Abstract
Background
Vanillin, a type of phenolic released during the pre-treatment of lignocellulosic materials, is toxic to microorganisms and therefore its presence inhibits the fermentation. The vanillin can be reduced to vanillyl alcohol, which is much less toxic, by the ethanol producer Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The reducing capacity of S. cerevisiae and its vanillin resistance are strongly correlated. However, the specific enzymes and their contribution to the vanillin reduction are not extensively studied. In our previous work, an evolved vanillin-resistant strain showed an increased vanillin reduction capacity compared with its parent strain. The transcriptome analysis suggested the reductases and dehydrogenases of this vanillin resistant strain were up-regulated. Using this as a starting point, 11 significantly regulated reductases and dehydrogenases were selected in the present work for further study. The roles of these reductases and dehydrogenases in the vanillin tolerance and detoxification abilities of S. cerevisiae are described.
Results
Among the candidate genes, the overexpression of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH6, acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene ALD6, glucose-6-phosphate 1-dehydrogenase gene ZWF1, NADH-dependent aldehyde reductase gene YNL134C, and aldo-keto reductase gene YJR096W increased 177, 25, 6, 15, and 18 % of the strain μmax in the medium containing 1 g L−1 vanillin. The in vitro detected vanillin reductase activities of strain overexpressing ADH6, YNL134C and YJR096W were notably higher than control. The vanillin specific reduction rate increased by 8 times in ADH6 overexpressed strain but not in YNL134C and YJR096W overexpressed strain. This suggested that the enzymes encoded by YNL134C and YJR096W might prefer other substrate and/or could not show their effects on vanillin on the high background of Adh6p in vivo. Overexpressing ALD6 and ZWF1 mainly increased the [NADPH]/[NADP+] and [GSH]/[GSSG] ratios but not the vanillin reductase activities. Their contribution to strain growth and vanillin reduction were balancing the redox state of strain when vanillin was presented.
Conclusions
Beside the reported Adh6p, the enzymes encoded by YNL134C and YJR096W were proved to have vanillin reduction activity in present study. While ALD6 and ZWF1 did not directly reduce vanillin to vanillyl alcohol, their contribution to vanillin resistance primarily depended on the enhancement of the reducing equivalent supply.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Lignocellulosic materials are a readily available and renewable resource for biofuel and chemical production instead of starch, sucrose, or other resources that are better suited as food. Pretreating the lignocellulosic materials, generally with diluted acid at a high temperature, is necessary to overcome the recalcitrant structure of lignocellulose and separate the cross-linked polysaccharides. However, with the release of sugars, toxic compounds, such as organic acids (acetic acid and formic acid), furans [furfural and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural (HMF)], and phenolics are produced during the pretreatment process [1, 2]. These toxic compounds inhibit the growth and fermentation efficiency of the microorganisms.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is recognized as a traditionally competitive cell factory for biorefining because of its superior tolerance to ethanol and low pH and its ease of genetic manipulation [3–5]. The resistance of S. cerevisiae to organic acids and furans was extensively investigated. Acetic acid enters yeast cells and causes a decrease of pH in the cytoplasm, inhibition of metabolism, and disruption of the proton gradient of the plasma membrane [6]. Inhibiting the plasma membrane channel Fps1p used for uptake of acetate and increasing the expression of major facilitator superfamily and ATP-binding cassette transporters, which are responsible for acetate excretion, increases the resistance of S. cerevisiae to acetic acid [6, 7]. Furans cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation in cells and decrease energy production by inhibiting glycolysis, which prolongs the lag phase [8–11]. Increasing the expression of Adh6p, Adh7p, Ald4p, Gre3p, Adh1p, Ari1p, and Gre2p, which have furfural or HMF reductase activity, or Zwf1p, Gnd1p, Gnd2p, Tdh1p, and Ald6p, which increase the NADPH supply, enhanced the rate of furfural and HMF detoxification in S. cerevisiae [12]. By comparison, only limited knowledge of S. cerevisiae tolerance to phenolics is reported.
