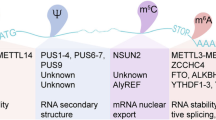
Abstract
Genetic and epigenetic changes deregulate RNA and protein expression in cancer cells. In this regard, tumors exhibit an abnormal proteome in comparison to the corresponding normal tissues. Translation control is a crucial step in the regulation of gene expression regulation under normal and pathological conditions that ultimately determines cellular fate. In this context, evidence shows that transfer and ribosomal RNA (tRNA and rRNA) modifications affect the efficacy and fidelity of translation. The number of RNA modifications increases with the complexity of organisms, suggesting an evolutionary diversification of the possibilities for fine-tuning the functions of coding and non-coding RNAs. In this review, we focus on alterations of modifications of transfer and ribosomal RNA that affect translation in human cancer. This variation in the RNA modification status can be the result of altered modifier expression (writers, readers or erasers), but also due to components of the machineries (C/D or H/ACA boxes) or alterations of proteins involved in modifier expression. Broadening our understanding of the mechanisms by which site-specific modifications modulate ribosome activity in the context of tumorigenesis will enable us to enrich our knowledge about how ribosomes can influence cell fate and form the basis of new therapeutic opportunities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Nucleotide modifications arise in most classes of RNA and more than 160 modifications are known [1]. Initial genetic studies in yeast and E. coli demonstrated that rRNA modifications play an important role in ribosome function [2,3,4], supported by further research in the area in the early 2000s [5]. Thenceforth, various ribosomal and transfer RNA modifications have been found to participate in determining cellular fate in cancer [6, 7]. For rRNA, modifications usually have an effect on early biogenesis steps, but the catalytic function of the ribosome in translation can also be subtly modulated by specific posttranscriptional modifications and selectively translate certain types of messenger RNA [8], such as the case for the rRNA methyltransferase NSUN5 [9]. Nevertheless, translational changes in the context of human cancer have been poorly studied, with most of the studies done describing how the expression of RNA modifiers could inform patient diagnosis or prognosis [10,11,12,13,14]. This lack of research can be explained in part by the great investment in effort and resources required to undertake a thorough study of an rRNA or tRNA modification —from cellular model construction and validation, through RNA-sequencing to visualize the transcriptome, to ribosome profiling and SILAC— in order to appreciate the differential translational efficiency of specific messengers, also known as translatomics [15]. In parallel, other methods are used to evaluate global protein synthesis, including the O-propargyl-puromycin assay and isotope pulse labeling with S35-labeled amino acid [16].
Alterations in the expression levels of few RNA modifiers of tRNA and rRNA have been linked to cancer as well as other human diseases [17,18,19,20]. However, the consequences of changes affecting the core machinery of protein translation are rarely explained. In the context of human cancer, after a brief description of the type of RNA and the machineries involved, we summarize the modifications that have been functionally characterized (Fig. 1; Tables 1 and 2). We also discuss which paths look promising in cancer therapy and provide a perspective on the possibilities for further deciphering the complex language of RNA modifications.
Ribosomal RNA
The ribosome is a complex system that translates the nucleotide code of messenger RNA into protein in cells. In humans, this complex machinery comprises four ribosomal RNAs (the 28S, 18S, 5.8S and 5S rRNAs) that are synthesized by polymerases I and III, and 80 ribosomal proteins (RPs) transcribed by polymerase II [46], all of which are organized in a large 60S subunit and a small 40S subunit. From the transcription of the ribosomal DNA to the final export into the cytoplasm, ribosome biogenesis involves more than 400 proteins and small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) [47]. Ribosome heterogeneity is the result of various changes including those in the diversity of the composition of RPs and RPs mutations, abnormalities in rRNA modifications during ribosomal biogenesis, and those due to specific endogenous or exogenous factors. This heterogeneity, which also appears between cell types, has been thoroughly reviewed by Maria Barna and colleagues [48, 49]. Changes in posttranscriptional modifications of rRNAs can influence translational fidelity, leading to nonsense suppressions or amino acid misincorporations, and modifying the preferential mode of translation initiation (i.e., CAP versus internal ribosome entry site (IRES)) of key cancer genes [50, 51]. Finally, a defect in rRNA posttranscriptional modifications may cause specific clinical syndromes and may be associated with a higher incidence of cancer, which is the case for DKC1 mutation related to X-linked dyskeratosis congenita (X-DC), and for Dyskerin overexpressed in prostate cancer [52,53,54,55].
2′-O-methylation (Nm) machinery and implications for human cancer
The association of snoRNAs in human cancer and their potential role in cancer diagnosis and therapy has recently been reviewed [56]. The RNA component of the 2′-O-methylation machinery is a C/D box snoRNA, an evolutionarily conserved noncoding small (70–120 nucleotide-long) nucleolar RNA [57]. The assembly and composition of C/D snoRNP complexes have been extensively reviewed [5, 19, 58], and are simply summarized here. C/D box snoRNAs catalyze the methylation of ribose residues (2′-O-methylation) and can affect every type of nucleotide (A; U; C; G and pseudouridine). It contains two short conserved sequence motifs (named C and D), located near the 5′ and 3′ ends of the snoRNA, respectively, and present in duplicate (C′ and D’). It is the most abundant rRNA modification in eukaryotes, with two, 42 and 68 sites modified in the 5.8S, 18S and 28S subunits, respectively [59]. The complex involves the methyltransferase fibrillarin (FBL), an RNA-binding protein 15.5 K (NHP2L1), and a heterodimer of two closely related proteins, NOP56 and NOP58. This complex is named C/D box snoRNP (SNORD). Modification of the expression of the different factors involved can directly influence the methylation status of the corresponding ribose.
High levels of fibrillarin (FBL) are accompanied by modifications of the rRNA methylation pattern, impairment of translational fidelity, and an increase of internal ribosome entry site (IRES)-dependent translation initiation of key cancer genes [21]. Indeed, FBL is overexpressed in prostatic neoplasia [60] and breast cancer [21, 22]. It was demonstrated that FBL expression correlates with RNA polymerase I transcriptional activity and production of ribosomal RNA, and is inversely correlated with cancer-cell doubling time [61].
Chronologically, the role of 2′-O-methylation in regulating the translation of selected mRNAs was first demonstrated through the observation of associations between altered 2′-O-methylation profiles and translation vector reporter assays in breast cancer models [21, 62] and subsequently in models in which expression of FBL was knocked down [21, 22, 50, 63].
In 2009, Belin and colleagues [62] observed that breast cancer cells with increased aggressiveness displayed non-modified global translational activity but had IRES-initiated translation, notably that of p53 mRNA, which was less efficient. They also noted that control of translational fidelity was substantially reduced. This suggests that this aggressive phenotype is associated with profound alterations of ribosomal control, leading to poorer quality control of translation in cancer cells.
The expression of FBL gene is decreased by the direct binding of the tumor suppressor transcription factor p53. In human mammary epithelial cells, the diminution or suppression of p53 expression leads to modifications in the rRNA methylation pattern at the single nucleotide level, impairment of translational fidelity, and increased IRES-dependent translation of key cancer-related genes, such as IGF-1R, C-MYC, VEGF-A, and FGF1/2 [21]. As TP53 is frequently mutated in cancer, the authors showed that the level of FBL is significantly higher in mutated breast cancer than in wild type cells. They obtained the same results in a retrospective statistical analysis. Specifically, the authors showed that the rRNA methylation pattern at 18 sites distributed along the rRNAs in functionally important domains were altered in cells with p53 knockdown, increasing the rRNA methylation status due to the increased expression of FBL. Functionally, the p53-mediated increase of FBL expression leads to an increased bypass of a premature stop-codon and the misincorporation of amino acids, demonstrating the combinatory roles of p53 and FBL in translational quality control. IRES-dependent translation was stronger, whereas the CAP-dependent mechanism showed no significant differences. The complementary experiment directly modulating FBL expression confirmed that the efficacy of IRES-dependent translation initiation is driven by rRNA methylation. Clinically, the same authors have shown that FBL overexpression is associated with tumorigenesis and poor survival in patients with breast cancer and promotes cellular proliferation and resistance to doxorubicin chemotherapy of MCF7 breast cancer cells [21].
