Abstract
Background
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) is one of the most important horticultural crops, with a marked preference for nitrate as an inorganic nitrogen source. The molecular mechanisms of nitrate uptake and assimilation are poorly understood in tomato. NIN-like proteins (NLPs) are conserved, plant-specific transcription factors that play crucial roles in nitrate signaling.
Results
In this study, genome-wide analysis identified six NLP members in tomato genome. These members were clustered into three clades in a phylogenetic tree. Comparative genomic analysis showed that SlNLP genes exhibited collinear relationships to NLPs in Arabidopsis, canola, maize and rice, and that the expansion of the SlNLP family mainly resulted from segmental duplications in the tomato genome. Tissue-specific expression analysis showed that one of the close homologs of AtNLP6/7, SlNLP3, was strongly expressed in roots during both the seedling and flowering stages, that SlNLP4 and SlNLP6 exhibited preferential expression in stems and leaves and that SlNLP6 was expressed at high levels in fruits. Furthermore, the nitrate uptake in tomato roots and the expression patterns of SlNLP genes were measured under nitrogen deficiency and nitrate resupply conditions. Four SlNLPs, SlNLP1, SlNLP2, SlNLP4 and SlNLP6, were upregulated after nitrogen starvation. And SlNLP1 and SlNLP5 were induced rapidly and temporally by nitrate.
Conclusions
These results provide significant insights into the potential diverse functions of SlNLPs to regulate nitrate uptake.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Nitrogen (N), an essential macronutrient for plants, serves as a component of amino acids, nucleotides, chlorophyll, hormones and coenzymes. The growth and development of plants depends on proper nitrogen supply. The availability of N in agricultural fields significantly affects crop yields [26]. Plants absorb inorganic N from the soils mainly in two forms, nitrate (NO3−) and ammonium (NH4+). Under mild climatic conditions, nitrate is the main nitrogen source in dry land [10]. The concentration of nitrate in the soils fluctuates between 10 μM and 100 mM [7]. To sustain vigorous growth, high-affinity and low-affinity (KM > 1 mM) transport systems have been evolved in plants to absorb nitrate efficiently from the environment. Nitrate is also an important signaling molecule for lateral root development, flowering and synergistic absorption of the other nutrients [31].
For nitrate signaling, NIN-like proteins (NLPs) are essential transcription factors [20]. It has been reported that the nutrient-Ca2+-NLP regulatory pathway plays a central role in nitrate signaling and integrates transcription, transport, metabolism and systemic growth programs in plants [4, 23, 25]. In Arabidopsis, nitrate transporter 1.1 (NPF6.3/NRT1.1) has been identified as a nitrate sensor at the plasma membrane [16]. In the presence of nitrate, calcium-dependent protein kinases 10/30/32 (CPK10/30/32) mediate Ca2+ signals by nitrate and phosphorylate NLP6/7 to ensure their location in the nucleus for transcriptional activation of the primary nitrate response genes [23].
NIN protein was first identified in the legume Lotus japonicus, with a regulatory function on symbiotic root nodule formation [29]. More NIN proteins and NLPs were found to widely exist among other nonleguminous plants including Arabidopsis, rice, wheat, and maize, but not in animals [21, 27, 30, 33]. Both NIN proteins and NLPs have a RWP-RK domain for DNA binding; NLPs carry an additional PB1 domain for protein–protein interactions [5]. Interactions between NLPs and other transcription factors such as nitrate regulatory gene 2 (NRG2) [34], PCF (TCP)-domain family protein 20 (TCP20) [14], and nitrate-inducible GARP-type transcriptional repressor 1 (NIGT1) [24] have been reported. Beyond nitrate signaling, extra functions of NLPs in the N starvation response [14], N and phosphate (P) interactions [24], nitrate-promoted seed germination [35], nitrate-dependent nodule symbiosis [28] and root cap cell release [19] have been clarified.
As one of the most important crops, tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) shows a marked preference for nitrate as an inorganic nitrogen source [8].
In the present study, comparative bioinformatics analysis of the tomato NLP genes was performed. Furthermore, the rate of root nitrate uptake and the expression of SlNLP genes under nitrogen deficiency and nitrate resupply conditions were detected to evaluate their potential roles in nitrate uptake regulation in roots.
