Abstract
Background
Amyloid PET plays a vital role in detecting the accumulation of in vivo amyloid-β (Aβ). The quantification of Aβ accumulation has been widely performed using the region of interest (ROI)-based mean cortical standardized uptake value ratio (mcSUVR). However, voxel-based statistical analysis has not been well studied. The purpose of this study was to examine the feasibility of analyzing amyloid PET scans by voxel-based statistical analysis. The results were then compared to those with the ROI-based mcSUVR. In total, 166 subjects who underwent 11C-PiB PET in the J-ADNI multi-center study were analyzed. Additionally, 18 Aβ-negative images were collected from other studies to form a normal database. The PET images were spatially normalized to the standard space using an adaptive template method without MRI. The mcSUVR was measured using a pre-defined ROI. Voxel-wise Z-scores within the ROI were calculated using the normal database, after which Z-score maps were generated. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to evaluate whether Z-sum (sum of the Z-score) and mcSUVR could be used to classify the scans into positive and negative using the central visual read as the reference standard. PET scans that were equivocal were regarded as positive.
Results
Sensitivity and specificity were respectively 90.8% and 100% by Z-sum and 91.8% and 98.5% by mcSUVR. Most of the equivocal scans were subsequently classified by both Z-sum and mcSUVR as false negatives. Z-score maps correctly delineated abnormal Aβ accumulation over the same regions as the visual read.
Conclusions
We examined the usefulness of voxel-based statistical analysis for amyloid PET. This method provides objective Z-score maps and Z-sum values, which were observed to be helpful as an adjunct to visual interpretation especially for cases with mild or limited Aβ accumulation. This approach could improve the Aβ detection sensitivity, reduce inter-reader variability, and allow for detailed monitoring of Aβ deposition.
Trial registration
The number of the J-ADNI study is UMIN000001374
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Find the latest articles, discoveries, and news in related topics.Background
Although accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) plaque in the cerebral cortex is not specific to Alzheimer’s disease (AD), it is believed to begin more than 10 years before the onset of cognitive impairment [1]. Amyloid PET imaging plays a vital role in the detection of in vivo Aβ accumulation as an imaging biomarker of AD [2, 3]. For amyloid PET, visual interpretation is the standard clinical practice to classify Aβ-positive or Aβ-negative in accordance with a neuropathological diagnosis [4,5,6]. Meanwhile, quantitative analysis of amyloid PET has been widely performed in conjunction with visual interpretation. Quantitative approaches may provide additional diagnostic information, increase diagnostic confidence of any visual interpretation [7], reduce inter-reader variability [8], and provide a longitudinal assessment of Aβ deposition in anti-Aβ therapeutic clinical trials [9] even though such approaches are still limited to research purposes [4, 5].
There are several methods to quantify Aβ accumulation using amyloid PET [10,11,12]. A commonly used approach is the region of interest (ROI)-based analysis with standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) between the target regions and a reference region. The cerebellar cortex, whole cerebellum, pons, and cerebral white matter have been used as reference regions as they are considered free of any abnormal fibrillar Aβ deposition [13, 14]. The ROI-based approach has been the de facto standard of quantitative analysis for amyloid PET because of its simplicity.
On the other hand, a voxel-based approach can also be used to analyze amyloid PET. Kemppainen et al. and Ziolko et al. both used statistical parametric mapping (SPM) software to visualize the difference in Aβ accumulation between AD patients and healthy control subjects [15, 16]. However, both these studies involved a limited number of subjects (total number of subjects < 30) and did not show individual maps, looking only at differences between the groups. To our knowledge, there has been no large-scale study conducted that examines the feasibility of voxel-based statistical analysis in assessing amyloid PET.
When looking to apply the voxel-based statistical analysis to amyloid PET, there were two main issues we needed to overcome. The first issue was that we needed to acquire a large dataset that contained both amyloid PET and high-resolution MRI to create a reliable normal database. This issue was resolved by obtaining a large dataset from large-scale multi-center studies on dementia, such as ADNI and J-ADNI [17,18,19]. These studies provide us with an open database of amyloid PET and high-resolution MRI for a large number of AD patients, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) subjects, and normal control subjects.