Thereafter, Su and colleagues found that FBL increased expression in association with an increasing abundance of a cluster of snoRNAs. The decrease of FBL had an anti-tumorigenic effect in vitro and in vivo, demonstrating the importance of the controlled regulation of rRNA modifications [22]. Complementary to the study of Marcel et al. [21], they revealed that FBL overexpression suppresses the p53 response to stress. As p53 mutation is relatively uncommon in breast cancer (around 20% of cases), this mechanism of FBL overexpression/p53 stress response suppression is thought to be an alternative option for p53 inactivation [22]. First, the authors showed that p53 protein stability was increased upon FBL knockdown and p53 mRNAs were enriched in polysomal fractions in these cells. They found that the level of IRES translation of p53 and other transcripts was significantly higher in FBL knockdown cells and that this mechanism is driven by the IRES trans-acting factor PTB in the context of nucleolar stress [22].
More recently, in 2017, Erales et al. characterized 2′-O-methylation in HeLa cells using a RiboMethSeq approach to quantitatively and qualitatively determine the modulation of the methylation pattern when FBL is knocked down [63]. Upon FBL knockdown, the frequency of 2′-O-methylation decreased at almost all sites, but not statistically significantly for all of them, and with differences among sites indicating site-specific regulation of 2′-O-methylation by FBL. Structurally, the affected sites were distributed throughout the ribosome structure, including functionally important regions like the A and P sites, the intersubunit bridges and the peptide exit tunnel, but in contrast, methylation sites close to the PTC and the decoding center within 18S rRNA were not affected. FBL knockdown reduced global protein synthesis, as shown by puromycylation assay and isotope pulse labeling with [35S]-labeled amino acids. At the mRNA-specific translational level, the authors used ribosome profiling of HeLa cells expressing an inducible FBL shRNA or control shRNA. They identified few translationally altered genes upon FBL knockdown [63]. Using a bicistronic reporter, they saw that knockdown of FBL induced a decrease in IRES-dependent translational initiation of FGF1, IGF-1R and the type II encephalomyocarditis virus (EMCV) IRES, but not of VEGFA IRES. Luciferase activity/mRNA ratios, which give an indication of the translation efficiency, showed a decrease in CAP-dependent translation, and a stronger decrease in the IRES-dependent one.
Fibrillarin affects ribosomal RNA 2′-O-methylation almost globally. Nevertheless, a few studies have identified particular snoRNA C/D boxes as site-specific writers with translational consequences in human cancer.
SNORD50 methylates rRNA at positions 28S-C2848 and 28S-G2863 in humans. Variation in SNORD50 expression has been observed in colon cancer, breast carcinoma, prostate cancer and, finally, B-cell lymphoma. Historically, the SNORD50 host gene was found by Tanaka in 2000 at a chromosome breakpoint in a human B-cell lymphoma [64]. Further studies have demonstrated an association between SNORD50 and clinical outcomes [65,66,67].
Regarding colon cancer, Pacilli and colleagues in 2013 studied the expression of SNORD50 in cell lines and tumors. They found that the level of SNORD50 expression was lower in tumors compared with normal counterparts, the difference being significant in a subgroup of low-stage tumors. They also found a significant association between the level of SNORD50 expression and tumor stage [23]. Notably, they showed that SNORD50 expression is inversely correlated with cellular proliferation, highlighting the fact that ribosome biogenesis requires rRNA modifications as part of the process. The overexpression of SNORD50 in HTC116 successfully increases both SNORD50 and C2848 methylation. They observed a general decrease in CAP-dependent translation and an increase in IRES-dependent translation for three IRESs: CrPV, HCV, and c-Myc, while EMCV IRES translation was not affected by changes in the methylation of this specific site [23]. Interestingly, the literature suggests that SNORD50 expression is inversely correlated with cellular proliferation and tumor progression, results that are not fully consistent with the oncogenic role fibrillarin and methylation activity play in tumors. Thus, it is possible that it is not the increase of methylation, but the aberrant 2′-o-methylation of specific positions which may be associated to different oncogenic effects.
In 2016, Zhou et al., studied an underlying mechanism of self-renewal that drives leukemogenesis. This study is an excellent example of workflow characterizing epitranscriptomic modifications in human malignancies. The authors identified a pathway that links the chimeric oncogene protein AML1-ETO to enhanced snoRNA functions via the amino-terminal enhancer of split (AES) and DDX21 interaction [24]. They showed that deletion of two snoRNAs (SNORD14D, which methylates the 18S-C462 site, and SNORD35A, which methylates the 28S-C4506 site close to the PTC) suppresses the clonogenic potential of leukemia cells in vitro and delayed leukemogenesis in vivo. Briefly, they demonstrated that AES is essential for AML1-ETO-induced self-renewal of leukemia cells in vitro and in vivo. Also in the AML1-ETO cells, snoRNAs were decreased by AES suppression. Indeed, microarray-based gene expression profiling in a comparison of fetal liver cells overexpressing AML1-ETO from mice wild-type (WT) for AES (Aes+/+) or Knockout (KO) (Aes f/f) revealed that 20 of the top 100 candidates were snoRNAs, all of which were severely reduced following AES deletion, and preferentially C/D box snoRNAs. Conversely, forced expression of AES in fetal liver cells induced snoRNA expression. At this point, they mapped the pseudouridylation to evaluate the impact of AES in rRNA modification and AES depletion weakly affected pseudouridylation in these cells. However, two 2′-O-methylation sites guided by SNORD43 and SNORD32A (methylating 18S-C1703 and 18S-G1328, respectively) showed decreased methylation. In line with a decrease in snoRNA expression, cell size was also significantly smaller in AES KO compared with WT. In AML1-ETO-induced expression cells with AES KO and a shRNA AES knockdown cell model, OP-Puro incorporation was significantly reduced, revealing a reduction in translation efficiency following AES depletion in AML1-ETO-transduced cells [24]. Depletion of NOP58 (a component of the C/D box complex) reduced C/D box snoRNA levels and rRNA methylation. Moreover, the colony formation of various leukemia cell lines was significantly reduced, suggesting a crucial role for rRNA 2′-O-methylation in clonogenicity. Knocking out six SNORDs showed that reduced levels of expression of SNORD34, SNORD35A and SNORD43 impaired clonogenic growth in the cell model, and curiously, depletion of SNORD14D reduced colony formation without affecting 18S-C762 methylation. Depletion of SNORD14D, SNORD34 (which methylates 28S-U2824), SNORD35 or SNORD43 resulted in a reduction of cell size and protein synthesis. In the context of AML1-ETO, knockout of SNORD14D or SNORD35A reduced colony formation in MV4–11 cells and delayed leukemogenesis in immunodeficient NSG mice. These results indicate that different snoRNAs have distinct roles and that some of them are important for leukemogenesis beyond AML1-ETO-induced leukemia. As expected, fibrillarin overexpression in AES-knocked-down cells increased 2′-O-methylation at various sites and promoted ribosome activity, implying that the functions of AES in AML1-ETO cells depend on both snoRNA regulation and rRNA methylation. These results are consistent with the oncogenic role fibrillarin plays in solid tumors [24].
Pseudouridylation (Ψ) machinery and implications for human cancer
Pseudouridylation is the most common modification in RNA and the second modification found in rRNA after 2′-O-methylation. There are approximately 106 pseudouridines in rRNA clustered close to functionally important sites [59]. These modifications are driven by a snoRNA H/ACA box or by a pseudouridine synthase (PSU). PSUs recognize substrate and catalyze the isomerization reaction of uridine to pseudouridine without using any cofactors. They are classified into six families [68]. The catalytic center involves aspartate as the nucleophile for all PSUs, even in cases where the mechanism of isomerization is poorly understood [68].
