Abstract
Background
The emergence of artemisinin resistance in Southeast Asia and Plasmodium falciparum kelch13 propeller gene mutations in sub-Saharan African pose the greatest threat to global efforts to control malaria. This is a critical concern in Uganda, where artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is the first-line treatment for uncomplicated falciparum. The objective of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine (DHA–PQ) and artemether–lumefantrine (AL) for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Ugandan children.
Methods
A search of PubMed and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials for retrieving randomized controlled trials comparing the efficacy and safety of DHA–PQ and AL for treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Ugandan children was done. The search was performed up to 31 August 2020. The data extracted from eligible studies and pooled as risk ratio (RR) with a 95% confidence interval (CI), using Rev Man Software (5.4). The protocol was registered in PROSPERO, ID: CRD42020182354.
Results
Eleven trials were included in this review and two of them only included under safety outcome. Total 3798 participants were enrolled. The PCR unadjusted treatment failure was significantly lower with DHA–PQ at day 28 (RR 0.30, 95% CI 0.19–0.49; participants = 7863; studies = 5; I2 = 93%, low quality evidence) and at day 42 (RR 0.53, 95% CI 0.38–0.76; participants = 1618; studies = 4; I2 = 79%, moderate quality of evidence). The PCR adjusted treatment failure at day 42 was significantly lower with DHA–PQ treatment group (RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.28 to 0.72; participants = 1370; studies = 5, high quality of evidence), and it was below 5% in both arms at day 28 (moderate quality of evidence). AL showed a longer prophylactic effect on new infections which may last for up to 63 days (PCR-adjusted treatment failure: RR 2.04, 95% CI 1.13–3.70; participants = 1311; studies = 2, moderate quality of evidence). Compared to AL, DHA–PQ was associated with a slightly higher frequency of cough (RR 1.07, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.13; 2575 participants; six studies; high quality of evidence). In both treatment groups, the risk of recurrent parasitaemia due to possible recrudescence was less than 5% at day 28. The appearance of gametocyte between 29 and 42 days was also significantly lower in DHA–PQ than AL (RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.56; participants = 623; studies = 2; I2 = 0%).
Conclusion
Compared to AL, DHA–PQ appeared to reduce treatment failure and gametocyte carriage in Ugandan children. This may trigger DHA–PQ to become the first-line treatment option. Both treatments were safe and well-tolerated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Malaria remains the major cause of mortality and morbidity in sub-Saharan Africa. According to the 2019 World Malaria report, there were 228 million cases and 405,000 deaths due to malaria in 2018, where 93% of cases and 94% of deaths were from Africa [1,2,3]. Children aged under 5 years were at high risk of malaria infection, with 24 million children in African infected in 2018 [1]. Plasmodium falciparum was the predominant and life-threatening parasite in Africa, causing 99.7% of estimated malaria cases in Africa [3]. Uganda was found to be the home for 16 million malaria cases and 10,500 deaths in 2013 [4]. According to the country’s 2016 national Demographic Health Survey (DHS), the prevalence of malaria had not been reduced nationally and P. falciparum remains the species responsible for the vast majority of malaria cases, and the number of malaria cases was increasing in the country, except the West Nile region [5].
Uncomplicated malaria consists of symptoms of malaria and positive parasitological test (microscopy or rapid diagnostic test [RDT]), but with no sign of severe malaria [2, 6]. If it is left untreated, it progresses to severe disease [2], with early diagnosis and treatment playing a crucial role in reducing mortality and morbidity [7]. Since 2004, all malaria-endemic countries have gradually updated their treatment policy from mono-therapy to the currently recommended artemisinin-based combinations [1]. The drug combinations include short-acting artemisinin derivatives, such as artesunate, artemether, or dihydroartemisinin, in combination with long-acting drugs. The artemisinin component covers two asexual cycles and rapidly decrease parasitaemia by a factor of approximately 10,000 in each 48-h asexual cycle. It is also active against the sexual stages that facilitate forward transmission to mosquitoes. Over several weeks after treatment, the partner drug eliminates residual parasites [6].
While the anti-malarial efficacies of presently endorsed artemisinin-based combinations have been excellent in Africa [8, 9], resistance to ACT in Southeast Asia has become an emerging concern [10]. In 2009, a reduction in parasite clearance rate by 100-fold was reported in western Cambodia, exhibiting artemisinin resistance [10]. Since then, artemisinin resistance has been defined as a parasite clearance half-life of ≥ 5 h cut-off after treatment with ACT or artesunate monotherapy [11]. Slow parasite clearance signifies a “partial” resistance that is articulated only in early-ring-stage parasites [12, 13]. Late parasite clearance following treatment with artemisinins, mediated predominantly by mutations in the kelch13 (k13) gene, was detected in the Greater Mekong Sub-region and dozens of k13-propeller mutations have been detected at very low frequency in 18 countries in sub-Saharan Africa [14].
Dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine (DHA–PQ) is a promising artemisinin-based combination recently endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a potential alternative treatment for uncomplicated malaria in Africa. Several clinical trials have revealed that DHA–PQ is safe and efficacious for treatment of uncomplicated malaria [15,16,17,18], but analysis of cardiac adverse events in clinical trials showed that QTc prolongation were reported more frequently in DHA–PQ treated patients than in those treated with comparator anti-malarial [19]. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the combination therapy for adults are well documented; however, there have been inconsistencies of these potential effects in children. The emergence of artemisinin resistance in Southeast Asia and P. falciparum k13 mutations in sub-Saharan African pose the greatest threat to global efforts to control malaria [10, 11, 13, 20]. This is a critical concern in Uganda, where ACT medicines is the first-line treatment option for uncomplicated falciparum. Additionally, in Uganda and other sub-Saharan African countries, malaria-HIV co-infection is associated with an increased frequency of clinical parasitaemia, increased parasite and viral load, impaired immunity to malaria in children, and impaired anti-malarial drug efficacy [21, 22]. The potential benefits of DHA–PQ over other artemisinin-based combinations [23] make it necessary to investigate this further among children in Uganda. This systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials aimed to synthesize the evidence on the efficacy and safety of DHA–PQ versus AL for the treatment of uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in Ugandan children.
Methods
The protocol for this systematic review and meta-analysis has been registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) database, ID: CRD42020182354 [24]. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA 2015) guidelines [25] was followed to choose studies to be included in this review.
Eligibility criteria
The studies included were randomized controlled trials conducted in Uganda that evaluated the efficacy and safety of DHA–PQ versus AL for treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in children, written in English and published between 01 January 2004 to 31 August 2020. Eligible studies were identified through the PICOS format [26].
