Abstract
Background
General antiviral agents such as oseltamivir are associated with certain adverse effects and the emergence of resistance. This study investigated the phytochemical properties, antiviral activities, and safety of three herbs used in traditional Korean medicine.
Methods
Extracts of three medicinal herbs (Brassica juncea, Forsythia suspensa, and Inula britannica) were prepared using ethanol or water. The total phenolic, flavonoid, and saponin content, condensed tannin content, and reducing sugar content of the herb extracts were determined via phytochemical screening. Tandem mass analysis was performed using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC)-electrospray ionization (ESI)-Q/Orbitrap instrument. Virus titrations were determined via tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) and cytotoxicity assays. Hemolysis and hepatotoxicity were measured to determine safety.
Results
Among the three medicinal herbs, F. suspensa showed the highest concentration of phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and saponins. The number of phytochemical compounds detected via tandem mass analysis of B. juncea, F. suspensa, and I. britannica was 5 (including sinigrin, m/z [M-H] = 358.02), 14 (including forsythoside A, m/z [M-H] = 623.19), and 18 (including chlorogenic acid, m/z [M-H] = 353.20), respectively. The antiviral effects of the B. juncea extracts (ethanol and water) and I. britannica extract (ethanol) were further investigated. The ethanol extract of B. juncea showed a 3 Log TCID50/25 μL virus titration reduction and the water extract showed a selectivity index of 13.668 against infected influenza H1N1 virus A/NWS/33. The B. juncea extracts did not show hemolysis activities and hepatotoxicity (< 20%). The ethanol extract of I. britannica showed the most effective virus titration decrease, whereas its hemolytic and hepatotoxicity values were the most significantly different compared to the control. Despite the high concentration of phytochemicals detected in F. suspensa, the extract showed approximately 1 Log TCID50/25 μL at the highest concentration.
Conclusion
B. juncea may show antiviral effects against H1N1 in a host. In addition, B. juncea may also show decreased disadvantages compared to other antiviral agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Medicinal herbs have been used for the treatment of various diseases in Korea, China, Japan, and other East Asian countries such as Malaysia and Vietnam [1]. In Korea, many traditional medicinal herbs have been researched and are used as edible medicines. For example, Allium hookeri root suppressed the lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in RAW 264.7 cells [2], Phragmitis rhizoma reduced the myelotoxicity of docetaxel, a commonly used anticancer agent [3], Rosa gallica exhibited in vitro antioxidant and anti-skin aging effects as a matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) inhibitor [4], and Acer okamotoanum prevented oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells [5].
The influenza virus thrives in a wide range of regions and hosts because of the occurrence of genetic recombination and cross species transmission of the influenza virus. This leads to huge economic losses in the poultry industry and threatens public health [6]. The influenza A virus subtypes H1N1 (A/H1N1) and H3N2 (A/H3N2) and influenza B virus have periodically spread in winter, causing more than 250,000 deaths [7]. Oseltamivir and zanamivir are antiviral agents approved by the United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) but these neuraminidase (NA) inhibitors cannot prevent the emergence of resistance [8]. M2 protein inhibitors such as amantadine and rimantadine are active only against the influenza A virus [9]. Therefore, novel antiviral agents are needed to counteract the disadvantages of existing antiviral agents.
Brassica juncea is a brown mustard seed that has a spicy flavor and is used as a condiment. In addition, it contains various bioactive chemicals and is inexpensive, and is therefore used in human foods and animal feeds [10]. Forsythia suspensa is known for its high saponin content and is used to treat various inflammatory symptoms, such as carbuncles or abscesses associated with swelling, common cold, and fever [11]. Inula britannica, a rich source of flavonoids [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20], is used as a traditional medicine to treat bronchitis, digestive disorders, and inflammation in Korea [12]. Considering these phytochemical properties, its antimicrobial effects against Helicobacter pylori [21] and its potential as a food additive in cheddar-type cheese [22] have been studied previously. This study aimed to investigate the phytochemical properties and antiviral effects of these traditional Korean medicinal herbs. In addition, the hepatotoxicity and hemolytic activities of these plants extracts were evaluated to determine their safety.
Methods
Chemicals and medicinal herbs
Folin-Ciocalteu’s phenol reagent, vanillin, saponin from quillaja bark, and (+)-catechin were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Gallic acid was purchased from Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan) and sodium carbonate was purchased from Samchun Chemical (Pyeongtaek, South Korea). Tamiflu were obtained from Roche (Seoul, Korea). B. juncea (seed), F. suspensa, (fruit) and I. britannica (seed) were obtained from Kyungdong-Market in Seoul, Korea. B. juncea, F. suspensa, and I. britannica were authenticated by Professor Hyun-Dong Paik at the Laboratory of Biotechnology (Konkuk University, Seoul, Korea) and stored as voucher specimen KU-H13, KU-H22 and KU-H26, respectively.