The second issue was the spatial normalization of amyloid PET. This was challenging if the subject data lacked MRI, and only PET was available as uptake patterns between Aβ-positive and Aβ-negative images are strikingly different. Although high-resolution MRI has been utilized for spatial normalization of amyloid PET [20], PET-only spatial normalization would be better in view of widespread applications in clinical practice. The spatial normalization issue of amyloid PET was solved using an adaptive template approach [21,22,23,24]. The adaptive template method provides us with robust and accurate spatial normalization of amyloid PET without MRI.
These effective breakthroughs have made it possible to create a reliable normal database and then to verify the feasibility of voxel-based analysis of amyloid PET. In this study, we investigated the feasibility of voxel-based statistical analysis of amyloid PET. We then compared the results with ROI-based quantitative analysis.
Methods
Subjects
We examined a total of 166 subjects [46 mild AD patients; 62 mild cognitive impairment (MCI) subjects; 58 normal control (NC) subjects] who underwent 11C-PiB PET scans. These data were obtained from the Japanese Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (J-ADNI) database, which are available from the National Bioscience Database Center Human Database, Japan (Research ID: hum0043.v1, 2016). The J-ADNI was launched in 2007 as a public-private partnership, led by principal investigator Takeshi Iwatsubo, MD. The primary goal of J-ADNI was to test whether serial MRI, PET, other biological markers, and clinical and neuropsychological assessments can be combined to measure the progression of late MCI and mild AD in the Japanese population. The clinical inclusion criteria of neuropsychological tests are described in the article by Iwatsubo et al. [19]. This study was approved by the ethics committee of participating centers, and all subjects had signed an informed consent form for the retrospective data analysis of this kind. The present analysis was also approved by the ethics committee of IBRI, which downloaded the J-ADNI data.
PET scanners
Table 1 shows PET scanners and the reconstruction parameters used in the J-ADNI study. All PET sites, including their scanners, imaging protocols, and 11C-PiB production, were certified by the J-ADNI PET QC core before scanning the first subject. Inter-scanner variability was minimized with the Hoffman three-dimensional (3D) phantom data by optimizing the reconstruction parameters so that the image quality and resolution was assured for each scanner [25].
Visual interpretation
All 11C-PiB PET images were centrally and independently classified into positive, equivocal, and negative by three physicians specializing in nuclear neuroimaging more than 15 years. The visual interpretation criteria are described in the article by Yamane et al. [26]. For those cases where the three physicians’ interpretation did not match, they discussed these in a consensus reading session. A unified read at these sessions was determined as the official interpretation. These visual read results included additional comments by the physicians made during the consensus reading session.
Generation of the normal database (NDB)
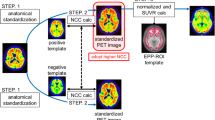
Eighteen Aβ-negative PET images from 2 AD patients, 6 MCI subjects, and 10 NC subjects were used to create the normal database (NDB) of 11C-PiB PET (Fig. 1). Table 2 shows mean cortical SUVR (mcSUVR) and maximum SUVR for each 11C-PiB PET image, which were calculated by the method described below. The mcSUVRs in all subjects were smaller than 1.45. These 11C-PiB PET images were acquired in other studies using the Discovery 690 PET/CT scanner in IBRI [27]. Imaging protocols such as the injection activity (555 MBq), uptake time (50 min), and scan duration (20 min) were the same as those used in the J-ADNI study [28]. The PET images were reconstructed using the 3D ordered subset expectation maximization (OSEM) algorithm (VUE point HD) with 4 iterations and 16 subsets. A Gaussian smoothing filter with 4 mm (n = 6) or 5 mm (n = 12) full width at half maximum (FWHM) was applied to the PET images. These parameters were determined by the phantom experiment mentioned earlier [29]. We used the PMOD ver. 3.7 and PNEURO tool for image analysis. In order to spatially normalize the PET images, we used the 3D T1-weighted MRI. The PET images were co-registered to the MRI with the normalized mutual information method implemented in the PMOD. The MRI was then spatially normalized to the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) T1 template [30, 31]. The co-registered PET images were also spatially normalized to the standard MNI space (matrix dimensions 91 × 109 × 91, voxel size 2 × 2 × 2 mm3) using the transformation data of the MRI spatial normalization. After that, the voxel values of the normalized PET images were divided by the mean value of the cerebellar cortex area, which was defined as the reference region in the empirical PiB-prone (EPP) ROI template (Fig. 2) [23]. The EPP-ROI template provided the target region, which characterized voxel-wise amyloid specific regions based on the actual human 11C-PiB PET images. Then, average and standard deviation (SD) images were created from the NDB. We picked up some voxels as well the entire EPP-ROI and examined the normality using the Shapiro-Wilk test. As a result, we assumed that the distributions of values per voxel followed the Gaussian distribution. Figure 3 shows the average and SD images after the white matter regions were masked based on the EPP-ROI template.