Participants
Children having uncomplicated falciparum malaria residing in Uganda, regardless of gender, were included.
Interventions
A target dose (range) of 4 (2–10) mg/kg bw per day dihydroartemisinin and 18 (16–27) mg/kg bw per day piperaquine given once a day for 3 days for adults and children weighing ≥ 25 kg. The target doses and ranges for children weighing < 25 kg are 4 (2.5–10) mg/kg bw per day dihydroartemisinin and 24 (20–32) mg/kg bw per day piperaquine once a day for 3 days.
Comparator
A total dose of 5–24 mg/kg bw of artemether and 29–144 mg/kg bw of lumefantrine. Artemether + lumefantrine is given twice a day for 3 days (total, six doses). The first two doses should, ideally, be given 8 h apart.
Outcome measures
Primary outcomes
The treatment outcome was determined according to the classification of WHO Methods and techniques for clinical trials on antimalarial drug efficacy: genotyping to identify parasite populations [27] classified as:
Early treatment failure (ETF): The development of danger signs or severe malaria on days 1, 2, or 3 in the presence of parasitaemia; or parasitaemia on day 2 higher than on day 0; or parasitaemia and axillary temperature > 37.5 °C on day three; or parasitaemia on day 3 > 20% of count on day 0 or development of danger signs, or severe malaria, after day 3 with parasitaemia; or presence of P. falciparum parasitaemia and axillary temperature > 37.5 °C on or after day 4; or presence of P. falciparum parasitaemia after day 7.
Late clinical failure (LCF): Danger signs or severe malaria in the presence of parasitaemia on any day between day 4 and day 28 (day 42) in patients who did not previously meet any of the criteria for early treatment failure; or Presence of parasitaemia on any day between day 4 and day 28 (day 42) with axillary temperature ≥ 37.5 °C in patients who did not previously meet any of the criteria for early treatment failure.
Late parasitological failure (LPF): Presence of parasitaemia on any day between day 7 and day 28 (day 42) with axillary temperature < 37.5 °C in patients who did not previously meet any of the criteria for early treatment failure or late clinical failure.
Adequate clinical and parasitological response (ACPR): Before and after Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) correction used to show the treatment success and it defined as absence of parasitaemia by the end of treatment (day 28) regardless of axillary temperature without previously meeting any of the benchmarks of early treatment failure or late clinical failure or late parasite logical failure.
PCR genotyping was used to define treatment failure corresponding to current WHO recommendations [27]. Adverse events including serious adverse events were also assessed.
PCR-unadjusted total failure (P. falciparum): Was calculated as the sum of late treatment failures and early treatment failures (without PCR adjustment). The denominator was excluding participants who did not satisfy the inclusion criteria after randomization and those outcomes not available (for example, those who were lost to follow-up, withdrew consent, other species infection, took another anti-malarial, or failed to complete treatment).
PCR-adjusted total failure (P. falciparum): Was calculated as the sum of early treatment failures plus late treatment failures due to PCR-confirmed recrudescence. Participants with indeterminate PCR results, missing PCR results or PCR-confirmed new infections were measured to be involuntary withdrawals and excluded them from the calculation. The denominator excludes participants who did not satisfy the inclusion criteria after randomization, participants with (falciparum reinfection, other species mixed with falciparum reinfection, and undetermined or missing PCR) and those participants for whom an outcome was not available (for example, those who were lost to follow-up, withdrew consent, Other species infection, took another anti-malarial, or failed to complete treatment).
Secondary outcomes
Fever clearance: The proportion of patients febrile on each day within 3 days.
Parasite clearance: The proportion of patients clear of parasites on each day within 3 days,
Gametocyte carriage at Baseline and Day 14 or 28 or 42, and
Change in serum hemoglobin level from baseline (minimum 28 days and 42 days follow-up) were also evaluated.
Search strategy
A computerized systematic search method was used to search for articles from PubMed and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL). The search was limited to human studies and published in English language until 31 August 2020. Additionally, we searched ClinicalTrials.gov and the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to search and assess ongoing or unpublished trials.
The search strategies in PubMed for the MeSH terms and text words was 'uncomplicated malaria in children' [MeSH Terms] OR 'uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children' [MeSH Terms] OR 'falciparum malaria in children' [MeSH Terms] OR 'asymptomatic malaria in children' [MeSH Terms] AND 'artemisinin based combination therapy' [MeSH Terms] OR 'artemisinin' [MeSH Terms] OR 'artemether lumefantrine' [MeSH Terms] OR 'coartem' [MeSH Terms] OR 'dihydroartemisinin piperaquine' [MeSH Terms] OR 'Duocotecxin' [MeSH Terms] OR 'Eurartesim' [MeSH Terms] OR 'D-Artepp' [MeSH Terms])) AND 'randomized controlled trial' [MeSH Terms] OR 'controlled clinical trial' [MeSH Terms] OR 'randomized' [MeSH Terms] OR 'drug therapy'[MeSH Terms] OR 'trial' [MeSH Terms] OR 'groups' [MeSH Terms] OR 'humans' [MeSH Terms]).
Study selection, data collection, and data analysis
The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [28], the RevMan 5.4 software, and the EndNote X7 were used for data management and analysis. Two authors independently reviewed the results and disagreements resolved through discussion. When clarification was necessary, the trial authors were contacted.
Data extraction and management
The title and abstract were produced from the electronic search and independently screened by two authors based on RCTs that were assessed human falciparum malaria. The information collected were trial characteristics including methods, participants, interventions, and outcomes as well as data on dose and drug ratios of the combinations. Relevant information such as title, name of the journal, year of publication, publication status, study design, study setting, follow-up period, sample size, funding source, baseline characteristics of study subjects, fever clearance, parasite clearance, treatment failure, and gametocyte carriage were extracted from each article using a structured data extraction format adapted from Cochrane. The number of participants randomized and the number analysed in each treatment group for each outcome were also captured. Two authors independently extracted the data and cross-checked. For dichotomous outcomes, the number of participants experiencing the event and the number of participants in each treatment group were documented. For continuous outcomes, the arithmetic means and standard deviations for each treatment group collectively with the numbers of participants in each group were extracted.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
The risk of bias for each trial was evaluated by two authors independently using the Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing the 'Risk of bias' [26]. The risks were classified as high risk, unclear risk, and low risk.
Measures of treatment effect
The main outcomes in this review were total treatment failure at days 28, 42, and 63; PCR-adjusted and PCR unadjusted. Dichotomous data were combined and presented using risk ratios. Continuous data were summarized by arithmetic means and standard deviations, and then data were combined using mean differences. Risk ratios and mean differences were accompanied by 95% CIs. In the forest plot, the upper and the bottom tips of the diamond (the centre of the diamond) represents point estimate and the left and right tips of the diamond represents confidence interval. Also, the treatment arm is on the left side and the one in the right side is comparator arm.
