Abstract
Background
Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP) is the only anti-malarial drug formulation approved for intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy (IPTp). However, mutations in the Plasmodium falciparum dhfr (Pfdhfr) and dhps (Pfdhps) genes confer resistance to pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine, respectively. Here, the frequencies of SP resistance-associated mutations from 2005 to 2018 were compared in samples from Kenyan children with malaria residing in a holoendemic transmission region.
Methods
Partial sequences of the Pfdhfr and Pfdhps genes were amplified and sequenced from samples collected in 2005 (n = 81), 2010 (n = 95), 2017 (n = 43), and 2018 (n = 55). The frequency of known mutations conferring resistance to pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine were estimated and compared. Since artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) is the current first-line treatment for malaria, the presence of mutations in the propeller domain of P. falciparum kelch13 gene (Pfk13) linked to ACT-delayed parasite clearance was studied in the 2017/18 samples.
Results
Among other changes, the point mutation of Pfdhps S436H increased in frequency from undetectable in 2005 to 28% in 2017/18. Triple Pfdhfr mutant allele (CIRNI) increased in frequency from 84% in 2005 to 95% in 2017/18, while the frequency of Pfdhfr double mutant alleles declined (allele CICNI from 29% in 2005 to 6% in 2017/18, and CNRNI from 9% in 2005 to undetectable in 2010 and 2017/18). Thus, a multilocus Pfdhfr/Pfdhps genotype with six mutations (HGEAA/CIRNI), including Pfdhps S436H, increased in frequency from 2010 to 2017/18. Although none of the mutations associated with ACT-delayed parasite clearance was observed, the Pfk13 mutation A578S, the most widespread Pfk13 SNP found in Africa, was detected in low frequency (2.04%).
Conclusions
There were changes in SP resistance mutant allele frequencies, including an increase in the Pfdhps S436H. Although these patterns seem consistent with directional selection due to drug pressure, there is a lack of information to determine the actual cause of such changes. These results suggest incorporating molecular surveillance of Pfdhfr/Pfdhps mutations in the context of SP efficacy studies for intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy (IPTp).
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Despite a worldwide decline, malaria remains a significant and resilient global health problem. Approximately 228 million cases and 405,000 associated deaths were reported globally in 2018; of those, more than 90% of the malaria morbidity and mortality occurred in Africa [1]. Plasmodium falciparum is the most prevalent malaria parasite in the African continent, accounting for 99.7% of the estimated cases in sub-Saharan Africa. Pregnant women and children under 5 years of age are the most vulnerable groups and account for 67% of all malaria deaths worldwide. The interventions available to mitigate the adverse effects of malaria during pregnancy include intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy (IPTp), insecticide-treated bed-nets (ITNs), and case management [2, 3]. Currently, sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP) is the only anti-malarial drug formulation approved for use in IPTp [3]. The SP drug inhibits the enzymes dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) and dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). These enzymes are involved in the folate pathway of nucleic acid synthesis [4, 5]. However, mutations in the parasite genes dhfr (Pfdhfr) and dhps (Pfdhps) confer different degrees of resistance to pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine, respectively [4,5,6,7,8]. Specifically, there are four-point mutations in Pfdhfr (N51I, C59R, S108N, and I164L) and five in Pfdhps (S436A/F, A437G, K540E, A581G, and A613S/T) [6, 7, 9,10,11,12,13].
Due to the increasing SP resistance and pervasive chloroquine resistance, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) as first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria in most endemic countries [3, 14]. However, ACT is still not approved for the prevention of malaria in pregnant women due to the absence of adequate safety data [3, 15]. Thus, SP remains the only drug used for IPTp and is being considered for intermittent preventive treatment in infants (IPTi) [15,16,17].
Several studies in Kenya have shown an association between the Pfdhfr triple mutant (N51I, C59R, S108N) combined with the Pfdhps double mutant (A437G, K540E), and resistance to SP in vivo [13, 18]. Even after SP was no longer the first-line drug in Kenya as of 2004, the Pfdhfr/Pfdhps quintuple mutant genotype (N51I, C59R, S108N/A437G, K540E) continued to be prevalent [13]. Given that SP remains in use for IPTp, is considered as a possible ACT partner drug, and is a candidate for IPTi, the frequencies of SP resistance-associated mutations were investigated in samples collected from pediatric malaria patients in Siaya (Western Kenya) during three periods: 2005, 2010, and 2017/18. Among other well-known mutations associated with SP resistance, the change in frequency of a novel mutation identified in Pfdhps (S436H) [19] was also estimated. In addition, to obtain a more comprehensive picture of the mutations related with anti-malarial drug resistance, the presence of mutations linked to the delayed parasite clearance phenotype against artemisinin-based combinations were assessed by studying the polymorphism in the propeller domain of the P. falciparum kelch13 gene (Pfk13) in a group of samples collected in 2017/18 [1, 20].