Voxel-based statistical analysis workflow
Figure 4 shows the workflow of voxel-based statistical analysis for amyloid PET. Firstly, the PET images were spatially normalized to the MNI space using the PET-only adaptive template normalization method [23]. Then, voxel values were divided by the mean value of the cerebellar cortex area in the same way as the above NDB generation process. After that, the PET images were compared voxel-by-voxel against the NDB, and Z-score maps were generated within the EPP-ROI area (Figs. 2 and 3). The Z-score was calculated on each voxel using the following equation:
where xi is the voxel value of the PET image, and \( \overline{x} \) and SD are the corresponding voxel value of the average and SD images, respectively, which are derived from the NDB (Fig. 2). After 3D Gaussian smoothing with 8 mm FWHM, Z-score values more than 2.0 were superimposed on the gray-scale PET images as a Z-score map. In addition to the Z-score map, we calculated a sum of the Z-score that were more than 2.0 within the EPP-ROI area (Z-sum).
SUVR measurement
In addition to the voxel-based approach, an ROI-based quantitative analysis was also applied to the normalized PET images to compare the results. We calculated a mean cortical standardized uptake value ratio (mcSUVR) within the EPP-ROI template [23]. This ROI template includes the frontal cortex, lateral temporal cortex, parietal cortex, posterior cingulate, precuneus, occipital cortex, and striatum as the target regions and the cerebellar cortex as the reference region. The reference region used was the same as in the voxel-based analysis.
ROC analysis
A receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis was performed to evaluate the capability of Z-sum and mcSUVR to classify the scans into positive and negative using the visual read as the reference standard, in which equivocal scans were regarded as positive.
Results
The 11C-PiB PET images had been visually classified as positive for 88 cases, equivocal for 10 cases, and negative for 68 cases. The proposed voxel-based analysis was successfully used on all PET images. Figure 5 shows the PET images and Z-score maps of representative positive and negative cases. The Z-scores in most voxels were lower than 2.0 in the negative case, while they were higher than 2.0 in the positive case. Figure 6 shows scatter plots of Z-sum and mcSUVR against visual read and clinical diagnosis. The Z-sum values for most negative cases were almost zero. ROC analysis was done to assess the differentiation of positive from negative cases. This indicated that sensitivity and specificity were 90.8% and 100% by Z-sum with a threshold of 100,000, and 91.8% and 98.5% by mcSUVR with a threshold of 1.5. Both Z-sum and mcSUVR showed high sensitivity and specificity. Most of the false-negative cases were visually equivocal [8/9 (88.9%) for the Z-sum and 7/8 (87.5%) for the mcSUVR].
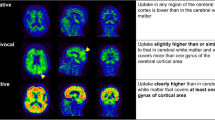
Three representative equivocal cases are shown in Fig. 7. The mcSUVR and Z-sum values of these equivocal cases were lower than their respective thresholds. As indicated by the red arrows in Fig. 7, the Z-score maps correctly delineated abnormal Aβ accumulation over the same regions as the visual interpretation even for the cases, in which the three physicians’ interpretation did not completely match.
PET images and Z-score maps in MNI space, and the three physicians’ visual read and consensus comments for three representative cases, in which official consensus interpretation was “equivocal.” There are the cases in which three physicians' visual read matched (a) or did not match (b and c). The Z-score maps correctly delineated abnormal Aβ accumulation over the same regions as the visual read (red arrows). F, L, Pa, Po, and S are frontal lobe, lateral temporal lobe, lateral parietal lobe, posterior cingulate gyrus and precuneus, and striatum, respectively. Class., Nega., Posi., and Equiv. are classification, negative, positive, and equivocal, respectively. The circle and triangle represent the positive and equivocal region, as judged by the physicians
Discussion
We established voxel-based statistical analysis for amyloid PET. Once the normal database is created, this analysis can be fully automatically applied to amyloid PET without MRI. This voxel-based approach gives us an objective Z-score map for each amyloid PET image. Some previous studies showed that SPM software provided a brain surface map showing the difference between patients with AD and healthy control groups [15, 32]. Our proposed method, however, can provide a voxel-by-voxel Z-score map for each subject. This is more useful for physicians to complement their visual interpretations when reading amyloid PET images for individual subjects.
