Abstract
An improved high-resolution gravimetric geoid model covering the four main islands of Japan (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu) was developed on a 1 × 1.5 arc-minute grid from EGM2008, GOCO02S/EGM2008, and terrestrial gravity data. A modified form of the Stokes-Helmert scheme was applied for the determination of the geoid using an empirically determined optimal spherical cap size. Handling of the topographical effects on gravity was accomplished using the integral formulae of Martinec and Vaníček, which were found to be more suitable for geoid modeling over Japan than the classical formulae. EGM2008 was used in Hokkaido, Honshu, and Kyushu Islands, whereas a combination of GOCO02S and EGM2008 was used in Shikoku Island and its immediate surroundings. The global geopotential models (GGMs) used in this study were chosen based on our earlier evaluation of the performance of EGM2008- and GOCE-related GGMs in Japan. In comparison with the previous geoid model for Japan, our new model shows an improvement in the standard deviation from ±8.3 to ±7.5 cm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Geoid determination over Japan has been the focus of numerous studies over the past few decades (e.g., Ganeko 1976; Kuroishi 1995, 2001a, b,2009; Fukuda et al. 1997; Kuroda et al. 1997; Kuroishi et al. 2002; Kuroishi and Denker 2001; Kuroishi and Keller 2005; Odera et al. 2012; Odera and Fukuda 2013), although precise geoid modeling remains a challenge. In this study, an improved high-resolution gravimetric geoid model is developed from EGM2008 (Pavlis et al. 2012), GOCO02S (Goiginger et al. 2011) combined with EGM2008 (GOCO02S/EGM2008), and local terrestrial gravity data. EGM2008 is complete to spherical harmonic degree and order 2,159 and contains additional coefficients extending to degree 2,190 and order 2,159.
The choice of global geopotential models (GGMs) used in this work is based on our earlier evaluation of GGMs that have recently been developed over Japan (Odera and Fukuda 2013). In that study, the performance of EGM2008 and the Gravity field and steady-state Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE)-related GGMs that were recently released by the European Space Agency were assessed, the latter being based on 2, 8, and 12 months of data collected by GOCE. This assessment was based on geoid undulations, obtained from 816 GPS/leveling points, and free-air gravity anomalies, obtained from 6,951 first-order gravity points. The distribution of these data over the four main islands of Japan is shown in Figure 1.
The evaluated GOCE and related GGMs included GOCE-DIR1, 2, 3 (Pail et al. 2011; Bruinsma et al. 2010), GOCE-TIM1, 2, 3 (Pail et al. 2011; Pail et al. 2010b), GOCE-SPW1, 2 (Migliaccio et al. 2011), and GOCO01S, 02S (Goiginger et al. 2011; Pail et al. 2010a). The performance of EGM2008 and GOCE-related GGMs over Japan was shown by Odera and Fukuda (2013) to be almost identical at a harmonic expansion to degree 150, although EGM2008 performs better at the 180-, 210-, and 240-degree spectral bands. Furthermore, comparisons over the four main islands reveal that EGM2008 performs better than the GOCE and related GGMs in Hokkaido, Honshu, and Kyushu at 180, 210, and 240 degrees. However, the GOCE and related GGMs perform better than EGM2008 in Shikoku.
Odera and Fukuda (2013) developed a gravimetric geoid model for Shikoku and the surrounding area from GOCE-TIM3/EGM2008 and terrestrial gravity data, with the aim of determining the magnitude of improvement in the model by using GOCE-only data. However, GOCO02S/EGM2008 performs slightly better than GOCE-TIM3/EGM2008 in this region. Therefore, in this work, a combination of GOCO02S (up to 180 degrees) and EGM2008 (from 181 to 2,190 degrees) is used to improve the geoid model over the Shikoku area, and EGM2008 is used in Hokkaido, Honshu, and Kyushu. Ship-track gravity data and satellite altimetry-derived marine gravity anomalies in the coastal areas were not considered because of the use of a high-resolution gravitational model (EGM2008). Furthermore, the interest of this study is limited to the land areas.