Methods
Study sites, sample collection, and DNA isolation
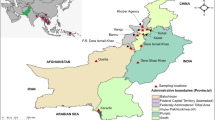
Samples were initially collected as part of an immunoepidemiologic study approved by the Ethics Committee of the Kenya Medical Research Institute, the University of New Mexico Institutional Review Board, the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) Institutional Review Board, and the Maseno University Ethics Review Committee. The study was conducted at Siaya County Referral Hospital (SCRH), a holoendemic P. falciparum transmission region in Western Kenya. Details of the study design and study area have been previously published [21]. Individuals inhabiting the study area are predominantly from the Luo ethnic group (> 96%). Children (primarily aged < 12 months), who presented at the paediatric ward for their first 'hospital contact' (for any reason), were identified and screened for malaria parasites. Children were enrolled in the cohort studies unless they met any of the following exclusion criteria: positive blood smears with non-P. falciparum species, previous hospitalization (for any reason), documented or reported use of anti-malarial therapy 2 weeks prior to enrollment, and/or cerebral malaria diagnosis (though rare in this study area). Informed written consent was obtained from the parents/legal guardians of all participating children. All children were treated with standard anti-malarials approved at the time following the local guidelines (Coartem™: artemether and lumefantrine). About 2 mL of venous blood was obtained from each study participant at enrollment or visit and used for genotyping analysis.
To explore changes in mutations linked to drug resistance, P. falciparum genomic DNA was extracted from 200 µl of 81 blood samples collected in 2005 and 95 blood samples collected in 2010 using QIAamp DNA Micro Kit (Qiagen, GmbH, Hilden, Germany). For samples collected in 2017/18, genomic DNA was extracted using Direct-zol DNA/RNA miniprep kit (Zymo Research, Tustin, CA, USA) from 200 µL aliquots of each of the 98 blood samples that were mixed with Tri reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
Genotyping analysis of P. falciparum drug resistance genes and Pfk13 gene
Drug resistance genes and kelch13 gene (Pfk13) of P. falciparum were amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). DNA samples were genotyped for mutations at: (1) P. falciparum hydroxymethyldihydropterin pyrophosphokinase-dihydropteroate synthase gene (Pfdhps) codons 436, 437, 540, 581, and 613; (2) P. falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene (Pfdhfr-ts) codons 51, 59, 108, and 164; and (3) the propeller domain coding region (720 bp) of Pfk13 (with an open reading frame of 2,181 bp in length). Pfk13 mutation analysis was only performed for samples collected in the period of 2017/18. A fragment of 750 out of 2418 bp for Pfdhps and a fragment of 1688 out of 1827 bp for Pfdhfr were amplified. Sequences of PCR primers used in this study were: (1) for Pfdhps, 5′-GAT ATA TGT ATT AAA AGA TAG AAT TTC-3′ (forward) and 5′-CTT GTC TTT CCT CAT GTA ATT C-3′ (reverse); (2) for Pfdhfr, 5′-GCM ATA TGT GCA TGT TGT AAR G-3′ (forward) and 5′-GCC ATA TCC ATT KAA ATT TTW TC-3′ (reverse); and (3) for Pfk13, 5′-GAT AAA CAA GGA AGA ATA TTC T-3′ (forward) and 5′-CGG AAT CTA ATA TGT TAT GTT CA-3′ (reverse) [22].