Both the quantitative values of mcSUVR and Z-sum showed high sensitivity and specificity. Most of the false-negative subjects were equivocal scans by visual interpretation. We believe that the Z-score map can effectively provide detection of Aβ accumulation in these cases. As shown in Fig. 7, for three representative equivocal scans, the Z-score maps correctly delineated the same regions as the individual and consensus visual reads. This was the case even in those whose mcSUVR was low. Although Z-score maps may not provide further benefit for obvious positive or negative cases, they may improve the Aβ detection sensitivity for cases with mild or limited regional Aβ accumulation. The Z-score maps also correctly delineated abnormal uptakes for the cases that three physicians’ interpretation did not match. Therefore, they might be useful in reducing inter-reader variability. Further study is warranted regarding the relationship between visual detection of abnormal or equivocal uptake and the maximum Z-score value within such areas. While the ROI-based quantitative approach can evaluate regional uptake to some extent, the proposed voxel-based approach can visualize voxel-wise Aβ accumulation in more detail. The proposed method may also provide closer monitoring of cerebral Aβ accumulation in follow up studies and treatment effect evaluations.
The NDB used in this study was derived from 18 Aβ-negative subjects including 2 AD patients, 6 MCI subjects, and 10 NC subjects. We confirmed that mcSUVR for each subject was smaller than 1.45 (Table 2). However, some MCI subjects showed somewhat higher maximum SUVR values compared with those of the NC subjects. These discrete high uptakes could affect the sensitivity of the Z-score mapping. If there are large datasets of NC subjects, it would be better to construct the NDB with only NC subjects.
In this study, voxel-based statistical analysis was successfully applied to a large dataset acquired with various PET scanners (Table 1). These results suggest that the proposed method would not be sensitive to the variability between PET scanners. As mentioned in the methods, before scanning the first subject, image resolutions of all PET scanners were harmonized by the Hoffman phantom test. This process might have effectively worked to minimize the difference between scanners. The NDB may be shareable if an appropriate reconstruction parameter is used so that the PET image resolution was 8 mm FWHM or better [25].
There are some limitations to this study. Firstly, the smoothing process and the parameters in creating the Z-score map have not been optimized. While the Z-score map was processed with a Gaussian smoothing filter of 8 mm FWHM, there is room for improvement in this point. Secondly, we used the PET-based spatial normalization method and the EPP-ROI template that we had proposed [23]. However, this approach may not completely eliminate contamination from white matter. When subjects have undergone MRI scans, MR-based spatial normalization and individual neocortical ROI would be less susceptible to contamination from the white matter. The white matter contamination might also affect the quantified value of cerebellar cortex in a different way. Thirdly, the Z-sum value largely depends on the number of calculation voxels. Z-sum was calculated by summing the voxel values within the EPP-ROI that were in the standard MNI space [23]. If we use a different ROI template and/or a different standard space [30], the appropriate threshold would likely be different. Lastly, we applied the proposed analysis only for 11C-PiB PET with the cerebellar cortex as the reference region. Our approach may be applicable to other amyloid or tau tracers [33, 34] but should be performed with a tracer-specific template, reference region, and database.
Conclusions
We established voxel-based statistical analysis for amyloid PET and evaluated its feasibility using the J-ADNI datasets. The voxel-based analysis provides an objective Z-score map and a quantitative Z-sum value for each subject. These are helpful as an adjunct to visual interpretation, especially for cases with mild or limited regional Aβ accumulation. This approach could improve the Aβ detection sensitivity, reduce inter-reader variability, and allow for detailed monitoring of Aβ deposition.
Availability of data and materials
The clinical datasets analyzed in this article are available from the Japanese Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (J-ADNI) database deposited in the National Bioscience Database Center Human Database, Japan (Research ID: hum0043.v1, 2016).