The classical Moritz formula (Moritz 1980) and a planar formula (Wichiencharoen 1982b) were used to compute the direct topographical effect (DTE) and the primary indirect topographical effect (PITE), respectively, in the previous geoid model for Japan. These two formulae (classical Moritz and planar) are hereafter referred to as the classical formulae and are given respectively as
and
where C is the DTE, N ind is the PITE, G is the Newtonian gravitational constant, ρ0 is the constant topographic density, H P is the orthometric height of the computation point, H is the height of the running point, σ is the surface integration element, and l o is the horizontal distance between the computation point and the running point.
The current geoid model for Japan has been developed using the integral formulae of Martinec and Vaníček (1994a, b) for the computation of DTE and PITE. Details concerning the procedure and data sets used to develop the previous geoid model can be found in Odera et al. (2012), these being generally the same as for the current computations, with the exception of topographical reductions.
This study further assesses the appropriate topographical gravity reduction procedure for precise geoid modeling in Japan. Gridding of the residual gravity anomalies is accomplished by kriging (Krige 1951) on a 1 × 1.5 arc-minute grid, Stokes's integral formula (Stokes 1849; Heiskanen and Moritz 1967) is used for geoid determination, and the modified Stokes's kernel proposed by Meissl (1971) is applied to minimize truncation errors.
Methods
Gravity data reductions and gridding
Most of the gravity data used in this study was obtained from a database developed by Nagoya University and other organizations that covers the southwestern parts of Japan (e.g., Shichi and Yamamoto 2001a, b). Another set of gravity data, mostly along the main leveling network covering the four main islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku), was provided by the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan (GSI). In total, there are 98,670 observed gravity data points in the study area that were obtained during the observation period approximately 1910 to 2001 (Figure 2). It should be noted that the northern parts of Japan (above latitude 37°N) are sparsely populated with gravity data points, whereas the southern parts are densely populated; however, most of these data was clustered together and even the well-covered areas contain wide data gaps.
Digital elevation models (DEMs) covering the four main islands were prepared in 1999 by the GSI. The Hokkaido area is covered by a 250-m DEM, whereas the other three main islands (Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu) are covered by a 50-m DEM. Both the DEMs and gravity data coordinates are based on the Tokyo Datum, and so an initial datum transformation to the Japanese Geodetic Datum 2000 (JGD2000) was carried out for DEMs and the gravity data. Figure 3 shows the approximate topography of the study area.
The method chosen for downward continuation of observed gravity on the topographical surface to the geoid plays a central role in precise geoid determination. Stokes's formula for the gravimetric geoid determination requires that no masses occur outside of the geoid and that the gravity anomaly should be referred to the geoid. This reduction was performed following the approach applied by Odera et al. (2012) to the previous geoid model for Japan. Although the classical Moritz formula (Moritz 1980) was used to estimate DTE in the previous geoid model for Japan, here, we evaluated DTE using the integral formula of Martinec and Vaníček (1994b). While both formulae use average topographic density, it should be noted that the classical Moritz formula is also based on the assumption that the distance between the computation and the running point is much greater than the height of the computation point (l o ≫ H P ), which implies that it can only be used effectively for the far-zone integration area (Martinec et al. 1996). As a result, the effect of the near zone and the Bouguer shell, which cannot be derived in the planar model, is completely missing (e.g., Martinec and Vaníček 1994a; Nahavandchi 2000).
In an attempt to account for the contribution of the near zone, Martinec and Vaníček (1994b) divided the integration area (σ) into a near zone (σ1) and a far zone (σ2) based on a spherical approximation of the geoid. The resulting expression for DTE is given as (Martinec and Vaníček 1994b)
where R is the mean radius of the Earth, H P is the height of the computation point, H is the height of the running point, σ is the surface integration element, ρ0 is the average topographic density, and G is the Newtonian gravitational constant. The spatial distances l and l o between the computation and the running points are given respectively as
and
where r is approximated as R + H P .
The near zone is defined by the spherical distance (ψ0) given by Martinec and Vaníček (1994b) as
The corresponding PITE on the geoid (e.g., Martinec and Vaníček 1994a) is given as
The other applied reductions include a secondary indirect topographical effect (Vaníček et al. 1999), a second-order free-air reduction (Heiskanen and Moritz 1967), and an atmospheric correction (Wichiencharoen 1982a). The residual gravity anomalies are obtained from the reduced gravity anomalies on the geoid and gravity anomalies obtained from EGM2008 (degree 2,190 and order 2,159) in the three islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, and Kyushu), and GOCO02S/EGM2008 (degree 2,190 and order 2,159) in Shikoku. Kriging (Krige 1951) on a 1 × 1.5 arc-minute grid was performed for gridding of the residual gravity anomalies.