PCR amplifications were carried out in 50 µl reactions using 2 µl of total genomic DNA, 1X PCR buffer, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM of each deoxynucleoside triphosphate, 0.4 µM of each primer, and 0.03 U/µl AmpliTaq polymerase (Applied Biosystems, Thermo Fisher Scientific). The PCR conditions for Pfdhps were a partial denaturation at 95 °C for 7 min, and 40 cycles with 30 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 50 °C and 1 min extension at 68 °C, and a final extension step of 5 min at 68 °C. For Pfdhfr, the conditions were a partial denaturation at 95 °C for 7 min, and 40 cycles with 1 min at 95 °C, 1 min at 54 °C and 2 min extension at 72 °C, and a final extension of 10 min at 72 °C. For Pfk13 gene, the PCR conditions were: a partial denaturation at 94 °C for 4 min, and 36 cycles with 1 min at 94 °C, 1 min at 53 °C and 2 min extension at 72 °C, and a final extension of 10 min at 72 °C. Negative control (nuclease-free dH2O as a template) and positive control (Pf DNA) were included in each batch of PCR. PCR products from each reaction (50ul) were resolved using 1% agarose electrophoresis, excised from the gel, and purified using the QIAquick® Gel extraction kit (Qiagen, GmbH, Hilden, Germany). Purified PCR products were directly sequenced for both strands using an Applied Biosystems 3730 capillary sequencer. All Pfk13 sequences obtained in this study were deposited in GenBank under the accession numbers MT130102 to MT130200.
Evaluation of Pfdhps and Pfdhfr allele frequencies
After thorough inspections of each electropherogram, mutations associated with drug resistance genes (Pfdhps and Pfdhfr) or artemisinin delayed parasite clearance resistance Pfk13 gene were identified and recorded. First, frequency of each (a) point mutations, (b) allele in Pfdhps and Pfdhfr genes, as well as (c) the combination of Pfdhps and Pfdhfr multilocus genotypes were estimated, dividing the total of point mutations/allele/combination of multilocus genotypes by the total of the samples (N) per year that successfully amplified, which corresponds to the frequency of patients with parasites that have a specific codon or allele. However, given the mixed infections found in these samples, the frequencies do not add 1. Additionally, via inspecting multiple peaks at the mutations of Pfdhps and Pfdhfr that were associated with drug resistance, polyclonal P. falciparum infections were identified, and their corresponding frequencies were estimated using the samples collected in the three periods (2005, 2010, and 2017/18). Statistical comparisons in the prevalence of all SNP mutations in dhps and dhfr genes in samples collected between the 2005 and 2017/18 surveys were performed using Fisher's exact tests. Statistical significance was defined by a two-sided p value < 0.05.
Results
Pfdhps and Pfdhfr allele frequencies and P. falciparum polyclonal infections
Figure 1 shows the frequencies of genotypes at each codon for Pfdhps and Pfdhfr genes. Pfdhps mutations at codons 437 and 540, i.e., A437G and K540E, were detected in more than 95% of all sampled years (frequency > 0.95). However, mutation S436A was found at a low frequency (0.02, two patients) only in 2010, while the mutation S436H [19] seemed to significantly increase in frequency from 0.12 in 2010 to 0.28 in 2017/18 (p value < 0.05, Fig. 1). The A581G mutation was also present at a low frequency in 2010 (0.01, one patient) and 2017/18 (0.03, three patients; Fig. 1), and mutation A613T was not detected in any of these groups of samples. In the case of Pfdhfr, only the N51I, C59R, and S108N mutations were found at high frequency (> 0.85) in all sampled years. The presence of I164L mutation was only detected in three patients (frequency of 0.04, Fig. 1) in 2017/18.
The frequencies of Pfdhfr and Pfdhps alleles, estimated by dividing the number of each Pfdhps and Pfdhfr alleles by the total of the samples (N) per year that successfully amplified, are shown in Fig. 2. Pfdhps SGEAA (Figs. 2a) and triple mutant for Pfdhfr CIRNI (Fig. 2b) are the most frequent alleles across the sampled periods in this study population. The Pfdhps HGEAA allele, having a novel mutation S436H, appears to significantly increase in frequency between 2010 and 2017/18 (p value < 0.05, Fig. 2a). Mutations associated with SP resistance in Pfdhps and Pfdhfr genes revealed 13 Pfdhps/Pfdhfr multilocus genotypes, with frequency changing through time during the sampled periods (Fig. 2c). SGEAA/CIRNI and SGEAA/CICNI were the most frequent multilocus genotypes for all sampled years; however, SGEAA/CICNI seems to be significantly decreasing over time (p value < 0.05, Fig. 2c). Interestingly, the multilocus genotype HGEAA/CIRNI was significantly increasing in frequency between 2010 and 2017/18 (p value < 0.05, Fig. 2c).
