Abstract
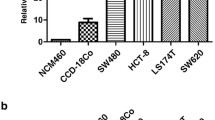
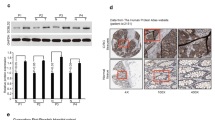
In previous studies, we identified rhomboid domain containing 2 (RHBDD2) gene to be markedly overexpressed in breast cancer patients that developed recurrence of the disease. In this study, we evaluated for the first time RHBDD2 gene expression in colorectal cancer (CRC). Five public available DNA microarray studies were compiled in a homogeneous dataset of 906 colorectal samples. The statistical analysis of these data showed a significant increase of RHBDD2 expression in the advanced stages of CRC (p < 0.01). We validated these findings by immunohistochemistry on 130 colorectal tissue samples; RHBDD2 protein overexpression was also observed in the advanced stages of the disease (p < 0.001). In addition, we investigated RHBDD2 expression in response to the chemotherapy agent 5-fluorouracile (5FU). We detected a significant increase of RHBDD2 mRNA and protein after 5FU treatment (20–40 μM; p < 0.001). Overall, these results showed that RHBDD2 overexpression might play a role in colorectal cancer progression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74.
Urban S, Lee JR, Freeman M. Drosophila rhomboid-1 defines a family of putative intramembrane serine proteases. Cell. 2001;107(2):173–82.
Lee JR, Urban S, Garvey CF, Freeman M. Regulated intracellular ligand transport and proteolysis control EGF signal activation in Drosophila. Cell. 2001;107(2):161–71.
Freeman M. Rhomboid proteases and their biological functions. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:191–210.
Spano JP, Milano G, Vignot S, Khayat D. Potential predictive markers of response to EGFR-targeted therapies in colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;66(1):21–30.
Mitsudomi T, Yatabe Y. Epidermal growth factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and cancer. FEBS J. 2010;277(2):301–8.
Krasinskas AM. EGFR signaling in colorectal carcinoma. Patholog Res Int. 2011;2011:932932.
Wang Y, Guan X, Fok KL, et al. A novel member of the Rhomboid family, RHBDD1, regulates BIK-mediated apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008;65(23):3822–9.
Yan Z, Zou H, Tian F, et al. Human rhomboid family-1 gene silencing causes apoptosis or autophagy to epithelial cancer cells and inhibits xenograft tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(6):1355–64.
Zou H, Thomas SM, Yan Z-W, et al. Human rhomboid family-1 gene RHBDF1 participates in GPCR-mediated transactivation of EGFR growth signals in head and neck squamous cancer cells. FASEB J. 2009;23(2):425–32.
Adrain C, Strisovsky K, Zettl M, et al. Mammalian EGF receptor activation by the rhomboid protease RHBDL2. EMBO Rep. 2011;12(5):421–7.
Abba MC, Sun H, Hawkins KA, et al. Breast cancer molecular signatures as determined by SAGE: correlation with lymph node status. Mol Cancer Res. 2007;5(9):881–90.
Abba MC, Lacunza E, Nunez MI, et al. Rhomboid domain containing 2 (RHBDD2): a novel cancer-related gene over-expressed in breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(10):988–97.
The Translational Genomics Research Institute. “Expression Project For Oncology (expO) Collects 1,000th Malignant Tumor Specimen.” ScienceDaily, 25 Oct. 2005. Web. 3 Sep. 2012.
Jorissen RN, Gibbs P, Christie M, et al. Metastasis-associated gene expression changes predict poor outcomes in patients with Dukes stage B and C colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(24):7642–51.
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Wu F, et al. Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;138(3):958–68.
Mariadason JM, Arango D, Shi Q, et al. Gene expression profiling-based prediction of response of colon carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil and camptothecin. Cancer Res. 2003;63(24):8791–812.
Boyer J, Allen WL, McLean EG, et al. Pharmacogenomic identification of novel determinants of response to chemotherapy in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(5):2765–77.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CONICET (PIP 2131) and FONCYT (PICT 0275) grants.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
PDF 449 kb
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacunza, E., Canzoneri, R., Rabassa, M.E. et al. RHBDD2: a 5-fluorouracil responsive gene overexpressed in the advanced stages of colorectal cancer. Tumor Biol. 33, 2393–2399 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0503-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0503-3