Abstract
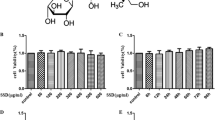
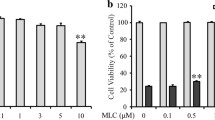
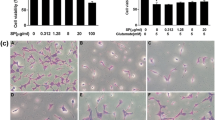
Oxidative stress by over-production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in brain is widely known as a cause of neurodegenerative disease. We investigated protective effects of Acer okamotoanum against oxidative stress by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells. Acer okamotoanum reduced ROS production and lactate dehydrogenase release in H2O2-induced SH-SY5Y cells, resulting in elevation of cell viability. To elucidate protective mechanisms, we measured inflammation and apoptosis-associated protein expressions. Treatment with A. okamotoanum dose-dependently decreased pro-inflammatory proteins such as inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2. Treatment with A. okamotoanum showed down-regulation of pro-apoptosis genes such as cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, and Bax, and up-regulation of anti-apoptosis protein including Bcl-2, in H2O2-induced SH-SY5Y cells. We demonstrated potential anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effect of A. okamotoanum in H2O2-induced SH-SY5Y cells. These results suggest that A. okamotoanum may possess neuroprotective potential, but further study is necessary to elucidate its pharmacological effects in neurodegenerative diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amor S, Puentes F, Baker D, Van Der Valk P. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 129: 154–169 (2010)
Bae KH. Medicinal Plants of Korea. Kyo-Hak Press, Seoul, Korea. pp. 301–302 (2000)
Barnes PJ, Karin M. Nuclear factor-κB—a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 336: 1066–1071 (1997)
Bi W, Gao Y, Shen J, He C, Liu H, Peng Y, Zhang C, Xiao P. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of the genus Acer (maple): a review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 189: 31–60 (2016)
Choi SY, Kim JH, Lee J, Lee S, Cho EJ. Protective effect of Acer okamotoanum from oxidative stress in C6 glial cells. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 60: 141–147 (2017a)
Choi SY, Lee J, Lee DG, Lee S, Cho EJ. Acer okamotoanum improves cognition and memory function in Aβ25–35-induced Alzheimer’s mice model. Appl. Biol. Chem. 60: 1–9 (2017b)
Finkel T, Holbrook NJ. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 408: 239–247 (2000)
Garcimartín A, Merino JJ, González MP, Sánchez-Reus MI, Sánchez-Muniz FJ, Bastida S, Benedí J. Organic silicon protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against hydrogen peroxide effects. BMC. Complement Altern. Med. 14: 384 (2014)
González-Sarrías A, Núñez-Sánchez MÁ, Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC. Neuroprotective effects of bioavailable polyphenol-derived metabolites against oxidative stress-induced cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 65: 752–758 (2016)
Gorman AM, McGowan A, O’Neill C, Cotter T. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Sci. 139: 45–52 (1996)
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE, Berg K. Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J. Immunol. Methods 119: 203–210 (1989)
Hu XL, Niu YX, Zhang Q, Tian X, Gao LY, Guo LP, Meng WH, Zhao QC. Neuroprotective effects of Kukoamine B against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis and potential mechanisms in SH-SY5Y cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 40: 230–240 (2015).
Jeong MH, Ha JH, Oh SH, Kim SS, Lee HJ, Kang HY, Lee HY. Comparison of biological activities of Acer mono and A. okamotoanum extracts by water extraction and low temperature high pressure extraction. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 17: 407–411 (2009)
Jin WY, Min BS, Youn UJ, Hung TM, Song KS, Seong YH, Bae KH. Chemical constituents from the leaf and twig of Acer okamotoanum Nakai and their cytotoxicity. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 14: 77–81 (2006)
Jin W, Thuong PT, Su ND, Min BS, Son KH, Chang HW, Bae K. Antioxidant activity of cleomiscosins A and C isolated from Acer okamotoanum. Arch. Pharm. Res. 30: 275–281 (2007)
Jin L, Han JG, Ha JH, Jeong HS, Kwon MC, Jeong MH, Lee HJ, Kang HY, Choi DH, Lee HY. Comparison of antioxidant and glutathione S-transferase activities of extracts from Acer mono and A. okamotoanum. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 16: 427–433 (2008)
Jung WK, Heo SJ, Jeon YJ, Lee CM, Park YM, Byun HG, Choi YH, Park SG, Choi IW. Inhibitory effects and molecular mechanism of dieckol isolated from marine brown alga on COX-2 and iNOS in microglial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57: 4439–4446 (2009)
Kim HJ, Woo ER, Shin CG, Park H. A new flavonol glycoside gallate ester from Acer okamotoanum and its inhibitory activity against human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) integrase. J. Nat. Prod. 61: 145–148 (1998)