Results
Identification of NLP Genes in tomato
A total of six NLP genes were identified from the tomato genome based on the presence of conserved RWP-RK (hmm, PF02042) and PB1 domains (hmm, PF00564). The nomenclature used for SlNLP genes was based on their distribution on the chromosomes (Table 1). The numbers of amino acids coded by SlNLP genes ranged from 841 (SlNLP1) to 1611 (SlNLP5). The relative molecular weights (Mw) were between 93.30 kDa (SlNLP1) and 180.95 kDa (SlNLP5). All SlNLP proteins had an isoelectric point near neutral (5.30–7.35), and low hydrophilicity indicated by GRAVY values (− 0.524 to − 0.327). The subcellular localizations were predicted to be in the nucleus/cytosol for all six SlNLPs.
Conserved motifs and phylogenetic analysis of SlNLP proteins
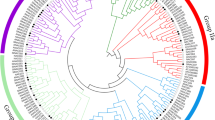
Based on a previous study, Arabidopsis NLP proteins were divided into three clades [30]. To analyze the evolutionary relationship of tomato NLP proteins, a neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree was constructed by comparing tomato NLP amino acid sequences with NLPs from four other plant species, including two dicotyledonous plants (Arabidopsis and canola) and two monocotyledonous plants (rice and maize) (Supplementary Table 1). The results (Fig. 1A) showed that Clade I contained 17 NLP members, including AtNLP1/2/3/4/5 and SlNLP1/2. Clade II contained 17 NLP members, including AtNLP6/7 and SlNLP3/5. Clade III contained 31 NLP members, including AtNLP8/9 and SlNLP4/6. Both dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous members existing in every clade indicated that gene expansion of the NLP gene family occurred before the ancestral divergence of monocotyledons and dicotyledons. Multiple sequence alignment (Fig. 1B and C) revealed that all the SlNLP proteins share similar motif patterns, including the conserved RWP-RK domain and PB1 domain. Interestingly, the SlNLP5 protein appeared to carry double RWP-RK domains and PB1 domains.
Phylogenetic tree and conserved motifs of the NLP gene family. A A neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree of NLPs from tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), canola (Brassica napus), rice (Oryza sativa) and maize (Zea mays). All NLP proteins were assigned into three clades. B Motifs were identified by MEME. The motifs are displayed in different colors. The scale bar represents 300 amino acids. The exon-intron structures were identified by GSDS. The untranslated regions (UTR) and coding sequences (CDS) are displayed in different colors. The scale bar represents 2000 nucleotides. C Sequences of identified motifs including three unknown domains (yellow, pink and red), the RWP-RK domain (yellow) and the PB1 domain (dark green)
Chromosomal distribution and syntenic analysis of SlNLP genes
Six SlNLP genes were distributed unevenly in the tomato genome (Fig. 2). SlNLP3, SlNLP4 and SlNLP5 were identified on chromosome 8. The other three SlNLP genes, SlNLP1, SlNLP2 and SlNLP6 genes were identified on chromosomes 1, 4 and 11, respectively. The interchromosomal relationship of SlNLP genes showed two pairs of segmental duplications (SlNLP1 and SlNLP2, SlNLP3 and SlNLP5), indicating that tomato NLP genes were mainly generated by gene duplication during evolution.
Chromosomal distribution and interchromosomal relationship of tomato NLP genes. The inner-species collinearity of SlNLPs. Gray lines indicate all syntenic blocks in the tomato genome, and the red lines indicate the duplicated SlNLP gene pairs. The number in the gray box area is the chromosome number
Furthermore, four comparative syntenic maps between tomato and Arabidopsis, canola, rice and maize, separately, were constructed to analyze the phylogenetic mechanisms of SlNLPs (Fig. 3). Tomato SlNLP genes showed 10 syntenic gene pairs with canola, 8 with Arabidopsis, 5 with maize and 3 with rice. Most background collinear blocks associated with NLP gene pairs identified between tomato and dicotyledon Arabidopsis/canola contained more genes than those between tomato and monocotyledon rice/maize (Supplementary Table 2). SlNLP1, SlNLP2 and SlNLP5 were found in the four comparative syntenic maps, suggesting that these orthologous pairs might already exist before evolutionary divergence of monocotyledons and dicotyledons. In addition, these three genes might have played fundamental roles in the NLP gene family. The ratio of nonsynonymous (Ka) to synonymous substitutions (Ks), presenting the selection type acting on the coding sequences, was also calculated (Supplementary Table 2). Two SlNLP gene pairs, SlNLP1 and SlNLP2, as well as SlNLP3 and SlNLP5, had Ka/Ks ratios of 1.01 and 1.46, respectively, indicating positive selection during evolution for functional divergence occurring after duplication. Most of the orthologous NLP gene pairs had a Ka/Ks ratio less than 1 (ranging from 0.10 to 0.96), suggesting purifying selective pressure during NLP gene family evolution and conserved functions of these genes. Three orthologous gene pairs, SlNLP1 and AtNLP5, SlNLP2 and BnaNLP4-4, SlNLP1 and ZmNLP1, had a Ka/Ks ratio greater than 1, indicating that these genes have undergone positive selection pressure and might have evolved new functions to help plants cope with their living environments.
