Abstract
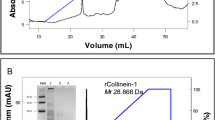
Salmosin, a snake venom-derived disintegrin, was successfully expressed in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris and secreted into the culture supernatant, as a 6 kDa protein. High-cell density fermentation of recombinant P. pastoris was optimized for the mass production of salmosin. In a 5 L jar fermentor, recombinant P. pastoris was fermented in growth medium containing 5% (w/v) glycerol at the controlled pH of 5.0. After culturing for 21 h, glycerol feeding medium was fed at one time into the culture broth. After 7 h (a total of 28 h), induction medium that contained methanol was increasingly added until the culture time totaled 75 h. Finally, these optimized culture conditions produced a high cell density of recombinant P. pastoris (dry cell weight of 113.38 g/L) and led to the mass production of salmosin (a total protein concentration of 369.2 mg/L). The culture supernatant containing salmosin inhibited platelet aggregation, resulting in a platelet aggregation of 9% compared to that of 94% in the control experiment, without culture supernatant. These results demonstrate that recombinant salmosin in culture supernatant from high cell density fed-batch fermentation can serve as a platelet aggregation inhibitor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae, C. S., M. S. Hong, S. G. Chang, D. Y. Kim, and H. C. Shin (1997) Optimization of fusion proinsulin production by high celldensity fermentation of recombinant E. coli. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2: 27–32.
Zhang, W., M. Inan, and M. M. Meagher (2000) Fermentation strategies for recombinant protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 5: 275–287.
Dasari, V. K. R., D. Are, V. R. Joginapally, L. N. Mangamoori, and K. S. B. R. Adibhatla (2008) Optimization of the downstream process for high recovery of rhG-CSF from inclusion bodies expressed in Escherichia coli. Proc. Biochem. 43: 566–575.
Cregg, J. M., J. F. Tschopp, C. Stillman, R. Siegel, M. Akong, W. S. Craig, R. G. Buckholz, K. R. Madden, A. Kellaris, G. R. Davis, B. L. Smiley, J. Cruze, R. Torregrossa, G. Velicelebi, and G. P. Thill (1987) High-level expression and efficient assembly of hepatitis B surface antigen in the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Nat. Biotechnol. 5: 479–485.
Zhang, Z., M. Moo-Young, and Y. Chisti (1996) Plasmid stability in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol. Adv. 14: 401–435.
Cregg, J. M., T. S. Vedvick, and W. C. Raschke (1993) Recent advances in the expression of foreign genes in Pichia pastoris. Nat. Biotechnol. 11: 905–910.
Kim, M. J., S. H. Kim, J. H. Lee, J. H. Seo, J. H. Lee, J. H. Kim, Y. H. Kim, and S. W. Nam (2008) High-level secretory expression of human procarboxypeptidase B by fed-batch cultivation of Pichia pastoris and its partial characterization. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18: 1938–1944.
Macauley-Patrick, S., M. L. Fazenda, B. McNeil, and L. M. Harvey (2005) Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris expression system. Yeast 22: 249–270.
Kim, S. J., J. A. Lee, K. Won, Y. H. Kim, and B. K. Song (2009) Functional expression of Coprinus cinereus peroxidase in Pichia pastoris. Proc. Biochem. 44: 731–735.
Wu, D., X. W. Yu, T. C. Wang, R. Wang, and Y. Xu (2011) High yield Rhizopus chinenisis prolipase production in Pichia pastoris: Impact of methanol concentration. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 16: 305–311.
Savage, B., U. M. Marzec, B. H. Chao, L. A. Harker, J. M. Maraganore, and Z. M. Ruggeri (1990) Binding of the snake venom-derived proteins applaggin and echistatin to the arginineglycine-aspartic acid recognition site(s) on platelet glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex inhibits receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 11766–11772.