Phenolic compounds, which are generated from the segmental degradation of lignin exhibit strong detrimental effects, even at low concentrations, on the fermentation of S. cerevisiae [2, 13]. This type of compound generally suppressed growth and ethanol production rate but had little effect on the ethanol yields (YEtOH). Three kinds of phenolics that contain para-hydroxyphenyl, guaiacyl, and syringyl, respectively, exist in lignocellulose hydrolysate. In general, the most toxic to least toxic of these phenolics in order is para-hydroxyphenyl > guaiacyl > syringyl. Adding a methoxy group to the aromatic ring can reduce the toxicity of phenolics by decreasing their hydrophobicity [2]. Low-molecular-mass phenolic compounds are more potent inhibitors towards S. cerevisiae than high-molecular-weight phenolics [9]. Vanillin is a simple guaiacyl phenol with high toxicity. At low concentrations, it is a more potent repressor of fermentation than other phenolic by-products derived from lignin [2]. Moreover, the de novo synthesis of vanillin, a common additive of foods and cosmetics, has been recently achieved in yeast cells [14]. Enhancing the strain resistance to vanillin is an important issue to achieve efficient vanillin production [14]. It was reported that vanillin triggers the accumulation of ROS in cells, fragments the mitochondria [14, 15], and represses the translation process by blocking ribosomes assembly, which cause the accumulation of processing bodies and stress granules [16]. Increasing the ergosterol level of S. cerevisiae enhanced the fluidity and stability of the membrane, improving the strain growth in the presence of vanillin [17]. Converting the vanillin to vanillyl alcohol, which is less toxic than vanillin, by reductases is another important and efficient way for vanillin detoxification in yeast [5, 12]. Thus, it is of interest to identify the proteins that function in vanillin reduction while minimizing any reduction in ethanol yield or increasing the production of by-products.
In our previous study, the oxidoreductase activity of the vanillin-tolerant S. cerevisiae strain EMV-8 was found to be significantly higher than its parent strain NAN-27 [5]. In the present work, the significantly up-regulated reductases and dehydrogenases in EMV-8 were identified and their roles in the detoxification of vanillin were characterized. The effect of overexpressing these genes on the ethanol fermentation was also studied.
Results
Up-regulated reductases in vanillin-tolerant S. cerevisiae
The vanillin-tolerant strain EMV-8 obtained by adaptive evolution exhibited a high vanillin reduction rate and antioxidant capacity. The transcriptional analysis of EMV-8 revealed an up-regulated oxidoreductase activity (GO: 0016491), which might convert the vanillin directly or supply the reduced coenzyme. To identify the roles of various dehydrogenases in vanillin tolerance, the up-regulated reductases and dehydrogenases in EMV-8 were selected as studying candidates (Table 1), as well as the gene ADH6, whose vanillin reductase activity has been previously identified [18].
Adh6p is an efficient but not sole protein with vanillin reduction activity in S. cerevisiae
It was reported that purified Adh6p has vanillin reduction activity in vitro [18]. Furthermore, vanillin breakdown was not observed in an adh6Δ strain [16]. Therefore, it was suggested that the vanillin conversion in S. cerevisiae was only dependent on Adh6p [16]. However, the transcriptional level of ADH6 in the vanillin-tolerant strain EMV-8 was not higher than its parent strain NAN-27 (Table 1). Therefore, Adh6p did not contribute to increasing the vanillin reduction rate in EMV-8.
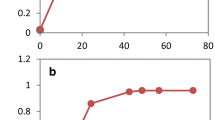
The role of Adh6p in vanillin tolerance was further studied in the lab strain CEN.PK102-3A. Overexpressing ADH6 increased the NADPH-dependent vanillin reduction activity by 97 % and remarkably enhanced the strain growth in the medium containing vanillin (Fig. 1a, Table 2). The strain overexpressing ADH6 reduced 1 g L−1 vanillin to vanillyl alcohol in 9 h compared with 40 h for the control strain (Fig. 1b). Deletion of ADH6 decreased the growth of the strain in vanillin (Fig. 1c) where the reduction of vanillin was delayed but not eliminated. The adh6Δ mutant reduced 1 g L−1 vanillin completely in 54 h (Fig. 1d). Our results revealed that Adh6p is an important and efficient vanillin reductase, but there are other reductases capable of acting on vanillin in S. cerevisiae.
