Abstract
Background
In many traits, not only individual trait levels are under genetic control, but also the variation around that level. In other words, genotypes do not only differ in mean, but also in (residual) variation around the genotypic mean. New statistical methods facilitate gaining knowledge on the genetic architecture of complex traits such as phenotypic variability. Here we study litter size (total number born) and its variation in a Large White pig population using a Double Hierarchical Generalized Linear model, and perform a genome-wide association study using a Bayesian method.
Results
In total, 10 significant single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were detected for total number born (TNB) and 9 SNPs for variability of TNB (varTNB). Those SNPs explained 0.83 % of genetic variance in TNB and 1.44 % in varTNB. The most significant SNP for TNB was detected on Sus scrofa chromosome (SSC) 11. A possible candidate gene for TNB is ENOX1, which is involved in cell growth and survival. On SSC7, two possible candidate genes for varTNB are located. The first gene is coding a swine heat shock protein 90 (HSPCB = Hsp90), which is a well-studied gene stabilizing morphological traits in Drosophila and Arabidopsis. The second gene is VEGFA, which is activated in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in the fetus. Furthermore, the genetic correlation between additive genetic effects on TNB and on its variation was 0.49. This indicates that the current selection to increase TNB will also increase the varTNB.
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting SNPs associated with variation of a trait in pigs. Detected genomic regions associated with varTNB can be used in genomic selection to decrease varTNB, which is highly desirable to avoid very small or very large litters in pigs. However, the percentage of variance explained by those regions was small. The SNPs detected in this study can be used as indication for regions in the Sus scrofa genome involved in maintaining low variability of litter size, but further studies are needed to identify the causative loci.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
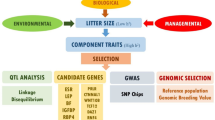
Conventional methods for studying the genetic architecture of complex traits focus on the level of those traits. In other words, the focus is on variation in trait level among genotypes. This implies that quantitative trait loci (QTL) can be defined as mean-controlling genes, as they affect the observed average phenotype of specific genotype. However, in many traits not only the mean is under genetic control, but also variation around the mean. Hence, genotypes not only differ in their average phenotypic level, but also in the variation around this average. In the following, we label this phenomenon as “phenotypic variability”, not to be confused with ordinary variability in average trait levels among genotypes. Therefore, development and application of statistical methods that allow studying phenotypic variability are required for a better understanding of the genetic architecture of complex traits [1–4].
The variation around the expected mean of a trait given its genotype, can be studied by analyzing the heterogeneity of residual variance across the observations [1]. It has been found that genotypes differ in residual variance [5]. Empirical evidence was found that the residual variance has a genetic component for litter size in rabbits [6], birth weight in pigs [7, 8], body weight in Atlantic salmon [9] and milk production traits in dairy cattle [10–12]. In addition, some studies have reported QTL that are associated with phenotypic variability, so-called vQTL [3]. The presence of vQTL in a population can indicate the existence of unmodeled interaction associated with the locus [3, 13, 14]. Three types of interactions can be distinguished, in which vQTL could be involved: interaction between the genes (epistasis) [3], interaction between the gene and known/unknown environmental factors [15, 16] or parallel presence of both of those interactions [3]. The fourth type of vQTL is one that controls the variance of a trait [17]. Several studies have reported vQTL in plant (maize [18], Arabidopsis thaliana [13]) and animal species (Drosophila melanogaster [5], rat [19], dairy cows [20] and in humans [15, 21]). One of the most well-studied genes involved in buffering effects of genetic and environmental factors is heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90). This gene was described in Drosophila and Arabidopsis as a gene stabilizing developmental and morphological traits [22–24].