Polyclonal infections detected by Pfdhps and Pfdhfr SNPs were found via examination of electropherograms. The frequency of the polyclonal Pfdhps infections significant increased to 0.2 in 2017/18 from 0.09 (in 2005) and 0.06 (in 2010) (p value < 0.05). It is worth noticing that 84% of these polyclonal infections have the novel Pfdhps mutation S436H (CAT substituted the codon TCT) in 2017/18. Since the Pfdhps mutation S436H is increasing in frequency and polyclonal infections are detectable by the polymorphism present at the sampled SNPs (Pfdhps and Pfdhfr in this case), it is not surprising that most of the Pfdhps S436H alleles are part of polyclonal infections. In contrast, the frequency of the polyclonal infections in Pfdhfr gene significantly decreased gradually from 0.23 in 2005 to 0.12 in 2010 and 0.05 in 2017/18 (p value < 0.05); this shows the fixation of the CIRNI allele.
Pfk13 population analyses
Upon inspecting sequences of the Pfk13 propeller domain in 98 samples collected in 2017/18, none of the mutations associated with the delayed parasite clearance phenotype were found [14, 22, 23]. However, in the Pfk13 propeller region, a nonsynonymous substitution at codon AGCT578STCT (2.04%, 2 patients), a nonsynonymous substitution at codon VGTT637IATT (2.04%, two patient), a synonymous substitution at the same codon VGTT637VGTA (1.02%, one patient), and a nonsynonymous substitution at codon EGAA642DGAT (2.04%, two patients) were detected in the paediatric malaria patients from Siaya (Western Kenya).
Discussion
Molecular surveillance is considered a valuable tool to monitor the prevalence of mutations that may affect the efficacy of anti-malarial drugs [24,25,26,27]. In the context of IPTp, following the dynamic of mutations conferring resistance to SP is critical because it is the only drug approved for use in pregnant women [3, 15].
This study found that the quintuple Pfdhps/Pfdhfr mutant (the Pfdhps double mutant A437G, K540E allele together with a Pfdhfr triple mutant N51I, C59R, S108N allele) associated with clinical SP treatment failure [12], remained high (0.86) in Siaya (Western Kenya) in 2010 and 2017/18 (Fig. 2c), more than a decade after the withdrawal of SP in Kenya (Fig. 3). The increase in Pfdhfr triple mutants is linked to a decline in the double mutant Pfdhfr alleles in the population, evidenced by the absence of the C59R, S108N allele in the 2010 and 2017/18 samples (Fig. 2). These patterns are consistent with the prediction made using 1992–1999 samples that allowed estimates of the relative fitness of these resistant alleles assuming drug pressure [28]. The triple Pfdhfr mutant that conferred higher resistance was found to have higher fitness than the two double mutant alleles [28]. Furthermore, the double Pfdhfr mutant alleles N51I, S108N showed a higher fitness than double mutant alleles C59R, S108N [28]. Thus, the less fit Pfdhfr allele under drug pressure (i.e., the allele of C59R, S108N) is absent in the more recent samples.
Temporal sequence describing SP use as an anti-malarial drug in Kenya and prevalence of Pfdhps and Pfdhfr alleles with mutations conferring resistance. Frequencies of Pfdhps and Pfdhfr alleles with mutations conferring resistance from 1992–1999 were previously reported by McCollum et al. [28]
Although the frequency of Pfdhps allele A437G, K540E was similar during the sampled years (0.91 in 2005 to 0.88 in 2017/18), there is an increase in the frequency of a triple mutant allele S436H, A437G, K540E (0.28), which has the mutation at codon 436. This mutation has been previously reported in low frequency in pregnant women from Nyanza Province (located in Western Kenya, covering the area of nowadays six counties, including Siaya county) between 2002 and 2009: 2.3% in 2002–2008 and 3.8% in 2008–2009 [19]. Although the results presented here are consistent with a scenario that positive directional selection is playing a role in the frequency increase of this new allele (S436H, A437G, K540E) in Western Kenya, the phenotypic effect of the Pfdhps S436H mutation to clinical drug resistance has not been determined. Thus, whether the results observed here relate to actual anti-malarial drug pressure or other processes is difficult to ascertain.
SP was the second-line anti-malarial drug until 1998 when it became the first-line malaria treatment [29]. Due to the increased frequency of chloroquine treatment failures, there was a growing SP drug pressure that may have led to the observed high prevalence of Pfdhfr mutations in 1998 [29]. Then, the increased use of SP selected for highly resistant mutations in Pfdhps [29]. By 2004, just after 5 years of SP usage in Kenya, the widespread treatment failures prompted a change in the malaria treatment drug policy to ACT in Kenya, like other African countries [30]. However, ACT did not have widespread distribution at many of the health facilities in Kenya until mid-2006. Considering the timeline described previously, the observed trends in Pfdhfr and Pfdhps mutations were unanticipated because SP has not been a first-line anti-malarial treatment in Kenya for almost 15 years.