Assessment of heterogeneity
Heterogeneity among trials was assessed by inspecting the forest plots (to detect overlapping CI) and the Cochrane Q and I2 statistic were used to measure heterogeneity among the trials in each analysis, the Chi2 test with a P < 0.10 to indicate statistical significance was used, and the results were interpreted following Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.0, Chapter 10: Analyzing data and undertaking meta-analyses [29]. When substantial heterogeneity (I2 > 50%) was identified, it was reported, and explored the possible causes by subgroup analyses.
Data synthesis
The meta-analyses were done consistent with the recommendations of Cochrane [28]. To aid interpretation, included trials were given identity codes including the first author and the year of publication. Trials were enumerated in forest plots in chronological order of the year the trials were published. A random-effects model was used, as trials were done by different researchers, operating independently, and it could be implausible that all the trials had functionally equivalent, with a common effect estimate.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
The potential sources of heterogeneity were investigated through the following subgroup analyses: the known studies with HIV negative participants were compared to studies with both HIV negative and positive participants in the overall assessment because HIV infection has an effect of parasite clearance [30].
Sensitivity analysis
Studies only with low risk of bias were included and to assess the small study effect, the fixed-effect and random-effect estimates of the intervention were compared.
Quality of evidence
Quality of evidence was assessed using GRADE criteria and the GRADE pro software [31]. The results were presented in a ‘Summary of Findings’ table. Randomized trials are initially categorized as high quality but downgraded after assessment of five criteria [32]. The levels of evidence were defined as 'high', 'moderate', 'low', or 'very low'. The recommendations of Section 8.5 and Chapter 13 of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions was followed [33]. The imprecision was judged based on the optimal information size criteria and CI [34].
Results
Search results
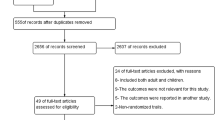
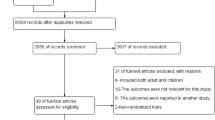
A total of 488 trials through the databases were searched, of which 52 full-text trials for eligibility were assessed and found 10 of them fulfilled the inclusion criteria for meta-analysis and an additional one for qualitative analysis (Fig. 1).
Study characteristics
In this review, 11 trials were included, which enrolled 3981 participants with uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria were included in this review (Table 1).
Methodological quality and risk of bias
The 'Risk of bias' assessments were summarized in Fig. 2.
Effect of interventions
Treatment failure
PCR-unadjusted total failure at day 28
At day 28, PCR PCR unadjusted treatment failures in five studies [30, 35,36,37,38] was significantly lower for participants treated with DHA–PQ than for those treated with AL (RR 0.30, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.49; participants = 7863; studies = 5; I2 = 93%, Fig. 3). There was considerable heterogeneity between the studies. To investigate the cause of heterogeneity, the sub-group analyses have done based on the HIV status of the participants in the included studies.
At day 28, in two studies with HIV negative participants, the PCR unadjusted treatment failures was significantly lower for participants treated with DHA–PQ than those treated with AL (RR 0.52, 95% CI 0.39 to 0.70; participants = 949; studies = 2; I2 = 25%, Fig. 3).
Consistently, in three studies (participants = 6914; [30, 35, 38]) with both HIV negative and positive participants, the PCR unadjusted treatment failures was significantly lower for participants treated with DHA–PQ than those treated with AL. The results were highly heterogeneous (Heterogeneity: Tau2 = 0.06; Chi2 = 9.11, df = 2 (P = 0.01); I2 = 78%). Relative risks for the individual studies were: 0.33 (95% confidence interval 0.23 to 0.46, [35]); 0.17 (95% confidence interval 0.12 to 0.24, [30]); and 0.20 (95% confidence interval 0.18 to 0.22, [38]). Hence, statistically significant difference was found between the two subgroups (Chi2 = 14.52, df = 1 (P = 0.0001), I2 = 93.1%, Fig. 3).
PCR-adjusted total failure at day 28
At day 28, the PCR adjusted treatment failures was below 5% in both treatment arms without significant difference between the two treatment groups (RR 0.70, 95% CI 0.40 to 1.23; participants = 2411; studies = 5; I2 = 0%, Fig. 4).
PCR-unadjusted total failure at day 42
At day 42, PCR unadjusted treatment failure in four trails [35, 39,40,41] (participants = 1618) were significantly lower in the DHA–PQ group than the AL group (RR 0.53, 95% CI 0.38 to 0.76; participants = 1618; studies = 4; I2 = 79%). The result had considerable heterogeneity and we couldn't pool the result. The PCR unadjusted treatment failures for the individual studies were: 0.79 (95% confidence interval 0.65, 0.97 [39]); 0.39 (95% confidence interval 0.24 to 0.63 [40]); 0.36 (95% confidence interval 0.21, 0.63, [35]) and 0.56 (95% confidence interval 0.44 to 0.70, [41], Fig. 5).
PCR-adjusted total failure at day 42
The overall PCR adjusted treatment failures was lower for participants treated with DHA–PQ than those treated with AL (RR 0.45, 95% CI 0.28 to 0.72; participants = 1370; studies = 5; I2 = 3%, Fig. 6).
PCR-unadjusted total failure at day 63
The PCR unadjusted treatment failure was not statistically different between the two treatment groups (RR 0.59, 95% CI 0.25 to 1.37; participants = 1514; studies = 2; I2 = 96%). The result had considerable heterogeneity. It is more useful to consider individual trial results. At day 63, in one study [36] the PCR unadjusted treatment failure in DHA–PQ arm was significantly lower than those treated with AL RR 0.38 (95% confidence interval 0.28 to 0.52) and although, no significant difference was found between the two treatment group in the other trial [35] 0.88 (95% confidence interval 0.77 to 1.02, Additional file 1: S1).
PCR-adjusted total failure at day 63
The pooled PCR adjusted treatment failure in participants treated with AL was significantly lower than those who are treated with DHA–PQ (RR 2.04, 95% CI 1.13 to 3.70; participants = 1311; studies = 2; I2 = 0%, Additional file 2: S2).