Geoid modeling over Japan
Although Stokes's integral formula for geoid determination (Stokes 1849; Heiskanen and Moritz 1967) was applied in this study, it requires that continuous gravity data be available and be used over the entire Earth. As this condition is not currently satisfied, a remove-compute-restore procedure was adopted here whereby a GGM provides the long-wavelength geoid undulations, a modified Stokes's formula provides the medium-wavelength components, and the indirect effect provides the short-wavelength components. In addition, the modified Stokes's kernel proposed by Meissl (1971) was used to minimize truncation errors. Hence, the expanded modified Stokes's formula, excluding small errors due to ellipsoidal effects, is given as
where N is the gravimetric geoid undulation, N GGM is the geoid undulation obtained from EGM2008 or GOCO02S/EGM2008 after applying the zero-degree term (with respect to GRS80), Δgr is the residual gravity anomaly, N ind is the indirect topographical effect, and SME(ψ) is Meissl's modified kernel.
The optimal spherical distance was evaluated empirically by comparing gravimetric and GPS/leveling geoid undulations at various spherical distances. These comparisons were performed at all 816 GPS/leveling points, and a standard deviation (S.D.) was computed for each spherical distance. As a result, a spherical cap size of 40 km was adopted for computations in this study because it gives the smallest S.D. when compared to the other spherical distances tested.
Results and discussion
Statistics relating to the topographical effects (computed by the integral formulae) and the corresponding values (computed by the classical formulae) are presented in Table 1. Computations were performed at the gravity data points.
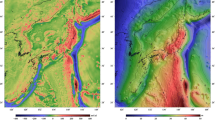
Figures 4 and 5 show the spatial distribution of DTE over Japan as computed by the classical Moritz formula and the integral formula of Martinec and Vaníček, respectively. Figures 6 and 7 show the spatial distribution of PITE over Japan as computed by a planar formula and the integral formula of Martinec and Vaníček, respectively. It should be noted that the spatial representation of the topographic effects over Japan was achieved by interpolation of the values from the gravity data points onto a 1 × 1.5 arc-minute grid for plotting, thus explaining why the minimum and maximum limits in Table 1 may vary slightly from those shown in Figures 4, 5, 6, 7.
The differences between gravimetric and GPS/leveling geoid undulations over Japan are shown in Figure 8, and the statistics of these comparisons are given in Table 2. The statistics of the differences between the previous gravimetric and GPS/leveling geoid undulations are also given in Table 2 in parentheses for comparison.
Table 2 shows that the West Honshu area has the smallest S.D. (±4.9 cm) between the gravimetric and GPS/leveling geoid undulations, while Central Honshu (a mountainous area) has the largest (±7.1 cm). When comparing these 816 GPS/leveling data points with the previous geoid model for Japan (Odera et al. 2012), there is a marked improvement in the overall S.D. from ±8.3 to ±7.5 cm.
It is evident that much of the improvement of the geoid is due to this study's treatment of the topography, given that the same data sets have been used for both models. For example, if EGM2008 is used over the four main islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu) and integral formulae are applied for the computation of topographic effects, the S.D. between gravimetric and GPS/leveling geoid undulations over the whole of Japan is ±7.6 cm, whereas it is ±8.7 cm over Shikoku only. Hence, the integral formulae of Martinec and Vaníček (1994a, b) seem to be more suitable for computing the DTE and PITE over Japan than the classical formulae. We also note the interesting effect of a deterioration of the S.D. over North Honshu as opportunity for further investigation. We suggest therefore that a significant improvement in the geoid model over Shikoku, from ±8.7 cm previously to ±6.6 cm currently, is mainly due to the contribution of GOCE data.
Conclusions
We described a procedure for the computation of an improved high-resolution gravimetric geoid model over Japan that exploits the currently available data sets. The integral formulae of Martinec and Vaníček (1994a, b) were used to compute the DTE and PITE over Japan for the first time and were found to perform better than the classical formulae over the studied area. A combination of GOCO02S and EGM2008 (GOCO02S/EGM2008) was used for geoid determination in the Shikoku area, while EGM2008 was used for geoid determination in the remaining islands (Hokkaido, Honshu, and Kyushu).