Unlike mutations linked to chloroquine resistance, SP resistant mutations have shown to be resilient in Africa even after the drug is no longer the first-line anti-malarial treatment [13, 30, 31]. A possibility in Africa is that mutations conferring resistance to SP may not have a relative fitness cost because of the lack of wild-type alleles in the population that can outcompete the resistant ones in the absence of drug pressure, as has been suggested in South America [32, 33]. However, the significant increase in the frequencies of the Pfdhfr triple mutant and the Pfdhps allele with the S436H mutation is consistent with selective drug pressure. This drug preassure can be explained, at least in part, by the fact that 56% of pregnant women in Kenya took at least two SP doses in the context of IPTp in 2018, as reported by the Maternal & Child Survival Program from USAID [34].
A factor to consider is the ongoing treatment of HIV/AIDS patients with cotrimoxazole, a bacterial dhfr/dhps inhibitor used to treat respiratory tract infections and to prevent opportunistic infections. The use of cotrimoxazole in the population may have played a role in the increased frequency of mutations linked to SP resistance in malarial parasites [35] and should be considered now. There were reports showing cross-resistance of P. falciparum in vitro to cotrimoxazole with pyrimethamine and sulfadoxine [35, 36]. However, a recent study showed that cotrimoxazole remains effective in controlling malaria infection despite the high prevalence of SP-resistant parasites, and its use does not select for mutations associated with SP resistance [37]. Thus, at this point, the use of cotrimoxazole is not a plausible selective force that can explain the pattern observed in Pfdhfr and Pfdhps mutations.
In the case of Pfdhps A581G and A613T mutations associated with high-level SP resistance, they have been observed in Africa [28, 38,39,40,41], South America, and Southeast Asia [9, 10, 42, 43]. However, these mutations were detected in low frequency in the samples included in this study, and the results presented here are consistent with previous reports from Western Kenya [13, 28, 30, 40].
ACT is the first-line anti-malarial treatment in holoendemic P. falciparum malaria-endemic nations, including Kenya. As a result, there is ongoing molecular surveillance aimed to detect Pfk13 mutations linked to delayed parasite clearance [1, 20]. Up to now, there is still no report on the presence of a delayed parasite clearance phenotype for ACT in Kenya. Mutation A578S, found in this study, is the most predominant mutation in sub-Saharan Africa [23, 44,45,46,47,48] and has been reported in both pre- and post-ACT parasites, with frequencies between 1.2 and 10% in samples from different malaria ecological zones in Kenya [48, 49]. For example, A578S mutation has a frequency of 2.8% in samples from Kisumu (Western Kenya) [45]. These results support the notion that A578S is the most widespread Pfk13 SNP observed in Africa, including countries such as Mali, Angola, Democratic Republic of Congo, Uganda, Gabon, Ghana, and Kenya [20, 22, 23, 45, 47, 48, 50,51,52]. However, in all the studies, this mutation was detected at low frequencies. This finding is consistent with the proposed model that many of these Pfk13 mutations are slightly deleterious and maintained as the P. falciparum population expanded, making selection less efficient [22]. Although the functional impact of A578S in terms of ACT efficacy remains unclear, recent studies have hinted at a potential effect. In particular, A578S is very close to the C580Y mutation, and molecular modelling and mutational sensitivity prediction performed by Mohon et al. [52] suggested that the A578S SNP could disrupt the function of the propeller domain. Nevertheless, experimental evidence is still lacking [20, 53].
Conclusion
Although the evolutionary processes driving the observed pattern remain elusive because of a lack of specific phenotypic information on the S436H mutation, its increase in frequency seems consistent with drug pressure. SP is no longer the first-line anti-malarial drug in Kenya, but it is still widely used as part of IPTp [15]. More studies are warranted to discern whether the Pfdhps/Pfdhfr multilocus mutant (S436H, A437G, K540E/ N51I, C59R, S108N) adversely impact the efficacy of SP in IPTp in the context of drug efficacy evaluations. Such information is critical, considering that SP in IPTp remains an essential tool for reducing disease burden in sub-Saharan Africa [15]. On a separate note, there is no evidence indicating that Pfk13 mutations linked with the delayed phenotype were present in Kenya when these samples were collected. However, sustaining the molecular surveillance is important since there are reports in China of an imported malaria case from Rwanda with the mutation R561H linked to artemisinin resistance [54].
