Abstract
The local vertical datum in Japan is based on the Helmert’s approximation of mean gravity along the plumbline. However, determination of a rigorous orthometric height requires that the integral-mean value of gravity along the plumbline between the geoid and the Earth surface has to be known precisely. An attempt has been made to obtain rigorous orthometric heights at 816 GPS/levelling points distributed over four main islands of Japan (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu) by applying corrections to the Helmert orthometric heights. The corrections to Helmert orthometric heights are evaluated from the differences between the integral-mean gravity and the approximate mean gravity along the plumbline. The corrections to Helmert orthometric heights vary from −30.9 cm to 0.0 cm with a mean value of −0.4 cm and standard deviation of ±1.7 cm. An improved high-resolution gravimetric geoid model covering four main islands of Japan from our previous study is used to compare the consistency of the two height systems to a regionally defined gravimetric geoid model. The standard deviation of the differences between gravimetric and GPS/levelling geoid undulations is ±7.5 cm, when Helmert orthometric heights are used. The standard deviation of the differences between gravimetric and GPS/levelling geoid undulations reduces to ±7.3 cm, when rigorous orthometric heights are used. This indicates that rigorous orthometric heights are more consistent with the gravimetric geoid model than Helmert orthometric heights.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
There are basically two different categories of height systems used in geodetic positioning. These are gravity field related (gravimetric) height system and ellipsoidal height system. The gravity field related heights are based on spirit levelling and gravity data along the levelling lines while the ellipsoidal heights are realised through satellite techniques. Gravimetric heights are obtained by dividing geopotential number by mean gravity between the geoid and the Earth’s surface. The way in which mean gravity is defined therefore determines the type of gravimetric height system. Orthometric height is one of the gravimetric height systems used in mapping, engineering works, navigation and other geophysical applications.
Orthometric height in the rigorous sense can be defined as the curved distance between the geoid and the Earth’s surface along the plumbline. The determination of a rigorous orthometric height therefore requires that the integral-mean value of gravity along the plumbline between the geoid and the Earth’s surface be known precisely. This is indeed an uphill task complicated further by the need to account for both lateral and radial mass-density variations.
It is important to note that there is no vertical datum in the world today that is based on a rigorous orthometric height system due to difficulty in obtaining integral-mean value of gravity along the plumbline between the geoid and the Earth surface. However, significant efforts have been made recently towards the realization of a rigorous orthometric height system (e.g. Santos et al. 2006; Tenzer et al. 2005; Kingdon et al. 2005; Dennis and Featherstone 2003; Tenzer and Vaníček 2003; Hwang and Hsiao 2003; Allister and Featherstone 2001; Kao et al. 2000).
Three techniques have been proposed and used in practice for the approximation of the integral-mean value of gravity between the geoid and the Earth’s surface along the plumbline. These include the Helmert method (Helmert 1890; Heiskanen and Moritz 1967), Mader method (Mader 1954) and Niethammer method (Niethammer 1932). Although Mader and Niethammer orthometric heights seem to be slightly more accurate than the Helmert orthometric heights, they are rarely used in practice; probably because of difficulty in the computations of the terrain correction, instead Helmert orthometric heights are in common use.
The Helmert orthometric heights are currently being used to assess the accuracy of local, regional and global gravimetric geoid models. For example, the difference between ellipsoidal height (obtained from GPS) and Helmert orthometric height (obtained from spirit levelling and gravity data) at a control point is compared with the gravimetric geoid undulation in the assessment of a geoid model. This comparison is affected by inherent errors in the gravimetric geoid model, ellipsoidal heights and orthometric heights.
This paper describes the procedure for determining corrections to Helmert orthometric heights at 816 GPS/levelling points over Japan. Comparisons between GPS/levelling and gravimetric geoid undulations (Odera and Fukuda 2014) are also presented. In this case, both Helmert and rigorous orthometric heights have been used for the comparisons. To avoid unnecessary repetitions in the subsequent sections, rigorous and Helmert orthometric heights are generally represented as H O and H respectively.
Methods
Description of orthometric height systems
Orthometric height is defined generally as the geometrical distance between the geoid and the point on the topographical surface, measured along the plumbline through the point. From a practical point of view, orthometric height may be represented geometrically as shown in Figure 1.