Extraction
The medicinal herbs were extracted according to a method previously described, with some modifications [23]. The herb powder (100 g) was extracted with 1 L distilled water and ethanol (1:10 w/v) at 70 °C in a boiling pot (OCOO, Boryeong, South Korea) for 6 h. The extracts were filtered through Whatman No. 2 paper via vacuum filtration. After filtration, the extracts were stored at 4 °C. The soluble solid content of the extracts was measured as per the methods used by the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) [24]. For quantification of phenolic compounds and cytotoxicity assay, all extracts were lyophilized before used.
Phytochemical screening
The total phenolic, flavonoid, and saponin content, condensed tannin content, and reducing sugar content of the herb extracts were determined via phytochemical screening. The extracts were filtered through a 0.45-μm membrane filter and their phytochemical properties were evaluated.
Total phenolic content was determined via Folin-Ciocalteu assay with modifications [23]. The extracts (90 μL) were mixed with 1.8 mL of 2% (w/v) sodium carbonate solution and 90 μL of 50% (v/v) Folin-Ciocalteu’s reagent and incubated for 30 min. Molybdenum oxide content was measured via spectrophotometry (X-ma 3200, Human corporation, Seoul, Korea) at a wavelength of 752 nm. Gallic acid was used as the standard and the compounds’ phenolic content was expressed as gallic acid equivalents (mg GAE/g solid).
Total flavonoid content was measured via aluminium chloride assay [25]. The extracts (100 μL) were incubated with 20 μL of 5% sodium nitrite and 800 μLof 60% ethanol to determine flavonoid content. After 6 min, 20 μL of 10% aluminum chloride was added and 60 μL of 4% sodium hydroxide was added 6 min later. The mixtures were then incubated for 30 min. The absorbance of the flavonoid and aluminum chloride complex (yellow) was measured using a microplate reader (Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA) at a wavelength of 405 nm. Quercetin was used as the standard and flavonoid content was expressed as quercetin equivalents (mg QE/g of solid).
Total saponin content was measured via the vanillin assay [26]. Briefly, 100 μL extracts were mixed with 100 μL of 8% (w/v) vanillin solution in methanol and 1 mL of 72% (v/v) sulfuric acid in methanol. The mixture was incubated at 60 °C for 10 min. After incubation, the mixture was cooled for 15 min, and the absorbance was measured using a microplate reader at a wavelength of 540 nm. Quillaja saponin was used as the standard and saponin content was expressed as quillaja saponin equivalents (mg QSE/g solid).
Condensed tannin content was measured via vanillin-HCl assay [25] with modifications. The reaction mixture comprised 20 μL extracts, 600 μL of 4% (w/v) vanillin solution in methanol, and 300 μL concentrated hydrochloric acid. The mixture was incubated at 25 °C in the dark. After 20 min, absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 500 nm using a spectrophotometer. (+)-Catechin was used as the standard and tannin content was expressed as catechin equivalents (mg CE/g solid).
Reducing sugar content was evaluated using 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) [27]. Briefly, 100 μL extracts were reacted with 100 μL DNS reagents for 10 min in boiling water. DNS solution was prepared by dissolving 2.5 g DNS in 25 mL distilled water at 80 °C. Potassium sodium tartrate (75 g) and 50 mL of 2 N sodium hydroxide solution was added to the cooled DNS solution. The final volume of DNS reagents was made up to a volume of 250 mL with distilled water. After the reaction, the mixtures were cooled on ice for 15 min and 1 mL distilled water was added. The absorbance was measured using a microplate reader at a wavelength of 540 nm. Glucose was used as the standard and reducing sugar content was expressed as glucose equivalents (mg GE/g solid).
Ultra-performance (UPLC)-electrospray ionization (ESI)-Q/Orbitrap mass analysis
Tandem mass analysis was performed using a UPLC-ESI-Q/Orbitrap instrument [28]. The UPLC system (Ultimate 3000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was coupled to a Q-Exactive Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The extracts were separated on a Hypersil GOLD™ C18 column (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 1.9 μm, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and ionized in negative mode.