Overexpression of ADH6 accelerated the growth in the presence of vanillin. The growth curve (a) and vanillin reduction (b) of strain BSPJ3 (containing empty vector, control; ■) and the strain overexpressing ADH6 (★) in the SC-URA medium with 1 g L−1 vanillin. Comparison of growth (c) and vanillin reduction (d) of ADH6 knock-out strain (▷) and CEN.PK102-3A (control; □) in the SD medium with 1 g L−1 vanillin. All the data are the mean value ± standard deviation of independent duplicate tests
Overexpressing YNL134C, YJR096W, ALD6, and ZWF1 enhanced strain growth in vanillin
The up-regulated genes in EMV-8 (Table 1) were overexpressed in strain CEN.PK102-3A. The empty vector transformed into CEN.PK102-3A resulted in BSJP3, which was used as the control.
Overexpressing YNL134C, YJR096W, and ALD6 slightly decreased the growth and ethanol yield of the resulting strains in vanillin-free medium (Table 2). However, when vanillin was present, overexpressing YNL134C, YJR096W, and ALD6 accelerated glucose consumption and ethanol production (Fig. 2). The maximum specific growth rates of the strains overexpressing YNL134C, YJR096W, and ALD6 were respectively 15, 18, and 25 % faster than that of BSJP3, which only contains empty vector, in the presence of 1 g L−1 vanillin. The ethanol yields of the strains overexpressing YJR096W and YNL134C both were 11 % higher than that of BSJP3 (Table 2). The vanillin specific reduction rates of the strains overexpression ADH6, ALD6, ZWF1, YNL134C and YJR096W were 0.584, 0.052, 0.082, 0.066, and 0.064 g g−1 h−1, respectively. Compared to the 0.065 g g−1 h−1 of control, only ADH6 and ZWF1 significantly increased the specific vanillin reduction rate. Other genes may accelerate growth more than vanillin reduction. Overexpressing the genes ARA1, ARA2, BDH1, BDH2, MDH3, and IDP3, which were up-regulated in the vanillin-tolerant strain EMV8, did not enhance strain growth in the presence of vanillin (Fig. 3).
The growth and fermentation characteristics of strains. The cell growth (a), vanillin reduction (b), glucose consumption (c), and ethanol production (d) curves are shown. The fermentation was conducted in SC-URA with 1 g L−1 of vanillin. All the data are the mean value ± standard deviation of independent duplicate tests. Symbols: BSPJ3 (control, Black square); strains overexpressing ALD6 (Red circle), ZWF1 (Blue triangle), YNL134C (Green triangle), and YJR09W (Violet diamond)
The growth curve (a) and vanillin reduction (b) of strains overexpressing ARA1 (Red circle); ARA2 (Blue triangle); BDH1 (Blue green triangle); BDH2 (Pink triangle); MDH3 (Yellow green triangle); IDP3 (Violet diamond) and the control BSPJ3 (■Black square) in the medium of SC-URA with additional 1 g L−1 vanillin. All the data were mean value ± standard deviation of independent two experiments
The vanillin reductase activity, the ratio of NAD(P)H to NAD(P)+, and the ratio of reduced glutathione (GSH) to oxidized glutathione (GSSG) of the strains were determined to distinguish whether the growth improvement was due to the enhanced vanillin reductase activity or the increased reduced-coenzyme and GSH supply. The enzymes encoded by ADH6, YNL134C and YJR096W prefer different coenzymes and exhibited notable vanillin reduction activity in vitro (Fig. 4a). The reductase activity encoded by ADH6 mainly depended on NADPH. Overexpressing ADH6 increased the vanillin reductase activity of strain by 3.5 times. The reductase activity encoded by YNL134C mainly depended on NADH. The strain overexpressing YNL134C exhibited 153 % of the NADH-dependent vanillin reduction activity of the control strain. The enzyme encoded by YJR096W had both NADH- and NADPH-dependent vanillin reduction activities. Overexpressing YJR096W increased strain NADH- and NADPH-dependent vanillin reduction activity by 45 and 69 %, respectively, while the Ald6p and Zwf1p did not contribute to the vanillin reduction activity of the test strains (Fig. 4a). The ratio of NADPH to NADP+ from the strains overexpressing ZWF1, ALD6, YNL134C, and YJR096W were 1.96, 1.55, 1.17, and 1.12 times the control, respectively (Fig. 4b). The ratio of NADH to NAD+ from the strains overexpressing ZWF1 also increased 21 % compared to the control strain (Fig. 4c). Furthermore, the ratio of GSH to GSSG from the strains overexpressing ZWF1, ALD6, YNL134C, and YJR096W were 1.4, 1.8, 0.9, and 1.0 times the control strain, respectively (Fig. 4d). This suggested that overexpressing ZWF1 and ALD6 enhanced the antioxidant capacity of the yeast strain.