In this study, we focus on litter size and its variability in a Large White pig population. Many studies have reported single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and QTL for the mean litter size of a genotype, and such QTL have been found on all Sus scrofa chromosomes (SSC) except SSC11, SSCX and SSCY (PigQTLdb, [25]). However, on top of the genetic variance in litter size, there is considerable residual variation between sows for litter size (total number born). Most issues are caused by extremely large litters (e.g. litter sizes greater than 25 piglets), which exceeds the physiological capacity of the sow to provide for the litter during gestation and post-farrowing. Sows with the large litters can experience welfare issues such as high energy demands during gestation [26] and shoulder sores during lactation [27, 28]. Moreover, these extreme litter sizes reduce also welfare and survival of the piglets pre-farrowing and until weaning. In current pig breeding, the goal is towards more sustainable production that will increase piglet survival regardless of increasing litter size [29–33]. Decreasing the variation in litter size between sows could lead to more sustainable breeding in terms of lower mortality of piglets and easier to manage sows. Therefore, it is desirable to reduce the variation in litter size from both an economic and an animal welfare perspective. Moreover, the detection of genes that buffer environmental factors, and thus decrease the variability of TNB is highly desirable. Thus far, Sorensen and Waagepetersen [34], Rönnegård et al. [2] and Felleki et al. [35] showed on the same dataset that variability in total number born in pigs is heritable. However, no study reported genomic regions associated with litter size variability or other traits in pigs [36]. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) for variability of litter size would give more insight in the genetic and biological control of variability in litter size.
The main objective of this study was to identify SNPs associated with litter size (TNB) and its variation (varTNB), through a multi-SNP GWAS applying a Bayesian method. In total, 10 SNPs were detected for TNB and 9 SNPs for varTNB. The most significant SNP for TNB was detected on SSC11 and for varTNB on SSC7. A possible candidate gene for TNB on SSC11 is ENOX1, which is involved in cell growth and survival. On SSC7, two possible candidate genes for varTNB are located. The first is a gene coding a swine heat shock protein 90 (HSPCB = Hsp90), which is a well-studied gene stabilizing morphological traits in Drosophila and Arabidopsis. The second is VEGFA, which is activated in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in the fetus. We also found a positive genetic correlation between TNB and its variance, indicating that single-trait selection for TNB will increase the varTNB. To our knowledge, this is the first study reporting SNPs for TNB on SSC11 and SNPs associated with varTNB in pigs.
Results and discussion
The main objective of this study was to detect regions associated with litter size (total number born, TNB) and its variation (varTNB) in a Large White pig population using a genome-wide association study (GWAS). Prior to the GWAS, the phenotypes for the association study had to be obtained. Therefore, as the first step, a Double Hierarchical GLM (DHGLM) was used to estimate variance components and estimated breeding values (EBV) of TNB and varTNB. Second, the EBV obtained with DHGLM were deregressed. Finally, the deregressed EBV were used as phenotypes in the GWAS. In this section, we present and discuss all the results that lead to detecting regions associated with TNB and varTNB.
DHGLM analysis of litter size and its variation
Table 1 shows estimates of variance components and heritability obtained from the univariate analysis of TNB, which are within the range known from the literature, where heritability estimates for TNB range from 0.10 to 0.16 [32, 33, 37–39]. The variance components estimated with univariate analysis of TNB were used as starting values for DHGLM.
The variance components and heritability for TNB from the DHGLM presented in Table 2 are also in the expected range [32, 33, 37–39]. For varTNB the estimate of additive genetic variance and heritability (Table 3) are lower than previously reported for this trait [2, 35]. It is worth noticing, that this heritability is a measure of the reliability of EBV for varTNB based on single observations; it does not reflect the magnitude of the genetic variance in varTNB [40].
To show the potential response to selection we propose to use the Genetic Coefficient of Variation on the standard deviation level (GCVSDe, i.e. the genetic standard deviation in residual standard deviation divided by the mean residual standard deviation of the trait (see Methods section for more details). The GCVSDe for varTNB in this study is 0.09, which is slightly lower than in previous studies focusing on litter size variation in pigs (0.10–0.15; [34, 41]), as reviewed by Hill and Mulder [1]. Nonetheless, the GCVSDe reported here indicates sufficient potential for selection to reduce variation in TNB. By assuming that in an efficient breeding program a response of ~1 genetic standard deviation per generation can be achieved, the GCVSDe of 0.09 indicates that the genetic standard deviation (SD) of TNB can be reduced by 9 % in one generation.
Table 3 shows the genetic correlations between random effects in the level and variance part of the model. The additive genetic correlation between TNB and varTNB is positive and moderate (0.49). This correlation is unfavorable, and indicates that sows with genetically large litters tend to have more variation in litter size. The correlation between the permanent sow effects on TNB and varTNB has the opposite sign: −0.83. This indicates that non-genetic (environmental) disturbances decrease the mean of TNB, with simultaneous increase in the variance of this trait.