Availability of data and materials
Sequences were deposited in the GenBank with the accession numbers MT130102 to MT130200.
Abbreviations
- ACT:
-
Artemisinin-based combination therapy
- CBC:
-
Complete blood counts
- DHFR:
-
Dihydrofolate reductase
- DHPS:
-
Dihydropteroate synthase
- IPTi:
-
Intermittent preventive treatment in infants
- IPTp:
-
Intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy
- ITNs:
-
Insecticide-treated bed-nets
- SP:
-
Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
World Health Organization. Technical expert group meeting on preventive chemotherapy: report of the technical consultation on intermittent preventive treatment in infants (IPTi). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2009.
World Health Organization. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. 3rd ed. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
Talisuna AO, Bloland P, D’Alessandro U. History, dynamics, and public health importance of malaria parasite resistance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004;17:235–54.
Gregson A, Plowe CV. Mechanisms of resistance of malaria parasites to antifolates. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57:117–45.
Peterson DS, Walliker D, Wellems TE. Evidence that a point mutation in dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase confers resistance to pyrimethamine in falciparum malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:9114–8.
Triglia T, Menting JG, Wilson C, Cowman AF. Mutations in dihydropteroate synthase are responsible for sulfone and sulfonamide resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:13944–9.
Lozovsky ER, Chookajorn T, Brown KM, Imwong M, Shaw PJ, Kamchonwongpaisan S, et al. Stepwise acquisition of pyrimethamine resistance in the malaria parasite. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:12025–30.
Foote SJ, Galatis D, Cowman AF. Amino acids in the dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase gene of Plasmodium falciparum involved in cycloguanil resistance differ from those involved in pyrimethamine resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:3014–7.
Plowe CV, Cortese JF, Djimde A, Nwanyanwu OC, Watkins WM, Winstanley PA, et al. Mutations in Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthase and epidemiologic patterns of pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine use and resistance. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1590–6.
Nzila-Mounda A, Mberu EK, Sibley CH, Plowe CV, Winstanley PA, Watkins WM. Kenyan Plasmodium falciparum field isolates: correlation between pyrimethamine and chlorcycloguanil activity in vitro and point mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase domain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42:164–9.
Kublin JG, Dzinjalamala FK, Kamwendo DD, Malkin EM, Cortese JF, Martino LM, et al. Molecular markers for failure of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine and chlorproguanil-dapsone treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:380–8.
Juma DW, Omondi AA, Ingasia L, Opot B, Cheruiyot A, Yeda R, et al. Trends in drug resistance codons in Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthase genes in Kenyan parasites from 2008 to 2012. Malar J. 2014;13:250.
World Health Organization. Artemisinin and artemisinin-based combination therapy resistance: status report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
Roh ME, Kuile FOT, Rerolle F, Glymour MM, Shiboski S, Gosling R, et al. Overall, anti-malarial, and non-malarial effect of intermittent preventive treatment during pregnancy with sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine on birthweight: a mediation analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8:e942–53.
ter Kuile FO, van Eijk AM, Filler SJ. Effect of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine resistance on the efficacy of intermittent preventive therapy for malaria control during pregnancy: a systematic review. JAMA. 2007;297:2603–16.
Gosling RD, Carneiro I, Chandramohan D. Intermittent preventive treatment of malaria in infants: how does it work and where will it work? Trop Med Int Health. 2009;14:1003–10.
Naidoo I, Roper C. Mapping “partially resistant”, “fully resistant”, and “super resistant” malaria. Trends Parasitol. 2013;29:505–15.
Iriemenam NC, Shah M, Gatei W, van Eijk AM, Ayisi J, Kariuki S, et al. Temporal trends of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP) drug-resistance molecular markers in Plasmodium falciparum parasites from pregnant women in western Kenya. Malar J. 2012;11:134.
WWARN K13 Genotype-Phenotype Study Group. Association of mutations in the Plasmodium falciparum Kelch13 gene (Pf3D7_1343700) with parasite clearance rates after artemisinin-based treatments-a WWARN individual patient data meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-018-1207-3.
Ong’echa JM, Keller CC, Were T, Ouma C, Otieno RO, Landis-Lewis Z, et al. Parasitemia, anemia, and malarial anemia in infants and young children in a rural holoendemic Plasmodium falciparum transmission area. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;74:376–85.