The UPLC separation system comprised a binary solvent system (A, 0.1% formic acid in water, and B, 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile) operating at a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min. The linear gradient used was as follows: 0–2.779 min (90–80% A, 10–20% B), 2.779–5.558 min (80% A, 20% B), 5.558–10.004 min (80–75% A, 20–25% B), 10.004–22.231 min (75–10% A, 25–90% B), 22.231–25.009 min (10–90% A, 90–10% B), and 25.009–31.000 min (90% A, 10% B). The injection volume was 1 μL. The following parameters were used: mass range, 100–1000 mass range; sheath gas flow rate, 40 arbitrary units (AU); auxiliary gas flow rate, 10 AU; heater temperature, 250 °C; capillary temperature, 320 °C; capillary voltage, − 3.5 V; and spray voltage, 2.5 kV. The resolution was set to 35,000 for full scan mass measurements and 17,500 for MS2 measurements. Data analysis was performed using Xcalibur™ software (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
Cell culture and virus
Madin-Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA) and maintained in minimum essential medium (MEM, Hyclone™, Logan, UT, USA) supplemented with 10% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS, Hyclone™) and 1% (v/v) penicillin-streptomycin (Hyclone™) [8].
The human influenza H1N1 virus A/NWS/33 was propagated in allantoic fluid (AF) obtained from 9- to 11-day-old embryonated chicken eggs for 48 h at 37 °C. After inoculation, virus-infected AF was harvested and stored at − 80 °C until further use [29].
Tissue culture infective dose (TCID50) determination
The TCID50 was evaluated in MDCK cells seeded in 96-well plates [8]. Equal volumes of medicinal extracts and viruses were mixed and incubated at 4 °C for 30 min. After incubation, the mixture was added to MDCK cells seeded at a density of 2 × 104 cells/well. The cells were incubated for 4 to 5 days at 37 °C and the cytopathic effect (CPE) was evaluated using 1% crystal violet solution.
Cytotoxicity assay
The 50% cytotoxic dose (CC50) and the 50% effective concentration (EC50) were measured to calculate the selectivity index (SI) [30]. MDCK cells were pre-incubated in 6-well plates until the formation of a monolayer. MDCK cell lines were infected influenza by incubating for 40 min. After infection, remaining viruses were removed and infected cells were incubated with 3 mL medium containing 1% agarose and extracts for 48 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2. After incubation, the cells were stained with 1% crystal violet solution to evaluate the presence of plaques. Cell viability was measured using neutral red dye (0.034%) and cells were stained for 2 h at 37 °C before extracting dye using ethanol-Sorenson citrate buffer (1:1) for 30 min in the dark. Absorbance was measured using a microplate reader at a wavelength of 540 nm. The SI was calculated by dividing the CC50 by the EC50.
Hepatotoxicity and hemolysis
To determine the safety of the antiviral agents studied, the hepatotoxicity and hemolysis of each extract were evaluated. HepG2 cells (hepatocellular carcinoma cells) were obtained from the Korean Cell Line Bank (KCLB, Seoul, Korea). The cells were maintained in MEM containing 10% (v/v) FBS and 1% (v/v) penicillin-streptomycin solution in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Defibrinated sheep blood was obtained from Kisanbio (Seoul, Korea).
Hepatotoxicity was evaluated via MTT assay [31]. HepG2 cells were seeded at a density of 105 cells/well in a 96-well microplate. After 20 h, the cells were treated with extracts and incubated for 48 h. After incubation, the medium was replaced with 2.5 mg/mL MTT solution and incubated to allow the reduction of tetrazolium to formazan. After 2 h, formazan was dissolved in 100 μL dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and the absorbance was measured using a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 570 nm. Cell viability was calculated according to the following formula:
where Acontrol is the absorbance of the control (without extract) and Asample is the absorbance of extract-treated samples.
The extracts’ hemolytic activities were evaluated in sheep blood [32]. Briefly, 100 μL extracts were added to 875 μL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Sheep blood (25 μL) was then added and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. After incubation, all mixtures were centrifuged at 5500×g for 1 min at 4 °C. Hemolytic activity was assessed by measuring the optical density of the supernatant at a wavelength of 540 nm. Hemolytic activity was calculated using to the following formula:
where Acontrol and Asample are the absorbance of the positive control and extracts, respectively. The lysis buffer (positive control) comprised 0.1 mM EDTA and 0.5% Triton X-100 in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4). PBS was used as the negative control.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the IBM SPSS Statistics version 18 software (IBM, New York, NY, USA). Two independent samples (containing controls) were compared by t-test at significant level (p < 0.05).
Results
Phytochemical screening and tandem mass analysis
The phytochemical properties and soluble solid concentrations of the three medicinal herbs are indicated in Table 1. The ethanol and water extracts of B. juncea comprised 62.6 mg QE/g solid and 62.7 mg QSE/g solid, respectively. F. suspensa was a rich source of phytochemicals and contained the following: phenols, 147.4 mg GAE/g solid; flavonoids, 242.3 mg QE/g solid; and saponins, 439.3 mg QSE/g solid. The ethanol extract of I. britannica contained 225.7 GAE/g solid (phenols) and 288.1 mg QSE/g solid (flavonoids). The following were detected in the I. britannica water extract: phenols, 50.8 GAE/g solid; flavonoids, 51.6 mg QE/g solid; and saponins, 82.9 mg QSE/g solid. All extracts showed low levels of condensed tannins and reducing sugars. Among the three medicinal herbs, F. suspensa showed the highest soluble solid content.
