Abstract
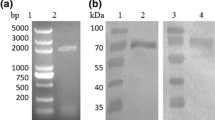
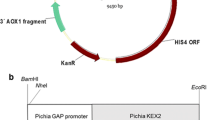
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) was a potential therapeutic drug for type II diabetes, mainly because of the stimulatory effect on insulin secretion under condition of high blood glucose. We used PCR to obtain a recombination gene, GGH, in which two GLP-1 (GLP-1A2G) mutants were connected in series and then fused to the N terminal of human serum albumin. The fusion gene was inserted into pGAPZaA plasmid with Saccharomyces cerevisiae α-factor secretion signal sequence, and was expressed by the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAP) promoter. The engineered strain was constructed by integrating the recombinant plasmid pGAPZαA/GGH into the genome of Pichia pastoris GS115. Genome PCR and western blot showed that the recombinant P. pastoris successfully expressed the fusion protein GGH. The yield of GGH reached 78 mg/L after 72 h fermentation in a flask, using glucose as the optimal carbon source. Fed-batch fermentation was investigated in a 5 L bioreactor, and the expression level of GGH reached 246 mg/L in 52 h. The fusion protein GGH was purified in four steps, and the final purity was 96.1%. The in vitro bioactivity of GGH was the same as that expressed in P. pastoris by the AOX1 promoter. This study described an efficient way to express GGH fusion protein in P. pastoris using GAP promoter, fermentation was easier to control without carbon source change and fermentation time was 20 h less than AOX1 promotercontrolled GGH fermentation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doyle, M. E. and J. M. Egan (2007) Mechanisms of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pancreas. Pharmacol. Therapeutics. 113: 546–593.
Yu, Z. W. and T. R. Jin (2010) New insights into the role of cAMP in the production and function of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Cellular Signalling. 22: 1–8.
Donnelly, D. (2012) The structure and function of the glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor and its ligands. British J. Pharmacol. 166: 27–41.
Chung, L. T. K., T. Hosaka, M. Yoshida, N. Harada, H. Sakaue, T. Sakai, and Y. Nakaya (2009) Exendin-4, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, directly induces adiponectin expression through protein kinase A pathway and prevents inflammatory adipokine expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 390: 613–618.
Gao, Z., G. Bai, J. Chen, Q. Zhang, P. Pan, F. Bai, and P. Geng (2009) Development, characterization, and evaluation of a fusion protein of a novel Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog and human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 73: 688–694.
Qian, J. (2001) Biological activities of glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. 40: 2860–2869.
Seo, M. -J., H. -J. Choi, K. -H. Chung, and Y. -R. Pyun (2012) Production of salmosin, a snake venom-derived disintegrin, in recombinant Pichia pastoris using high cell density fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 17: 1068–1075.
Liu, Y., J. Pan, P. Wei, J. Zhu, L. Huang, J. Cai, and Z. Xu (2012) Efficient expression and purification of recombinant alcohol oxidase in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 17: 693–702.
Waterham, H. R., M. E. Digan, P. J. Koutz, S. V. Lair, and J. M. Cregg (1997) Isolation of the Pichia pastoris glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene and regulation and use of its promoter. Gene. 186: 37–44.
Chen, G. H., L. J. Yin, I. H. Chiang, and S. T. Jiang (2007) Expression and purification of goat lactoferrin from Pichia pastoris expression system. J. Food Sci. 72: M67–M71.
Goodrick, J. C., M. Xu, R. Finnegan, B. M. Schilling, S. Schiavi, H. Hoppe, and N. C. Wan (2001) High-level expression and stabilization of recombinant human chitinase produced in a continuous constitutive Pichia pastoris expression system. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 74: 492–497.
Zhang, A. L., J. X. Luo, T. Y. Zhang, Y. W. Pan, Y. H. Tan, C. Y. Fu, and F. Z. Tu (2009) Recent advances on the GAP promoter derived expression system of Pichia pastoris. Mol. Biol. Rep. 36: 1611–1619.
Dou, W.-F., J. -Y. Lei, L. -F. Zhang, Z. -H. Xu, Y. Chen, and J. Jin (2008) Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant human serum albumin fusion protein with two human glucagon-like peptide-1 mutants in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expres. Purif. 61: 45–49.
Wu, S. X. and G. J. Letchworth (2004) High efficiency transformation by electroporation of Pichia pastoris pretreated with lithium acetate and dithiothreitol. Biotechniq. 36: 152–154.
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Kobayashi, K., S. Kuwae, T. Ohya, T. Ohda, M. Ohyama, H. Ohi, K. Tomomitsu, and T. Ohmura (2000) High-level expression of recombinant human serum albumin from the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris with minimal protease production and activation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 89: 55–61.
Zhang, Y. P., W. Yang, L. J. Chen, Y. Shi, G. Li, and N. M. Zhou (2011) Development of a novel DnaE intein-based assay for quantitative analysis of G-protein-coupled receptor internalization. Anal. Biochem. 417: 65–72.
Poutou-Pinales, R. A., H. A. Cordoba-Ruiz, L. A. Barrera-Avellaneda, and J. M. Delgado-Boada (2010) Carbon source feeding strategies for recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris and Pichia methanolica. African J. Biotechnol. 9: 2173–2184.
Gao, M. and Z. Shi (2013) Process control and optimization for heterologous protein production by methylotrophic Pichia pastoris. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 21: 216–226.
Periyasamy, S., N. Govindappa, S. Sreenivas, and K. Sastry (2013) Isolation, characterization and evaluation of the Pichia pastoris sorbitol dehydrogenase promoter for expression of heterologous proteins. Protein Expres. Purif. 92: 128–133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, K., Gong, X., Guan, B. et al. Efficient expression of glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue with human serum albumin fusion protein in Pichia pastoris using the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20, 694–700 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0818-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0818-6