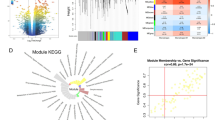
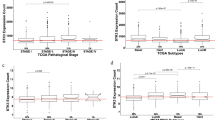
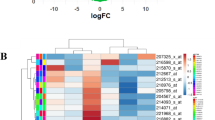
Abstract
It is well-established that breast cancer is a highly prevalent malignancy among women, emphasizing the need to investigate mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis and metastasis. In this study, the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database was utilized to conduct differential expression analysis in breast cancer and adjacent tissues. Upregulated genes were selected for prognostic analysis of breast cancer. The expression of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), also known as PLAUR, was assessed using RT-qPCR and western blot. Immunofluorescence staining was employed to determine PLAUR localization. Various cellular processes were analyzed, including proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and cell cycle. Bioinformatics analysis was used to predict transcription factors of PLAUR, which were subsequently validated in a double luciferase reporter gene experiment. Rescue experiments confirmed the impact of PLAUR on the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of MDA-MB-231 cells. Furthermore, the effects of PLAUR were evaluated in an orthotopic tumor transplantation and lung metastasis nude mouse model. Our findings substantiated the critical involvement of PLAUR in the progression of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) in vitro and among TNBC patients with a poor prognosis. Additionally, we demonstrated Yin Yang-1 (YY1) as a notable transcriptional regulator of PLAUR, whose activation could transcriptionally enhance the proliferation and invasion capabilities of TNBC cells. We also identified the downstream mechanism of PLAUR associated with PLAU, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), and AKT. Overall, these findings offer a novel perspective on PLAUR as a potential therapeutic target for TNBC.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used and/or analyzed in this study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aguirre Ghiso JA (2002) Inhibition of FAK signaling activated by urokinase receptor induces dormancy in human carcinoma cells in vivo. Oncogene 21:2513–2524. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205342
Ahmed S, Bradshaw AD, Gera S, et al. (2017) The TGF-β/Smad4 signaling pathway in pancreatic carcinogenesis and its clinical significance. J Clin Med 6 https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm6010005
Anh H, Lam VQ, Takami A, et al. (2022) Cytotoxic mechanism of momilactones A and B against acute promyelocytic leukemia and multiple myeloma cell lines. Cancers 14 https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194848
Chen JS, Chang LC, Wu CZ et al (2016) Significance of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its receptor in the progression of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in clinical and mouse models. J Biomed Sci 23:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-016-0242-7
Connolly BM, Choi EY, Gårdsvoll H et al (2010) Selective abrogation of the uPA-uPAR interaction in vivo reveals a novel role in suppression of fibrin-associated inflammation. Blood 116:1593–1603. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-03-276642
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI et al (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res : an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 13:4429–4434. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-06-3045
Dou WT, Xu F, Xu CX et al (2021) Graphene nanoribbon-based supramolecular ensembles with dual-receptor targeting function for targeted photothermal tumor therapy. Chem Sci 12:11089–11097. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1sc02154k
Duffy MJ, McGowan PM, Harbeck N et al (2014) uPA and PAI-1 as biomarkers in breast cancer: validated for clinical use in level-of-evidence-1 studies. Breast Cancer Res : BCR 16:428. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-014-0428-4
Faustino-Rocha A, Oliveira PA, Pinho-Oliveira J et al (2013) Estimation of rat mammary tumor volume using caliper and ultrasonography measurements. Lab Anim 42:217–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/laban.254
Geenen JJJ, Dackus G, Schouten PC et al (2021) A phase I dose-escalation study of two cycles carboplatin-olaparib followed by olaparib monotherapy in patients with advanced cancer. Int J Cancer 148:3041–3050. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.33498
Guo Q, Wang T, Yang Y et al (2020) Transcriptional factor Yin Yang 1 promotes the stemness of breast cancer cells by suppressing miR-873-5p transcriptional activity. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 21:527–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.06.018
Heissig B, Eiamboonsert S, Salama Y et al (2016) Cancer therapy targeting the fibrinolytic system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 99:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2015.11.010
Januškevičienė I, Petrikaitė V (2019) Heterogeneity of breast cancer: the importance of interaction between different tumor cell populations. Life Sci 239:117009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117009
LeBeau AM, Duriseti S, Murphy ST et al (2013) Targeting uPAR with antagonistic recombinant human antibodies in aggressive breast cancer. Can Res 73:2070–2081. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-3526