The tandem mass analysis of the medicinal herb extracts is shown in Table 2. The phenolic and other phytochemical compounds detected here are in accordance with the results reported in previous studies [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20, 33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. Five compounds were detected in the B. juncea extracts, including sinigrin, a member of the glucosinolate family [34]. Fourteen compounds were detected in the F. suspensa extracts, including caffeic acid (a member of the hydroxycinnamic acids class), quercetin, and kaempferol (flavonols). 6-Methoxyluteolin was not previously reported in F. suspensa but its presence was assumed from the m/z [M-H] and MS2 fragments of I. britannica. In I. britannica, 18 compounds were identified, including chlorogenic acid (hydroxycinnamic acids) and patuletin (flavonols). Rutin and hispidulin were also detected in the I. britannica extract.
Antiviral effects
The virus titration results of the medicinal herb extracts are shown in Table 3. The ethanol extract of B. juncea showed approximately 3 Log TCID50/25 μL reduction at the highest concentration. Whereas the water extract of B. juncea did not show reduction of virus titer comparing to control. In the ethanol extract of I. britannica, no virus was detected at the highest concentration and a titer of 2.5 Log TCID50/25 μL was observed after a 10-fold dilution of the extract. Water extract of I. britannica reduced approximately 1 Log TCID50/25 μL of virus titer at highest concentration but low concentration of water extract of I. britannica were not effective in H1N1 virus A/NWS/33. All F. suspensa extracts caused a 12.59% decrease in the virus titers (3.9 Log TCID50/25 μL) although these were considered ineffective compared to the B. juncea and I. britannica extracts.
The antiviral effects of the extracts against virus-infected cells are reported in Table 4. The water extract of B. juncea showed a CC50 of 9.73 mg and an EC50 of 0.71 mg (SI = 13.668). The other extracts did not show significant antiviral effects on virus-infected cells. In addition, all extract of F. suspensa and I. britannica were showed higher toxicity than extract of B. juncea.
Safety test
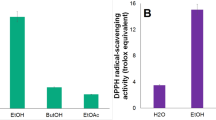
The hemolytic activities and hepatotoxicity of the medicinal herb extracts are shown in Fig. 1. The B. juncea extracts (ethanol and water) did not show significant hemolytic activity at any dilution. The I. britannica extract showed 24.03, 32.48, 43.86, and 95.85% hemolysis at 100-, 50-, 10-, and 1-fold dilutions, respectively. The hemolytic activities of the extracts used at 50-, 10-, and 1-fold dilutions were significantly greater than that of the negative control (24.40%, p < 0.001).
Hemolytic and cytotoxicity of medicinal herb extracts. (a, d, and g) Qualitative analysis of hemolysis; (b, e, and h) Quantitative analysis of hemolysis; (c, f, and i) Viability of HepG2 cells. The soluble solid concentrations of extracts (×1) were 14.1 (Brassica juncea ethanol extract), 0.3 (Brassica juncea water extract), and 18.0 mg/mL (Inula britannica ethanol extract). Data are shown as means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 indicated significant differences compared to the negative control
The viability of cells treated with 100-, 50-, 10-, and 1-fold dilutions of B. juncea ethanol extract was 111.71, 104.71, 97.71, respectively, and 96.89%, and viability was 107.14, 89.42, 85.89, and 79.97% in cells treated with the water extract, respectively. I. britannica extract treatment (100-, 50-, and 10-fold dilutions) resulted in 110.92, 95.34, and 75.36% cell viability, respectively. High toxicity (2.09% viability) was observed in cells treated with the extract diluted 1-fold (p < 0.05).
Discussion
Phenolic compounds are commonly found in fruits, vegetables, grains, herbs, and spices. Phenolic acids, stilbenes, flavonoids, lignans, and ellagic acids are phenolic compounds found in plant foods. The bio-functionalities of these compounds have been studied and they can be used to treat various diseases and disorders without adverse effects [43]. Various phenolic compounds also show antiviral effects [8, 30, 44,45,46,47]. Chlorogenic acid, a caffeoylquinic acid, showed inhibitory effects on NA and H1N1 infection [45]. Quercetin [46, 47], kaempferol [46, 47], isorhamnetin [46], rutin [47], and isoquercetin [47] showed antiviral effects by suppressing viral mRNA expression, hemagglutinin (HA), and NA. Moreover, kaempferol attenuated inflammatory symptoms and decreased mortality in H9N2-infected mice [48]. In this study, the phytochemical properties and antiviral effects of three medicinal herbs were investigated. Five compounds were identified from B. juncea, including chlorogenic acid and kaempferol, and 18 compounds were detected in I. britannica, which included the antiviral phenolic compounds mentioned above (Table 2).