Discussion
The vanillin tolerance of S. cerevisiae can be primarily attributed to its antioxidative and vanillin detoxification capacity [15]. The vanillin detoxification in yeast depends on the reduction of vanillin [12]. In the present study, we confirmed that overexpressing ADH6, YNL134C, YJR096W, ALD6, and ZWF1 enhanced strain growth and accelerated vanillin reduction in the presence of vanillin. The enzymes encoded by ADH6, YNL134C, and YJR096W show in vitro detected vanillin reductase activities, however, only ADH6 increased the vanillin specific reduction rate. The enzymes encoding by YNL134C and YJR096W may have more prefer substrates in vivo during the fermentation. For example, the acetaldehyde was one of favorite substrates of enzyme encoding by YNL134C [19]. Furthermore, effects of YNL134C and YJR096W could be concealed on the high background activity of Adh6p. Therefore, overexpressing YNL134C and YJR096W did not increase the vanillin specific reduction rate. However, their whole accumulative contribution on vanillin detoxification should not be underestimated. YJR096W were found to response to DNA damage [20] and YNL134C encodes a non-zinc-containing MDR (medium-chain dehydrogenases/reductases), which type of proteins behaved protective functions [19, 21]. These characteristics may related to the enhancement of strain growth in the medium containing vanillin, but the mechanism is still not clear. While overexpression of ALD6 and ZWF1 enhanced the NADPH supply, and increased the ratio of cellular GSH to GSSG, which helped to improve the antioxidant activity of the strain.
Certain aldehydes, such as furfural and HMF that derived from sugars and various phenolics that generated from the breakdown of lignin, are the main toxic compounds in lignocellulose hydrolysates. Their detoxification is directly related to their reduction. Therefore, the organism may benefit more from a multifunctional reductase than an enzyme specific to one or two aldehydes. The enzymes encoded by ADH6, YNL134C, and YJR096W all accept a wide range of substrates. The purified Adh6p possessed a specific NADPH-dependent reductase activity and accepted a broad range of substrates, including linear and branched-chain primary alcohols and aldehydes, substituted cinnamyl alcohols and aldehydes, as well as substituted benzaldehydes and their corresponding alcohols [18]. Its high reduction activities towards furfural and HMF were also demonstrated [12, 22]. The enzyme encoded by YNL134C was previously described as a NADH-dependent aldehyde reductase with activity towards formaldehyde, acetaldehyde, and furfural [19]. The enzyme encoded by YJR096W is known as an arabinose reductase [23]. It also has high catalytic efficiencies towards aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehydes and phenylglyoxal [24]. Therefore, these genes may be of use to increase the strain tolerance to lignocellulosic materials. The reduced coenzyme is another limiting factor involved in aldehyde reduction. Zwf1p catalyzes the first step (also the rate-limiting step) of the pentose phosphate pathway, which is the primary route for generating NADPH in yeast [25, 26]. Ald6p provides NADPH by converting acetaldehyde to acetate [26]. Overexpressing ALD6 and ZWF1 increases the intracellular NADPH radio, therefore enhancing the reduction of furfural, HMF [27], and vanillin in our work. NADPH is also an electron acceptor of GSH regeneration [28]. The GSH is the main component of the antioxidant system in living cells, scavenging ROS by oxidizing to GSSG. The increased ratio of GSH to GSSG may help to protect the cells from intracellular ROS accumulation induced by vanillin [15]. Therefore, overexpressing ALD6 and ZWF1 may be a general strategy to increase the strain tolerance to lignocellulosic materials. However, because the generation of NADPH is coupled with carbon flow to the pentose phosphate pathway and pathways generate byproducts, further effort is required to fine tune the expression of these genes to balance the product yield and strain tolerance.