Organ-dependent expression of SlNLPs
To obtain evidence of physiological function, the tissue-specific transcript abundance of six SlNLP genes was analyzed by qRT-PCR at different developmental stages (Fig. 4). SlNLP1 expression levels in roots were set to 1 for comparison of expression levels of SlNLPs. At both the seedling and flowering stages, SlNLP2 and SlNLP3 were preferentially expressed in roots (Fig. 4A and B). SlNLP2 and SlNLP3 showed the highest transcript abundance in roots at the seedling stage (Fig. 4A). When flowering, SlNLP3 still showed the highest abundance in roots, followed by SlNLP2 and SlNLP6 (Fig. 4B). In the red fruits, the transcript abundance of all the SlNLP genes was in the relatively high level. Interestingly, SlNLP6 exhibited increasing transcript accumulation in all the test tissues after flowering. And in particular, significantly higher SlNLP6 expression was observed in fruits (Fig. 4B).
Tissue-specific expression of SlNLPs. A Relative expression levels of SlNLPs in roots, leaves and stems at the seedling stage; B Relative expression levels of SlNLPs in roots, leaves, stems and flowers at the flowering stage and in red fruits. Gene expression levels were normalized to the SlEF1a gene. And SlNLP1 expression levels in roots were set to 1. Data shown as mean ± s.d. of four independent biological replicates
Expression of SlNLPs in response to nitrogen deficiency
Nitrate absorption in tomato roots was found to be influenced by two-days’ nitrogen starvation treatment, as indicated by the 15NO3− influx assay after different treatments (Fig. 5A). The results showed that the root high-affinity nitrate uptake ability was enhanced under nitrogen starvation, but root low-affinity nitrate uptake ability was repressed. To obtain evidence of possible roles of SlNLPs in root nitrate absorption regulation during nitrogen deficiency, the transcript abundance of SlNLP genes in roots was examined by qRT-PCR after starvation treatments (Fig. 6). The expression of SlNLP1, SlNLP2, SlNLP4 and SlNLP6 was upregulated 6.2-, 3.1-, 17- and 1.5-fold, respectively, after nitrogen starvation.
Root high-affinity and low-affinity 15NO3– uptake assay under nitrogen starvation and nitrate induction. A Seedlings were treated with nitrogen starvation (-N) for 2 days. Seedlings grown in normal hydroponic medium were used as the control; B Nitrogen-starved seedlings were then resupplied with 5 mM KNO3 for 2 h. Nitrogen-starved seedlings resupplied with 5 mM KCl were used as the control. The root high-affinity and low-affinity 15NO3– uptake abilities were detected in 0.1 mM or 5 mM K15NO3 solution, respectively, for 5 min. Data shown as mean ± s.d. of three independent biological replicates, ** p < 0.01
Expression of SlNLPs in response to nitrogen deficiency. Seedlings were treated with nitrogen starvation (-N) for 2 days. Total RNA was extracted from roots after treatment and subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. Gene expression levels were normalized to the SlEF1a gene. And SlNLP1 expression level in normal hydroponic medium was set to 1. Data shown as mean ± s.d. of four independent biological replicates, ** p < 0.01
Nitrate-dependent expression of SlNLPs and nitrogen metabolism genes
When nitrate was resupplied to the nitrogen-starved seedlings, both the root high-affinity and low-affinity nitrate uptake rates were enhanced, as shown by the results of the 15NO3− influx assay (Fig. 5B). The expression levels of SlNLPs and nitrogen metabolism genes in roots were examined at 0.5, 1 and 2 h during the nitrate induction process. The results (Fig. 7A) showed that the transcript abundance of SlNLP1 and SlNLP5 increased rapidly and temporally in response to nitrate. SlNLP1 and SlNLP5 expression reached the maximum levels (4.1- and 2.8-fold increases, respectively) 0.5 h after nitrate was supplied. The expression of SlNLP2 and SlNLP4 was repressed significantly after nitrate resupply for 1 h. In contrast, SlNLP3 and SlNLP6 did not show any response to nitrate at the transcription level. The transcript abundance of the nitrate transporters and nitrate assimilation genes is presented in Fig. 7B. The expression of the high-affinity nitrate transporter genes SlNRT2.1, SlNRT2.2 and SlNRT2.3, and the nitrate reductase gene SlNR and nitrite reductase genes SlNiR1 and SlNiR2 increased rapidly and violently within the first 30 min of exposure to nitrate, and remained at very high levels. The expression level of the low-affinity nitrate transporter gene SlNRT1.2 increased to twofold at 0.5 h after nitrate resupply and further increased by greater than fourfold at 1 and 2 h. Minimal stimulation of transcription of another low-affinity nitrate transporter gene, SlNRT1.1, was demonstrated by an temporary 1.6-fold increased at 1 h after nitrate resupply. No mRNA expression change in the glutamine synthetase gene SlGS was detected during the 2-h nitrate induction period. Protein interaction networks of SlNLP proteins were predicted (Supplementary Figure 1). SlNLP3, SlNLP4, SlNLP5 and SlNLP6 showed potential interactions with nitrate reductase SlNR. SlNLP3 and SlNLP5 showed additional potential interactions with nitrite reductases SlNiR1 and SlNiR2 implying their central role in nitrate responses. SlNLP1 and SlNLP2 displayed major interactions with the transcription factor GRAS16, indicating they might act as regulators associated with plant development.