Several studies have reported the use of medicinal herbs in various forms including solvent extracts [44, 49, 50], essential oils [51], and powders [52]. Ghoke et al. [49] reported that hydro-methanol leaf plant extracts decreased HA titers and virus genome copy numbers. Hossan et al. [44] confirmed that embelin, the most abundant compound in Embelia ribes extract, was able to dock with HA, thus hindering the binding of HA to sialic acid-glycoprotein receptors on the host cells. In addition, Tang et al. [52] demonstrated that a mixture of medicinal herb powders inhibited influenza A virus H5N1 infection in mice. The benefits of medicinal herbs are now widely recognized and the demand for natural medicines has increased [53], requiring further research into medicinal herbs containing antiviral agents.
Oseltamivir, which is generally used to treat influenza, causes adverse effects such as nausea and vomiting [54, 55]. In severe cases, enterorrhagia, alimentary tract hemorrhage, and liver injury occurred after treatment with oseltamivir. Feng et al. [54] reported that a 6-year-old boy treated with 60 mg oseltamivir twice a day showed increased alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels. In addition, bilirubin content was increased by liver damage. Powder formulation of zanamivir, another NA inhibitor, was reportedly well tolerated, although inhalation resulted in low bioavailability [56, 57]. Conversely, intravenous administration of aqueous zanamivir resulted in higher bioavailability but this was accompanied by severe adverse effects [56]. Furthermore, Kiatboonsri et al. [58] reported nebulization treatment with zanamivir caused fatal respiratory events in a 25-year-old pregnant woman. In the current study, the hepatotoxicity and hemolytic activities of three medicinal herb extracts showing antiviral effects were measured to assess safety. The ethanol extract of B. juncea did not show hepatotoxicity or hemolytic activity, but decreased virus titers from 4.6 to 1.5 Log TCID50/25 μL. Treatment with the water extract of B. juncea resulted in 80% cell viability, and no hemolytic activity was observed at the highest treatment concentration. Furthermore, the SI was 13.668 when cells were treated with the CC50 (9.73 mg). Ding et al. [45] reported that the SI of chlorogenic acid was 8.12 and Dayem et al. [46] reported that the SI of kaempferol in H1N1-infected MDCK cells was 7. In this study, chlorogenic acid and kaempferol of SI were measured 2.920 and 7.585, respectively. By comparing the SI of B. juncea extract with those of chlorogenic acid and kaempferol, we can conclude that the extract showed higher antiviral effects, as it contains phenolic compounds as well as both chlorogenic acid and kaempferol. This suggests the potential of B. juncea as a potent antiviral agent.
Conclusions
The phytochemical properties and antiviral effects of three medicinal herbs were analyzed. Two antiviral compounds (chlorogenic acid and kaempferol) were detected in B. juncea, and six antiviral phenolic compounds were identified in I. britannica. The SI of the water extract of B. juncea was higher than those of chlorogenic acid and kaempferol. Moreover, B. juncea did not show hemolytic activity and hepatotoxicity. These properties suggest the potential of B. juncea as an antiviral agent.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- AF:
-
Allantoic fluid
- ALT:
-
Alanine transaminase
- AST:
-
Aspartate transaminase
- ATCC:
-
American Type Culture Collection
- CC:
-
Cytotoxic concentration
- CPE:
-
Cytopathic effect
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DNS:
-
(3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid)
- EC:
-
Effective concentration
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- FDA:
-
United States (US) Food and Drug Administration
- HA:
-
Hemagglutinin
- KCLB:
-
Korean Cell Line Bank
- MDCK:
-
Madin-Darby Canine Kidney
- MEM:
-
Minimum essential medium
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NA:
-
Neuraminidase
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- SI:
-
Selectivity index
- TCID50 :
-
Tissue culture infective dose at 50%
References
Qu C, Wang LY, Lin H, Shang EX, Tang YP, Yue SJ, Jin Y, Tao WW, Li SP, Hua YQ, Liu P, Su SL, Zhou H, Qian DW, Duan JA. Hierarchical identification of bioactive components in a medicinal herb by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography and selective knock-out strategy. J Pharmaceut Miomed. 2017;135:206–16.