Conclusions
The enzymes encoded by ADH6, YNL134C, and YJR096W have vanillin reductase activity, while overexpression of ALD6 and ZWF1 had positive effects on vanillin resistance and detoxification in S. cerevisiae, which was attributed to the enhancement of the NADPH supply. Overexpressing these genes enhanced the growth and metabolism of S. cerevisiae in environment containing the inhibitor vanillin. Additionally, since the benefits of those genes to strain tolerance towards other toxic compounds found in lignocellulosic hydrolysates, such as furfural, were suggested, overexpression of select genes may represent a general strategy for increasing the tolerance of S. cerevisiae to lignocellulosic materials and warrants further investigation.
Methods
Construction of plasmids and yeast strains
The genes expressed in this work were amplified from the genomic DNA of the lab strain CEN.PK102-3A (MATa; ura3-52, His3Δ1, leu2-3,112) [29]. The 2 μ plasmid pJFE3 [30] was transformed into CEN.PK102-3A to yield BSPJ3, which was used as the control. The genes were inserted into plasmid pJFE3 under the control of the TEF1 promoter and PGK1 terminator. The resulting recombinant plasmids were transformed into strain CEN.PK102-3A to yield the respective gene overexpression strains. The gene deletion was performed through homologous recombination. The primers (Additional file 1: Table S1) used to amplify the destruction cassette from plasmid pUG6 contain a sequence that is homologous with the deleted gene and the KanMX expression cassette. The destruction cassette was transformed into the lab strain CEN.PK102-3A and the mutants were screened in YPD medium (10 g L−1 yeast extract, 20 g L−1 tryptone, 20 g L−1 glucose, pH 5.0) containing 400 mg L−1 G418.
Fermentation
SD or SC-URA medium, which containing 20 g L−1 glucose, 1.7 g L−1 yeast nitrogen base (YNB, Sangon, China), and 5 g L−1 ammonium sulfate (Sangon, China) replenished with CSM or CSM-URA (MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH, USA), and 1 g L−1 vanillin was used for batch fermentation. A single colony was inoculated into 3 mL SD or SC-URA, cultured 24 h at 30 °C, transferred into 10 mL fresh medium with OD600 at 0.2 and cultured 12 h. Then, the cells were inoculated into 100-mL flasks containing 40 mL of fermentation medium with an initial OD600 of 0.5. The fermentation was performed at 30 °C and 200 rpm.
Analyses of extracellular metabolite
The concentrations of glucose and ethanol were tested using a HPLC prominence LC-20A (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with an Aminex HPX-87H ion exchange column (Bio-Rad, USA) and refractive index detector RID-10A (Shimadzu, Japan); 5 mmol L−1 H2SO4 was used as a mobile phase with flow rate of 0.6 mL min−1 at 45 °C [4]. Vanillin and vanillyl were also determined by HPLC using a BioSil-C18 column (Bio-Rad, USA). The peaks were detected at room temperature using ultraviolet detection (SPD-M20A) at 210 nm with a mobile phase containing 40 % aqueous methanol supplied at a flow rate of 0.6 mL min−1 [13].
Calculation of physiological parameters
The biomass concentrates were estimated according to the measured OD 600 -dry weight correlation. One unit of OD 600 equals 0.23 g L−1 biomass. The maximum growth rates are the linear regression coefficients of the ln OD 600 versus time during the exponential growth phase. Specific consumption rates of vanillin were calculated using the following equation:
Where r is the specific consumption rate during the phase from sampling point m to sampling point n; A, B, and t are the metabolite concentration, biomass concentration, and time, respectively, at sampling points n, i, and m, as previously described [31]. The ethanol yields are the ethanol concentrate versus the consumed sugar.
Enzyme activity assay
The cells were cultured in SC-URA medium. When the OD reached 4.0, the cells were harvested and re-suspended in 33 mM Na3PO4 buffer (pH = 7.0) with 1 mM PMSF, which was used to inhibit any protease activity. Then, the cells were broken by φ 0.5-mm glass beads using a Fast Prep cell homogenizer (ThermoSavant, Germany) and centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 10 min. The supernatant was collected as a cell-free extract for the enzyme activity assay.