The orthometric height can be represented functionally as (Heiskanen and Moritz 1967, Equations 4 to 21)
where H O is the rigorous orthometric height and \( \overline{g} \) is the integral-mean value of gravity along the plumbline between the geoid and the terrain point (or any other point below or above the geoid), given as (Heiskanen and Moritz 1967, Equations 4 to 20)
Due to the difficulty in the determination of integral-mean value of gravity along the plumbline, approximations are normally made for practical determination of orthometric heights. This gives rise to various orthometric heights depending on the approximation method used for the determination of the mean gravity along the plumbline. Helmert orthometric height system is one of the orthometric height systems that is widely used. Other orthometric height systems include; Mader orthometric heights (Mader 1954; Krakiwsky 1965) and Niethammer orthometric heights (Niethammer 1932; Krakiwsky 1965). Although, normal heights (Molodensky et al. 1960), and normal-orthometric heights (Rapp 1961; Heck 2003) are used for the establishment of vertical datum in many countries, they are not referred to the geoid.
Helmert (1890) defined the approximate value for the mean gravity along the plumbline using Poincaré-Prey’s gravity gradient. A simplified Poincaré-Prey relationship for mean gravity can be given as (Heiskanen and Moritz 1967, Equations 4 to 25; Torge 1991)
where g is the observed gravity at the topographical surface, \( \frac{\partial \gamma }{\partial h} \) is the linear vertical gradient of normal gravity, normally taken as − 0.3086 mGal/m, G is the universal gravitational constant and ρ 0 is the constant topographic density, normally taken as 2,670 kg/m3. From Equation 3, we have a simplified mean gravity along the plumbline for the computation of Helmert’s orthometric height as (Heiskanen and Moritz 1967, Equations 4 to 24)
where the units of g and H are mGal and m respectively.
Practical determination of orthometric height is always achieved through precise spirit levelling (geodetic levelling). Helmert orthometric heights can be considered as the sufficient approximation of the rigorous orthometric heights for most practical applications. However, it should be noted that this approximation embeds a constant topographic mass-density for the Bouguer shell and completely neglects terrain roughness residual to the Bouguer shell (Santos et al. 2006).
Determination of rigorous orthometric heights over Japan
Determination of a rigorous orthometric height requires that the integral-mean value of gravity along the plumbline between the geoid and the topographical surface be known precisely. The gravity acceleration at a point, ignoring the small gravitational effect of atmospheric masses can be represented as (Santos et al. 2006)
where g NT is the gravity generated by masses contained within the geoid (e.g. Vaníček et al. 2004) and g T is the gravitational attraction generated by the topography.
The gravity generated by masses inside the geoid, can further be divided into the contribution of normal gravity (γ) and that of gravity disturbance due to masses inside the geoid (δg NT, e.g. Vaníček et al. 2004). The gravitational attraction generated by the topography can be decomposed into the gravitational acceleration generated by Bouguer shell (g B T), terrain roughness residual to the Bouguer shell (g R T) and the lateral variations in mass-density within the topography (g δρ). If we ignore the small gravitational effects of atmospheric masses, and the radial variation of the topographic mass-density, then a complete representation of the total gravity is given as (Tenzer et al. 2005)
The integral-mean gravity along the plumbline is then expressed as (Santos et al. 2006)
The difference between rigorous and Helmert orthometric heights is mainly due to the approximation of mean gravity along the plumbline between the geoid and the Earth’s surface, because both of them use the same geopotential number at each point. It follows that the correction to Helmert orthometric height can be obtained if the integral-mean gravity along the plumbline is known. This correction is expressed as (Santos et al. 2006)
where \( {\varepsilon}_{H^H} \) is the correction to Helmert orthometric height and \( {\varepsilon}_{\overline{g}} \) is the difference between the integral-mean gravity along the plumbline and the approximate value (i.e. \( {\varepsilon}_{\overline{g}}=\overline{g}-{\overline{g}}^H \)).
The establishment of the Japanese vertical datum can be traced to the levelling survey carried out by the Army Land Survey in 1883 (Imakiire and Hakoiwa 2004). The vertical datum was obtained through tidal observations from 1873 to 1879 at Reigan-jima in Tokyo Bay (e.g. Matsumura et al. 2004). Initially, normal-orthometric height system was used in Japan before conversion to the current Helmert orthometric height system obtained by incorporating measured gravity data. The first set of Helmert orthometric heights was published in 2002 by Geospatial Information Authority of Japan.
Data sets described in Odera et al. (2012) have been used in this study. We give only a summary of the data sets here. The bulk of the gravity data was obtained from the database developed by Nagoya University and other organizations covering south western parts of Japan (Shichi and Yamamoto 2001a, b). Another set of gravity data mainly along the main levelling network covering Japanese four main islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu and Shikoku) was provided by Geospatial Information Authority of Japan. In total there are 98,670 observed gravity data in the study area. Figure 2 shows the distribution of gravity data over the four Japanese main islands.
Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) covering the four main islands were prepared in 1999 by Geographical Survey Institute (the current Geospatial Information Authority of Japan). The Hokkaido area is covered by a 250-m DEM while the other three main islands (Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu) are covered by a 50-m DEM. Japan is mostly mountainous, with the lowest point being −4 m at Hachiro-Gata and the highest point being 3,776 m at the top of Mt. Fuji. The mean elevation is 407 m with a standard deviation of ±330 m. Figure 3 shows the topography of the study area.
The GPS/levelling network in Japan is mostly on the low areas ranging from 0.3 to 1,672.7 m. It consists of 816 benchmarks with the height of 99.9% of the points (815) ranging between 0.3 to 903.4 m and only one point has a height of 1,672.7 m. This network is chosen because it enables the envisaged comparison between GPS/levelling and gravimetric geoid undulations, using rigorous orthometric heights. Figure 4 shows the distribution of GPS/levelling points and their height variations.
If we assume that disregarding water bodies, the variation of actual topographical mass density from the mean is within ±300 kg/m3 (e.g. Martinec 1998), then the effect of the laterally varying topographical density on the orthometric height is less than 1 cm for all the points (height range 0.3 – 903.4 m) except one (height 1,672.7 m), where the effect is 3.6 cm. A part from the magnitude, the contribution of laterally varying topographical density has been ignored in this work strictly because of lack of actual topographical density model in the area of study. Equation 7 can then be re-written as
The integral-mean normal gravity (\( \overline{\gamma} \)) is evaluated using a second-order Taylor expansion for the analytical downward continuation of normal gravity (Heiskanen and Moritz 1967). The mean gravity disturbance generated by the geoid is given as (Tenzer et al. 2005)
where Ω is a dummy argument representing the spatial position (φ and λ), and \( \overline{K} \) represents the intermediary integration kernel (averaged Poisson’s kernel).
The geoid-generated gravity disturbance is approximated as (e.g. Vaníček et al. 1999, 2004)
where \( \varDelta {g}_{cg}^H \) is the Helmert’s gravity anomaly evaluated at the co-geoid, V g CT is the gravitational potential of condensed topographical masses on the geoid, V g T is the gravitational potential of topographical masses computed at the geoid, the disturbing potential at the geoid (T g ) in the second term and the third term [in the bracket] are related to the geoid undulation (N) and indirect effect (N ind ) respectively through Bruns’s formula, and the last term is the gravitational attraction of the condensed layer on the geoid. The geoid related terms are obtained from the recent geoid model for Japan (Odera and Fukuda 2014).
The mean value of the gravitational attraction generated by the Bouguer shell (\( {\overline{g}}_B^T \)) is given as (Tenzer et al. 2005; Santos et al. 2006)
while the mean value of the gravitational attraction generated by the terrain roughness residual to the Bouguer shell (\( {\overline{g}}_R^T \)) is given as (Santos et al. 2006),
For practical evaluations, the rigorous orthometric height (H O) is approximated by the Helmert orthometric height (H) where necessary. The computation of the integral-mean value of gravity along the plumbline is done at each of the 816 GPS/levelling points. There are no observed gravity data at the GPS/levelling points; hence the approximate value (Helmert’s mean gravity) is derived from the interpolated observed gravity (Figure 3) around each point using refined Bouguer gravity anomalies. The ideal situation would be to have observed gravity at the GPS/levelling points to avoid interpolation errors. Given that most of the points are in the low areas, which also happen to have good coverage of gravity data, the interpolation errors are significantly minimised. The rigorous orthometric height is then obtained as
where H H is the Helmert orthometric height and \( {\varepsilon}_{H^H} \) is the correction to Helmert orthometric height.
Results and discussions
The statistics of components of rigorous mean gravity along the plumbline are given in Table 1. Generally, there is a significant under-estimation of integral-mean gravity along the plumbline by Helmert’s mean gravity approximation in high altitude areas than in low areas. We also note a slight over-estimation of integral-mean gravity along the plumbline by Helmert’s mean gravity approximation in very low areas (0 to 100 m). The differences range between −11.36 to 180.80 mGal, with a mean of 3.84 mGal and standard deviation of ±22.48 mGal.
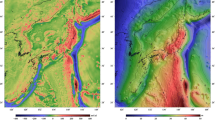
Spatial distribution of corrections to Helmert orthometric heights over Japan are shown in Figure 5. These corrections range between −30.87 to 0.03 cm, with a mean of −0.43 cm and standard deviation of ±1.66 cm at the 816 precise levelling points over Japan. There is only one point at a height of 1,672.7 m which has a correction value of −30.9 cm. The magnitude of the corrections is generally larger (in the absolute sense) in high areas than low areas. However, a closer investigation of Figure 5 reveals that, some low areas have larger corrections than slightly higher areas. This can be attributed to the contributions of gravitational attraction due to terrain roughness and geoid generated gravity disturbance. There may be other geophysical explanations beyond this study.