Jang JY, Lee MJ, You BR, Jin JS, Lee SH, Yun YR, Kim HJ. Allium hookeri root extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects by nuclear factor-κB down-regulation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells. BMC Complem Altern M. 2017;17:126.
Kim J, Lee YJ, Kim YA, Cho ES, Huh E, Bang OS, Kim NS. Aqueous extract of Phragmitis rhizoma ameliorates myelotoxicity of docetaxel in vitro and in vivo. BMC Complem Altern M. 2017;17:393.
Shin EJ, Han AR, Lee MH, Song YR, Lee KM, Nam TG, Lee P, Lee SY, Lim TG. Extraction conditions for Rosa gallica petal extracts with anti-skin aging activities. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2019:1–8.
Kim JH, Lee S, Cho EJ. Acer okamotoanum protects SH-SY5Y neuronal cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2019;28(1):191–200.
Chothe SK, Bhushan G, Nissly RH, Yeh YT, Brown J, Turner G, Fisher J, Sewall BJ, Reeder DM, Terrones M, Jayarao BM, Kuchipudi SV. Avian and human influenza virus compatible sialic acid receptors in little brown bats. Sci Rep-UK. 2017;7:660.
Lee HS, Noh JY, Song JY, Cheong HJ, Choi WS, Jeong HW, Wie SH, Kim WJ. Molecular genetic characteristics of influenza a virus clinically isolated during 2011-2016 influenza seasons in Korea. Influenza Other Resp. 2018;12(4):497–507.
Law AHY, Yang CLH, Lau ASY, Chan GCF. Antiviral effect of forsythoside a from Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl fruit against influenza a virus through reduction of viral M1 protein. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;209:236–47.
Astrahan P, Arkin IT. Resistance characteristics of influenza to amino-adamantyls. BBA-Biomembranes. 2018;1808(2):547–53.
Okunade OA, Ghawi SK, Methven L, Niranjan K. Thermal and pressure stability of myrosinase enzymes from black mustard (Brassica nigra L. W.D.J. Koch. Var. nigra), brown mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern. Var. juncea) and yellow mustard (Sinapsis alba L. subsp. maire) seeds. Food Chem. 2015;187:485–90.
Lee JJ, Kim KH, Kim EJ, Choi JY, Kim SJ, Jeong SI, Kim JI, Joo M. Anti-inflammatory activity of the decoction of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl is related to Nrf2 and A20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;227:97–104.
Park EJ, Kim Y, Kim J. Acylated Flavonol glycosides from the flower of Inula britannica. J Nat Prod. 2000;63(1):34–6.
Khan AL, Hussain J, Hamayun M, Gilani SA, Ahmad S, Rehman G, Kim YH, Kang SM, Lee IJ. Secondary metabolites from Inula britannica L. and their biological activities. Molecules. 2010;15(3):1562–77.
Cai Y, Luo Q, Sun M, Corke H. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer. Life Sci. 2004;74(17):2157–84.
Seca AML, Pinto DCGA, Silva AMS. Metabolomic profile of the genus Inula. Chem Biodivers. 2015;12(6):859–906.
Cai YZ, Sun M, Xing J, Luo Q, Corke H. Structure–radical scavenging activity relationships of phenolic compounds from traditional Chinese medicinal plants. Life Sci. 2006;78(25):2872–88.
Kim SR, Park MJ, Lee MK, Sung SH, Park EJ, Kim J, Kim SY, Oh TH, Markeloins GJ, Kim YC. Flavonoids of Inula britannica protect cultured cortical cells from necrotic cell death induced by glutamate. Free Radical Bio Med. 2002;32(7):596–604.
Bai N, Zhou Z, Zhu N, Zhang L, Quan Z, He K, Zheng QY, Ho CT. Antioxidative flavonoids from the flower of Inula britannica. J Food Lipids. 2005;12(2):141–9.
Geng HM, Zhang DQ, Zha JP, Qi JL. Simultaneous HPLC determination of five flavonoids in Flos Inulae. Chromatographia. 2007;66(3–4):271–5.
Zarei M, Mohammadi S, Komaki A. Antinociceptive activity of Inula britannica L. and patuletin: In vivo and possible mechanisms studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;219:351–8.
Lee YH, Lee NK, Paik HD. Antimicrobial characterization of Inula britannica against Helicobacter pylori on gastric condition. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;26(6):1011–7.
Lee NK, Jeewanthi RKC, Park EH, Paik HD. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of Cheddar-type cheese fortified with Inula britannica extract. J Dairy Sci. 2016;99(1):83–8.
Park EH, Bae WY, Kim JY, Kim KT, Paik HD. Antimelanogenic effects of Inula britannica flower petal extract fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum KCCM 11613P. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B. 2017;18(9):816–24.