The dehydrogenase activity towards vanillin was determined according to the method of Larroy [18]. Enzyme activities towards vanillin were assayed in 0.6-mL reaction mixtures containing 33 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 0.5 mM NADPH, and 1 mM vanillin (using 0.2-cm path length cuvettes). The molar absorption coefficient (ε365) was 7.71 mM−1 cm−1 for vanillin plus NADPH. One unit (U) of enzyme activity is defined as the amount of enzyme that can reduce 1 μmol of NADPH plus vanillin per minute. Protein concentrations were measured using a BCA protein assay reagent kit (Beyotime, China). The specific enzyme activity (U mg−1 protein) was the enzyme activity per milligram of protein.
Quantification of NAD(P)+ and NAD(P)H
Cells were cultured in 40 mL SC-URA medium in a 100-mL flask starting at an initial OD600 of 0.2. When the OD600 reached 4.0, 20 mL of culture were injected into 30 mL of −80 °C precooled methanol to quench the cells. Cells were collected by centrifugation at −20 °C at 12,000 × g for 5 min and washed twice with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Then, the cells were resuspended in 150 μL of 0.2 M NaOH (for NAD(P)H extraction) or 150 μL of 0.2 M HCl (for NAD(P) +extraction) and multi-gelated by liquid nitrogen. The extracts were neutralized by adding 150 μL of 0.1 M HCl (for NAD(P)H extraction) or 150 μL of 0.1 M NaOH (for NAD(P)+ extraction). The cellular debris was removed by centrifugation at 12,000 × g for 5 min. The supernatants were transferred to new tubes and stored at −80 °C until the assay.
The concentration of NADP(H) was quantified using a sensitive enzymatic cycling assay as reported previously [32, 33]. The cycling assay was carried out in a reagent mixture containing equal volumes of 1.0 M bicine buffer (pH 8.0), 30 mM glucose-6-phosphate, 40 mM EDTA (pH 8.0), 4.2 mM 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide, twice the volume of 16.6 mM phenazine ethosulfate, and 3 volumes of water, previously incubated at 25 °C. Then, 0.9 mL of the reagent mixture, 50 μL neutralized extract, and 50 μL of yeast glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (10 U mL−1, Sigma, USA) were added to start the NADP(H) assay in 1-mL cuvettes. The absorbance at 570 nm was recorded for 1 min at 25 °C. The standard curves of NADPH and NADP+ were conducted in the aforementioned assay buffer using a gradient concentration of NADPH or NADP+ instead of the neutralized extract.
For NAD(H) determination, the final concentration of 10 % (v/v) ethanol was used instead of glucose-6-phosphate in the reaction mixture, and the reaction was started by adding 50 μl of yeast ethanol dehydrogenase II (500 U mL−1 in Bicine buffer, Sigma, USA) instead of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Quantification of GSH and GSSG
The cells were cultured in SC-URA medium and collected when the OD600 reached 4.0 and then were washed by PBS. The mixture of cells were added to three times the volume of deproteinization buffer M from the GSH and GSSG Assay Kit (Beyotime S0053, China) and then were alternately subjected to multi-gelation twice in liquid nitrogen and 37 °C water. After centrifugation (12,000 × g, 10 min, 4 °C), the supernatant was collected for GSH and GSSG determination. The levels of GSH and GSSG were determined using a GSH and GSSG Assay Kit (Beyotime S0053) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
The transcriptional dataset supporting the conclusions of this article is available in the Supplementary Materials of reference 5 (doi:10.1007/s10295-014-1515-3).
Abbreviations
- GSH/GSSG:
-
reduced/oxidized form of glutathione
- HMF:
-
5-hydroxymethyl furfural
- NADH/NAD+ :
-
reduced/oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- NADPH/NADP+ :
-
Reduced/oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
References
Kim SK, Jin YS, Choi IG, Park YC, Seo JH. Enhanced tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to multiple lignocellulose-derived inhibitors through modulation of spermidine contents. Metab Eng. 2015;29:46–55.