Fever clearance
Fever clearance at Day 1
Six studies with 2978 were reported in this outcome, but the pooled result showed considerable heterogeneity between studies. The result of studies was heterogeneous (RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.01; participants = 2978; studies = 6; I2 = 78%). Four trials with HIV negative participants, in two studies [40, 41] the patients treated with DHA–PQ experienced high resolution of fever than AL (RR 0.81 95% CI 0.70 to 0.95 and RR 0.90 95% CI 0.82 to 1.00) and one study [39] no significant difference was found between the two intervention groups (RR 1.00 95% CI 0.87 to 1.14). However, another study [37] reported that the patients treated with AL experienced high resolution of fever (RR 1.67 95% CI 1.08 to 2.58), Additional file 3: S3).
Two studies [30, 35] with both HIV negative and positive participants reported that more participants from DHA–PQ treatment group experienced fast resolution of fever (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.57 to 0.88; participants = 1441; studies = 2; I2 = 51%, Fig. 9). There was statistically significant difference found between the two subgroups (Chi2 = 4.91, df = 1 (P = 0.03), I2 = 79.6%).
Fever clearance at Day 2
By day 2 in five trials, the patients experienced high resolution of fever without a statistically significant difference between the two groups, and in one trial patients treated with DHA–PQ experienced high resolution of fever [37]. The results were highly heterogeneous (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.61 to 1.16; participants = 2978; studies = 6; I2 = 69%). Relative risks for the individual studies were: 0.35 (95% confidence interval 0.21, 0.59 [37]); 0.91 (95% confidence interval 0.69, 1.20 [39]); 1.10 (95% confidence interval 0.74, 1.63 [40]); 0.70 (95% confidence interval 0.34, 1.41 [35]); 1.62 (95% confidence interval 0.66, 3.97 [30]); and 0.99 (95% confidence interval 0.74, 1.32, [41], participants = 2978; studies = 6, Additional file 4: S4).
Fever clearance at Day 3
The prevalence of fever was similar over 3 days of follow up in both treatment groups in two trials [37, 39]. The overall pooled result was (RR 1.01, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.27; participants = 2978; studies = 6; I2 = 0%, Additional file 5: S5).
Parasite clearance
The percentage of patients with parasitaemia at day one in two trials was significantly lower in the DHA–PQ treatment group than AL (RR 0.85, 95% CI 0.75 to 0.97; participants = 1369; studies = 2; I2 = 66%, Additional file 6: S6). However, at day 2 and 3, the overall result shows that the percentage of patients with parasitaemia was lower in both treatment groups without statistically significant difference (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.47 to 1.01; participants = 2978; studies = 6; I2 = 21, Additional file 6: S6) and (RR 1.46, 95% CI 0.40 to 5.36; participants = 2978; studies = 6; I2 = 0%, Additional file 6: S6).
Gametocytes
Gametocyte carriage at baseline
There was no significant difference in the appearance of gametocytes at baseline between two treatment groups (RR 0.71, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.10; participants = 2083; studies = 5; I2 = 61%, Additional file 7: S7).
Gametocyte carriage
The overall gametocyte appearance at day 1–14 and 29–42 was significantly lower in patients treated with AL than DHA–PQ (RR 3.82, 95% CI 1.27 to 11.47; participants = 1484; studies = 4; I2 = 0%, Fig. 7) and (RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.56; participants = 623; studies = 2; I2 = 0%, Fig. 7). However, at day 15–28, the appearance of gametocyte carriage was lower in both treatment groups and there was no significant difference in the appearance of gametocyte in both groups (RR 0.25, 95% CI 0.04 to 1.69; participants = 1474; studies = 4; I2 = 36%, Fig. 7) and (RR 0.43, 95% CI 0.11 to 1.65; participants = 599; studies = 1; I2 = 0%, Fig. 7).
Anaemia
Mean haemoglobin (g/dL) at baseline
No significant difference was found in the mean haemoglobin (g/dL) at baseline in both treatment groups (MD 0.06, 95% CI − 0.07 to 0.18; participants = 2982; studies = 6; I2 = 0%, Additional file 8: S8).
Mean haemoglobin (g/dL) at Day 28 and 42
All five studies reported some measure of haematological recovery from baseline to day 28 in both treatment groups and no significant difference was found between the two groups in haematological recovery (Day 28, MD 0.04, 95% CI − 0.19 to 0.27; participants = 778; studies = 2; I2 = 0%, Additional file 8: S8). However, there was significant haematological recovery found among patients treated with DHA–PQ than AL at (Day 42, MD 0.35, 95% CI 0.12 to 0.59; participants = 1434; studies = 3; I2 = 35%, Additional file 8: S8).
Adverse event
Gastrointestinal
Studies reported vomiting, anorexia, and abdominal pain as an adverse event. However, no significant difference was found between the two intervention groups (RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.12; participants = 2575; studies = 6; I2 = 0%, Fig. 8), (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.83 to 1.12; participants = 2575; studies = 6; I2 = 0%, Fig. 8), and (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.64 to 1.31; participants = 574; studies = 4; I2 = 42%, Fig. 8).
Diarrhoea
Six studies reported diarrhoea as an adverse event. Diarrhoea was slightly more frequent in patients treated with DHA–PQ, but it was not statistically significant. Hence, there was no significant difference on the risk of diarrhoea in both treatment groups (RR 1.14, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.47; participants = 2575; studies = 6; I2 = 57%, high quality of evidence, Fig. 9).
In one study [42], considering 63 days of follow-up among all 837 treatments with study drugs; 415 adverse events due to cough (373 mild and 42 moderate severity), 179 adverse events due to diarrhea (168 mild, 10 moderate, and one severe), and 56 adverse events due to vomiting (all mild) were reported. Any adverse event due to cough, diarrhea, or vomiting occurred in 296 of 412 (72%) treatments with AL and 313 of 425 (74%) treatments with DHA–PQ. There were no statistically significant differences in the risks of these adverse events between the treatment arms for any time interval.
Neuropsychiatric
Studies reported headache and weakness or malaise as an adverse event and there was no significant difference between the two treatment groups (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.46 to 1.39; participants = 237; studies = 1, Fig. 9) and (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.09; participants = 2575; studies = 6; I2 = 0%, Fig. 10).
Cardiorespiratory
Six studies reported cough as an adverse event. However, compared to AL, DHA–PQ was associated with a slightly higher frequency of cough (RR 1.07, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.13; participants = 2575; studies = 6; I2 = 0%, Fig. 11). In the other hand, studies reported that coryza and pallor were also slightly more frequent in patients treated with DHA–PQ than AL, but no significant difference have found between the two treatment group (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.92 to 1.10; participants = 832; studies = 2; I2 = 0%, Fig. 11) and (RR 1.70, 95% CI 0.87 to 3.31; participants = 599; studies = 1, Fig. 11).