To investigate further the large difference between the permanent and genetic correlations obtained with the DHGLM, we also performed a conventional bivariate analysis. To compare methods, models need to be on the same scale. A DHGLM takes a logarithm of residual variance in exponential model. Thus, in the conventional analysis we used mean TNB and the log-transformed variance of mean TNB (log(var(TNB))) per sow. The estimated additive genetic variances for mean TNB and for log(var(TNB)) were similar to values obtained from the DHGLM (Table 2). The conventional bivariate analysis yields also correlations between additive genetic effects and residuals of mean TNB and log(var(TNB)) (Table 3). (Note that the conventional analysis has no permanent sow effect, since there is only a single observation per sow.) The estimated additive genetic correlation was 0.68, whereas the residual correlation was–0.12. The genetic correlation has the same sign as the one from the DHGLM, but is slightly different in magnitude. The residual correlation in the conventional analysis has the same sign as the permanent environment correlation in the DHGLM, but is much closer to zero. When considering the covariances rather than the correlations, the residual covariance from the conventional analysis (−0.82) exceeds the permanent covariance from the DHGLM (−0.27). In the DHGLM, we assumed that the residuals are independent from each other. Hence, in the DHGLM, the permanent covariance has to account fully for non-genetic covariance between TNB and varTNB, which probably causes the extremely negative correlation between permanent effects.
Felleki et al. [35] reported an additive genetic correlation of–0.6 between TNB and varTNB, which has the opposite sign to the value reported here. The model used by Felleki et al. [35], however, did not include a covariance for permanent sow effect. When this covariance is not included, the model does not separate the effects properly. When the permanent covariance was omitted in our study, the additive genetic correlation had a negative value of–0.57. To account fully for all existing effects it is necessary to include the covariance structure between both permanent and additive genetic effects in the two parts of the model.
Significant associations for TNB and varTNB
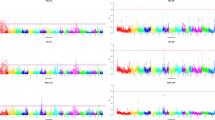
In total, 10 significant SNPs were detected for TNB (Fig. 1) and 9 SNPs for varTNB (Fig. 2). Associations found for TNB where located mostly on the same Sus scrofa chromosomes (SSC) as reported in previous GWAS for this trait [25]. Since this is the first GWAS to report SNPs for variance of litter size in pigs, there are no studies available for comparison.
Overall, the significant SNPs explained 0.83 % of the total genetic variance in TNB, and 1.44 % of the genetic variance in varTNB (Tables 4 and 5). The SNPs reported on SCC11 for TNB and all the SNPs for varTNB are the first SNPs reported for those traits in pigs. The chromosomes with the most variance explained were SSC11 for TNB and SSC7 for varTNB (Figs 3 and 4). On SSC11, ASGA0050328 associated with TNB explained 0.36 % of the total genetic variance. The estimated allele substitution effect at this locus was 0.105 piglets (Table 4). Previous studies that detected QTL for TNB, reported percentage of phenotypic variance explained by markers, rather than genetic variance, on the level between 0.3 % to 15 % [42–45], so higher than in this study. On SSC7, INRA0025193 explained 0.5 % of the genetic variance for varTNB. The allele substitution effect at this locus was 2.3 % of the mean value of varTNB (Table 5; note that values are given on log-variance scale). The small proportion of genetic variance explained by the significant associations indicates that both litter size and its variation are highly polygenic traits.
Percentage of genetic variance of litter size variability (varTNB) explained per chromosome by significant SNPs with Bayes Factor (BF) above or equal to 30 (SNP BF ≥ 30), SNPs with BF equal or larger than 10 but lower than 30 (SNP 10 < BF > 30), and non-significant SNPs with BF below 10 (SNP BF < 10)
The estimated genetic correlation between TNB and its variation (0.49) could suggest presence of pleiotropic effects or SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (LD). However, we did not identify overlap in regions significant for TNB and varTNB (Figs 1 and 2). Only on SSC13, SNPs for both traits are located close to each other (Tables 4 and 5), but they are not in LD.