AOAC. Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). 17th ed. Arlinton, VA, USA: Association of Official Analytical Chemists International; 2000.
Friedman M, Kozukue N, Kim HJ, Choi SH, Mizuno M. Glycoalkaloid, phenolic, and flavonoid content and antioxidative activities of conventional nonorganic and organic potato peel powders from commercial gold, red, and russet potatoes. J Food Compos Anal. 2017;62:69–75.
Chan KW, Iqbal S, Khong NMH, Ooi DJ, Ismail M. Antioxidant activity of phenolics–saponins rich fraction prepared from defatted kenaf seed meal. LWT-Food Sci Technol. 2014;56(1):181–6.
Ballesteros LF, Teixeira JA, Mussatto SI. Extraction of polysaccharides by autohydrolysis of spent coffee grounds and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Carbohyd Polym. 2017;157:258–66.
Zhuang Y, Ma Q, Guo Y, Sun L. Protective effects of rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum) peel phenolics on H2O2-induced oxidative damages in HepG2 cells and D-galactose-induced aging mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;108:554–62.
Ren T, Dormitorio TV, Qiao M, Huang TS, Weese J. N-halamine incorporated antimicrobial nonwoven fabrics for use against avian influenza virus. Vet Microbiol. 2018;218:78–83.
Ha SY, Youn H, Song CS, Kang SC, Bae JJ, Kim HT, Lee KM, Eom TH, Kim IS, Kwak HH. Antiviral effect of flavonol glycosides isolated from the leaf of Zanthoxylum piperitum on influenza virus. J Microbiol. 2014;52(4):340–4.
Yu HS, Lee NK, Choi AJ, Choe JS, Bae CH, Paik HD. Anti-inflammatory potential of probiotic strain Weissella cibaria JW15 isolated from Kimchi through regulation of NF-κB and MAPKs pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 Cells. J Microbiol Biotechn. 2019;29(7):1022–32.
Shi C, Zhao X, Yan H, Meng R, Zhang Y, Li W, Liu Z, Guo N. Effect of tea tree oil on Staphylococcus aureus growth and enterotoxin production. Food Control. 2016;62:257–63.
Popova IE, Morra MJ. Simultaneous quantification of sinigrin, sinalbin, and anionic glucosinolate hydrolysis products in Brassica juncea and Sinapis alba seed extracts using ion chromatography. J Agr Food Chem. 2014;62(44):10687–93.
Lee NK, Lee JH, Lim SM, Lee KA, Kim YB, Chang PS, Paik HD. Antiviral activity of subcritical water extract of Brassica juncea against influenza virus A/H1N1 in nonfat milk. J Dairy Sci. 2014;97(9):5383–6.
Lin LZ, Sun J, Chen P, Harnly J. UHPLC-PDA-ESI/HRMS/MSn analysis of anthocyanins, flavonol glycosides, and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in red mustard greens (Brassica juncea Coss variety). J Agr Food Chem. 2011;59(22):12059–72.
Kuo PC, Chen GF, Yang ML, Lin YH, Peng CC. Chemical constituents from the fruits of Forsythia suspensa and their antimicrobial activity. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:304830.
Bai Y, Li J, Liu W, Jiao XC, He J, Liu J, Ma L, Gao XM, Chang YX. Pharmacokinetic of 5 components after oral administration of Fructus Forsythiae by HPLC-MS/MS and the effects of harvest time and administration times. J Chromatogr B. 2015;(993–994):36–46.
Wang Z, Xia Q, Liu X, Liu W, Huang W, Mei X, Luo J, Shan M, Lin R, Zou D, Ma Z. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, quality control and future research of Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl: a review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;210:318–39.
Ge Y, Wang Y, Chen P, Wang Y, Hou C, Wu Y, Zhang M, Li L, Huo C, Shi Q, Gao H. Polyhydroxytriterpenoids and phenolic constituents from Forsythia suspensa (Thunb.) Vahl leaves. J Agr Food Chem. 2016;64(1):125–31.
Cui Y, Wang Q, Shi X, Zhang X, Sheng X, Zhang L. Simultaneous quantification of 14 bioactive constituents in Forsythia Suspensa by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation–mass spectrometry. Phytochem Analysis. 2009;21(3):253–60.
Chun JK, Seo DW, Ahn SH, Park JH, You JS, Lee CH, Lee JC, Kim YK, Han JW. Suppression of the NF-κB signalling pathway by ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone, in HeLa cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007;59(4):561–6.
Bai N, Lai CS, He K, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Quan Z, Zhu N, Zheng QY, Pan MH, Ho CT. Sesquiterpene lactones from Inula britannica and their cytotoxic and apoptotic effects on human cancer cell lines. J Nat Prod. 2006;69(4):531–5.