RNA-dependent pseudouridylation involves an H/ACA box RNA that complexes with a set of proteins. Box H/ACA RNAs are noncoding RNAs that fold into a hairpin–hinge–hairpin–tail secondary structure. The hinge and tail regions contain evolutionarily conserved box H with the consensus sequence “ANANNA” (N for any type of nucleotide) and the trinucleotide Box “ACA,” respectively. The two hairpins contain an internal loop known as the pseudouridylation guide pocket, which has a short specific sequence complementary to the substrate RNA. The guiding pockets recognize the sites of modifications through Watson–Crick base-pairing interactions with substrate RNAs, thereby positioning the uridine to be modified at the base of the upper stem and leaving it unpaired. This brings the target site between 13 and 16 nucleotides upstream of either box H or box ACA [69, 70]. The core proteins are dyskerin (encoded by DKC1 gene), glycine–arginine-rich protein 1 (GAR1), non-histone protein 2 (NHP2), and nucleolar protein 10 (NOP10) [69, 71]. Dyskerin is the protein that exhibits the enzymatic activity within this complex, which is known as H/ACA snoRNP. This enzyme has two distinct functions: the pseudouridylation necessary for rRNA processing, and the stabilization of the telomerase RNA component that is essential for telomerase activity. Similar to fibrillarin for C/D box RNPs, DKC1 or dyskerin regulation affects its rRNA epitranscriptomic activity. In 1998, Heiss et al. identified the mutation responsible for X-linked recessive dyskeratosis congenita in a gene named XAP101 [52]. This disease is characterized by bone marrow failure, skin abnormalities, and an increased susceptibility to develop cancer [72]. Pseudouridylation is thought to play a role in translation, modulating the interactions between tRNA, rRNA and mRNA. The influence of modified nucleosides on the local structure of the antisense loop is essential for the proper binding of tRNA to the ribosome [73]. Maintenance of the proper conformation of the three anticodon residues helps foster correct codon–anticodon interactions. This may increase translational accuracy by reducing the rate of peptide bond formation, thereby allowing more time to reject incorrect codon–anticodon pairs [73].
In 2006, Montanaro and colleagues showed that, in human breast cancer, low levels of expression of dyskerin, as determined by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR, were associated with a better outcome [74]. The same year, Yoon et al. were the first to report the influence of dyskerin expression on translation, although this time it occurred in X-linked dyskeratosis congenita (X-DC) [75]. Using a knocked-in DKC1 point-mutation mouse model, they saw that reduced rRNA pseudouridylation did not affect total protein synthesis. They then analyzed the translationally active ribosome-associated mRNAs from steady state and activated primary splenic lymphocytes, one of the hematopoietic lineages affected in X-DC. They identified three out of 1500 mRNAs whose expression was specifically decreased in polysome-associated fractions for DKC1m lymphocytes: the p27 tumor suppressor, the anti-apoptotic proteins XIAP (X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein), both of which harbor IRES elements, and Bcl-xL showed a significant decrease in their association with polysomes in DKC1m cells compared with wild-type cells [75]. The decrease was observed only at the protein level, where a specific translation in DKC1 cells was revealed. Yoon et al. confirmed IRES-dependent translation of p27 and XIAP and also established that BCL-XL contains a previously unreported IRES element. In 2010, the same group, headed by Davide Ruggero, showed that DKC1 is mutated in pituitary adenoma and that this genotype causes a defect in pseudouridylation activity and reduced expression of p27 [25]. They observed that this translation was reduced in the pituitary of DKC1m mice. DKC1m/p27+/− mice developed a similar pituitary malignancy to that of p27−/− mice. Finally, they found a DKC1 mutation in patients with pituitary adenoma that drastically reduced DKC1 expression and pseudouridylation, but also brought about a reduction in p27 expression. Therefore, DKC1 is a tumor suppressor that controls translation by its direct role in rRNA modifications [25]. In parallel, they also established that p53 IRES-dependent translation is impaired in DCK1m cells during oncogene-induced senescence in X-DC [76]. Normally, during this senescence transition, IRES translation is facilitated, promoting the translation of p53. This mechanism in X-DC is close to that controlling fibrillarin overexpression, which inhibits p53 expression [21]. In 2013, Rocchi et al. found that angiogenesis in human breast epithelial cells was promoted by enhanced VEGF-IRES-mediated translation associated to the lack of dyskerin [26].
A H/ACA box RNP has been identified as playing a role in tumorigenesis by regulating translation. A recent study by McMahon and colleagues has shown the regulation of SNORA24 in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its collaboration with RAS mutation to promote cancer [27]. SNORA24 drives two pseudouridylations in the 18S rRNA at positions 609 and 863. Ribosomes lacking the corresponding modifications exhibited perturbations in the aminoacyl-transfer RNA (aa-tRNA) selection and altered pre-translocation ribosome complex dynamics [27].
Further research is needed to fully understand the interplay between genetic alterations, regulation of epitranscriptomics and translation in human tumorigenesis.
Other modifications of ribosomal RNA affecting translation in human cancer
Only two recent studies have identified other types of rRNA modification impairment that influence translation in human cancer.
The first, by Ma and colleagues in 2018, identified the N6-methyladenosine ZCCHC4 as being responsible for modifying the rRNA at position 4220, and this methyltransferase is overexpressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma [28]. This position is not in a functionally important region but, as seen before, changes in translation are not linked to changes of modifications in these regions. Using a luciferase reporter and then l-homopropargylglycine-derived metabolic labeling of newly synthesized proteins, the authors showed that ZCCHC4 KO in hepG2 cells displayed a lower level of global translation than in WT. After a sucrose density gradient and polysome-associated mRNA sequencing, they suggested that loss of m6A methylation should result in a reduction of the tight control of translation in mRNA populations, and might increase the translation of a subset of mRNAs. Finally, gene ontology indicated that genes affected by ZCCHC4 are involved in membrane protein targeting, the mRNA catabolic process, ER localization, and translation initiation. We recently studied the role of NSUN5, an m5C methyltransferase, in human gliomagenesis [9]. NSUN5 methylates the rRNA at position 28S-C3761 (old nomenclature 3782) and influences global translation, since, under conditions of stress, reduced OP-puro and H3-leucine incorporations were observed in cell lines depleted in NSUN5 [9]. This condition also leads to a specific translation in response to stress, as determined for some proteins regulated only at the translational level. We chose to validate NQO1 as a relevant candidate for therapeutic targeting [9].
Other rRNA modifiers have been linked to human cancer, but the underlying mechanisms driving translational change require further investigation. NAT10, for example, is a N-acetyltransferase involved in histone and microtubule modification, pre-rRNA processing, but also in the acetylation of rRNA at positions C1337 and C1842, and the acetylation of leucine/serine tRNA [77, 78]. NAT10 has been found upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [79], ovarian cancer [80] and AML [13], and correlates with poor survival of patients. This upregulation also promotes metastasis of HCC cells [81, 82]. Also, sub-cellular redistribution of NAT10 in colorectal cancer is able to promote cell motility through modifying cytoskeleton dynamics [83]. Another modifier, NOP2 (also named NSUN1 or p120), a probable rRNA methyltransferase for position C4447 of the human 28S RNA [84], has been described as overexpressed in lung adenocarcinoma [14, 85]. In HCC, Wang and colleagues have described that LncRNA-hPVT1 stabilizes NOP2, thereby increasing cell cycle rate, and promoting both cell proliferation and the acquisition of stem cell-like properties [86]. The cytosine methylated by NOP2 is part of the A-loop of the peptidyl transferase center. This is a critical position within an area responsible for the initial interaction with the incoming peptidyl-tRNAs, as well as the presentation of tRNAs in the correct conformation for the optimal peptidyl transfer reaction [84]. This mechanism could have major impact on protein synthesis in cancer cells with NOP2 expression changes. Overall, the role of rRNA modifications in the tumorigenic mechanisms driven by these two modifiers will need further investigation.