Nitrate-dependent gene expression. Seedlings were nitrogen-starved for 2 days and resupplied with 5 mM nitrate or 5 mM KCl as a control for 2 h. Total RNA was extracted from roots at 0, 0.5, 1 and 2 h after treatment and subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. A SlNLP genes; B nitrate transport- and metabolism-associated genes. Gene expression levels were normalized to the SlEF1a gene, and the expression level in samples at 0 h in 5 mM KCl medium was set to 1. Data shown as mean ± s.d. of four independent biological replicates. “#” represents the control, ** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05
Discussion
In the present study, genome-wide analysis revealed six tomato NLPs (Table 1). The NLP family size of Solanum lycopersicum is similar to that of Arabidopsis thaliana (9), Oryza sativa (5) and Zea mays (9), and much smaller than that of Brassica napus (31). Phylogenetic analysis showed that every NLP family has members belonging to three groups (Fig. 1A). All of SlNLPs have conserved RWP-RK and PB1 domains. SlNLP5 is special for double RWP-RK and PB1 domains (Fig. 1B). The expansion of the tomato NLP gene family was mainly generated by gene duplication in the genome (Fig. 2). Orthologous gene pairs associated with SlNLP1, SlNLP2 or SlNLP5 were indicated to have existed before the ancestral divergence of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants (Fig. 3). It is worth noting that the Ka/Ks ratios of two paralogous SlNLP gene pairs (SlNLP1 and SlNLP2, SlNLP3 and SlNLP5) and three orthologous NLP gene pairs (SlNLP1 and AtNLP5, SlNLP2 and BnaNLP4-4, SlNLP1 and ZmNLP1) were greater than 1 (Supplementary Table 2), representing positive selection and fast evolutionary rates in these SlNLPs at the protein level. Therefore, it is implied that NLPs in tomato might have evolved some new functions to meet their growth and development demands of the plant.
Tissue-dependent expression patterns showed that all 6 SlNLP genes were expressed in all tested tissues including roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits (Fig. 4), which is similar to NLPs in Arabidopsis [5], maize (Ge et al. [13]) and Brassica napus [5]. SlNLP3, one of the close homologs of AtNLP6/7 (Fig. 1A), the key component of nitrate signaling [23], has the highest expression level in roots at both the seedling and flowering stages. In addition to SlNLP3, SlNLP2 and SlNLP6 were also expressed at high levels in roots, at different stages of development, implying their different functions in nitrate uptake regulation, rather than simple functional redundancy. Two SlNLPs from Clade III, SlNLP4 and SlNLP6, were preferentially expressed in aboveground tissues and their transcriptional abundance was strongly upregulated during flowering, suggesting that they might probably regulate nitrogen translocation and assimilation to support flower and fruit development. In contrast to SlNLP4, SlNLP6 had higher transcript abundance in both roots and aboveground tissues. Moreover, SlNLP6 showed extremely higher expression levels than all the other five SlNLPs in fruits (Fig. 4B). Interestingly, SINLP6 also showed its uniqueness in syntenic analysis between NLP genes (Fig. 2). The close homolog of SlNLP6 is AtNLP8 (Fig. 1A). AtNLP8 has been reported as a master regulator of nitrate-promoted seed germination [35], which might provide some hints for functional roles of SlNLP6 in fruits.