Klinke HB, Thomsen AB, Ahring BK. Inhibition of ethanol-producing yeast and bacteria by degradation products produced during pre-treatment of biomass. Appl Microb Biot. 2004;66(1):10–26.
Liu ZL, Ma MG, Song MZ. Evolutionarily engineered ethanologenic yeast detoxifies lignocellulosic biomass conversion inhibitors by reprogrammed pathways. Mol Genet Genomics. 2009;282(3):233–44.
Zhang X, Shen Y, Shi W, Bao X. Ethanolic cofermentation with glucose and xylose by the recombinant industrial strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae NAN-127 and the effect of furfural on xylitol production. Bioresour Technol. 2010;101(18):7104–10.
Shen Y, Li H, Wang X, Zhang X, Hou J, Wang L, Gao N, Bao X. High vanillin tolerance of an evolved Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain owing to its enhanced vanillin reduction and antioxidative capacity. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;41(11):1637–45.
Zhang JG, Liu XY, He XP, Guo XN, Lu Y, Zhang BR. Improvement of acetic acid tolerance and fermentation performance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by disruption of the FPS1 aquaglyceroporin gene. Biotechnol Lett. 2011;33(2):277–84.
Mira NP, Teixeira MC, Sa-Correia I. Adaptive response and tolerance to weak acids in saccharomyces cerevisiae: a genome-wide view. Omics. 2010;14(5):525–40.
Allen SA, Clark W, McCaffery JM, Cai Z, Lanctot A, Slininger PJ, Liu ZL, Gorsich SW. Furfural induces reactive oxygen species accumulation and cellular damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2010;3:2.
Almeida JRM, Modig T, Petersson A, Hähn-Hägerdal B, Lidén G, Gorwa-Grauslund MF. Increased tolerance and conversion of inhibitors in lignocellulosic hydrolysates by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Chem Technol Biot. 2007;82(4):340–9.
Banerjee N, Bhatnagar R, Viswanathan L. Inhibition of glycolysis by furfural in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1981;11(4):226–8.
Modig T, Lidén G, Taherzadeh MJ. Inhibition effects of furfural on alcohol dehydrogenase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 2002;363:769–76.
Liu ZL. Molecular mechanisms of yeast tolerance and in situ detoxification of lignocellulose hydrolysates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011;90(3):809–25.
Ji L, Shen Y, Xu LL, Peng BY, Xiao YZ, Bao XM. Enhanced resistance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to vanillin by expression of lacA from Trametes sp AH28-2. Bioresource Technol. 2011;102(17):8105–9.
Hansen EH, Møller BL, Kock GR, Bünner CM, Kristensen C, Jensen OR, Okkels FT, Olsen CE, Motawia MS, Hansen J. De novo biosynthesis of vanillin in fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe) and Baker’s yeast (saccharomyces cerevisiae). Appl Environ Microb. 2009;75(9):2765–74.
Kim JH, Lee HO, Cho YJ, Kim J, Chun J, Choi J, Lee Y, Jung WH. A vanillin derivative causes mitochondrial dysfunction and triggers oxidative stress in Cryptococcus neoformans. Plos One. 2014;9(2):e89122.
Iwaki A, Ohnuki S, Suga Y, Izawa S, Ohya Y. Vanillin inhibits translation and induces messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) granule formation in saccharomyces cerevisiae: application and validation of high-content, image-based profiling. Plos One. 2013;8(4):e61748.
Endo A, Nakamura T, Shima J. Involvement of ergosterol in tolerance to vanillin, a potential inhibitor of bioethanol fermentation, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Fems Microbiol Lett. 2009;299(1):95–9.
Larroy C, Fernández MR, González E, Parés X, Biosca JA. Characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae YMR318C (ADH6) gene product as a broad specificity NADPH-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase: relevance in aldehyde reduction. Biochem J. 2002;361:163–72.
Zhao X, Tang J, Wang X, Yang R, Zhang X, Gu Y, Li X, Ma M. YNL134C from Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a novel protein with aldehyde reductase activity for detoxification of furfural derived from lignocellulosic biomass. Yeast. 2015;32(5):409–22.