In summary, few studies have clearly identified changes in translation in human cancer, but there are enough of them to reveal the importance of this regulation in human tumorigenesis (Fig. 1a; Table 1).
Transfer RNA
Transfer RNAs are small RNAs that carry amino acids to ribosomes that translate an mRNA. This allows amino acid incorporation into the synthesized peptide according to the corresponding codon. In humans, tRNAs can carry up to 21 different amino acids. tRNAs present five functional arms or loops. The aminoacylation arm is where the aminoacyl synthase incorporates the corresponding amino acid, whereas the anticodon loop is the region containing the three nucleosides that pair with the mRNA codon. There are also the D-loop, so called because of the dihydrouridines it contains, the T-loop for the conserved TψC sequence, and the variable arm, whose length differs in each tRNA [87].
tRNAs are synthesized by RNA polymerase III and all pre-tRNAs undergo 5′ and 3′ end processing, and addition of CCA to the processed 3′ end. Some tRNAs also require intron cleavage and subsequent ligation. tRNA biogenesis occurs in the nucleus and mitochondria, depending where they are codified. Those that are synthesized in the nucleus are exported to the cytoplasm as a final step [88, 89]. Aminoacylation is the covalent attachment of amino acids to their corresponding tRNA, the reaction being catalyzed by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. There is at least one enzyme for each amino acid, and they can function in the cytoplasm, the mitochondria, or in both locations [90]. Throughout this process, tRNA can undergo nucleoside modifications, some of which are introduced into all tRNAs, whereas others are tRNA-specific. Modifications can also vary between cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNA.
RNA polymerase III, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and other proteins involved in tRNA maturation steps are known to be altered in a wide range of tumors. This can be explained by the need for tRNA availability and translation efficiency to supply the higher level of protein synthesis that occurs in cancer cells [91, 92].
During different steps of their maturation, modifications are anchored to tRNA, allowing the correct folding of their secondary (cloverleaf) and tertiary (L-shaped) structures through correct base-pairing, codon recognition and binding. These ensure the fidelity of translation, structural stability and integrity [29, 37, 93]. Disturbances in the regulation of these steps can create opportunities for cancer to arise.
Transfer RNA modifications in human cancer
5-methylcytidine (m5C)
5-methylcytidine is incorporated at different positions of tRNA by NSUN2, NSUN3, NSUN6, and TRDMT1.
NSUN2 and TRDMT1 are the best functionally characterized epitranscriptomic enzymes. TRDMT1 methylation prevents tRNA cleavage [94, 95]. tRNA fragment accumulation and loss of cytosine-5 methylation in tRNAs was associated to decreased ribosome density in mRNAs and increased ribosome density in 5′ UTRs [96]. In mice, methylation also confers stability to their tRNA substrates as loss of 5-methylcytidine causes tRNA degradation, and loss of Trdmt1 and Nsun2 leads to a global decrease of protein synthesis [29]. Upregulation of NSUN2 expression was identified in one-third of primary breast tumors and breast cancer cell lines. Also, high levels of NSUN2 expression were detected in head and neck carcinoma. In these studies, this aberrant expression significantly increases mortality [30,31,32]. Moreover, the oncogene RLP6 has been found to partially regulate NSUN2 translation and so tumorigenesis function in human gallbladder carcinoma [33].
m7G
METTL1 and WDR4 are both necessary for the introduction of the 7-methylguanosine at position 46 [34]. In 2018, Lin et al. have reported that METTL1 knockdown reduces the m7G fraction, which causes tRNA destabilization and ribosome pausing at m7G tRNA-dependent codons that leads to a decrease in translation [35]. Overexpression of METTL1 in hepatocellular carcinoma has been shown to promote cell proliferation and migration, and to lead to poor prognosis in HCC [36].
mcm5U
5-methoxycarbonylmethyluridine (mcm5U) is a common modification in the wobble position. ALKBH8, with TRM112 as a partner, catalyzes the methylation of 5-carboxymethyluridine (cm5U) to mcm5U [37, 38]. tRNASec is one of the targets of ALKBH8, this tRNA transfers the amino acid selenocysteine during selenoprotein translation. A large number of selenoproteins are involved in the detoxification of ROS. It has been shown that ALKBH8 deficiency causes a decrease in selenocysteine protein translation and consequently ROS stress that triggers oxidative DNA damage [38, 97]. It has been reported both in vitro and in vivo that ALKBH8 promotes the expansion, survival and invasion of bladder cancer [39, 98]. Cancer cells use AKBH8 expression as an antioxidant system against the ROS stress generated during tumorigenic transformation [97].
Msm5U is necessary for the formation of some derivatives, such as 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thiouridine (mcm5s2U). CTU1, CTU2 and ELP3 are the thiolation effectors with URM1 as the sulfur donor [37, 40, 99]. The mcm5s2U complex is heavily implicated in cancer. On one hand, its enzymes levels have been detected at higher levels in human tumor biopsies and in cultured melanoma cells with BRAFV600E mutation. An in silico analysis revealed that this kind of melanoma also has high levels of hypoxia-induced factor 1α (HIF1α), which is known for its involvement in tumorigenesis progression. The mRNA sequence of HIF1α is rich in U34 codons that require tRNA modification for correct translation. Thus, U34-related enzyme overexpression triggers increased HIF1α translation and thereby cancer transformation [41]. Similarly, U34-related enzymes were found to be overexpressed in breast cancer patients. The IRES trans-acting factor (ITAF) protein DEK has U34 codon-dependent translation regulation. DEK promotes the translation through the IRES sequence of LEF1, whose expression is associated with a higher risk of metastases [42].
Isopentenyladenosine (i6A)
TRIT1 introduces a dimethylallyl pyrophosphate at position 37, generating an isopentenylated adenosine in both cytoplasmic and mitochondrial tRNA [100,101,102]. In particular, it has been related to selenoprotein expression since tRNASec is one of its targets [103]. Expression of some selenoproteins are influenced by TRIT1 depletion [43]. Spinola et al. observed downregulation of TRIT1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma patients and noted that expression of TRIT1 in a lung adenocarcinoma cell line diminishes tumorigenesis. Its tumor suppressor effect is indicated by the role of some selenoproteins in diminishing oxidative stress [104]. However, as demonstrated in the case of ALKBH8, which modifies mcm5U34, cancer can also use selenoproteins to maintain oxidative stress at sublethal levels. Similarly, i6A is needed for ALKBH8 modification to take place [43].
Queuosine (Q)
Queuosine (7-(((4,5-cis-dihydroxy-2-cyclopenten-1-yl)amino)methyl)-7-deazaguanosine) is a derivative of the 7-deazagunine located in the wobble position. This modification is introduced by the tRNA-guanine transglycosylase (TGT) heterodimer formed by QTRT1 (catalytic subunit) and QTRT2 [44]. Eukaryotes cannot synthesize queuine but they obtain it from gut microbes or food. Tuorto et al. suggested that G34-containing tRNAs cause a translational delay that induces an accumulation of misfolded proteins and hence, endoplasmic reticulum stress and an unfolded protein response. In order to avoid this situation, Q modification prevents the elongation from slowing down [105]. Reduced Q content has been detected in a wide range of cancers [45].
This overview of the modifications affecting transfer RNAs (Fig. 1b; Table 2) summarizes the characteristics that influence cellular fate and that can drive tumorigenic processes.
Conclusions
Regulation of translation is crucial for cell proliferation and cell fate in human malignancies. There is increasing evidence that epitranscriptional modifications affect translation by modifying the affinity or the stability of mRNAs, tRNAs, or the interactions between them inside the ribosome.