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- EPP:
-
Empirical PiB-prone
- FWHM:
-
Full width at half maximum
- IBRI:
-
Institute of Biomedical Research and Innovation
- J-ADNI:
-
Japanese Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- mcSUVR:
-
Mean cortical standardized uptake value ratio
- MNI:
-
Montreal neurological institute
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NC:
-
Normal control
- NDB:
-
Normal database
- OSEM:
-
Ordered subset expectation maximization
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristics
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SPM:
-
Statistical parametric mapping
- SUVR:
-
Standardized uptake value ratio
References
Bateman RJ, Xiong C, Benzinger TL, Fagan AM, Goate A, Fox NC, et al. Clinical and biomarker changes in dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:795–804.
Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt DP, et al. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:306–19.
Frisoni GB, Bocchetta M, Chetelat G, Rabinovici GD, de Leon MJ, Kaye J, et al. Imaging markers for Alzheimer disease: which vs how. Neurology. 2013;81:487–500.
Minoshima S, Drzezga AE, Barthel H, Bohnen N, Djekidel M, Lewis DH, et al. SNMMI procedure standard/EANM practice guideline for amyloid PET imaging of the brain 1.0. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:1316–22.
Johnson KA, Minoshima S, Bohnen NI, Donohoe KJ, Foster NL, Herscovitch P, et al. Appropriate use criteria for amyloid PET: a report of the Amyloid Imaging Task Force, the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, and the Alzheimer’s Association. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:476–90.
Seibyl J, Catafau AM, Barthel H, Ishii K, Rowe CC, Leverenz JB, et al. Impact of training method on the robustness of the visual assessment of 18F-florbetaben PET scans: results from a phase-3 study. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:900–6.
Pontecorvo MJ, Arora AK, Devine M, Lu M, Galante N, Siderowf A, et al. Quantitation of PET signal as an adjunct to visual interpretation of florbetapir imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44:825–37.
Nayate AP, Dubroff JG, Schmitt JE, Nasrallah I, Kishore R, Mankoff D, et al. Use of standardized uptake value ratios decreases interreader variability of [18F] florbetapir PET brain scan interpretation. Am J Neuroradiol. 2015;36:1237–44.
Delrieu J, Ousset PJ, Caillaud C, Vellas B. “Clinical trials in Alzheimer’s disease”: immunotherapy approaches. J Neurochem. 2012;120:186–93.
Heurling K, Buckley C, Van Laere K, Vandenberghe R, Lubberink M. Parametric imaging and quantitative analysis of the PET amyloid ligand [(18)F]flutemetamol. Neuroimage. 2015;121:184–92.
Tuszynski T, Rullmann M, Luthardt J, Butzke D, Tiepolt S, Gertz H-J, et al. Evaluation of software tools for automated identification of neuroanatomical structures in quantitative β-amyloid PET imaging to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016;43:1077–87.
Lopresti BJ, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Hoge JA, Ziolko SK, Lu X, et al. Simplified quantification of Pittsburgh Compound B amyloid imaging PET studies: a comparative analysis. J Nucl Med. 2005;46:1959–72.
Chen K, Roontiva A, Thiyyagura P, Lee W, Liu X, Ayutyanont N, et al. Improved power for characterizing longitudinal amyloid-β PET changes and evaluating amyloid-modifying treatments with a cerebral white matter reference region. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:560–566.
Landau SM, Fero A, Baker SL, Koeppe R, Mintun M, Chen K, et al. Measurement of longitudinal β-amyloid change with 18F-florbetapir PET and standardized uptake value ratios. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:567–74.
Kemppainen NM, Aalto S, Wilson I, Nagren K, Helin S, Bruck A, et al. Voxel-based analysis of PET amyloid ligand [11C]PIB uptake in Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2006;67:1575–80.
Ziolko SK, Weissfeld LA, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Hoge JA, Lopresti BJ, et al. Evaluation of voxel-based methods for the statistical analysis of PIB PET amyloid imaging studies in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage. 2006;33:94–102.
Mueller SG, Weiner MW, Thal LJ, Petersen RC, Jack C, Jagust W, et al. The Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2005;15:869–77 xi–xii.
Iwatsubo T. Japanese Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: present status and future. Alzheimers Dement. 2010;6:297–9.
Iwatsubo T, Iwata A, Suzuki K, Ihara R, Arai H, Ishii K, et al. Japanese and North American Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative studies: harmonization for international trials. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018;14:1077–87.
Nordberg A, Carter SF, Rinne J, Drzezga A, Brooks DJ, Vandenberghe R, et al. A European multicentre PET study of fibrillar amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:104–14.