Lee MW, Kim BJ, Choi HK, Ryu MJ, Kim SB, Kang KM, Cho EJ, Youn HD, Huh WK, Kim ST. Global protein expression profiling of budding yeast in response to DNA damage. Yeast. 2007;24(3):145–54.
Nordling E, Jornvall H, Persson B. Medium-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (MDR) - Family characterizations including genome comparisons and active site modelling. Eur J Biochem. 2002;269(17):4267–76.
Petersson A, Almeida JR, Modig T, Karhumaa K, Hahn-Hagerdal B, Gorwa-Grauslund MF, Liden G. A 5-hydroxymethyl furfural reducing enzyme encoded by the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADH6 gene conveys HMF tolerance. Yeast. 2006;23(6):455–64.
Träff KL, Jönsson LJ, Hahn-Hägerdal B. Putative xylose and arabinose reductases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 2002;19(14):1233–41.
Chang Q, Griest TA, Harter TM, Petrash JM. Functional studies of aldo-keto reductases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bba-Mol Cell Res. 2007;1773(3):321–9.
Grabowska D, Chelstowska A. The ALD6 gene product is indispensable for providing NADPH in yeast cells lacking glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(16):13984–8.
Minard KI, McAlister-Henn L. Sources of NADPH in yeast vary with carbon source. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(48):39890–6.
Park SE, Koo HM, Park YK, Park SM, Park JC, Lee OK, Park YC, Seo JH. Expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 6 reduces inhibitory effect of furan derivatives on cell growth and ethanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresource Technol. 2011;102(10):6033–8.
Ask M, Mapelli V, Hock H, Olsson L, Bettiga M. Engineering glutathione biosynthesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae increases robustness to inhibitors in pretreated lignocellulosic materials. Microb Cell Factories. 2013;12:87.
Entian KD, Kötter P. Yeast mutant and plasmid collections. Method Microbiol. 1998;26:431–49.
Shen Y, Chen X, Peng BY, Chen LY, Hou J, Bao XM. An efficient xylose-fermenting recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain obtained through adaptive evolution and its global transcription profile. Appl Microbiol Biot. 2012;96(4):1079–91.
Peng BY, Shen Y, Li XW, Chen X, Hou J, Bao XM. Improvement of xylose fermentation in respiratory-deficient xylose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng. 2012;14(1):9–18.
Zhou YJJ, Yang W, Wang L, Zhu ZW, Zhang SF, Zhao ZBK. Engineering NAD(+) availability for Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalysis: a case study for dihydroxyacetone production. Microb Cell Factories. 2013;12:103.
Zhou Y, Wang L, Yang F, Lin X, Zhang S, Zhao ZK. Determining the extremes of the cellular NAD(H) level by using an Escherichia coli NAD(+)-auxotrophic mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(17):6133–40.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2014BAD02B07), the grants of the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2014AA021903, 2012AA022106), the Project of National Energy Administration of China (NY20130402), the State Key Laboratory of Motor Vehicle Biofuel Technology (KFKT2013002, 2013004), and Shandong Key Laboratory of Straw Biorefinement Technologies.
Funding
The design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript was supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2014BAD02B07), the grants of the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2014AA021903, 2012AA022106), the Project of National Energy Administration of China (NY20130402), the State Key Laboratory of Motor Vehicle Biofuel Technology (KFKT2013002, 2013004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author’s contributions
XB, YS, and XW conceived and designed the study; XW and ZL participated in the design of experiments and data collection; XW and YS analyzed data and drafted the manuscript; YS and XB contributed to the analysis of the results and manuscript writing. YS, XB and JH supervised and coordinated the overall study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Xinning Wang, Ph.D. student of State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Shandong University.
Zhenzhen Liang, Master student of State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Shandong University.
Jin Hou, Xiaoming Bao, and Yu Shen are staffs of State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Shandong University.
Additional file
Additional file 1: Table S1.
DNA primers used in this work. (DOCX 20 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Liang, Z., Hou, J. et al. Identification and functional evaluation of the reductases and dehydrogenases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae involved in vanillin resistance. BMC Biotechnol 16, 31 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-016-0264-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-016-0264-y