Pacheco MA, Kadakia ER, Chaudhary Z, Perkins DJ, Kelley J, Ravishankar S, et al. Evolution and genetic diversity of the k13 gene associated with artemisinin delayed parasite clearance in Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:e02550-e2618.
Conrad MD, Bigira V, Kapisi J, Muhindo M, Kamya MR, Havlir DV, et al. Polymorphisms in K13 and falcipain-2 associated with artemisinin resistance are notprevalent in Plasmodium falciparum isolated from Ugandan children. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e105690.
Escalante AA, Ferreira MU, Vinetz JM, Volkman SK, Cui L, Gamboa D, et al. Malaria molecular epidemiology: lessons from the international centers of excellence for Malaria Research Network. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;93:79–86.
Dalmat R, Naughton B, Kwan-Gett TS, Slyker J, Stuckey EM. Use cases for genetic epidemiology in malaria elimination. Malar J. 2019;18:163.
Escalante AA, Pacheco MA. Malaria molecular epidemiology: An evolutionary genetics perspective. Microbiol Spectr. 2019;7:1128.
Shretta R, Omumbo J, Rapuoda B, Snow RW. Using evidence to change anti-malarial drug policy in Kenya. Trop Med Int Health. 2000;5:755–64.
McCollum AM, Schneider KA, Griffing SM, Zhou Z, Kariuki S, Ter-Kuile F, et al. Differences in selective pressure on dhps and dhfr drug resistant mutations in western Kenya. Malar J. 2012;11:77.
Amin AA, Zurovac D, Kangwana BB, Greenfield J, Otieno DN, Akhwale WS, et al. The challenges of changing national malaria drug policy to artemisinin-based combinations in Kenya. Malar J. 2007;6:72.
Spalding MD, Eyase FL, Akala HM, Bedno SA, Prigge ST, Coldren RL, et al. Increased prevalence of the pfdhfr/phdhps quintuple mutant and rapid emergence of pfdhps resistance mutations at codons 581 and 613 in Kisumu. Kenya Malar J. 2010;9:338.
Artimovich E, Schneider K, Taylor TE, Kublin JG, Dzinjalamala FK, Escalante AA, et al. Persistence of sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine resistance despite reduction of drug pressure in Malawi. J Infect Dis. 2015;212:694–701.
Zhou Z, Griffing SM, de Oliveira AM, McCollum AM, Quezada WM, Arrospide N, et al. Decline in sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine-resistant alleles after change in drug policy in the Amazon region of Peru. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:739–41.
Pacheco MA, Forero-Peña DA, Schneider KA, Chavero M, Gamardo A, Figuera L, et al. Malaria in Venezuela: changes in the complexity of infection reflects the increment in transmission intensity. Malar J. 2020;19:176.
Maternal and Child Survival Program, USAID from American People. 2020. https://www.mcsprogram.org/. Accessed 05 Oct 2020.
Iyer JK, Milhous WK, Cortese JF, Kublin JG, Plowe CV. Plasmodium falciparum cross-resistance between trimethoprim and pyrimethamine. Lancet. 2001;358:1066–7.
Khalil I, Ronn AM, Alifrangis M, Gabar HA, Satti GM, Bygbjerg IC. Dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthase genotypes associated with in vitro resistance of Plasmodium falciparum topyrimethamine, trimethoprim, sulfadoxine, and sulfamethoxazole. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68:586–9.
Juma DW, Muiruri P, Yuhas K, John-Stewart G, Ottichilo R, Waitumbi J, et al. The prevalence and antifolate drug resistance profiles of Plasmodium falciparum in study participants randomized to discontinue or continue cotrimoxazole prophylaxis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;13:e0007223.
McCollum AM, Poe AC, Hamel M, Huber C, Zhou Z, Shi YP, et al. Antifolate resistance in Plasmodium falciparum: multiple origins and identification of novel dhfr alleles. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:189–97.
Gebru-Woldearegai T, Hailu A, Grobusch MP, Kun JFJ. Molecular surveillance of mutations in dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropterate synthase genes of Plasmodium falciparum in Ethiopia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:1131–4.
Shah M, Omosun Y, Lal A, Odero C, Gatei W, Otieno K, et al. Assessment of molecular markers for anti-malarial drug resistance after the introduction and scale-up of malaria control interventions in western Kenya. Malar J. 2015;14:75.