Bourgeat P, Villemagne VL, Dore V, Brown B, Macaulay SL, Martins R, et al. Comparison of MR-less PiB SUVR quantification methods. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(Suppl 1):S159–66.
Thurfjell L, Lilja J, Lundqvist R, Buckley C, Smith A, Vandenberghe R, et al. Automated quantification of 18F-flutemetamol PET activity for categorizing scans as negative or positive for brain amyloid: concordance with visual image reads. J Nucl Med. 2014;55:1623–8.
Akamatsu G, Ikari Y, Ohnishi A, Nishida H, Aita K, Sasaki M, et al. Automated PET-only quantification of amyloid deposition with adaptive template and empirically pre-defined ROI. Phys Med Biol. 2016;61:5768–80.
Lilja J, Leuzy A, Chiotis K, Savitcheva I, Sörensen J, Nordberg A. Spatial normalization of [18F]flutemetamol PET images utilizing an adaptive principal components template. J Nucl Med. 2018.
Ikari Y, Nishio T, Makishi Y, Miya Y, Ito K, Koeppe RA, et al. Head motion evaluation and correction for PET scans with 18F-FDG in the Japanese Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (J-ADNI) multi-center study. Ann Nucl Med. 2012;26:535–44.
Yamane T, Ishii K, Sakata M, Ikari Y, Nishio T, Ishii K, et al. Inter-rater variability of visual interpretation and comparison with quantitative evaluation of (11)C-PiB PET amyloid images of the Japanese Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (J-ADNI) multicenter study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017;44:850–7.
Bettinardi V, Presotto L, Rapisarda E, Picchio M, Gianolli L, Gilardi MC. Physical performance of the new hybrid PET∕CT Discovery-690. Med Phys. 2011;38:5394–411.
Ikari Y, Akamatsu G, Nishio T, Ishii K, Ito K, Iwatsubo T, et al. Phantom criteria for qualification of brain FDG and amyloid PET across different cameras. EJNMMI Phys. 2016;3:23.
Akamatsu G, Ikari Y, Nishio T, Nishida H, Ohnishi A, Aita K, et al. Optimization of image reconstruction conditions with phantoms for brain FDG and amyloid PET imaging. Ann Nucl Med. 2016;30:18–28.
Evans AC, Janke AL, Collins DL, Baillet S. Brain templates and atlases. Neuroimage. 2012;62:911–22.
Laird AR, Robinson JL, McMillan KM, Tordesillas-Gutiérrez D, Moran ST, Gonzales SM, et al. Comparison of the disparity between Talairach and MNI coordinates in functional neuroimaging data: validation of the Lancaster transform. Neuroimage. 2010;51:677–83.
Mikhno A, Devanand D, Pelton G, Cuasay K, Gunn R, Upton N, et al. Voxel-based analysis of 11C-PIB scans for diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:1262–9.
Rowe CC, Villemagne VL. Brain amyloid imaging. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:1733–40.
Villemagne VL, Fodero-Tavoletti MT, Masters CL, Rowe CC. Tau imaging: early progress and future directions. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:114–24.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 16 K19882.
J-ADNI was supported by the following grants: Translational Research Promotion Project from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization of Japan; Research on Dementia, Health Labor Sciences Research Grant; Life Science Database Integration Project of Japan Science and Technology Agency; Research Association of Biotechnology (contributed by Astellas Pharma Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck-Banyu, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Pfizer Inc., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon, and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company), Japan; and a grant from an anonymous foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
GA wrote the manuscript and performed the image analysis. YI, AO, KM, and HN contributed to the data analysis. YY and MS made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This study was approved by the ethics committee of IBRI.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
Yasuhiko Ikari is an employee of CMIC Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan. Hiroyuki Nishida is an employee of Micron, Inc., Tokyo, Japan. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Data used in preparation of this article were obtained from the Japanese Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (J-ADNI) database deposited in the National Bioscience Database Center Human Database, Japan (Research ID: hum0043.v1, 2016). As such, the investigators within J-ADNI contributed to the design and implementation of J-ADNI and/or provided data but did not participate in analysis or writing of this report.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Akamatsu, G., Ikari, Y., Ohnishi, A. et al. Voxel-based statistical analysis and quantification of amyloid PET in the Japanese Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative (J-ADNI) multi-center study. EJNMMI Res 9, 91 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-019-0561-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-019-0561-2