As one of the fundamental regulatory elements at the transcriptional level, NLPs play important roles in nitrate uptake and assimilation regulation [11, 15]. In Arabidopsis, nlp7 mutants show features of a nitrogen-starved plant [4],AtNLP7 overexpression increases plant biomass under both nitrogen-poor and nitrogen-rich conditions (Yu et al. [36]). Expression of rice NLPs (OsNLP1, OsNLP4 and OsNLP5) was promoted by nitrogen deficiency as well as nitrate supply [18]. Overexpression of OsNLP1 could enhance rice nitrogen use efficiency [2]. For tomato, nitrate is a more favorable inorganic nitrogen source form. Nitrate uptake in tomato roots is under precise regulation with complex interactions between nitrogen and the other essential macronutrients phosphate and/or potassium availability [31]. When the environmental nitrogen source was depleted, the root low-affinity nitrate influx rate decreased, but the high-affinity nitrate influx rate increased (Fig. 5A). Similar results have been reported: higher nitrate influx was detected in tomatoes growing in nutrient solutions containing 5 mM nitrate than in tomatoes growing in nutrient solutions containing 0.1 mM nitrate [1]. Both low-affinity and high-affinity nitrate uptake in roots increased after nitrate was resupplied to the nitrogen-starved tomato seedlings (Fig. 5B). The question is whether some SlNLPs play the important roles in nitrogen absorption regulation during nitrogen starvation and/or nitrate induction.
To answer this question, the transcript abundance of SlNLPs in roots was detected under nitrogen deficiency (Fig. 6) and nitrate resupply (Fig. 7A). Most of SlNLPs (SlNLP1, SlNLP2, SlNLP4 and SlNLP6) showed upregulated expression after nitrogen starvation for 2 days. When nitrate was resupplied, the temporal expression of SlNLP2 and SlNLP4 was repressed, but SlNLP1 was still showed rapidly upregulated. SlNLP3, which showed the highest expression level in roots during both seedling and flowering stages (Fig. 4), had potential interactions with nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase (Supplementary Figure 1). These results imply the central role of SlNLP3 in nitrate responses. However, SlNLP3 did not show any response to nitrate in the transcriptional level (Fig. 7A). The other close homolog of AtNLP6/7, SlNLP5, showed little transcriptional response to nitrogen starvation but was induced rapidly and temporally by nitrate. It is noteworthy that AtNLP6/7 responds to nitrate signaling not at the transcriptional level [23]. It is possible that a similar situation also exists in tomato. Therefore, the protein levels and protein modifications (including phosphorylation) of SlNLPs should be examined. It is interesting to determine how SlNLP3 participates in nitrogen deficiency response and/or nitrate signaling pathway in the future.
Conclusions
In summary, this study provided a genome-wide analysis of NLP genes in tomato. NLP genes are highly conserved among tomato, Arabidopsis, canola, maize and rice. Segmental duplication was the major driving force of SlNLP gene evolution. Some SlNLP genes have undergone positive selection during evolution, probably leading to functional divergence in gene families. The expression patterns of SlNLP genes provide hints for their diverse physiological roles in tomato growth and development, especially in nitrate uptake regulation. Further functional analysis for each SlNLP, especially SlNLP3 and SlNLP6, will be necessary to explore their regulatory functions. It is believed that a comprehensive understanding of the roles of SlNLP under fluctuating nutrition conditions is an essential step towards deciphering the molecular mechanism of nitrogen utilization and promoting nitrogen use efficiency in tomato.
Methods
Database search for NLP proteins
Raw hidden Markov model (HMM) data of the conserved RWP-RK (PF02042) and PB1 (PF00564) domains downloaded from Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org) [9] were used to search for their orthologs in the tomato genome (Solanum_lycopersicum.SL3.0), with an e-value of less than 1e − 10 in Phytozome (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/info/Slycopersicum_ITAG2_4). Then, the results were confirmed by based on the SMART (http://smart.embl.de/), NCBI Conserved Domains Database (CDD) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd), and Plant Transcription Factor Database (TFDB) (http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn/) databases. The physicochemical properties of SlNLP proteins, including peptide length (aa), molecular weight (Mw), isoelectric point (pI) and grand average of hydrophilicity (GRAVY) were predicted using ExPASy ProtParam (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/) [12]. Subcellular localizations of SlNLP proteins were predicted using CropPAL2020 (https://www.crop-pal.org) [17].