It is interesting to note that the biggest problem in geoid determination is also encountered in the mountainous areas. This brings to question the use of Helmert orthometric heights in validating gravimetric geoid models in general and specifically in mountainous areas, in view of the increasing accuracy in geoid modelling. It may be interesting to find out the contribution of the differences between rigorous and Helmert’s orthometric heights on downward continuation of gravity anomalies onto the geoid, especially in mountainous areas, where there are significant differences.
The rigorous orthometric heights at the 816 GPS/levelling points are then used in the comparisons between gravimetric and GPS/levelling geoid undulations (Table 2) using the recent geoid model over Japan (Odera and Fukuda 2014). For comparison purposes, the statistics of the differences between gravimetric and GPS/levelling geoid undulations using Helmert orthometric heights (Odera and Fukuda 2014) are also given in Table 2.
Table 2 shows that there is a slight improvement in the standard deviation in all the regions (Hokkaido, North Honshu, Central Honshu, West Honshu, Shikoku and Kyushu), with Central Honshu (a mountainous region) having the largest improvement (from ±7.1 to ±6.9 cm), when rigorous orthometric heights are used. The standard deviation improves from ±7.5 to 7.3 cm in the whole area of study. This shows that the rigorous orthometric heights are more consistent with the determined gravimetric geoid model than Helmert orthometric heights over Japan. We would like to note that, this observation is only indicative given the scope of this study.
A histogram of the differences between gravimetric and GPS/levelling geoid undulations at 816 points over Japan using rigorous orthometric heights is given in Figure 6. The differences in 658 points (80.6%) vary from −10 cm to 10 cm. The standard deviation reduces to ±7.0 cm by removing only four points suspected to be outliers (i.e. <−16 and >28 cm) as reflected in the histogram (Figure 6).
Conclusions
An attempt has been made to determine rigorous orthometric height system in Japan. Corrections to the existing Helmert orthometric heights at 816 GPS/levelling points have been computed. These corrections vary from −30.9 cm to 0.0 cm with a mean value of −0.4 cm and a standard deviation of ±1.7 cm. The gravitational attraction due to the laterally varying topographical density is ignored in this work because of lack of actual topographical density model in the area of study. Considering the heights of the GPS/levelling points, the magnitude of the gravitational attraction due to the laterally varying topographical density is small, hence may not affect the determined corrections significantly in this case. However, this effect requires a careful investigation.
An improved high-resolution gravimetric geoid model covering four main islands of Japan from our previous study is used to compare the consistency of the two height systems to a regionally defined gravimetric geoid model. The standard deviation of the differences between gravimetric and GPS/levelling geoid undulations is ±7.5 cm, when Helmert orthometric heights are used. The standard deviation of the differences reduces to ±7.3 cm, when rigorous orthometric heights are used. This indicates that rigorous orthometric heights are more consistent with the gravimetric geoid model than Helmert orthometric heights. Therefore rigorous orthometric height system should be used in validating gravimetric geoid models in general and specifically in mountainous areas, in view of the increasing accuracy in geoid modelling.
Although lateral topographic density model has been ignored in this study, partly because of the effective height range (0.3 to 903.4 m), its contribution is significant for more accurate determination of orthometric heights over Japan, if the full height range (−4 to 3,776 m) is considered. Observed gravity data at the benchmark points would improve the accuracy of rigorous orthometric height determination. Finally we recommend a determination and inclusion of lateral topographical density model in similar future studies covering the full height range over Japan to validate our initial proposal for the adoption of a rigorous orthometric height system in Japan.
References
Allister NA, Featherstone WE (2001) Estimation of Helmert orthometric heights using digital barcode levelling, observed gravity and topographic mass-density data over part of Darling Scarp, Western Australia. Geomatics Res Australasia 75:25–52.
Dennis ML, Featherstone WE (2003) Evaluation of orthometric and related height systems using a simulated mountain gravity field. In: Tziavos IN (ed) 3rd meeting of the International Gravity and Geoid 2002, Dept of Surv and Geodesy. Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, pp 389–394.
Heck B (2003) Rechenverfahren und Auswertemodelle der Landesvermessung (third edition). Wichman, Karlsruhe, Germany.
Heiskanen WA, Moritz H (1967) Physical Geodesy. Freeman, San Francisco.