Musculoskeletal/dermatological
Studies reported skin rash and pruritus as an adverse event and no significant difference was found between the two treatment groups (RR 1.34, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.93; participants = 599; studies = 1; I2 = 0%, Fig. 12) and (RR 1.19, 95% CI 0.56 to 2.50; participants = 1431; studies = 3; I2 = 62%, Fig. 12).
Serious adverse event
Four studies reported 18 serious adverse events in DHA–PQ and 11 in the AL treatment group. However, the distributions of serious adverse events were not significantly different in the two treatment groups (RR 1.55, 95% CI 0.72 to 3.33; participants = 2105; studies = 4; I2 = 0%, Fig. 13). All serious adverse events were judged to be unrelated to study medications. No death has occurred in all studies. However, in one study [42] there were only five serious adverse events (two in the AL group and three in the DP group) and all were due to the development of severe anemia, which was likely a consequence of malaria and not the study drugs.
Quality of the evidence
The quality of the evidence in this review was assessed using the GRADE approach and presented the evidence in six summary of findings tables for efficacy and safety (Summary of findings for the main comparison; Additional file 9: Additional Tables).
The evidence that DHA–PQ is more effective than AL at day 28, 42, and 63 unadjusted by genotyping was of low, moderate, and very low quality of evidence. There was considerable heterogeneity between studies at day 28 and 63. In addition, DHA–PQ consistently superiority over AL at day 42 adjusted by genotyping was of high quality of evidence and both DHA–PQ and AL performed better than the WHO standard of 5% PCR-adjusted treatment failure at day 28 in all trials (moderate quality of evidence). The quality of evidence was assessed on comparative adverse effects; cough slightly more frequent in DHA–PQ arm was of high quality of evidence. Generally, the quality of evidence of safety of the two treatments ranges from low to high quality.
Discussion
Summary of findings
This systematic review and meta-analysis focused on the safety and efficacy of DHA–PQ and AL for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in children. The main finding of this meta-analysis is that the PCR unadjusted risk of recurrent falciparum parasitaemia at day 28 and 42 was significantly lower for participants treated with DHA–PQ than those treated with AL (low and moderate quality of evidence).
Early treatment failure was observed in three patients from the DHA–PQ group and 16 from the AL group had an early treatment failure in the three trials. At day 28, the PCR adjusted treatment failure was below 5% in both treatment arms without significant difference between the two treatment groups were observed (moderate quality of evidence). The PCR adjusted treatment failure day 42 was significantly lower for participants treated with DHA–PQ than those treated with AL (high quality of evidence). Nevertheless, at day 63 the PCR adjusted treatment failure in participants treated with AL was significantly lower than those who are treated with DHA–PQ (moderate quality of evidence).
The appearance of gametocyte at day 29–42 was significantly lower in patients treated with DHA–PQ than AL (moderate quality of evidence). In addition, In this review, most of the adverse events were mild or moderate severity and consistent with symptoms due to malaria. However, some adverse events like cough, anorexia, diarrhoea, and vomiting were the most common adverse events. In most studies, no significant difference was found in the proportion of study participants who experienced an adverse event of moderate and great severity between the DHA–PQ and AL treatment groups. But, cough was significantly more frequent in patients treated with DHA–PQ than AL (high quality of evidence).
Public health implications
The observed high efficacy of DHA–PQ was similar to that of other studies conducted in Africa [43, 44] and a high transmission setting in Indonesia [45]. However, in a study done in Somalia, the recurrence of parasitaemia was lower in DHA–PQ as compared to AL arm [46] and after day 3, in both treatment groups none of the participants were parasitaemic. However, Pfk13 non-synonymous mutations (R622I) with unknown impact on the parasite resistance phenotype have been seen at a very low rate.
Recent studies conducted in Mali, Somalia, Angola, and Papua New Guinea also reported that both DHA–PQ and AL were highly effective in the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria [8, 47,48,49]. Similarly, a former review also reported that in Asia and Oceania, PCR-adjusted treatment failure at day 28 was similar between treatments [23]. However, one study conducted in Cambodia–Thailand border reported high recrudescence on DHA–PQ treatment group [50] and this might be related to artemisinin resistance in the sub-region [51, 52]. The reason for the rapid occurrence of DHA–PQ resistance in this sub-region unknown; however, pre-existing circulation of parasites resistant to artemisinin or PQ in this area was probably a major mediator for their evolution to multidrug resistance. Furthermore, two studies conducted in Angola in 2013 and 2015 reported PCR adjusted cure rate of 88% in AL at one site [53, 54]. This result is lower compared to other previous studies conducted in different sub-Saharan African countries [46, 55, 56]. Despite this, those patients who were enrolled in both Angolan studies took the evening doses of AL at home without any supervision, and the higher treatment failure rate might be explained by this.
Similarly, a recent study in Rwanda reported that 42 day PCR corrected efficacy was significantly better in patients with falciparum malaria treated with DHA–PQ [57]. Hence, Studies conducted in western Kenya and Mali reported that the risk of treatment failure in both group was below 5% at day 42 [44]. For interventions such as mass drug administrations or seasonal malaria prevention [58], an ACT which protects against subsequent infections, such as DHA–PQ [59], could play a crucial role.
In this review several studies using microscopic detection of gametocytes have shown no difference [17, 56, 60,61,62] and an increased risk of gametocyte detection after treatment with DHA–PQ [36, 43, 63]. Consequently, membrane-feeding experiments have confirmed that both microscopic and sub-patent gametocytaemia result in infectivity to mosquitoes, with a positive association between gametocyte density and mosquito infection rates [64]. Increasing age and recurrent parasitaemia were associated with an increased risk of first detection of gametocytes after therapy [65], but the estimated mean duration of gametocytaemia for children below 5, children from 5 to 9 and children 10 years and above was 9.4, 7.8, and 4.1 days, respectively [66]. Furthermore, one previous study have reported that prolonged gametocytaemia after treatment could be an early sign of the occurrence of drug resistance, which is also the case in the emergence of recrudescent infections [67].
In this systematic review, significant haematological recovery from the baseline has been observed among patients treated with AL than DHA–PQ at day 42. Recent studies in Africa have reported that there was significant haematological recovery from the baseline in both treatment groups [44, 56]. One study in Tanzania reported a significant increase in serum haemoglobin level in AL treatment arm at day 28 than DHA–PQ [55]. However, patients enrolled in one site had relatively high haemoglobin at baseline and maintained throughout the follow-up period. This might be related to the difference in nutritional status and other health conditions associated with anaemia, such as helminthic infections and concurrent infections [68,69,70]. Age difference could also be the reason for this [55]. Studies done elsewhere in Africa [55, 71, 72] reported that improvements in haemoglobin during follow-up could suggest that malaria might be a major causing factor to anaemia and the low haemoglobin levels at recruitment.