Candidate genes and QTL associated with TNB
The two regions detected on SSC11 are the first SNPs associated with TNB on this chromosome. Thus far, no other study available in PigQTLdb (based on February 2015 search) reported significant associations for TNB on SSC11. Only one study reported QTL for a reproduction trait within the region of the most significant SNP (ASGA0050328) for TNB, which was a QTL for number of teats [46].
No candidate genes could be identified within the region of ±50kbp around ASGA0050328 (Ensembl Sscrofa 10.2; February 2015). The nearest candidate gene named ENOX1 was found at 24.16-24.48 Mb. One of the SNPs associated with TNB (with BF = 10.2) was located in this region. The ENOX1 is a protein coding gene from the ecto-CNOX family being part of electron transport pathways associated with mitochondrial membranes [47]. Functions of ENOX1 are cellular defense and growth as well as cell survival [47]. The functions of ENOX1 indicate that this gene might be a new region relevant for TNB in pigs.
In addition, the region detected on SSC18 (58.86-58.88 Mb) shows relevance for TNB in pigs. Three QTL related to reproduction traits were previously described within this region ([25]; February 2015). Those QTL were for: TNB [43], corpus luteum number [48], and gestation length [43]. Moreover, we have identified a possible candidate gene from the galectin family named LGALS8 within the detected region. The LGALS8 is widely expressed in tumoral tissues and seems to be involved in integrin-like cell interactions, cell-cell adhesion, cell-matrix interaction and growth regulation [49].
Candidate genes and QTL for variability of TNB
Quantitative trait loci associated with phenotypic variability are defined in the literature as vQTL [50]. In this study, the SNPs associated with varTNB are the first vQTL reported in pigs. Detected SNPs for varTNB were located at the positions of several known QTL related to reproduction traits in pigs. Those QTL are summarized in Table 5.
Within the region of the most significant SNP (INRA0025193) for varTNB at 43.76 Mb on SSC7, one candidate gene was located named CUL9 (SSC7:43,72-43,76 Mb) CUL9 is a cytoplasmic anchor protein in complex associated with p53 [51, 52]. The p53 is a protein, which regulates the cycle of the cell and acts as a tumor suppressor [53]. The CUL9 is controlling the localization and the function of p53 in the cell [51, 52]. Even though CUL9 was not yet described in swine, its functions can be important in affecting litter size variability in pigs, especially since CUL9 is expressed in embryonic, placental, and uterus tissues in the human [54].
Two more SNPs on SSC7 associated with varTNB (with BF 10.2 and 17.5) were located within the regions of two other possible candidate genes already described in swine: HSPCB (SSC7: 45.11-45.12 Mb) and VEGFA (SSC7: 44.46-44.47 Mb). The first gene belongs to the Sus scrofa heat shock protein family. This protein family is referred to as molecular chaperones since they are activated under various stress condition, such as heat [55], hyperthermia [56], and inflammation [57]. Their function is to maintain proper folding of the proteins within a cell as well as re-folding denatured proteins post-stress [58, 59]. Known in Drosophila and Arabidopsis as Hsp90, it is well described as a gene stabilizing developmental and morphological traits. The Hsp90 was describe to buffer environmental (e.g. heat shock, inflammation) and genetic (e.g. unfavorable mutations) factors, resulting in low variation of developmental and morphological traits [22–24]. Even though Hsp90 was shown to be one of many genes with buffering effects [60, 61], it is a very promising candidate gene detected for varTNB in this study. The second gene, named VEGFA, is a vascular endothelial growth factor. A VEGFA is a protein mediator growth factor activated in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in the fetus (and adult) [62] as well as in endothelial cell growth [63]. These two candidate genes detected on SSC7 are highly relevant, since those genes affect the response of the pig to environmental and stress factors (HSPCB) and provide the vascular network to the placenta (VEGFA).
Implications for pig breeding
An important aim in pig production is to obtain a high number of slaughter pigs per sow per year [26, 64, 65]. Therefore, in pig breeding, genetic selection continues to increase litter size. The annual genetic trend for litter size in different pig breeding programs was shown to be +0.16 [29, 66], +0.25 [67], and even up to +0.5 [68] piglets per year on average. Next to genetic variation in litter size, there is considerable residual variation in this trait, both between sows and between parities within a sow.
