Abstract
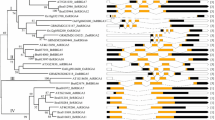
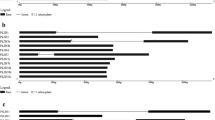
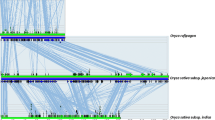
Genetic studies in Lotus japonicus and pea have identified Nin as a core symbiotic gene required for establishing symbiosis between legumes and nitrogen fixing bacteria collectively called Rhizobium. Sequencing of additional Lotus cDNAs combined with analysis of genome sequences from Arabidopsis and rice reveals that Nin homologues in all three species constitute small gene families. In total, the Arabidopsis and rice genomes encode nine and three NIN-like proteins (NLPs), respectively. We present here a bioinformatics analysis and prediction of NLP evolution. On a genome scale we show that in Arabidopsis, this family has evolved through segmental duplication rather than through tandem amplification. Alignment of all predicted NLP protein sequences shows a composition with six conserved modules. In addition, Lotus and pea NLPs contain segments that might characterize NIN proteins of legumes and be of importance for their function in symbiosis. The most conserved region in NLPs, the RWP-RK domain, has secondary structure predictions consistent with DNA binding properties. This motif is shared by several other small proteins in both Arabidopsis and rice. In rice, the RWP-RK domain sequences have diversified significantly more than in Arabidopsis. Database searches reveal that, apart from its presence in Arabidopsis and rice, the motif is also found in the algae Chlamydomonas and in the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Thus, the origin of this putative DNA binding region seems to predate the fungus–plant divide.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
InstitutionalAuthorNameThe Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) ArticleTitleAnalysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana Nature 408 796–815
SL Baldauf (2003) ArticleTitleThe deep roots of eukaryotes Science 300 1703–1706 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1085544
AY Borisov LH Madsen VE Tsyganov Y Umehara VA Voroshilova AO Batagov N Sandal A Frederiksen L Schauser N Ellis IA Tikhonovich J Stougaard (2003) ArticleTitleThe Sym35 gene required for root nodule development in Pisum sativum is an orthologue of Nin from Lotus japonicus Plant Physiol 131 1009–1017
JE Bowers BA Chapman J Rong AH Paterson (2003) ArticleTitleUnravelling angiosperm genome evolution by phylogenetic analysis of chromosomal duplication events Nature 422 383–384
J Felsenstein (1995) PHYLIP. Phylogeny inference package, version 3.5 Department of Genetics, University of Washington Seattle
SA Goff et al. (2002) ArticleTitleA draft dequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica) Science 296 92–100 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1068275 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivVSqtrw%3D Occurrence Handle11935018
T Inoue M Higuchi Y Hashimoto M Seki M Kobayashi T Kato S Tabata K Shinozaki T Kakimoto (2001) ArticleTitleIdentification of CRE1 as a cytokinin receptor from Arabidopsis Nature 409 1060–1063
C Kistner M Parniske (2002) ArticleTitleEvolution of signal transduction in intracellular symbiosis Trends Plant Sci 7 511–518 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1360-1385(02)02356-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xotlyltbs%3D Occurrence Handle12417152
L Krusell LH Madsen S Sato G Aubert A Genua K Szczyglowski G Duc T Kaneko S Tabata F de Bruijn E Pajuelo N Sandal J Stougaard (2002) ArticleTitleShoot control of root development and nodulation is mediated by a receptor-like kinase Nature 420 422–425
S Kumar K Tamura IB Jakobsen M Nei (2001) MEGA2: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software) Arizona State University Tempe 1–2
M Lynch J Conery (2000) ArticleTitleThe evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicated genes Science 290 1151–1155 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.290.5494.1151 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotVChsb8%3D Occurrence Handle11073452
EB Madsen LH Madsen S Radutoiu M Olbryt M Rakwalska K Szczyglowski S Sato T Kaneko S Tabata N Sandal J Stougaard (2003) ArticleTitleA receptor kinase gene of the LysM type is involved in legume perception of rhizobial signals Nature 425 637–640 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature02045 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvV2hsLs%3D Occurrence Handle14534591