Multiple sequences alignment and phylogenetic analysis
Clustal W (version 2.1) was employed for the multiple sequence alignment and sequence identity matrix of the proteins [22]. Then, the deduced amino acid sequences in the RWP-RK and PB1 domains were adjusted manually using GeneDoc software. A phylogenetic tree was constructed with the MEGAX program (http://www.megasoftware.net/) using the neighbor-joining method. Proportions of amino acid differences were computed using Poisson correction distances to estimate evolutionary distances. The pairwise deletion option was used to circumvent the gaps and missing data. The conserved protein motifs of SlNLP proteins were analyzed using MEME server v5.3.0 (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) [3]. The parameters for the search were as follows: the max motif number to find is 5, and min–max motif width is 2–40. The matched motifs with low quality were manually removed based on an e-value of less than 1e − 15. The exon-intron structures of the SlNLP genes were identified on the Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS 2.0, http://gsds.gao-lab.org/). Sequences of NLP proteins of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), canola (Brassica napus), rice (Oryza sativa) and maize (Zea mays) were downloaded from Phytozome (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/).
Chromosomal distribution and gene duplication
Chromosome distribution and gene duplication events were analyzed using the Multiple Collinearity Scan toolkit MCScanX. The syntenic analysis maps of orthologous NLP genes were constructed using the Dual Systeny Plotter software (https://github.com/CJ-Chen/TBtools) [6]. Nonsynonymous (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) substitutions of each duplicated NLP gene were calculated using KaKs_Calculator 2.0 [32].
Analysis of protein–protein interaction networks
To study the protein–protein interaction network, SlNLP protein sequences were analyzed in Ensembl Database SL3.0 (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html) followed by prediction of interaction partners and networks using the STRING tool (http://string-db.org/).
Plant materials and treatments
Tomato ecotype Micro-Tom was used in this study. The seeds were germinated and grown on vermiculite for 7 d before transfer to hydroponics. The hydroponic minimal medium comprised 2 mM KH2PO4, 2 mM MgSO4, 25 μM H3BO3, 2 μM ZnSO4, 2 μM MnCl2, 0.5 μM CuSO4, 0.5 μM Na2MoO4, and 20 μM Fe-EDTA. This medium was supplemented with 1.3 mM Ca(NO3)2, 1.5 mM KNO3, 0.14 mM KH2PO4, and 1 mM MgSO4 under normal conditions. The pH of the solutions was maintained at approximately 5.8. Nutrient solutions were completely replaced weekly. Plants were grown at 28/22 °C with a 16/8 h light/dark photoperiod. Plants grown in hydroponics for 4 weeks were used for nitrogen starvation treatment and nitrate induction treatment. For nitrogen starvation treatment (-N), hydroponic minimal medium with 1 mM CaCl2, 0.6 mM K2SO4, 0.25 mM KH2PO4, and 0.5 mM MgSO4 was used for 2 days. For nitrate induction treatment, N-starved plants were resupplied with 5 mM nitrate medium (hydroponic minimal medium with KNO3) for the indicated time.
RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis, and qRT-PCR
Total RNA of different tissues was extracted using M5 SuperPure Total RNA Extraction Reagent (Mei5 Biotechnology Co. Ltd). Then, the DNA-free RNA was used to synthesize cDNA by using a RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Cat. No. K1622, Thermo). Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed using a SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Life Technologies) in 7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). Relative expression levels of SlNLPs were examined at the seedling stage, at the flowering stage and in red fruits. The housekeeping tomato EF1a gene (Solyc06g009970.3) was used as an internal control. Primer sequences used for qRT-PCR are listed in Supplementary Table 3.
15NO3 − uptake assay
15NO3− influx in roots was determined as previously described [37]. Tomato roots were washed in 0.1 mM CaSO4 for 1 min and then submerged in medium containing 1 mM or 5 mM K15NO3 (atom% 15 N: 99%) for 5 min and finally in 0.1 mM CaSO4 for 1 min. Roots were separated from the shoots immediately after the final transfer to CaSO4, and frozen in liquid nitrogen. After grinding, an aliquot of the frozen powder was dried overnight at 80 °C. The 15N concentration was measured using an isotope ratio mass spectrometer (IRMS; DELTAplus XP). The influx of 15NO3− was calculated from the 15N content of the roots (1 mg DW).
Statistical analysis
Data were processed using the statistics program SPSS version 21. The statistical significance of differences in 15N influx and gene expression was examined by Student’s t-test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01).