A recent study in Papua New Guinea reported a high frequency of cough without significant difference between the two treatment groups [47]. A former study conducted in Zambia reported a high frequency of cough in DHA–PQ group than AL [18]. A study on AL and DHA–PQ safety and tolerability reported cough, diarrhoea, vomiting, and anaemia as the most commonly reported adverse events [42]. In a review done in Asia, gastrointestinal complaints were the most common adverse events associated with DHA–PQ, with no evidence of severe drug toxicity [73] and recent study in Africa also reported vomiting as a common adverse event in patients treated with DHA–PQ [74]. In breastfeeding infants DHA–PQ has previously been linked to an increased risk of vomiting [75]. The mechanism accountable for the increased risk of early vomiting among breastfeeding participants treated with DHA–PQ is not known. However, the temporal relationship suggests that the susceptibility of gastric mucosa of breastfed infants could be related to the pro-emetic effect of piperaquine than that in weaned infants [75]. To determine whether the co-administered milk may also affect this interaction further assessment might be needed. However, the absence of effect with AL implies that the mechanism is given to DHA–PQ, most likely piperaquine.
In this systematic review, four studies reported 21 serious adverse events in DHA–PQ and 13 in the AL treatment group. However, the distributions of serious adverse events were not significantly different in the two treatment groups. All serious adverse events were not related to study medications. No death has occurred in any of the studies. This might be justified by the fact that these studies were conducted among participants with uncomplicated malaria rather than the severe form which can lead to death.
Treatment failure could be occurred due to the drug’s ineffectiveness or development of resistance, as it may be due to insufficient drug levels [65]. Furthermore, treatment failure may occur due to resistance, sub-therapeutic levels that may occur due to non-adherence, or inadequate absorption. To identify risk factors for treatment failure further studies should be conducted. Also, further trials with detailed descriptions of patients’ characteristics with recrudescence are also very important. Besides, to investigate the association of AL and DHA–PQ resistance in the places where P. falciparum is endemic molecular surveillance may also play an important role in detecting genetic markers.
Study limitations
The study has some limitations. A majority of included studies were conducted in Tororo District Eastern region Uganda where malaria transmission intensity is high. The result of this study might not be representative of other regions in Uganda where malaria transmission intensity is low and moderate. Most studies reported treatment failure at 28 and 42 days, this review might not provide strong evidence about the long-term post-treatment prophylactic effect of the two drugs.
Conclusion
This systematic review provides comprehensive evidence about the treatment efficacy and safety of ACT in children in an area of malaria-endemic areas in Uganda. The overall parasite clearance, drug efficacy, and safety were good enough. Compared to AL, DHA–PQ appeared to reduce treatment failure and gametocyte carriage in Ugandan children. This may trigger DHA–PQ to become the first-line treatment option. Both treatments were safe and tolerable. As ACT resistance is emerging in different parts of the world, continuous studies that measure the efficacy of DHA–PQ and AL with 42 and 63 days follow-up are needed.
Availability of data and materials
All relevant data are within the manuscript and its additional information files.
Abbreviations
- ACT:
-
Artemisinin-based combination therapy
- ACPR:
-
Adequate clinical and parasitological response
- AL:
-
Artemether–lumefantrine
- BW:
-
Body weight
- CENTRAL:
-
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CM:
-
Complicated malaria
- DHA–PQ:
-
Dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine
- DHS:
-
Demographic Health Survey
- ETF:
-
Early treatment failure
- GADE:
-
Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations
- Hgb:
-
Haemoglobin
- LCT:
-
Late clinical failure
- LPF:
-
Late parasitological failure
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PICO:
-
Population, intervention, comparison, and outcome
- PRISMA:
-
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- RDT:
-
Rapid diagnostic test
- SAE:
-
Serious adverse event
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
WHO. World malaria report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2019. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2019/en/.
WHO. Guidelines for treatment of malaria. 3rd edn. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2015. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241549127/en/.
WHO. Malaria fact sheets. Geneva: World Health Ogranization. 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malaria.
Ministry of Health Republic of Uganda. National Malaria Control Programme. https://www.health.go.ug/programs/national-malaria-control-program/.
President’s malaria initiative. Uganda, Malaria Operational Plan FY 2018. Kampala. 2018. https://www.pmi.gov/where-we-work/uganda.
WHO. World MALARIA Report 2014. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2014. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world_malaria_report_2014/en.
WHO. Global Malaria Programme. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK254223/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK254223.pdf.
Plucinski MM, Dimbu PR, Macaia AP, Ferreira CM, Samutondo C, Quivinja J, et al. Efficacy of artemether–lumefantrine, artesunate–amodiaquine, and dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Angola, 2015. Malar J. 2017;16:62.
Davlantes E, Dimbu PR, Ferreira CM, Florinda Joao M, Pode D, Félix J, et al. Efficacy and safety of artemether–lumefantrine, artesunate–amodiaquine, and dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in three provinces in Angola, 2017. Malar J. 2018;17:144.
Dondorp AM, Nosten F, Yi P, Das D, Phyo AP, Tarning J, et al. Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:455–67.
Ashley EA, Dhorda M, Fairhurst RM, Amaratunga C, Lim P, Suon S, et al. Spread of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:411–23.
Dogovski C, Xie SC, Burgio G, Bridgford J, Mok S, McCaw JM, et al. Targeting the cell stress response of Plasmodium falciparum to overcome artemisinin resistance. PLoS Biol. 2015;13:e1002132.
Witkowski B, Khim N, Chim P, Kim S, Ke S, Kloeung N, et al. Reduced artemisinin susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum ring stages in western Cambodia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:914–23.
WHO. Artemisinin and artemisinin-based combination therapy resistance. Status report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/artemisinin-resistance-april2017/en/.
Agarwal A, McMorrow M, Onyango P, Otieno K, Odero C, Williamson J, et al. A randomized trial of artemether-lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine in the treatment of uncomplicated malaria among children in western Kenya. Malar J. 2013;12:254.
Ebenebe JC, Ntadom G, Ambe J, Wammanda R, Jiya N, Finomo F, et al. Efficacy of artemisinin-based combination treatments of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in under-five-year-old Nigerian children ten years following adoption as first-line antimalarials. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;99:649–64.
Grandesso F, Guindo O, Woi Messe L, Makarimi R, Traore A, Dama S, et al. Efficacy of artesunate-amodiaquine, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine and artemether-lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Maradi, Niger. Malar J. 2018;17:52.