Helmert FR (1890) Die Schwerkraft im Hochgebirge, Insbesondere in den Tyroler Alpen, Veröff. Königl. Preuss Geod Inst No. 1, Berlin.
Hwang C, Hsiao YS (2003) Orthometric height corrections from leveling, gravity, density and elevation data: a case study in Taiwan. J Geod 77:279–291. doi:10.1007/s00190-003-0325-6
Imakiire T, Hakoiwa E (2004) JGD2000 (vertical) - The New Height System of Japan. Bulletin of the Geogr Surv I 51:31–51.
Kao SP, Rongshin H, Ning FS (2000) Results of field test for computing orthometric correction based on measured gravity. Geomatics Res Australasia 72:43–60.
Kingdon R, Vaníček P, Santos M, Ellmann A, Tenzer R (2005) Toward improved orthometric height system for Canada. Geomatica 59:241–249.
Krakiwsky EJ (1965) Heights. Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying, Ohio State University, Columbus, MSc thesis
Mader K, (1954) Die orthometrische Schwerekorrektion des Präzisions-Nivellements in den Hohen Tauern. Österreichische Zeitschrift für Vermessungswesen, Sonderheft 15, Vienna.
Martinec Z (1998) Boundary value problems for gravimetric determination of a precise geoid model. Lecture notes in Earth Sciences 73. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Matsumura S, Murakami M, Imakiire T (2004) Concept of the New Japanese Geodetic System. Bulletin of the Geogr Surv I 51:1–9.
Molodensky MS, Yeremeev VF, Yurkina MI (1960) Methods for study of the external gravitational field and figure of the Earth. Trudy Ts NIIGAiK 131 Geodezizdat, Moscow, Russia (English translation by Israel Program for Scientific Translation, Jerusalem 1962).
Niethammer T (1932) Nivellement und Schwere als Mittel zur Berechnung wahrer Meereshöhen. Schweizerische Geodätische Kommission, Berne.
Odera PA, Fukuda Y (2014) Improvement of the geoid model over Japan using integral formulae and combination of GGMs. Earth Planets Space 66:22. doi:10.1186/1880-5981-66-22
Odera PA, Fukuda Y, Kuroishi Y (2012) A high-resolution gravimetric geoid model for Japan from EGM2008 and local gravity data. Earth Planets Space 64(5):361–368. doi:10.5047/eps.2011.11.004
Rapp RH (1961) The orthometric height. Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying, Ohio State University, Columbus, MSc thesis.
Santos MC, Vaníček P, Featherstone WE, Kingdon R, Ellmann A, Martin BA et al (2006) The relation between rigorous and Helmert’s definition of orthometric heights. J Geod 80(12):691–704. doi:10.1007/s00190-006-0086-0
Shichi R, Yamamoto A (2001a) List of Gravity Data Measured by Nagoya University. Special Report 9 Part I, Bulletin of the Nagoya University Museum.
Shichi R, Yamamoto A (2001b) List of Gravity Data Measured by Organizations other than Nagoya University. Special Report 9 Part II, Bulletin of the Nagoya University Museum.
Tenzer R, Vaníček P (2003) Correction to Helmert’s orthometric height due to actual lateral variation of topographical density. Brazilian Journal of Cartography - Revista Brasileira de Cartografia 55(02):44–47.
Tenzer R, Vaníček P, Santos M, Featherstone WE, Kuhn M (2005) The rigorous determination of orthometric heights. J Geod 79(1):82–92. doi:10.1007/s00190-005-0445-2
Torge W (1991) Geodesy (second edition). Walter de Gruyter-Berlin, New York
Vaníček P, Huang J, Novák P, Pagiatakis S, Véronneau M, Martinec Z et al (1999) Determination of the boundary values for the Stokes-Helmert problem. J Geod 73(4):180–192. doi:10.1007/s001900050235
Vaníček P, Tenzer R, Sjöberg LE, Martinec Z, Featherstone WE, 2 (2004) New views of the spherical Bouguer gravity anomaly. Geophys J Int 159(2):460–472. 10.111/j.1365-246X.2004.02435.x
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan for providing GPS/levelling and other additional data sets covering the study area. Nagoya University and other organizations in Japan provided a detailed gravity database, covering south western parts of Japan. We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions that have helped improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
PAO and YF designed the research, and YF facilitated the data acquisition and interpretation. PAO carried out the computations and related analyses. He also wrote and revised the paper. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0), which permits use, duplication, adaptation, distribution, and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Odera, P.A., Fukuda, Y. Comparison of Helmert and rigorous orthometric heights over Japan. Earth Planet Sp 67, 27 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0194-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0194-2