Zhang H, Tsao R. Dietary polyphenols, oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2016;8:33–42.
Hossan MS, Fatima A, Rahmatullah M, Khoo TJ, Nissapatorn V, Galochkina AV, Slita AV, Shtro AA, Nikolaeva Y, Zarubaev VV, Wiart C. Antiviral activity of Embelia ribes Burm. f. against influenza virus in vitro. Arch Virol. 2018;163(8):2121–31.
Ding Y, Cao Z, Cao L, Ding G, Wang Z, Xiao W. Antiviral activity of chlorogenic acid against influenza a (H1N1/H3N2) virus and its inhibition of neuraminidase. Sci Rep-UK. 2017;7:45723.
Dayem AA, Choi HY, Kim YB, Cho SG. Antiviral effect of methylated flavonol isorhamnetin against influenza. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121610.
Rakers C, Schwerdtfeger SM, Mortier J, Duwe S, Wolff T, Wolber G, Melzig MF. Inhibitory potency of flavonoid derivatives on influenza virus neuraminidase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24(17):4312–7.
Zhang R, Ai X, Duan Y, Xue M, He W, Wang C, Xu T, Xu M, Liu B, Li C, Wang Z, Zhang R, Wang G, Tian S, Liu H. Kaempferol ameliorates H9N2 swine influenza virus-induced acute lung injury by inactivation of TLR4/MyD88-mediated NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:660–72.
Ghoke SS, Sood R, Kumar N, Pateriya AK, Bhatia S, Mishra A, Dixit R, Singh VK, Desai DN, Kulkarni DD, Dimri U, Singh VP. Evaluation of antiviral activity of Ocimum sanctum and Acacia arabica leaves extracts against H9N2 virus using embryonated chicken egg model. BMC Complem Altern M. 2018;18:174.
Mehrbod P, Abdalla MA, Njoya EM, Ahmed AS, Fotouhi F, Farahmand B, Gado DA, Tabatabaian M, Fasanmi OG, Eloff JN, McGaw LJ, Fasina FO. South African medicinal plant extracts active against influenza a virus. BMC Complem Altern M. 2018;18:112.
Shayeganmehr A, Vasfi Marandi M, Karimi V, Barin A, Ghalyanchi-Langeroudi A. Zataria multiflora essential oil reduces replication rate of avian influenza virus (H9N2 subtype) in challenged broiler chicks. Brit Poultry Sci. 2018;59(4):389–95.
Tang Y, Wang Z, Huo C, Guo X, Yang G, Wang M, Tian H, Hu Y, Dong H. Antiviral effects of Shuanghuanglian injection powder against influenza a virus H5N1 in vitro and in vivo. Microb Pathogenesis. 2018;121:318–24.
Jokar NK, Noorhosseini SA, Allahyari MS, Damalas CA. Consumers' acceptance of medicinal herbs: an application of the technology acceptance model (TAM). J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;207:203–10.
Fang S, Qi L, Zhou N, Li C. Case report on alimentary tract hemorrhage and liver injury after therapy with oseltamivir. Medicine. 2018;97(38):e12497.
Guzmán DC, Herrera MO, Brizuela NO, Mejía GB, García EH, Olguín HJ, Ruíz NL, Peraza AV. Oseltamivir and indomethacin reduce the oxidative stress in brain and stomach of infected rats. APMIS. 2018;126(2):128–34.
Cleary PR, Crofts J, Parry-Ford F, Chand M, Phin N. Characteristics and mortality of severe influenza cases treated with parenteral aqueous zanamivir, United Kingdom, October 2009 to January 2011. Influenza Other Resp. 2019;13(1):44–53.
Takizawa N, Yamasaki M. Current landscape and future prospects of antiviral drugs derived from microbial products. J Antibiot. 2018;71:45–52.
Kiatboonsri S, Kiatboonsri C, Theerawit P. Fatal respiratory events caused by zanamivir nebulization. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(4):620.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry (IPET) through Agri-Bio industry Technology Development Program funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) [grant numbers 116136–3]. This funding body was not involved in the design of the study or collection, analysis, or interpretation of data or in writing manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WYB performed analysis and processed the data. HYK designed and performed the experiments. NKL and KSC contributed substantially to the analysis and interpretation of the data. KHC, YHH, and JSE provided supported during the analysis. HDP critically reviewed the manuscript and experimental results. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, WY., Kim, HY., Choi, KS. et al. Investigation of Brassica juncea, Forsythia suspensa, and Inula britannica: phytochemical properties, antiviral effects, and safety. BMC Complement Altern Med 19, 253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2670-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-019-2670-x