Here, we have reviewed the various modifications of transfer and ribosomal RNAs that are known to have consequences for translation in human cancer (Fig. 2). We chose to exclude modifications affecting other types of RNAs and alterations in the expression and activity of specific translation factors, not only because these have already been extensively reviewed [106, 107], but also to present a consistent overview of the role of RNA modifications in the core functions of translation.
The role of epigenetics in cancer is now very firmly established, to the extent that corresponding therapies exist. However, the recent expansion of our knowledge about epitranscriptomics has not yet resulted in any clinical applications, although there is evidence of prognostic markers and possible treatments. In this sense, the exhaustive characterization and classification of RNA modifiers in each relevant cell type as tumor suppressor or oncogene will provide us with tools to identify new targets and design specific treatments that disrupt the carcinogenic pathways [108, 109]. Certainly, it is very important to identify the cellular background, as for a specific cancer type, different environments can be beneficial or lead to apoptosis [110].
Studies highlight that fibrillarin is frequently overexpressed in human cancer, and its expression controls the fine-tuning of ribose 2′-O-methylation of the rRNA in human cancer. FBL depletion leads to the regulation of IRES translation globally, but some specific mRNAs are altered in a different way, such as p53, whose expression increases when FBL is knocked down, and also revealed by ribosome profiling [21]. Further studies would certainly confirm the qualitative and quantitative role of FBL in human cancer translation and would produce substantial information about identifying the downstream molecular and cellular functions affected by this mechanism. Cellular context is a critical factor as a stress influence on the translational response to FBL modulation [21]. Clinically, fibrillarin has not yet been exploited as an oncological target, but a recent review emphasizes its potential as a therapeutic target that could lower the genotoxic effects of anti-cancer treatment. This could be achieved by exploiting the association between low levels of FBL expression and better breast cancer survival, and its functions in ribosome biogenesis and p53 regulation [111]. Other 2′-O-methylation modifiers have shown therapeutic potential, such as SNORD44 in colorectal cancer and SNORD47 in glioblastoma [112, 113].
Few studies have highlighted the relevance of dyskerin in driving cancer development. Their findings can explain in part the increased risk of cancer observed in X-DC. In some other studies, the translational impact of pseudouridylation defects is not clear. This is the case for SNORA42 in lung cancer [10], in which SNORA42 is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer and its suppression inhibits cell growth, proliferation and tumorigenicity of cancer cells by inducing p53-dependent apoptosis. These results were partially confirmed 2 years later [114], but a translational shift driven by SNORA42 remains to be conclusively demonstrated. Strikingly, Bellodi et al., found that SNORA42 expression is increased in DKC1(ΔL37)-mutated lymphocytes, which raises the possibility that certain snoRNAs may be selectively increased as a compensatory mechanism for perturbations in subsets of H/ACA snoRNAs [115]. They also observed an unexpected heterogeneity of expression of the H/ACA snoRNAs in cells of patients with X-DC harboring distinct DKC1 mutations. This is in line with the unexpected 2′-O-methylation alteration observed in X-DC. Very recently, a study linked the rRNA 2′-O-methylation alteration caused by NPM1 mutations to the development of congenital dyskeratosis [116]. These results demonstrate the complex etiology of such diseases and how a common phenotype can arise as the result of different alterations.
Modifications can directly influence the level of tRNAs by modulating their stability. The by-products formed by angiogenin cleavage regulate translation in human cancer. There are many examples in the literature of efforts that have been made to improve our understanding of the subtle influence of proteomic modifications and the consequent tumorigenesis. Another aspect emerging from these studies is the difficulty of appreciating the enzyme-site-specific role. Indeed, this is the case for ribosomal RNA modifiers also, lots of enzymes have a panel of activities, and the modulation of its expression can have side effects that also play a role in translational changes. For example, TRIT1 and ALKBH8 functions are deeply related as mcm5U have been described as i6A dependent, although they are described as a tumor suppressor and oncogene respectively, some hypotheses exist as other functions of the genes but more research are needed to clarify it. This is also the case for NSUN5, we related the translational changes to the modification on the rRNA as it logically seems to have the most direct role on ribosome function. Nevertheless, considering the clinical implications of these modifiers, it is certain that the global phenotype takes precedence over the single modification. A nuance is the relevance of a cancer-specific translation in drug development and therapeutic opportunities [117]. For example, in 1990, the discovery that eIF4E overexpression could drive tumor initiation has led to the development of strategies to decrease its expression. To go further, ribosomal RNA modifications can lead to antibiotic resistance in yeast, so antibiotic-like drugs could specifically target the altered RNAs in cancer. In this regard, in 2013 Begley and colleagues found that tRNA methyltransferase 9-like protein (hTRM9L) was downregulated in breast, bladder, colorectal, cervix and testicular carcinomas and this downregulation was associated with altered tRNA modification levels [118]. Importantly, hTRM9L-deficient tumors were highly sensitive to aminoglycoside antibiotics [118]. Regarding tRNAs, NSUN2 overexpression indicates a shorter overall survival in head and neck carcinomas [32]. Another example is ALKBH8, which is crucial in bladder cancer transformation. It has been proposed that an intravesical injection of ALKBH8 siRNA may reverse the invasive character of the neoplasm in patients [38, 98]. It has also been described that a deficit of ALKBH8 increases the sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents and could complement the previous strategy [38]. Moreover, Rapino et al. proposed that targeting wobble uridine 34 (U34) tRNA (U34 enzymes) can avoid the resistance to Vemurafenib in BRAFV600E melanoma [41].
RNA modifications have a promising future. The relatively small number of studies, whether considering tRNA or rRNA, that completely describe the translational role of a specific modification in this context highlights the significant gap that remains to be filled if we are to better understand the complex mechanism of tumorigenesis (Fig. 1; Tables 1 and 2). In this puzzle, the addition or removal of a piece (RNA modifications) can effectively change the final picture.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
Abbreviations
- FBL:
-
Fibrillarin
- IRES:
-
Internal ribosome entry site
- i6A:
-
Isopentenyladenosine
- ITAF:
-
IRES trans-acting factor
- m5C:
-
5-methylcytidine
- mcm5U:
-
5-methoxycarbonylmethyluridine
- m7G:
-
7-methylguanosine
- PSU:
-
Pseudouridine synthase
- Q:
-
Queuosine
- RPs:
-
Ribosomal proteins
- rRNA:
-
Ribosomal RNA
- SILAC:
-
Stable Isotope Labeling by/with Amino acids in Cell culture
- SNORD:
-
C/D box snoRNP
- snoRNAs:
-
Small nucleolar RNAs
- TGT:
-
tRNA-guanine transglycosylase
- tRNA:
-
Transfer RNA
- X-DC:
-
X-linked dyskeratosis congenita
References
Boccaletto P, Machnicka MA, Purta E, Piątkowski P, Bagiński B, Wirecki TK, et al. MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D303–7.
Poldermans B, Bakker H, Van Knippenberg PH. Studies on the function of two adjacent N 6 , N 6 -dimethyladenosines near the 3′ end of 16 S ribosomal RNA of Escherichia coli. IV. The effect of the methylgroups on ribosomal subunit interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980;8(1):143–52.
Sirum-Connolly K, Mason T. Functional requirement of a site-specific ribose methylation in ribosomal RNA. Science. 1993;262(5141):1886–9.
Sirum-Connolly K, Peltier JM, Crain PF, McCloskey JA, Mason TL. Implications of a functional large ribosomal RNA with only three modified nucleotides. Biochimie. 1995;77(1–2):30–9.
Decatur WA, Fournier MJ. rRNA modifications and ribosome function. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002;27(7):344–51.
Popis MC, Blanco S, Frye M. Posttranscriptional methylation of transfer and ribosomal RNA in stress response pathways, cell differentiation, and cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2016;28(1):65–71.