When comparing these 816 GPS/leveling data points with the previous gravimetric geoid model for Japan, a marked improvement in the overall S.D. from ±8.3 to ±7.5 cm was observed. It was noted that much of the improvement in the accuracy of the geoid over the study area was due to the use of the integral formulae for handling the topographical effects on gravity.
With the recent improvements in geoid determination techniques, the handling of the DTE and PITE needs further attention. However, the need for denser coverage and more accurate gravity data over Japan cannot be overemphasized. Despite this, the gravimetric geoid model obtained in this study performs significantly better than the previous versions and makes an important contribution towards the establishment of a geoid-consistent vertical datum over Japan.
References
Bruinsma SL, Marty JC, Balmino G, Biancale R, Förste C, Abrikosov O, Neumayer H: GOCE gravity field recovery by means of the direct numerical method. Paper presented at the ESA living planet symposium, Bergen; 2010.
Fukuda Y, Kuroda J, Takabatake Y, Itoh J, Murakami M: Improvement of JGEOID93 by the geoidal heights derived from GPS/levelling survey. In Gravity, geoid and marine geodesy, IAG symposia 117. Edited by: Segawa J, Fujimoto H, Okubo S. Tokyo; 1997:589–596. 30 Sept–5 Oct 1996 30 Sept–5 Oct 1996
Ganeko Y: Astrogeodetic geoid of Japan. Special report 372. Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. 1976.
Goiginger H, Höck E, Rieser D, Mayer-Gürr T, Maier A, Krauss S, Pail R, Fecher T, Gruber T, Brockmann JM, Krasbutter I, Schuh WD, Jäggi A, Prange L, Hausleitner W, Baur O, Kusche J: The combined satellite-only global gravity field model GOCO02S. Presented at the 2011 General Assembly of the European Geosciences Union, Vienna; 2011.
Heiskanen W, Moritz H: Physical geodesy. Freeman WH, San Francisco; 1967.
Krige DG: A statistical approach to some basic mine valuation problems on the Witwatersrand. J Chem Metall Min Soc S Afr 1951, 52(6):119–139.
Kuroda J, Takabatake J, Matsushima M, Fukuda Y: Integration of gravimetric geoid and GPS/levelling survey by least squares collocation (in Japanese). J Geogr Surv Inst 1997, 87: 1–3.
Kuroishi Y: Precise gravimetric determination of geoid in the vicinity of Japan. Bull Geogr Surv Inst 1995, 41: 1–93.
Kuroishi Y: An improved gravimetric geoid for Japan, JGEOID98, and relationships to marine gravity data. J Geod 2001, 74(11–12):745–755.
Kuroishi Y: A new geoid model for Japan, JGEOID2000. In Gravity, geoid and geodynamics 2000, IAG symposia 123, Banff, 31 July–4 Aug 2000 Edited by: Sideris MG. 2001b, 329–333.
Kuroishi Y: Improved geoid determination for Japan from GRACE and a regional gravity field model. Earth Planets Space 2009, 61: 807–813.
Kuroishi Y, Denker H: Development of improved gravity field models around Japan. In Gravity, geoid and geodynamics 2000, IAG symposia 123, Banff, 31 July–4 Aug 2000 Edited by: Sideris MG. 2001, 317–322.
Kuroishi Y, Keller W: Wavelet approach to improvement of gravity field–geoid modelling for Japan. J Geophys Res 2005, 110: B03402.
Kuroishi Y, Ando H, Fukuda Y: A new hybrid geoid model for Japan, GSIGEO 2000. J Geod 2002, 76: 428–436. 10.1007/s00190-002-0266-5
Martinec Z, Vaníček P: The indirect effect of topography in the Stokes-Helmert technique for a spherical approximation of the geoid. Manuscr Geodaet 1994a, 19: 213–219.
Martinec Z, Vaníček P: Direct topographical effect of Helmert's condensation for a spherical approximation of the geoid. Manuscr Geodaet 1994b, 19: 257–268.