Li W, Hu S, Han Z et al (2022) YY1-induced transcriptional activation of FAM111B contributes to the malignancy of breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 22:e417–e425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clbc.2021.10.008
Lin HJ, Liu Y, Lofland D, et al. (2022) Breast cancer tumor microenvironment and molecular aberrations hijack tumoricidal immunity. Cancers 14 https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020285
Liu Y, Pan YF, Xue YQ et al (2018) uPAR promotes tumor-like biologic behaviors of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol Immunol 15:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2016.60
Liu M, Chen S, Zhang A et al (2021) PLAUR as a potential biomarker associated with immune infiltration in bladder urothelial carcinoma. J Inflamm Res 14:4629–4641. https://doi.org/10.2147/jir.S326559
Liu S, Zhao Y, Zhang J et al (2023) Application of single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of novel breast cancer phenotypes based on the activation of ferroptosis-related genes. Funct Integr Genomics 23:173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01086-0
Ou X, Huo J, Huang Y et al (2019) Transcription factor YY1 is essential for iNKT cell development. Cell Mol Immunol 16:547–556. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-018-0002-6
Qiao K, Ning S, Wan L et al (2019) LINC00673 is activated by YY1 and promotes the proliferation of breast cancer cells via the miR-515-5p/MARK4/Hippo signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res : CR 38:418. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1421-7
Schafer JM, Lehmann BD, Gonzalez-Ericsson PI, et al. (2020) Targeting MYCN-expressing triple-negative breast cancer with BET and MEK inhibitors. Sci Transl Med 12 https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw8275
Shen Z, Zhang P, Zhang W et al (2023) IL-1RA inhibits esophageal carcinogenesis and lymphangiogenesis via downregulating VEGF-C and MMP9. Funct Integr Genomics 23:164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01049-5
Sliutz G, Eder H, Koelbl H et al (1996) Quantification of uPA receptor expression in human breast cancer cell lines by cRT-PCR. Breast Cancer Res Treat 40:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01806814
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tabouret E, Wang H, Amin N, et al. (2020) TP5, a peptide inhibitor of aberrant and hyperactive CDK5/p25: a novel therapeutic approach against glioblastoma. Cancers 12 https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071935
Tao Q, Lu Y, Qi Y et al (2022) Hypoxia promotes the expression of Von Willebrand factor in breast cancer cells by up-regulating the transcription factor YY1 and down-regulating the hsa-miR-424. Euro J Pharmacol 934:175308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175308
Vastrad C, Vastrad B (2018) Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profiles to diagnose crucial and novel genes in glioblastoma multiform. Pathol Res Pract 214:1395–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2018.07.015
Wang Q, Yu W, Wang T et al (2023) Circular RNA circDLG1 contributes to HCC progression by regulating the miR-141-3p/WTAP axis. Funct Integr Genomics 23:179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01096-y
Xie F, Wang J, Zhang B (2023) RefFinder: a web-based tool for comprehensively analyzing and identifying reference genes. Funct Integr Genomics 23:125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01055-7
Yang Y, Zhang X, Lin F et al (2019) Bispecific CD3-HAC carried by E1A-engineered mesenchymal stromal cells against metastatic breast cancer by blocking PD-L1 and activating T cells. J Hematol Oncol 12:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0723-8
Yi C, Li G, Wang W, et al. (2021) Disruption of YY1-EZH2 interaction using synthetic peptides inhibits breast cancer development. Cancers 13 https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102402
Zhang T, Wang B, Su F et al (2022a) TCF7L2 promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis of gastric cancer by transcriptionally activating PLAUR. Int J Biol Sci 18:4560–4577. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.69933
Zhang YL, Cao JL, Zhang Y et al (2022b) RNF144A exerts tumor suppressor function in breast cancer through targeting YY1 for proteasomal degradation to downregulate GMFG expression. Med Oncol (Northwood, London, England) 39:48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-021-01631-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YG contributed to the conception and design of the research. CZ performed the research, and data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. SC and WW contributed significantly to the data analyses and experiment. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent participate
Not applicable.
Human and animal rights and informed consent
All animal experiments were conducted according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Research Council, 1996). All animal experiments in the present study were approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical College (Ref No. 2023469).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Chen, S., Wang, W. et al. YY1 regulates the proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer via activating PLAUR. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 269 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01193-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01193-y