Nachtergaele S, He C. The emerging biology of RNA post-transcriptional modifications. RNA Biol. 2017;14(2):156–63.
Motorin Y, Helm M. RNA nucleotide methylation. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2(5):611–31.
Janin M, Ortiz-Barahona V, de Moura MC, Martínez-Cardús A, Llinàs-Arias P, Soler M, et al. Epigenetic loss of RNA-methyltransferase NSUN5 in glioma targets ribosomes to drive a stress adaptive translational program. Acta Neuropathol. 2019;138;1053–74.
Mei Y-P, Liao J-P, Shen J, Yu L, Liu B-L, Liu L, et al. Small nucleolar RNA 42 acts as an oncogene in lung tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2012;31(22):2794–804.
Braicu C, Zimta A-A, Harangus A, Iurca I, Irimie A, Coza O, et al. The function of non-coding RNAs in lung cancer tumorigenesis. Cancers. 2019;11(5):605.
Yang X, Li Y, Li L, Liu J, Wu M, Ye M. SnoRNAs are involved in the progression of ulcerative colitis and colorectal cancer. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49(5):545–51.
Liang P, Hu R, Liu Z, Miao M, Jiang H, Li C. NAT10 upregulation indicates a poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Probl Cancer. 2019;2:100491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2019.06.006.
Uchiyama B, Saijo Y, Kumano N, Abe T, Fujimura S, Ohkuda K, et al. Expression of nucleolar protein p120 in human lung cancer: difference in histological types as a marker for proliferation. Clin Cancer Res. 1997;3(10):1873–7.
Zhao J, Qin B, Nikolay R, Spahn CMT, Zhang G. Translatomics: the global view of translation. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(1):212.
Iwasaki S, Ingolia NT. The growing toolbox for protein synthesis studies. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(8):612–24.
Jonkhout N, Tran J, Smith MA, Schonrock N, Mattick JS, Novoa EM. The RNA modification landscape in human disease. RNA. 2017;23(12):1754–69.
Kadumuri RV, Janga SC. Epitranscriptomic code and its alterations in human disease. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24(10):886–903.
Therizols G, Laforêts F, Marcel V, Catez F, Bouvet P, Diaz J-J. Ribosomal RNA methylation and cancer. In: Epigenetic cancer therapy: Elsevier; 2015. p. 115–39. [cited 2019 Nov 5].
Wei F-Y, Tomizawa K. tRNA modifications and islet function. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20:20–7.
Marcel V, Ghayad SE, Belin S, Therizols G, Morel A-P, Solano-Gonzàlez E, et al. p53 acts as a safeguard of translational control by regulating Fibrillarin and rRNA methylation in Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2013;24(3):318–30.
Su H, Xu T, Ganapathy S, Shadfan M, Long M, Huang TH-M, et al. Elevated snoRNA biogenesis is essential in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33(11):1348–58.
Pacilli A, Ceccarelli C, Treré D, Montanaro L. SnoRNA U50 levels are regulated by cell proliferation and rRNA transcription. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(7):14923–35.
Zhou F, Liu Y, Rohde C, Pauli C, Gerloff D, Köhn M, et al. AML1-ETO requires enhanced C/D box snoRNA/RNP formation to induce self-renewal and leukaemia. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(7):844–55.
Bellodi C, Krasnykh O, Haynes N, Theodoropoulou M, Peng G, Montanaro L, et al. Loss of function of the tumor suppressor DKC1 perturbs p27 translation control and contributes to pituitary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2010;70(14):6026–35.
Rocchi L, Pacilli A, Sethi R, Penzo M, Schneider RJ, Treré D, et al. Dyskerin depletion increases VEGF mRNA internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(17):8308–18.
McMahon M, Contreras A, Holm M, Uechi T, Forester CM, Pang X, et al. A single H/ACA small nucleolar RNA mediates tumor suppression downstream of oncogenic RAS. eLife. 2019;8:e48847.
Ma H, Wang X, Cai J, Dai Q, Natchiar SK, Lv R, et al. N6-Methyladenosine methyltransferase ZCCHC4 mediates ribosomal RNA methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2019;15(1):88–94.
Tuorto F, Liebers R, Musch T, Schaefer M, Hofmann S, Kellner S, et al. RNA cytosine methylation by Dnmt2 and NSun2 promotes tRNA stability and protein synthesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012;19(9):900–5.
Yi J, Gao R, Chen Y, Yang Z, Han P, Zhang H, et al. Overexpression of NSUN2 by DNA hypomethylation is associated with metastatic progression in human breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(13):20751–65.
Frye M, Dragoni I, Chin S-F, Spiteri I, Kurowski A, Provenzano E, et al. Genomic gain of 5p15 leads to over-expression of Misu (NSUN2) in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2010;289(1):71–80.
Lu L, Zhu G, Zeng H, Xu Q, Holzmann K. High tRNA Transferase NSUN2 gene expression is associated with poor prognosis in head and neck squamous carcinoma. Cancer Investig. 2018;36(4):246–53.
Gao Y, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Zhu Q, Yang Y, Jin Y, et al. NOP2/Sun RNA methyltransferase 2 promotes tumor progression via its interacting partner RPL6 in gallbladder carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019;110(11):3510–9.
Bahr A, Hankeln T, Fiedler T, Hegemann J, Schmidt ER. Molecular analysis of METTL1, a novel human methyltransferase-like gene with a high degree of phylogenetic conservation. Genomics. 1999;57(3):424–8.
Lin S, Liu Q, Lelyveld VS, Choe J, Szostak JW, Gregory RI. Mettl1/Wdr4-Mediated m7G tRNA Methylome Is Required for Normal mRNA Translation and Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Differentiation. Mol Cell. 2018;71(2):244–255.e5.
Tian Q-H, Zhang M-F, Zeng J-S, Luo R-G, Wen Y, Chen J, et al. METTL1 overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma via PTEN. J Mol Med Berl Ger. 2019;97(11):1535–45.
Songe-Møller L, van den Born E, Leihne V, Vågbø CB, Kristoffersen T, Krokan HE, et al. Mammalian ALKBH8 possesses tRNA methyltransferase activity required for the biogenesis of multiple wobble uridine modifications implicated in translational decoding. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(7):1814–27.
Fu D, Brophy JAN, Chan CTY, Atmore KA, Begley U, Paules RS, et al. Human AlkB homolog ABH8 is a tRNA methyltransferase required for wobble uridine modification and DNA damage survival. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30(10):2449–59.
Shimada K, Nakamura M, Anai S, De Velasco M, Tanaka M, Tsujikawa K, et al. A novel human AlkB homologue, ALKBH8, contributes to human bladder cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2009;69(7):3157–64.
Liu Y, Vinyard DJ, Reesbeck ME, Suzuki T, Manakongtreecheep K, Holland PL, et al. A [3Fe-4S] cluster is required for tRNA thiolation in archaea and eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(45):12703–8.
Rapino F, Delaunay S, Rambow F, Zhou Z, Tharun L, De Tullio P, et al. Codon-specific translation reprogramming promotes resistance to targeted therapy. Nature. 2018;558(7711):605–9.
Delaunay S, Rapino F, Tharun L, Zhou Z, Heukamp L, Termathe M, et al. Elp3 links tRNA modification to IRES-dependent translation of LEF1 to sustain metastasis in breast cancer. J Exp Med. 2016;213(11):2503–23.
Fradejas N, Carlson BA, Rijntjes E, Becker N-P, Tobe R, Schweizer U. Mammalian Trit1 is a tRNA([Ser]sec)-isopentenyl transferase required for full selenoprotein expression. Biochem J. 2013;450(2):427–32.
Chen Y-C, Kelly VP, Stachura SV, Garcia GA. Characterization of the human tRNA-guanine transglycosylase: confirmation of the heterodimeric subunit structure. RNA N Y N. 2010;16(5):958–68.