Martinec Z, Vaníček P, Mainville A, Véronneau M: Evaluation of topographical effects in precise geoid computation from densely sampled heights. J Geod 1996, 70: 746–754. 10.1007/BF00867153
Meissl P: Preparations for the numerical evaluation of second-order Molodensky-type formulas. Report 163, Department of Geodetic Science & Surveying, Ohio State University, Columbus; 1971.
Migliaccio F, Reguzzoni M, Gatti A, Sansò F, Herceg M: A GOCE-only global field model by the space-wise approach. Proceedings of the 4th international GOCE user workshop, Munich, 31 Mar–1 Apr 2011 2011.
Moritz H: Advanced physical geodesy. Wichmann Verlag, Karlsruhe; 1980.
Nahavandchi H: The direct topographical correction in gravimetric geoid determination by the Stokes-Helmert method. J Geod 2000, 74(6):488–496. 10.1007/s001900000110
Odera PA, Fukuda Y: Towards an improvement of the geoid model in Japan by GOCE data: a case study of the Shikoku area. Earth Planets Space 2013, 65(4):361–366. 10.5047/eps.2012.07.005
Odera PA, Fukuda Y, Kuroishi Y: A high-resolution gravimetric geoid model for Japan from EGM2008 and local gravity data. Earth Planets Space 2012, 64(5):361–368. 10.5047/eps.2011.11.004
Pail R, Goiginger H, Mayrhofer R, Schuh WD, Brockmann JM, Krasbutter I, Höck E, Fecher T Presented at the ESA living planet symposium, Bergen, 27 June–2 July 2010. Global gravity field model derived from orbit and gradiometry data applying the time-wise method 2010a.
Pail R, Goiginger H, Schuh WD, Höck E, Brockmann JM, Fecher T, Gruber T, Mayer-Gürr T, Kusche J, Jäggi A, Rieser D: Combined satellite gravity field model GOCO01S derived from GOCE and GRACE. Geophys Res Lett 2010b, 37: L20314.
Pail R, Bruinsma S, Migliaccio F, Förste C, Goiginger H, Schuh WD, Höck E, Reguzzoni M, Brockmann JM, Abrikosov O, Veicherts M, Fecher T, Mayrhofer R, Krasbutter I, Sansò F, Tscherning CC: First GOCE gravity field models derived by three different approaches. J Geod 2011, 85(11):819–843. 10.1007/s00190-011-0467-x
Pavlis NK, Holmes SA, Kenyon SC, Factor JK: The development and evaluation of the Earth gravitational model 2008 (EGM2008). J Geophys Res 2012, 117: B04406.
Shichi R, Yamamoto A Special report 9. In List of gravity data measured by Nagoya University. Part I, Bulletin of the Nagoya University Museum; 2001a.
Shichi R, Yamamoto A Special report 9. In List of gravity data measured by organizations other than Nagoya University. Part II, Bulletin of the Nagoya University Museum; 2001b.
Stokes GG: On the variation of gravity on the surface of the Earth. Trans Camb Philos Soc 1849, 8: 672–695.
Vaníček P, Huang J, Novák P, Pagiatakis S, Véronneau M, Martinec Z, Featherstone WE: Determination of the boundary values for the Stokes-Helmert problem. J Geod 1999, 73(4):180–192. 10.1007/s001900050235
Wichiencharoen C Internal report. In FORTRAN programs for computing geoid undulations from potential coefficients and gravity anomalies. Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying, Ohio State University, Columbus; 1982a.
Wichiencharoen C Report 336. In The indirect effects on the computation of geoid undulations. Department of Geodetic Science and Surveying, Ohio State University, Columbus; 1982b.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan for providing GPS/leveling and other additional data sets covering the study area. We appreciate the efforts of Nagoya University and other organizations for developing and providing a detailed gravity database covering the southwestern parts of Japan. We are grateful to Prof. Zdeněk Martinec and an anonymous reviewer for their constructive comments and suggestions that have helped to improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
PAO and YF designed the research, and YF facilitated the data acquisition and interpretation. PAO carried out the computations and related analyses. He also wrote and revised the paper. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Odera, P.A., Fukuda, Y. Improvement of the geoid model over Japan using integral formulae and combination of GGMs. Earth Planet Sp 66, 22 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1880-5981-66-22
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1880-5981-66-22