Availability of data and materials
The databases used in the study includes Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org), Phytozome (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/), SMART (http://smart.embl.de/), NCBI Conserved Domains Database (CDD) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd), Plant Transcription Factor Database (TFDB) (http://planttfdb.cbi.pku.edu.cn/), ExPASy ProtParam (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/), CropPAL2020 (https://www.crop-pal.org), MEGAX (http://www.megasoftware.net/), MEME server v5.3.0 (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme), Dual Systeny Plotter software (https://github.com/CJ-Chen/TBtools), Ensembl Database SL3.0 (http://plants.ensembl.org/index.html), STRING (http://string-db.org/). The public access to all these databases is open. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- NLPs:
-
NIN-like proteins
- NRTs:
-
Nitrate transporters
References
Abenavoli MR, Longo C, Lupini A, Miller AJ, Araniti F, Mercati F, Princi MP, Sunseri F. Phenotyping two tomato genotypes with different nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2016;107:21–32.
Alfatih A, Wu J, Zhang ZS, Xia JQ, Jan SU, Yu LH, Xiang CB. Rice NIN-LIKE PROTEIN 1 rapidly responds to nitrogen deficiency and improves yield and nitrogen use efficiency. J Exp Bot. 2020;71:6032–42.
Bailey TL, Johnson J, Grant CE, Noble WS. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:W39-49.
Castaings L, Camargo A, Pocholle D, Gaudon V, Texier Y, Boutet-Mercey S, Taconnat L, Renou JP, Daniel-Vedele F, Fernandez E, Meyer C, Krapp A. The nodule inception-like protein 7 modulates nitrate sensing and metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009;57(3):426–35.
Chardin C, Girin T, Roudier F, Meyer C, Krapp A. The plant RWP-RK transcription factors: key regulators of nitrogen responses and of gametophyte development. J Exp Bot. 2014;65:5577–87.
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol Plant. 2020;13:1194–202.
Crawford NM. Nitrate: nutrient and signal for plant growth. Plant Cell. 1995;7:859–68.
Errebhi M, Wilcox GE. Tomato growth and nutrient uptake pattern as influenced by nitrogen form ratio. J Plant Nutr. 1990;13:1031–43.
Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J, Mitchell AL, Potter SC, Punta M, Qureshi M, Sangrador-Vegas A, Salazar GA, Tate J, Bateman A. The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:D279–85.
Forde BG, Clarkson DT. Nitrate and ammonium nutrition of plants: physiological and molecular perspectives. Adv Bot Res. 1999;30:1e90.
Gaudinier A, Rodriguez-Medina J, Zhang L, Olson A, Liseron-Monfils C, Bågman AM, Foret J, Abbitt S, Tang M, Li B, Runcie DE, Kliebenstein DJ, Shen B, Frank MJ, Ware D, Brady SM. Transcriptional regulation of nitrogen-associated metabolism and growth. Nature. 2018;563:259–64.
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A. Protein Identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM, editor. The proteomics protocols handbook. Berlin: Springer; 2005. p. 571–607.
Ge M, Wang Y, Liu Y, Jiang L, He B, Ning L, Du H, Lv Y, Zhou L, Lin F, Zhang T, Liang S, Lu H, Zhao H. The NIN-like protein 5 (ZmNLP5) transcription factor is involved in modulating the nitrogen response in maize. Plant J. 2020;102:353–68.
Guan P, Ripoll JJ, Wang R, Vuong L, Bailey-Steinitz LJ, Ye D, Crawford NM. Interacting TCP and NLP transcription factors control plant responses to nitrate availability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114:2419–24.
Guan P. Dancing with Hormones: a current perspective of nitrate signaling and regulation in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:1697.
Ho CH, Lin SH, Hu HC, Tsay YF. CHL1 functions as a nitrate sensor in plants. Cell. 2009;138:1184–94.
Hooper CM, Castleden IR, Aryamanesh N, Black K, Grasso SV, Millar AH. CropPAL for discovering divergence in protein subcellular location in crops to support strategies for molecular crop breeding. Plant J. 2020;104:812–27.
Jagadhesan B, Sathee L, Meena HS, Jha SK, Chinnusamy V, Kumar A, Kumar S. Genome wide analysis of NLP transcription factors reveals their role in nitrogen stress tolerance of rice. Sci Rep. 2020;10:9368.
Karve R, Suárez-Román F, Iyer-Pascuzzi AS. The transcription factor NIN-LIKE PROTEIN7 controls border-like cell release. Plant Physiol. 2016;171:2101–11.
Konishi M, Yanagisawa S. Arabidopsis NIN-like transcription factors have a central role in nitrate signalling. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1617.
Kumar A, Batra R, Gahlaut V, Gautam T, Kumar S, Sharma M, Tyagi S, Singh KP, Balyan HS, Pandey R, Gupta PK. Genome-wide identification and characterization of gene family for RWP-RK transcription factors in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS One. 2018;13:e0208409.