Vinayak M, Pathak C. Queuosine modification of tRNA: its divergent role in cellular machinery. Biosci Rep. 2009;30(2):135–48.
Dalla Venezia N, Vincent A, Marcel V, Catez F, Diaz J-J. Emerging role of eukaryote ribosomes in translational control. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1226.
Bohnsack KE, Bohnsack MT. Uncovering the assembly pathway of human ribosomes and its emerging links to disease. EMBO J 2019;38(13). [cited 2019 Nov 11].
Genuth NR, Barna M. Heterogeneity and specialized functions of translation machinery: from genes to organisms. Nat Rev Genet. 2018;19(7):431–52.
Xue S, Barna M. Specialized ribosomes: a new frontier in gene regulation and organismal biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(6):355–69.
Basu A, Das P, Chaudhuri S, Bevilacqua E, Andrews J, Barik S, et al. Requirement of rRNA methylation for 80S ribosome assembly on a cohort of cellular internal ribosome entry sites. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(22):4482–99.
Ruggero D. Translational control in Cancer etiology. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(2):a012336.
Heiss NS, Knight SW, Vulliamy TJ, Klauck SM, Wiemann S, Mason PJ, et al. X-linked dyskeratosis congenita is caused by mutations in a highly conserved gene with putative nucleolar functions. Nat Genet. 1998;19(1):32–8.
Ruggero D. Dyskeratosis Congenita and Cancer in mice deficient in ribosomal RNA modification. Science. 2003;299(5604):259–62.
Sieron P, Hader C, Hatina J, Engers R, Wlazlinski A, Müller M, et al. DKC1 overexpression associated with prostate cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 2009;101(8):1410–6.
Alawi F, Lin P. Dyskerin is required for tumor cell growth through mechanisms that are independent of its role in telomerase and only partially related to its function in precursor rRNA processing. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50(5):334–45.
Liang J, Wen J, Huang Z, Chen X, Zhang B, Chu L. Small Nucleolar RNAs: insight into their function in Cancer. Front Oncol. 2019;9:587.
Monaco P, Marcel V, Diaz J-J, Catez F. 2′-O-methylation of ribosomal RNA: towards an Epitranscriptomic control of translation? Biomolecules. 2018;8(4):106.
Watkins NJ, Bohnsack MT. The box C/D and H/ACA snoRNPs: key players in the modification, processing and the dynamic folding of ribosomal RNA: box C/D and H/ACA snoRNPs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012;3(3):397–414.
Taoka M, Nobe Y, Yamaki Y, Sato K, Ishikawa H, Izumikawa K, et al. Landscape of the complete RNA chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(18):9289–98.
Koh CM, Gurel B, Sutcliffe S, Aryee MJ, Schultz D, Iwata T, et al. Alterations in Nucleolar structure and gene expression programs in prostatic Neoplasia are driven by the MYC oncogene. Am J Pathol. 2011;178(4):1824–34.
Derenzini M, Trerè D, Pession A, Montanaro L, Sirri V, Ochs RL. Nucleolar function and size in cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 1998;152(5):1291–7.
Belin S, Beghin A, Solano-Gonzàlez E, Bezin L, Brunet-Manquat S, Textoris J, et al. Dysregulation of ribosome biogenesis and translational capacity is associated with tumor progression of human breast Cancer cells. PLoS One. 2009;4(9):e7147.
Erales J, Marchand V, Panthu B, Gillot S, Belin S, Ghayad SE, et al. Evidence for rRNA 2′-O-methylation plasticity: control of intrinsic translational capabilities of human ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2017;114(49):12934–9.
Tanaka R, Satoh H, Moriyama M, Satoh K, Morishita Y, Yoshida S, et al. Intronic U50 small-nucleolar-RNA (snoRNA) host gene of no protein-coding potential is mapped at the chromosome breakpoint t(3;6)(q27;q15) of human B-cell lymphoma. Genes Cells. 2000;5(4):277–87.
Dong X-Y, Rodriguez C, Guo P, Sun X, Talbot JT, Zhou W, et al. SnoRNA U50 is a candidate tumor-suppressor gene at 6q14.3 with a mutation associated with clinically significant prostate cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17(7):1031–42.
Dong X-Y, Guo P, Boyd J, Sun X, Li Q, Zhou W, et al. Implication of snoRNA U50 in human breast cancer. J Genet Genomics. 2009;36(8):447–54.
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Pickard MR, Hedge VL, Farzaneh F, Williams GT. GAS5, a non-protein-coding RNA, controls apoptosis and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2009;28(2):195–208.
Rintala-Dempsey AC, Kothe U. Eukaryotic stand-alone pseudouridine synthases – RNA modifying enzymes and emerging regulators of gene expression? RNA Biol. 2017;14(9):1185–96.
De Zoysa MD, Yu Y-T. Posttranscriptional RNA Pseudouridylation. In: The Enzymes: Elsevier; 2017. p. 151–67. [cited 2019 Nov 11].
Yu Y-T, Terns RM, Terns MP. Mechanisms and functions of RNA-guided RNA modification. In: Grosjean H, editor. Fine-Tuning of RNA Functions by Modification and Editing. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2004. p. 223–62. [cited 2019 Nov 11].
Penzo M, Montanaro L. Turning Uridines around: role of rRNA Pseudouridylation in ribosome biogenesis and ribosomal function. Biomolecules. 2018;8(2):38.
Marrone A, Dokal I. Dyskeratosis congenita: molecular insights into telomerase function, ageing and cancer. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2004;6(26):1–23.
Gray MC, Michael W. Pseudouridine in RNA: what, where, how, and why. IUBMB Life Int Union Biochem Mol Biol Life. 2000;49(5):341–51.
Montanaro L, Brigotti M, Clohessy J, Barbieri S, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, et al. Dyskerin expression influences the level of ribosomal RNA pseudo-uridylation and telomerase RNA component in human breast cancer. J Pathol. 2006;210(1):10–8.
Yoon A. Impaired control of IRES-mediated translation in X-linked Dyskeratosis Congenita. Science. 2006;312(5775):902–6.
Bellodi C, Kopmar N, Ruggero D. Deregulation of oncogene-induced senescence and p53 translational control in X-linked dyskeratosis congenita. EMBO J. 2010;29(11):1865–76.
Sleiman S, Dragon F. Recent advances on the structure and function of RNA Acetyltransferase Kre33/NAT10. Cells. 2019;05:8(9).
Sharma S, Langhendries J-L, Watzinger P, Kötter P, Entian K-D, Lafontaine DLJ. Yeast Kre33 and human NAT10 are conserved 18S rRNA cytosine acetyltransferases that modify tRNAs assisted by the adaptor Tan1/THUMPD1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(4):2242–58.
Li Q, Liu X, Jin K, Lu M, Zhang C, Du X, et al. NAT10 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and enhances mutant p53 activity. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):605.
Tan TZ, Miow QH, Huang RY, Wong MK, Ye J, Lau JA, et al. Functional genomics identifies five distinct molecular subtypes with clinical relevance and pathways for growth control in epithelial ovarian cancer. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(7):1051–66.
Ma R, Chen J, Jiang S, Lin S, Zhang X, Liang X. Up regulation of NAT10 promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(10):4215–23.
Zhang X, Chen J, Jiang S, He S, Bai Y, Zhu L, et al. N-Acetyltransferase 10 enhances doxorubicin resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines by promoting the epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:1–14.
Zhang H, Hou W, Wang H-L, Liu H-J, Jia X-Y, Zheng X-Z, et al. GSK-3 -regulated N-Acetyltransferase 10 is involved in colorectal Cancer invasion. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(17):4717–29.
Sharma S, Yang J, Watzinger P, Kötter P, Entian K-D. Yeast Nop2 and Rcm1 methylate C2870 and C2278 of the 25S rRNA, respectively. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(19):9062–76.