Huang, T. F., C. Z. Liu, C. H. Ouyang, and C. M. Teng (1991) Halysin, an antiplatalet Arg-Gly-Asp-containing snake venom peptide, as fibrinogen receptor antagonist. Biochem. Pharmacol. 42: 1209–1219.
Kang, I. C., K. H. Chung, S. J. Lee, Y. D. Yoon, H. M. Moon, and D. S. Kim (1998) Purification and molecular cloning of a platelet aggregation inhibitor from the snake (Agkistrodon halys brevicaudus) venom. Thromb. Res. 91: 65–73.
Hong, S. Y., Y. S. Koh, K. H. Chung, and D. S. Kim (2002) Snake venom disintegrin, saxatilin, inhibits platelet aggregation, human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation, and smooth muscle cell migration. Thromb. Res. 105: 79–86.
Hong, S. Y., H. Lee, W. K. You, K. H. Chung, D. S. Kim, and K. Song (2003) The snake venom disintegrin salmosin induces apoptosis by disassembly of focal adhesions in bovine capillary endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 302: 502–508.
Min, C. K., J. W. Lee, K. H. Chung, and H. W. Park (2010) Control of specific rate to enhance the production of a novel disintegrin, saxatilin, in recombinant Pichia pastoris. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 110: 314–319.
Seo, M. J., H. J. Choi, K. H. Chung, and Y. R. Pyun (2011) Production of a platelet aggregation inhibitor, salmosin, by high cell density fermentation of recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 21: 1053–1056.
Chiruvolu, V., K. Eskridge, J. Cregg, and M. Meagher (1998) Effects of glycerol concentration and pH on growth of recombinant Pichia pastoris yeast. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 75: 163–173.
Poutou-Piñales, R. A., H. A. Córdoba-Ruiz, L. A. Barrera-Avellaneda, and J. M. Delgado-Boada (2010) Carbon source feeding strategies for recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris and Pichia methanolica. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 9: 2173–2184.
Gurramkonda, C., A. Adnan, T. Gäbel, H. Lunsdorf, A. Ross, S. K. Nemani, S. Swaminathan, N. Khanna, and U. Rinas (2009) Simple high-cell density fed-batch technique for high-level recombinant protein production with Pichia pastoris: Application to intracellular production of Hepatitis B surface antigen. Microb. Cell Fact. 8: 13–20.
Koganesawa, N., T. Aizawa, H. Shimojo, K. Miura, A. Ohnishi, M. Demura, Y. Hayakawa, K. Nitta, and K. Kawano (2002) Expression and purification of a small cytokine growth-blocking peptide from armyworm Pseudaletia separata by an optimized fermentation method using the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr. Purif. 25: 416–425.
Imai, T. and T. Ohno (1995) Measurement of yeast intracellular pH by image processing and the change it undergoes during growth phase. J. Biotechnol. 38: 165–172.
Tanner, R. D., N. T. Souki, and R. M. Russell (1977) A fermentation process for producing both ethanol and lysine-enriched yeast. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 19: 27–42.
Stratton, J., V. Chiruvolu, and M. Meagher (1998) High cell-density fermentation. Methods Mol. Biol. 103: 107–120.
Packham, M. A. and J. F. Mustard (1977) Clinical pharmacology of platelets. Blood 50: 555–573.
Srivastava, K. C. (1984) Aqueous extracts of onion, garlic and ginger inhibit platelet aggregation and alter arachidonic acid metabolism. Biomed. Biochim. Acta 43: 335–346.
Neiva, T. J. C., L. Morais, M. Polack, C. M. O. Simões, and E. A. D’Amico (1999) Effects of catechins on human blood platelet aggregation and lipid peroxidation. Phytother. Res. 13: 597–600.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Two authors contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, MJ., Choi, HJ., Chung, KH. et al. Production of salmosin, a snake venom-derived disintegrin, in recombinant Pichia pastoris using high cell density fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17, 1068–1075 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0647-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0647-9