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:2947–8.
Liu KH, Niu Y, Konishi M, Wu Y, Du H, Sun Chung H, Li L, Boudsocq M, McCormack M, Maekawa S, Ishida T, Zhang C, Shokat K, Yanagisawa S, Sheen J. Discovery of nitrate-CPK-NLP signalling in central nutrient-growth networks. Nature. 2017;545:311–6.
Maeda Y, Konishi M, Kiba T, Sakuraba Y, Sawaki N, Kurai T, Ueda Y, Sakakibara H, Yanagisawa S. A NIGT1-centred transcriptional cascade regulates nitrate signalling and incorporates phosphorus starvation signals in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun. 2018;9:1376.
Marchive C, Roudier F, Castaings L, Bréhaut V, Blondet E, Colot V, Meyer C, Krapp A. Nuclear retention of the transcription factor NLP7 orchestrates the early response to nitrate in plants. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1713.
Miller AJ, Cramer MD. Root nitrogen acquisition and assimilation. Plant Soil. 2005;274:1–36.
Mu X, Luo J. Evolutionary analyses of NIN-like proteins in plants and their roles in nitrate signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76:3753–64.
Nishida H, Tanaka S, Handa Y, Ito M, Sakamoto Y, Matsunaga S, Betsuyaku S, Miura K, Soyano T, Kawaguchi M, Suzaki T. A NIN-LIKE PROTEIN mediates nitrate-induced control of root nodule symbiosis in Lotus japonicus. Nat Commun. 2018;9:499.
Schauser L, Roussis A, Stiller J, Stougaard J. A plant regulator controlling development of symbiotic root nodules. Nature. 1999;402:191–5.
Schauser L, Wieloch W, Stougaard J. Evolution of NIN-like proteins in Arabidopsis, rice, and Lotus japonicus. J Mol Evol. 2005;60:229–37.
Vidal EA, Alvarez JM, Araus V, Riveras E, Brooks MD, Krouk G, Ruffel S, Lejay L, Crawford NM, Coruzzi GM, Gutiérrez RA. Nitrate in 2020: thirty years from transport to signaling networks. Plant Cell. 2020;32:2094–119.
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2010;8:77–80.
Wang Z, Zhang L, Sun C, Gu R, Mi G, Yuan L. Phylogenetic, expression and functional characterizations of the maize NLP transcription factor family reveal a role in nitrate assimilation and signaling. Physiol Plant. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12696.
Xu N, Wang R, Zhao L, Zhang C, Li Z, Lei Z, Liu F, Guan P, Chu Z, Crawford NM, Wang Y. The Arabidopsis NRG2 protein mediates nitrate signaling and interacts with and regulates key nitrate regulators. Plant Cell. 2016;28:485–504.
Yan D, Easwaran V, Chau V, Okamoto M, Ierullo M, Kimura M, Endo A, Yano R, Pasha A, Gong Y, Bi YM, Provart N, Guttman D, Krapp A, Rothstein SJ, Nambara E. NIN-like protein 8 is a master regulator of nitrate-promoted seed germination in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13179.
Yu LH, Wu J, Tang H, Yuan Y, Wang SM, Wang YP, Zhu QS, Li SG, Xiang CB. Overexpression of Arabidopsis NLP7 improves plant growth under both nitrogen-limiting and -sufficient conditions by enhancing nitrogen and carbon assimilation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:27795.
Zou X, Liu MY, Wu WH, Wang Y. Phosphorylation at Ser28 stabilizes the Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT2.1 in response to nitrate limitation. J Integr Plant Biol. 2020;62:865–76.
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Jin Kong from China Agricultural University for donating tomato Micro-Tom seeds.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2020YFA0509902), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32025004). The funder provided the research fund and had no role in the experimental design, data analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW2 and ML designed the research plan and analyzed the data, ML performed the experiments, and XZ assisted in tomato hydroponics. The manuscript was written by YW2. YW1 helped to revise the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental research on plants performed in this study complies with institutional, national and international guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Supplementary Table 1. NLP genes from tomato, Arabidopsis, canola, rice and maize.
Additional file 2:
Supplementary Table 2. One-to-one orthologous relationships between tomato and the other four plant species.
Additional file 3:
Supplementary Table 3. Primers used in qRT-PCR.
Additional file 4: Supplementary Figure
1. Protein-protein interaction network of SlNLP proteins.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Zhi, X., Wang, Y. et al. Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of NIN-like Protein (NLP) genes reveals its potential roles in the response to nitrate signaling in tomato . BMC Plant Biol 21, 347 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03116-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-021-03116-0