Heuchert A, Abduselam N, Zeynudin A, Eshetu T, Löscher T, Wieser A, et al. Molecular markers of anti-malarial drug resistance in southwest Ethiopia over time: regional surveillance from 2006 to 2013. Malar J. 2015;14:208.
Biswas S, Escalante A, Chaiyaroj S, Angkasekwinai P, Lal AA. Prevalence of point mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthetase genes of Plasmodium falciparum isolates from India and Thailand: a molecular epidemiologic study. Trop Med Int Health. 2000;5:737–43.
Vinayak S, Alam MT, Mixson-Hayden T, McCollum AM, Sem R, Shah NK, et al. Origin and evolution of sulfadoxine resistant Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1000830.
Isozumi R, Uemura H, Kimata I, Ichinose Y, Logedi J, Omar AH, et al. Novel mutations in K13 propeller gene of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:490–2.
Kamau E, Campino S, Amenga-Etego L, Drury E, Ishengoma D, Johnson K, et al. K13-propeller polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum parasites from sub-Saharan Africa. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:1352–5.
Ouattara A, Kone A, Adams M, Fofana B, Maiga AW, Hampton S, et al. Polymorphisms in the K13-propeller gene in artemisinin-susceptible Plasmodium falciparum parasites from Bougoula-Hameau and Bandiagara. Mali Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015;92:1202–6.
Taylor SM, Parobek CM, DeConti DK, Kayentao K, Coulibaly SO, Greenwood BM, et al. Absence of putative artemisinin resistance mutations among Plasmodium falciparum in Sub-Saharan Africa: a molecular epidemiologic study. J Infect Dis. 2015;211:680–8.
de Laurent ZR, Chebon LJ, Ingasia LA, Akala HM, Andagalu B, Ochola-Oyier LI, et al. Polymorphisms in the K13 gene in Plasmodium falciparum from different malaria transmission areas of Kenya. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98:1360–6.
Wamae K, Okanda D, Ndwiga L, Osoti V, Kimenyi KM, Abdi AI, et al. No evidence of P. falciparum K13 artemisinin conferring mutations over a 24-year analysis in Coastal Kenya, but a near complete reversion to chloroquine wild type parasites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63:e01067-e1119.
Muwanguzi J, Henriques G, Sawa P, Bousema T, Sutherland CJ, Beshir KB. Lack of K13 mutations in Plasmodium falciparum persisting after artemisinin combination therapy treatment of Kenyan children. Malar J. 2016;15:36.
Ocan M, Bwanga F, Okeng A, Katabazi F, Kigozi E, Kyobe S, et al. Prevalence of K13-propeller gene polymorphisms among Plasmodium falciparum parasites isolated from adult symptomatic patients in northern Uganda. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16:428.
Lu F, Culleton R, Zhang M, Ramaprasad A, von Seidlein L, Zhou H, et al. Emergence of indigenous artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Africa. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:991–3.
Mohon A, Alam M, Bayih A, Folefoc A, Shahinas D, Haque R, et al. Mutations in 386 Plasmodium falciparum K13 propeller gene from Bangladesh (2009–2013). Malar J. 2014;13:431.
Wang X, Ruan W, Zhou S, Huang F, Lu Q, Feng X, et al. Molecular surveillance of Pfcrt and k13 propeller polymorphisms of imported Plasmodium falciparum cases to Zhejiang Province, China between 2016 and 2018. Malar J. 2020;19:59.
Acknowledgements
We thank Scott Bingham from the DNA laboratory at the School of Life Sciences (Arizona State University) for their technical support. This study was supported in part by grants from the US National Institute of Health, R01AI130473.
Funding
This study was supported by grant R01AI130473 from the US National Institutes of Health to D. J. Perkins.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MAP, AAE, and DJP conceived the study. DJP supervised the sample collection, trained field personal, and supported the fieldwork. QC, EOM, CN, CO, ER, SBA, CO conducted the field and lab work in Kenya, including the sample collection and administrated the informed consent forms. MAP genotyped the samples. MAP, KS, and AAE analyzed the data. MAP and AAE wrote a first draft of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Kenya Medical Research Institute, the University of New Mexico Institutional Review Board, the Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) Institutional Review Board and the Maseno University Ethics Review Committee.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Pacheco, M.A., Schneider, K.A., Cheng, Q. et al. Changes in the frequencies of Plasmodium falciparum dhps and dhfr drug-resistant mutations in children from Western Kenya from 2005 to 2018: the rise of Pfdhps S436H. Malar J 19, 378 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-020-03454-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-020-03454-8