Nambozi M, Van Geertruyden JP, Hachizovu S, Chaponda M, Mukwamataba D, Mulenga M, et al. Safety and efficacy of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodiumfalciparum malaria in Zambian children. Malar J. 2011;10:50.
European Medicines Agency. Eurartesim (dihydroartemisinin/piperaquine) 20 mg/160 mg and 40 mg/320 mg film-coated tablets: EU summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/eurartesim-epar-product-information_en.pdf.
Amaratunga C, Lim P, Suon S, Sreng S, Mao S, Sopha C, et al. Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Cambodia: a multisite prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:357–65.
Kwenti TE. Malaria and HIV coinfection in sub-Saharan Africa: prevalence, impact, and treatment strategies. Res Rep Trop Med. 2018;9:123–36.
Katrak S, Day N, Ssemmondo E, Kwarisiima D, Midekisa A, Greenhouse B, et al. Community-wide prevalence of malaria parasitemia in HIV-infected and uninfected populations in a high-transmission setting in Uganda. J Infect Dis. 2016;213:1971–8.
Zani B, Gathu M, Donegan S, Olliaro PL, Sinclair D. Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treating uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014:CD010927.
Assefa D, Zeleke ED. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of dihydroartemisinin piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in infants and children in Uganda, 2020. https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42020182354.
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;350:g7647.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions; 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org.
WHO. Methods for surveillance of antimalarial drug efficacy. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241597531/en/.
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al., editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Muhindo MK, Kakuru A, Jagannathan P, Talisuna A, Osilo E, Orukan F, et al. Early parasite clearance following artemisinin-based combination therapy among Ugandan children with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Malar J. 2014;13:32.
Cochrane Community. GRADEproGDT. McMasterUniversity (developed by Evidence Prime). 2020. https://gradepro.org/.
Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A. Introduction to GRADE handbook (Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach). 2013. https://gradepro.org.
Higgins JPT, Savovic J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions, version 6.0 (updated July 2019). Cochrane. 2019. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence–imprecision. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:1283–93.
Arinaitwe E, Sandison TG, Wanzira H, Kakuru A, Homsy J, Kalamya J, et al. Artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for falciparum malaria: a longitudinal, randomized trial in young Ugandan children. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49:1629–37.
Four Artemisinin-Based Combinations Study Group. A head-to-head comparison of four artemisinin-based combinations for treating uncomplicated malaria in African children: a randomized trial. PLoS Med. 2011;8:e1001119.
Yeka A, Tibenderana J, Achan J, D’Alessandro U, Talisuna AO. Efficacy of quinine, artemether-lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine as rescue treatment for uncomplicated malaria in Ugandan children. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e53772.
Wanzira H, Kakuru A, Arinaitwe E, Bigira V, Muhindo MK, Conrad M, et al. Longitudinal outcomes in a cohort of Ugandan children randomized to artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of malaria. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:509–16.
Kamya MR, Yeka A, Bukirwa H, Lugemwa M, Rwakimari JB, Staedke SG, et al. Artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treatment of malaria: a randomized trial. PLoS Clin Trials. 2007;2:e20.
Yeka A, Dorsey G, Kamya MR, Talisuna A, Lugemwa M, Rwakimari JB, et al. Artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treating uncomplicated malaria: a randomized trial to guide policy in Uganda. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e2390.
Yeka A, Wallender E, Mulebeke R, Kibuuka A, Kigozi R, Bosco A, et al. Comparative efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in Ugandan children. J Infect Dis. 2019;219:1112–20.
Katrak S, Gasasira A, Arinaitwe E, Kakuru A, Wanzira H, Bigira V, et al. Safety and tolerability of artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for malaria in young HIV-infected and uninfected children. Malar J. 2009;8:272.
Onyamboko MA, Fanello CI, Wongsaen K, Tarning J, Cheah PY, Tshefu KA, et al. Randomized comparison of the efficacies and tolerabilities of three artemisinin-based combination treatments for children with acute Plasmodium falciparum malaria in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58:5528–36.
Dama S, Niangaly H, Djimde M, Sagara I, Guindo CO, Zeguime A, et al. A randomized trial of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Mali. Malar J. 2018;17:347.
Ratcliff A, Siswantoro H, Kenangalem E, Maristela R, Wuwung RM, Laihad F, et al. Two fixed-dose artemisinin combinations for drug-resistant falciparum and vivax malaria in Papua, Indonesia: an open-label randomised comparison. Lancet. 2007;369:757–65.
Warsame M, Hassan AM, Hassan AH, Jibril AM, Khim N, Arale AM, et al. High therapeutic efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Somalia. Malar J. 2019;18:231.
Tavul L, Hetzel MW, Teliki A, Walsh D, Kiniboro B, Rare L, et al. Efficacy of artemether–lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in Papua New Guinea. Malar J. 2018;17:350.
Dama S, Niangaly H, Djimde M, Sagara I, Guindo CO, Zeguime A, et al. A randomized trial of dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine versus artemether–lumefantrine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Mali. Malar J. 2018;17:347.
Warsame M, Hassan AM, Hassan AH, Jibril AM, Khim N, Arale AM, et al. High therapeutic efficacy of artemether–lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Somalia. Malar J. 2019;18:231.
Song J, Socheat D, Tan B, Seila S, Xu Y, Ou F, et al. Randomized trials of artemisinin-piperaquine, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine phosphate and artemether-lumefantrine for the treatment of multi-drug resistant falciparum malaria in Cambodia-Thailand border area. Malar J. 2011;10:231.
Imwong M, Hien TT, Thuy-Nhien NT, Dondorp AM, White NJ. Spread of a single multidrug resistant malaria parasite lineage (PfPailin) to Vietnam. Lancet Infect Dis. 2017;17:1022–3.
Phuc BQ, Rasmussen C, Duong TT, Dong LT, Loi MA, Ménard D, et al. Treatment failure of dihydroartemisinin/piperaquine for Plasmodium falciparum malaria, Vietnam. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:715–7.
Plucinski MM, Dimbu PR, Macaia AP, Ferreira CM, Samutondo C, Quivinja J, et al. Efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine, artesunate-amodiaquine, and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Angola, 2015. Malar J. 2017;16:62.
Plucinski MM, Talundzic E, Morton L, Dimbu PR, Macaia AP, Fortes F, et al. Efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treatment of uncomplicated malaria in children in Zaire and Uige Provinces, angola. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:437–43.
Mandara CI, Kavishe RA, Gesase S, Mghamba J, Ngadaya E, Mmbuji P, et al. High efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Muheza and Kigoma Districts, Tanzania. Malar J. 2018;17:261.
