Abstract
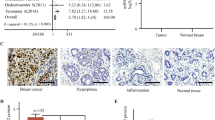
Rhomboid is an evolutionary conserved and functionally diversified group of proteins composed of proteolytically active and inactive members that are involved in the modulation of multiple biological processes such as epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway, endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation, cell death, and proliferation. Recently, several human rhomboid genes have been associated with the development of chronic myeloid leukemia and pituitary, colorectal, ovarian, and breast cancers. In this study, we evaluated the mRNA and protein expression profiles of rhomboid genes in cancer cell lines and breast tissue/tumor samples. In silico analysis of publicly available gene expression datasets showed that different rhomboid genes are specifically expressed according to the breast cancer intrinsic subtypes. Quantitative reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis showed a significant RHBDD2 mRNA overexpression in advanced breast cancer compared with normal tissue samples (p = 0.012). In addition, we found that RHBDL2 and PARL mRNA expression was associated with a low/intermediate histologic tumor grade (p = 0.024 and p = 0.015, respectively). Immunohistochemistry analysis showed a significant increase of RHBDD2 protein expression in association with breast cancer samples negative for progesterone receptor (p = 0.015). Moreover, protein expression analysis corroborated the quantitative RT-PCR results, indicating that breast primary tumors belonging to patients with a more disseminated disease expressed significantly increased levels of RHBDD2 protein compared with less disseminated tumors (p = 0.01).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freeman M. Proteolysis within the membrane: rhomboids revealed. Nature. 2004;5:188–97.
Sturtevant MA, Roark M, Bier E. The Drosophila rhomboid gene mediates the localized formation of wing veins and interacts genetically with components of the EGF-R signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 1993;7(6):961–73.
Pascall JC, Brown KD. Characterization of a mammalian cDNA encoding a protein with high sequence similarity to the Drosophila regulatory protein Rhomboid. FEBS Lett. 1998;429(3):337–40.
Bergbold N, Lemberg MK. Emerging role of rhomboid family proteins in mammalian biology and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.03.025.
Adrain C, Zettl M, Christova Y, Taylor N, Freeman M. Tumor necrosis factor signaling requires iRhom2 to promote trafficking and activation of TACE. Science. 2012;335:225–8.
Jeyaraju DV, Xu L, Letellier MC, Bandaru S, Zunino R, Berg EA, et al. Phosphorylation and cleavage of presenilin-associated rhomboid-like protein (PARL) promotes changes in mitochondrial morphology. PNAS. 2006;103(49):18562–7.
Fleig L, Bergbold N, Sahasrabudhe P, Geiger B, Lemberg MK. Ubiquitin-dependent intramembrane rhomboid protease promotes ERAD of membrane proteins. Mol Cell. 2012;47:558–69.
Bahar A, Simpson DJ, Cutty SJ, Bicknell JE, Hoban PR, Holley S, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel pituitary tumor apoptosis gene. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;19(7):1827–39.
Bahar A, Whitby P, Holley S, Hoban PR, Elder JB, Deakin M, et al. Primary colorectal tumors fail to express the proapoptotic mediator PTAG and its reexpression augments drug-induced apoptosis. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2007;46(2):202–12.
Wang Y, Guan X, Fok KL, Li S, Zhang X, Miao S, et al. A novel member of the Rhomboid family, RHBDD1, regulates BIK-mediated apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008;65(23):3822–9.
Wan C, Fu J, Wang Y, Miao S, Song W, Wang L. Exosome-related multi-pass transmembrane protein TSAP6 is a target of rhomboid protease RHBDD1-induced proteolysis. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37452.
Pellegrini L, Scorrano L. A cut short to death: Parl and Opa1 in the regulation of mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(7):1275–84.
Sanjuán Szklarz LK, Scorrano L. The antiapoptotic OPA1/Parl couple participates in mitochondrial adaptation to heat shock. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1817(10):1886–93.
Ren X, Song W, Liu W, Guan X, Miao F, Miao S, et al. Rhomboid domain containing 1 inhibits cell apoptosis by upregulating AP-1 activity and its downstream target Bcl-3. FEBS Lett. 2013;587(12):1793–8.
Liu XN, Tang ZH, Zhang Y, Pan QC, Chen XH, Yu YS, et al. Lentivirus-mediated silencing of rhomboid domain containing 1 suppresses tumor growth and induces apoptosis in hepatoma HepG2 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(1):5–9.