Sato G, Saijo Y, Uchiyama B, Kumano N, Sugawara S, Fujimura S, et al. Prognostic value of Nucleolar protein p120 in patients with resected lung adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17(9):2721.
Wang F, Yuan J-H, Wang S-B, Yang F, Yuan S-X, Ye C, et al. Oncofetal long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2: WANG ET AL. Hepatology. 2014;60(4):1278–90.
Lorenz C, Lorenz C, Lünse CE, Mörl M. tRNA modifications: impact on structure and thermal adaptation. Biomolecules. 2017;7(2):E35.
Lopes RRS, Kessler AC, Polycarpo C, Alfonzo JD. Cutting, dicing, healing and sealing: the molecular surgery of tRNA. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015;6(3):337–49.
Maraia RJ, Lamichhane TN. 3′ processing of eukaryotic precursor tRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011;2(3):362–75.
Rajendran V, Kalita P, Shukla H, Kumar A, Tripathi T. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases: structure, function, and drug discovery. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;111:400–14.
Park SG, Schimmel P, Kim S. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases and their connections to disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(32):11043–9.
Goodarzi H, Nguyen HCB, Zhang S, Dill BD, Molina H, Tavazoie SF. Modulated expression of specific tRNAs drives gene expression and Cancer progression. Cell. 2016;165(6):1416–27.
Helm M, Giegé R, Florentz C. A Watson-crick base-pair-disrupting methyl group (m1A9) is sufficient for cloverleaf folding of human mitochondrial tRNALys. Biochemistry. 1999;38(40):13338–46.
Schaefer M, Pollex T, Hanna K, Tuorto F, Meusburger M, Helm M, et al. RNA methylation by Dnmt2 protects transfer RNAs against stress-induced cleavage. Genes Dev. 2010;24(15):1590–5.
Tuorto F, Herbst F, Alerasool N, Bender S, Popp O, Federico G, et al. The tRNA methyltransferase Dnmt2 is required for accurate polypeptide synthesis during haematopoiesis. EMBO J. 2015;34(18):2350–62.
Blanco S, Bandiera R, Popis M, Hussain S, Lombard P, Aleksic J, et al. Stem cell function and stress response are controlled by protein synthesis. Nature. 2016;534(7607):335–40.
Endres L, Begley U, Clark R, Gu C, Dziergowska A, Małkiewicz A, et al. Alkbh8 regulates Selenocysteine-protein expression to protect against reactive oxygen species damage. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0131335.
Ohshio I, Kawakami R, Tsukada Y, Nakajima K, Kitae K, Shimanoe T, et al. ALKBH8 promotes bladder cancer growth and progression through regulating the expression of survivin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;477(3):413–8.
Schlieker CD, Van der Veen AG, Damon JR, Spooner E, Ploegh HL. A functional proteomics approach links the ubiquitin-related modifier Urm1 to a tRNA modification pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(47):18255–60.
Golovko A, Hjälm G, Sitbon F, Nicander B. Cloning of a human tRNA isopentenyl transferase. Gene. 2000;258(1–2):85–93.
Lamichhane TN, Blewett NH, Maraia RJ. Plasticity and diversity of tRNA anticodon determinants of substrate recognition by eukaryotic A37 isopentenyltransferases. RNA N Y N. 2011;17(10):1846–57.
Schweizer U, Bohleber S, Fradejas-Villar N. The modified base isopentenyladenosine and its derivatives in tRNA. RNA Biol. 2017;14(9):1197–208.
Lamichhane TN, Mattijssen S, Maraia RJ. Human cells have a limited set of tRNA anticodon loop substrates of the tRNA isopentenyltransferase TRIT1 tumor suppressor. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33(24):4900–8.
Spinola M, Galvan A, Pignatiello C, Conti B, Pastorino U, Nicander B, et al. Identification and functional characterization of the candidate tumor suppressor gene TRIT1 in human lung cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24(35):5502–9.
Tuorto F, Legrand C, Cirzi C, Federico G, Liebers R, Müller M, et al. Queuosine-modified tRNAs confer nutritional control of protein translation. EMBO J. 2018;37(18):e99777.
Silvera D, Formenti SC, Schneider RJ. Translational control in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(4):254–66.
Robichaud N, Sonenberg N, Ruggero D, Schneider RJ. Translational control in Cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019;11(7):a032896.
Okamoto M, Fujiwara M, Hori M, Okada K, Yazama F, Konishi H, et al. tRNA modifying enzymes, NSUN2 and METTL1, determine sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in HeLa cells. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(9):e1004639.
Lewinska A, Adamczyk-Grochala J, Kwasniewicz E, Deregowska A, Semik E, Zabek T, et al. Reduced levels of methyltransferase DNMT2 sensitize human fibroblasts to oxidative stress and DNA damage that is accompanied by changes in proliferation-related miRNA expression. Redox Biol. 2018;14:20–34.
Pelicano H, Carney D, Huang P. ROS stress in cancer cells and therapeutic implications. Drug Resist Updat Rev Comment Antimicrob Anticancer Chemother. 2004;7(2):97–110.
El Hassouni B, Sarkisjan D, Vos JC, Giovannetti E, Peters GJ. Targeting the ribosome biogenesis key molecule fibrillarin to avoid chemoresistance. Curr Med Chem. 2018;26 [cited 2019 Nov 13].
Yuan S, Wu Y, Wang Y, Chen J, Chu L. An Oncolytic adenovirus expressing SNORD44 and GAS5 exhibits antitumor effect in colorectal Cancer cells. Hum Gene Ther. 2017;28(8):690–700.
Xu B, Ye M-H, Lv S-G, Wang Q-X, Wu M-J, Xiao B, et al. SNORD47, a box C/D snoRNA, suppresses tumorigenesis in glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8(27):43953–66.
Mannoor K, Shen J, Liao J, Liu Z, Jiang F. Small nucleolar RNA signatures of lung tumor-initiating cells. Mol Cancer. 2014;13(1):104.
Bellodi C, McMahon M, Contreras A, Juliano D, Kopmar N, Nakamura T, et al. H/ACA small RNA dysfunctions in disease reveal key roles for noncoding RNA modifications in hematopoietic stem cell differentiation. Cell Rep. 2013;3(5):1493–502.
Nachmani D, Bothmer AH, Grisendi S, Mele A, Bothmer D, Lee JD, et al. Germline NPM1 mutations lead to altered rRNA 2′-O-methylation and cause dyskeratosis congenita. Nat Genet. 2019;51(10):1518–29.
Chu J, Pelletier J. Therapeutic opportunities in eukaryotic translation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(6):a032995.
Begley U, Sosa MS, Avivar-Valderas A, Patil A, Endres L, Estrada Y, et al. A human tRNA methyltransferase 9-like protein prevents tumour growth by regulating LIN9 and HIF1-α. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5(3):366–83.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Funding
We thank the CERCA Programme / Generalitat de Catalunya for institutional support. ME is an ICREA Research Professor. Research at ME lab is supported by the Secretariat for Universities and Research of the Ministry of Business and Knowledge of the Government of Catalonia (2017SGR1080); MCIU/AEI/FEDER, UE (RTI2018–094049-B-I00 and SAF2014–55000) and Olga Torres Foundation and from Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII), co-financed by the European Development Regional Fund, ‘A way to achieve Europe’ ERDF (grant CB16/12/00312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Maxime Janin and Laia Coll-SanMartin have contributed equally to this article. All authors were involved in writing the manuscript. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All authors consent to publication.
Competing interests
ME is a consultant of Ferrer International and Quimatryx. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Janin, M., Coll-SanMartin, L. & Esteller, M. Disruption of the RNA modifications that target the ribosome translation machinery in human cancer. Mol Cancer 19, 70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01192-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01192-8