Ursing J, Rombo L, Rodrigues A, Kofoed PE. Artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children aged less than 15 years in Guinea-Bissau—an open-label non-inferiority randomised clinical trial. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0161495.
Uwimana A, Penkunas MJ, Nisingizwe MP, Warsame M, Umulisa N, Uyizeye D, et al. Efficacy of artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria among children in Rwanda: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2019;113:312–9.
WHO. Policy recommendation: seasonal malaria chemoprevention (SMC) for Plasmodium falciparum malaria control in highly seasonal transmission areas of the Sahel sub-region in Africa. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2012. https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/who_smc_policy_recommendation/en/.
Bretscher MT, Griffin JT, Hugo P, Baker M, Ghani A, Okell L. A comparison of the duration of post-treatment protection of artemether-lumefantrine, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine and artesunate-amodiaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated malaria. Malar J. 2014;13:P19.
Zongo I, Dorsey G, Rouamba N, Dokomajilar C, Sere Y, Rosenthal PJ, et al. Randomized comparison of amodiaquine plus sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine, artemether-lumefantrine, and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Burkina Faso. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:1453–61.
Yavo W, Faye B, Kuete T, Djohan V, Oga SA, Kassi RR, et al. Multicentric assessment of the efficacy and tolerability of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine compared to artemether-lumefantrine in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Malar J. 2011;10:198.
Omondi P, Burugu M, Matoke-Muhia D, Too E, Nambati EA, Chege W, et al. Gametocyte clearance in children, from western Kenya, with uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria after artemether-lumefantrine or dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine treatment. Malar J. 2019;18:398.
WWARN Gametocyte Study Group. Gametocyte carriage in uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria following treatment with artemisinin combination therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. BMC Med. 2016;14:79.
Ouédraogo AL, Bousema T, Schneider P, de Vlas SJ, Ilboudo-Sanogo E, Cuzin-Ouattara N, et al. Substantial contribution of submicroscopical Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte carriage to the infectious reservoir in an area of seasonal transmission. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e8410.
Kakuru A, Jagannathan P, Arinaitwe E, Wanzira H, Muhindo M, Bigira V, et al. The effects of ACT treatment and TS prophylaxis on Plasmodium falciparum gametocytemia in a cohort of young Ugandan children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013;88:736–43.
Bousema JT, Gouagna LC, Drakeley CJ, Meutstege AM, Okech BA, Akim IN, et al. Plasmodium falciparum gametocyte carriage in asymptomatic children in western Kenya. Malar J. 2004;3:18.
Delves MJ, Ruecker A, Straschil U, Lelievre J, Marques S, Lopez-Barragan MJ, et al. Male and female Plasmodium falciparum mature gametocytes show different responses to antimalarial drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:3268–74.
Ngui R, Lim YA, Chong Kin L, Sek Chuen C, Jaffar S. Association between anaemia, iron deficiency anaemia, neglected parasitic infections and socioeconomic factors in rural children of West Malaysia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6:e1550.
Magalhaes RJ, Clements AC. Mapping the risk of anaemia in preschool-age children: the contribution of malnutrition, malaria, and helminth infections in West Africa. PLoS Med. 2011;8:e1000438.
Sousa-Figueiredo JC, Gamboa D, Pedro JM, Fancony C, Langa AJ, Magalhaes RJ, et al. Epidemiology of malaria, schistosomiasis, geohelminths, anemia and malnutrition in the context of a demographic surveillance system in northern Angola. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e33189.
Shayo A, Buza J, Ishengoma DS. Monitoring of efficacy and safety of artemisinin-based anti-malarials for treatment of uncomplicated malaria: a review of evidence of implementation of anti-malarial therapeutic efficacy trials in Tanzania. Malar J. 2015;14:135.
Ndiaye JL, Faye B, Gueye A, Tine R, Ndiaye D, Tchania C, et al. Repeated treatment of recurrent uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Senegal with fixed-dose artesunate plus amodiaquine versus fixed-dose artemether plus lumefantrine: a randomized, open-label trial. Malar J. 2011;10:237.
Myint HY, Ashley EA, Day NP, Nosten F, White NJ. Efficacy and safety of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2007;101:858–66.
Davlantes E, Dimbu PR, Ferreira CM, Florinda Joao M, Pode D, Felix J, et al. Efficacy and safety of artemether-lumefantrine, artesunate-amodiaquine, and dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in three provinces in Angola, 2017. Malar J. 2018;17:144.
Creek D, Bigira V, Arinaitwe E, Wanzira H, Kakuru A, Tappero J, et al. Increased risk of early vomiting among infants and young children treated with dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine compared with artemether-lumefantrine for uncomplicated malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010;83:873–5.
Bassat Q, Mulenga M, Tinto H, Piola P, Borrmann S, Menendez C, et al. Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine and artemether-lumefantrine for treating uncomplicated malaria in African children: a randomised, non-inferiority trial. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e7871.
Kakuru A, Achan J, Muhindo MK, Ikilezi G, Arinaitwe E, Mwangwa F, et al. Artemisinin-based combination therapies are efficacious and safe for treatment of uncomplicated malaria in HIV-infected Ugandan children. Clin Infect Dis. 2014;59:446–53.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the Center for Innovative Drug Development and Therapeutic Trials for Africa (CDT-Africa), College of Health Sciences, Addis Ababa University, for supporting the study.
Funding
This review did not receive any specific grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DGA and EDZ developed the protocol, reviewed the reference list, extracted data, and entered it into RevMan 5.4. DGA conducted the analyses, constructed summary of findings tables, and evaluated the quality of evidence using the GRADE approach. DB, EDZ, HAT, EG, MJ (second authors), and TM were responsible for the quality assessment and reviewing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
We declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: S1.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: PCR-unadjusted treatment failures at day 63.
Additional file 2: S2.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: PCR-adjusted treatment failures at day 63.
Additional file 3: S3.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: Fever clearances on day 1.
Additional file 4: S4.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: Fever clearances on day 2.
Additional file 5: S5.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: Fever clearances on day 3.
Additional file 6: S6.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: Parasite clearances.
Additional file 7: S7.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: Gametocyte carriages at baseline.
Additional file 8: S8.
Forest plot of comparison: Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine versus artemether-lumefantrine, outcome: Anemia.
Additional file 9.
Additional Tables: GRADE Summary of finding tables.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Assefa, D.G., Zeleke, E.D., Bekele, D. et al. Efficacy and safety of dihydroartemisinin–piperaquine versus artemether–lumefantrine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Ugandan children: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Malar J 20, 174 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-021-03711-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-021-03711-4