Yan Z, Zou H, Tian F, Grandis JR, Mixson AJ, Lu PY, et al. Human rhomboid family-1 gene silencing causes apoptosis or autophagy to epithelial cancer cells and inhibits xenograft tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(6):1355–64.
Blaydon DC, Etheridge SL, Risk JM, Hennies HC, Gay LJ, Carroll R, et al. RHBDF2 mutations are associated with tylosis, a familial esophageal cancer syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90(2):340–6.
Wojnarowicz PM, Provencher DM, Mes-Masson AM, Tonin PN. Chromosome 17q25 genes, RHBDF2 and CYGB, in ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(6):1865–80.
Lin YN, Gui FM, Shen H, Wang F, Cao Z, Li QH, et al. Expression of RHBDD1 gene in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia and its clinical significance. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013;21(1):12–5.
Adrain C, Strisovsky K, Zettl M, Hu L, Lemberg MK, Freeman M. Mammalian EGF receptor activation by the rhomboid protease RHBDL2. EMBO Rep. 2011;5(12):421–7.
Zou H, Thomas SM, Yan ZW, Grandis JR, Vogt A, Li LY. Human rhomboid family-1 genes RHBDF1 participates in GPCR-mediated transactivation of growth signals in head and neck squamous cancer cells. FASEB J. 2009;23:425–32.
Yan Z, Zou H, Tian F, Grandis JR, Mixson AJ, Lu PY, et al. Human rhomboid family-1 gene silencing causes apoptosis or autophagy to epithelial cancer cells and inhibits xenograft tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7:1355–64.
Etheridge SL, Brooke MA, Kelsell DP, Blaydon DC. Rhomboid proteins: a role in keratinocyte proliferation and cancer. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;351(2):301–7.
Abba MC, Lacunza E, Nunez MI, Colussi A, Isla-Larrain M, Segail-Eiras A, et al. Rhomboid domain containing 2 (RHBDD2): a novel cancer-related gene over-expressed in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(10):988–97.
Lacunza E, Canzoneri R, Rabassa ME, Zwenger A, Segal-Eiras A, Croce MV, et al. RHBDD2: a 5-fluorouracil responsive gene overexpressed in the advanced stages of colorectal cancer. Tumor Biol. 2012;33(6):2393–9.
Taminau J, Meganck S, Lazar C, Steenhoff D, Coletta A, Molter C, et al. Unlocking the potential of publicly available microarray data using inSilicoDb and inSilicoMerging R/Bioconductor packages. BMC Bioinforma. 2012;13:335.
Cox ML, Schray CL, Luster CN, Stewart ZS, Korytko PJ, Khan KNM, et al. Assessment of fixatives, fixation, and tissue processing on morphology and RNA integrity. Exp Mol Pathol. 2006;80:183–91.
Cipolat S, Rudka T, Hartmann D, Costa V, Serneels L, Craessaerts K, et al. Mitochondrial rhomboid PARL regulates cytochrome c release during apoptosis via OPA1-dependent cristae remodeling. Cell. 2006;126:163–75.
Frezza C, Cipolat S, Martins de Brito O, Micaroni M, Beznoussenko GV, Rudka T, et al. OPA1 controls apoptotic cristae remodeling independently from mitochondrial fusion. Cell. 2006;126:177–89.
Hill RB, Pellegrini L. The PARL family of mitochondrial rhomboid proteases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2010;21(6):582–92.
Saftig P, Reiss K. The “A Disintegrin And Metalloproteases ADAM10 and ADAM17: novel drug targets with therapeutic potential? Eur J Cell Biol. 2011;90(6–7):527–35.
Peschon JJ, Slack JL, Reddy P, Stocking KL, Sunnarborg SW, Lee DC, et al. An essential role for ectodomain shedding in mammalian development. Science. 1998;282(5392):1281–4.
Cancello G, Maisonneuve P, Rotmensz N, Viale G, Mastropasqua MG, Pruneri G, et al. Progesterone receptor loss identifies Luminal B breast cancer subgroups at higher risk of relapse. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(3):661–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the CONICET (PIP-2131) and FONCYT (PICT-0275) grants (Abba MC).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canzoneri, R., Lacunza, E., Isla Larrain, M. et al. Rhomboid family gene expression profiling in breast normal tissue and tumor samples. Tumor Biol. 35, 1451–1458 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1199-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1199-8