Koo BS, Lee WC, Chung KH, Ko JH, Kim CH. A water extract of Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae) rescues PC12 cell death caused by pyrogallol or hypoxia/reoxygenation and attenuates hydrogen peroxide induced injury in PC12 cells. Life Sci. 75: 2363–2375 (2004)
Lee J, Lee DG, Rodriguez JP, Park JY, Cho EJ, Jacinto SD, Lee S. Determination of flavonoids in Acer okamotoanum and their aldose reductase inhibitory activities. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 59: 131–177 (2018)
Li J, Li W, Su J, Liu W, Altura BT, Altura BM. Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis in cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells: possible relation to neurodegenerative diseases and strokes. Brain Res. Bull. 62: 101–106 (2003)
Mandel SA, Amit T, Weinreb O, Reznichenko L, Youdim MB. Simultaneous manipulation of multiple brain targets by green tea catechins: a potential neuroprotective strategy for Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. CNS. Neurosci. Ther. 14: 352–365 (2008)
Miller NJ, Rice-Evans CA. The relative contributions of ascorbic acid and phenolic antioxidants to the total antioxidant activity of orange and apple fruit juices and blackcurrant drink. Food Chem. 60: 331–337 (1997)
Minghetti L. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 63: 901–910 (2004)
Moon HS, Kwon SD. Sap collection and major components of Acer okamotoanum Nakai native in Ullungdo. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 12: 249–254 (2004)
Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 65: 55–63 (1983)
Nirmaladevi D, Venkataramana M, Chandranayaka S, Ramesha A, Jameel NM, Srinivas C. Neuroprotective effects of bikaverin on H2O2-induced oxidative stress mediated neuronal damage in SH-SY5Y cell line. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 34: 973–985 (2014)
Park HR, Lee H, Park H, Jeon JW, Cho WK, Ma JY. Neuroprotective effects of Liriope platyphylla extract against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. BMC. Complement Altern. Med. 15: 171 (2015)
Pastorino JG, Chen ST, Tafani M, Snyder JW, Farber JL. The overexpression of Bax produces cell death upon induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 7770–7775 (1998)
Perticone P, Gensabella G, Cozzi R. Damage proneness induced by genomic DNA demethylation in mammalian cells cultivated in vitro. Mutagenesis 12: 259–264 (1997)
Qadir SA, Kim CH, Kwon MC, Lee HJ, Kang HY, Choi DH, Lee HY. Comparison of anticancer and immuno-modulatory activities in the different parts of the Acer mono Max. and Acer okamotoanum. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 15: 405–410 (2007)
Racher J, Looby D, Griffiths JB. Use of lactate dehydrogenase release to assess changes in culture viability. Cytotechnology 3: 301–307 (1990)
Shi C, Liu J, Wu F, Yew DT. Ginkgo biloba extract in Alzheimer’s disease: from action mechanisms to medical practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 11: 107–123 (2010)
Shin KY, Lee GH, Park CH, Kim HJ, Park SH, Kim S, Kim HS, Lee KS, Won BY, Lee HG, Choi JH A novel compound, maltolyl p‐coumarate, attenuates cognitive deficits and shows neuroprotective effects in vitro and in vivo dementia models. J. Neurosci. Res. 85: 2500–2511 (2007)
Somayajulu M, McCarthy S, Hung M, Sikorska M, Borowy-Borowski H, Pandey S. Role of mitochondria in neuronal cell death induced by oxidative stress; neuroprotection by Coenzyme Q 10. Neurobiol. Dis. 18: 618–627 (2005)
Tabner BJ, Turnbull S, El-Aganf O, Allsop D. Production of reactive oxygen species from aggregating proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 1: 507–517 (2001)
Thayyullathil F, Chathoth S, Hago A, Patel M, Galadari S. Rapid reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation induced by curcumin leads to caspase-dependent and-independent apoptosis in L929 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 45: 1403–1412
Tilstra JS, Clauson CL, Niedernhofer LJ, Robbins PD. NF-κB in aging and disease. Aging Dis. 2: 449–465 (2014)
Wang RG, Zhu XZ. Subtoxic concentration of manganese synergistically potentiates 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 961: 131–138 (2003)
Wang X, Ohnishi K, Takahashi A, Ohnishi T. Poly (ADP-ribosyl) ation is required for p53-dependent signal transduction induced by radiation. Oncogene 17: 2819–2825 (1998)
Zhang L, Yu H, Sun Y, Lin X, Chen B, Tan C, Cao G, Wang Z. Protective effects of salidroside on hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 564: 18–25 (2007)
Zhou N, Tang Y, Keep RF, Ma X, Xiang J. Antioxidative effects of Panax notoginseng saponins in brain cells. Phytomedicine 21: 1189–1195 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2015R1D1A1A01058868), Republic of Korea. This research was supported by Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2016_H1A2A1906940).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.H., Lee, S. & Cho, E.J. Acer okamotoanum protects SH-SY5Y neuronal cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 191–200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0381-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0381-6