression of cadmium concentration in wheat grains by silicon is related to its application rate and cadmium accumulating abilities of cultivars. J Sci Food Agric 95:2467–2472
Panda P, Nath S, Chanu TT, Sharma GD, Panda SK (2011) Cadmium stress-induced oxidative stress and role of nitric oxide in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Acta Physiol Plant 33:1737–1747
Saifullah, Sarwar N, Bibi S, Ahmad M, Ok YS (2014) Effectiveness of zinc application to minimize cadmium toxicity and accumulation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ Earth Sci 71:1663–1672
Samane E (2020) Translocation, leaf distribution, and nutritional status of manganese in cucumber plants as affected by foliar application of exogenous amino acids. J Plant Growth Regul 39:1191–1204
Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricutural land (GB15618-2018)
Tavarez M, Macri A, Sankaran RP (2015) Cadmium and zinc partitioning and accumulation during grain filling in two near isogenic lines of durum wheat. Plant Physiol Bioch 97:461–469
Wang BS (2019) Effects of different amendments on rice growth and heavy metal absorption and accumulation under Cd, As, and Ni stress. Guizhou normal university
Wang Z, Li Q, Wu W, Guo J, Yang Y (2017) Cadmium stress tolerance in wheat seedlings induced by ascorbic acid was mediated by NO signaling pathways. Ecotox Environ Safe 135:75–81
Wang H, Xu C, Luo ZC, Zhu HH, Wang SS, Zhu QH, Huang DY, Zhang YZ, Xiong J, He YB (2018a) Foliar application of Zn can reduce cd concentrations in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:29287–29294
Wang L, Gu PL, Li R, Xu YM, Sun YB, Liang XF, Dai JJ (2018b) Efect of foliar zinc application on bioaccessibility of cadmium and zinc in pakshoi. Environ Sci 39:2944–2952
Wang YM, Yang RX, Zheng JY, Shen ZG, Xu XM (2019) Exogenous foliar application of fulvic acid alleviate cadmium toxicity in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Ecotox Environ Safe 167:10–19
Wang Z, Wang H, Xu C, Lv G, Li B (2020) Foliar application of Zn-EDTA at early filling stage to increase grain Zn and Fe and reduce grain Cd, Pb and grain yield in rice (Oryza sativa L). B Environ Contam Tox 105:428–432
Wang W, Lu T, Liu L, Yang X, Zhou D (2021) Zeolite-supported manganese oxides decrease the Cd uptake of wheat plants in Cd-contaminated weakly alkaline arable soils. J Hazard Mater 419:126464
Wei L, Wang K, Noguera DR, Jiang J, Oyserman BO, Zhao N, Zhao QL, Cui F (2016) Transformation and speciation of typical heavy metals in soil aquifer treatment system during long time recharging with secondary effluent: Depth distribution and combination. Chemosphere 165:100–109
Wu C, Dun Y, Zhang Z, Li M, Wu G (2020) Foliar application of selenium and zinc to alleviate wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cadmium toxicity and uptake from cadmium-contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110091
Yadu S, Yadu, Dewangan TL, Chandrakar V, Keshavkant S (2017) Imperative roles of salicylic acid and nitric oxide in improving salinity tolerance in Pisum sativum L. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 23:43–58
Yan BF, Nguyen C, Pokrovsky OS, Candaudap F, Coriou C, Bussière S, Robert T, Cornu JY (2019) Cadmium allocation to grains in durum wheat exposed to low Cd concentrations in hydroponics. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 184:109592
Yang QQ, Li ZY, Lu XN, Duan QN, Huang L, Bi J (2018) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700
Zhou Z, Zhang B, Liu HT, Liang XD, Ma WL, Shi ZY, Yang SQ (2019) Zinc effects on cadmium toxicity in two wheat varieties (Triticum aestivum L.) differing in grain cadmium accumulation. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 183:109562
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education institutions and Special Project of Fundamental Scientific Research Funds for Nanjing Agricultural University (KYQN202061), the National Key Research and Development Program (2016YFD08007003), the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-10-B24; CARS-23-A03), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31901180; 31800525), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M651845).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Xia, S., Li, J. et al. Screening of Foliar Barrier Agents and Reduces the Absorption and Transport of Cd in Wheat. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 108, 372–378 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03370-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03370-w