S Ohno (1970) Evolution by gene duplication Springer Verlag, Heidelberg Germany
AH Paterson JE Bowers BA Chapman (2004) ArticleTitleAncient polypoidization predating divergence of cereals, and its consequences for comparative genomics Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101 9903–9908 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.0307901101
S Pelaz GS Ditta E Baumann E Wisman MF Yanofsky (2000) ArticleTitleB and C floral organ identity functions require SEPALLATA MADS-box genes Nature 405 200–203 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35012103 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsFyjsr0%3D Occurrence Handle10821278
CP Ponting T Ito J Moscat MT Diaz-Meco F Inagaki H Sumimoto (2002) ArticleTitleOPR, PC and AID: all in the PB1 family Trends Biochem Sci 27 10
S Radutoiu LH Madsen EB Madsen HH Felle Y Umehara M Grønlund S Sato Y Nakamura S Tabata N Sandal J Stougaard (2003) ArticleTitlePlant recognition of symbiotic bacteria requires two LysM receptor-like kinases Nature 425 585–592 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature02039 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXnvV2hsLo%3D Occurrence Handle14534578
JL Riechmann J Heard G Martin L Reuber C-Z Jiang J Keddie L Adam O Pineda OJ Ratcliffe RR Samaha R Creelman M Pilgrim P Broun JZ Zhang D Ghandehari BK Sherman G-L Yu (2000) ArticleTitleArabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes Science 290 2105–2110 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.290.5499.2105
L Schauser K Handberg N Sandal J Stiller T Thykjaer E Pajuelo A Nielsen J Stougaard (1998) ArticleTitleSymbiotic mutants deficient in nodule establishment identified after T-DNA transformation of Lotus japonicus Mol Gen Genet 259 414–423
L Schauser A Roussis J Stiller J Stougaard (1999) ArticleTitleA symbiotic regulator controlling development of symbiotic root nodules Nature 402 191–195
C Simillion K Vandepoele ParticleVan MC Montagu M Zabeau Y Peer ParticleVan de (2002) ArticleTitleThe hidden duplication past of Arabidopsis thaliana Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99 13627–13632
InstitutionalAuthorNameStougaard (2001) ArticleTitleGenetics and genomics of root symbiosis Curr Opin Plant Biol 4 328–333
S Stracke C Kistner S Yoshida L Mulder S Sato T Kaneko S Tabata N Sandal J Stougaard K Szczyglowski M Parniske (2002) ArticleTitleA plant receptor-like kinase required for both bacterial and fungal symbiosis Nature 417 959–962 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature00841 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XkvVagsbg%3D Occurrence Handle12087405
JD Thompson TJ Gibson F Plewniak F Jeanmougin DG Higgins (1997) ArticleTitleThe ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools Nucleic Acids Res 24 4876–4882 Occurrence Handle10.1093/nar/25.24.4876
TJ Vision DG Brown SD Tanksley (2000) ArticleTitleThe origins of genomic duplications in Arabidopsis Science 290 2114–2117
JV White CM Stultz TF Smith (1994) ArticleTitleProtein classification by stochastic modeling and optimal filtering of amino-acid sequences Math Biosci 119 35–75
N Wikstrom V Savolainen MW Chase (2001) ArticleTitleEvolution of the angiosperms: calibrating the family tree Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 268 2211–2220
Y-W Yang K-N Lai P-Y Tai W-H Li (1999) ArticleTitleRates of nucleotide substitution in angiosperm mitichondrial DNA sequences and dates of divergence between Brassica and other angiosperm lineages J Mol Evol 48 597–604
J Yu et al. (2002) ArticleTitleA draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. Indica) Science 296 79–92 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1068037 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivVSqtr8%3D Occurrence Handle11935017
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Lene Heedgaard Madsen for critical comments on the manuscript. L.S. is supported by Danish Research Council Grant SNF 21-01-0329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Reviewing Editor: Professor David Guttman
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schauser, L., Wieloch, W. & Stougaard, J. Evolution of NIN-Like Proteins in Arabidopsis, Rice, and Lotus japonicus. J Mol Evol 60, 229–237 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-0144-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-004-0144-2