We showed that residual variance in litter size has a genetic component, and can thus be changed by selection. The results of our study also show presence of an unfavorable positive genetic correlation between litter size and its variation. So far, main inefficiency in fecundity was the presence of too small litters. More and more, however, too large litters are becoming the prevailing problem. Therefore, simultaneous selection of litter size and it variation is necessary to achieve a higher mean litter size and at the same time a lower variance in litter size. This is important for pig production, since both small and oversized litters can be detrimental for farm economy. Although the genetic correlation was 0.49, we did not identify overlap in regions significant for TNB and varTNB (Tables 4 and 5).
Current breeding programs can use the knowledge of this study in the genomic evaluation of selection candidates. Genomic selection can greatly increase accuracy of selection also for non-phenotyped individuals. This is beneficial for traits such as litter size variability, which has low heritability and is recorded only long after the moment of selection of the candidate.
Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first study reporting SNPs for TNB on SSC11 and first SNPs associated with varTNB in pigs. In total, 10 SNPs were detected for TNB and 9 SNPs for varTNB. The most significant SNP for TNB was detected on SSC11. A possible candidate gene for TNB on SSC11, named ENOX1, is involved in cell growth and survival. Also on SSC18, another possible candidate gene for TNB is located, named LGALS8. Two genes located on SSC7 (HSPCB and VEGFA) are the most promising candidate genes identified for varTNB. The HSPCB is coding the heat-shock protein involved in buffering environmental and genetic factors, whereas VEGFA is activated in angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in the fetus. We also found a positive genetic correlation between TNB and its variation. This indicates that in breeding practice simultaneous selection of those traits is necessary to achieve a higher mean litter size and lower variance of this trait. The SNPs detected in this study can be used as an indication for regions in the Sus scrofa genome involved in maintaining low variability of litter size, but further studies are needed to confirm causative mutations.
Methods
Phenotypes
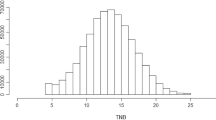
Data for this study were collected between February 1998 and July 2014. In total 264,419 litter size (total number born, TNB) observations were available from 69,549 Large White sows. Litters were kept in the data if they contained at least 4 piglets in TNB (1,331 litters removed), whereas litters of 27 piglets or larger were all considered “27” (43 litters). Most sows had repeated observations; only 15,379 sows had a single observation. Number of parities recorded per sow varied between 1 and 16, with an average of 3.8 per sow, and with 974 sows with 10 or more parities recorded. The parities 10 and higher were put on the same level of explanatory variable in the model (2,512 litters). After data editing 263,088 litters from 69,238 Large White sows remained for the analysis. The average TNB in edited data was 13.5 (±3.5). The pedigree was traced back 5 generations if available and consisted of 83,571 animals.
Conventional univariate and bivariate analysis of litter size and its variance
The conventional univariate analysis of TNB was performed in ASReml 2.0 [69] using the following model:
where y is a vector of observation on TNB in the litter; b is a vector of fixed effects (parity of the sow and farm_year_season of the farrowing) on y; a is a vector of random additive genetic effects on y, with a ~ N(0, A σ 2a ); pe is a vector of random non-genetic permanent sow effects on y, with pe ~ N(0, A σ 2pe ); and e is a vector of residual, with e ~ N(0, I e σ 2e ).
The variance component estimates obtained with the conventional univariate analysis were used as starting values in the Double Hierarchical Generalized Linear model (DHGLM).
The conventional bivariate analysis of litter size and its variation was performed on average TNB per sow (meanTNB) and log-transformed variance of TNB per sow (log(var(TNB))). The log-transformation was necessary to obtain results on the same scale in the conventional analysis and in the DHGLM. In the conventional bivariate analysis, only sows with 3 or more parities were used to allow proper estimation of the variance. In total, observations on 43,490 sows were used. The bivariate analysis was performed in ASReml 2.0 [69] with model:
where y mean is a vector of observations on average TNB per sow and y v is a vector of the log-transformed variance of meanTNB; b mean and b v are vectors of fixed effects of farm_year_season of the farrowing on y mean and y v; a mean and a v are vectors of random additive genetic effects on y mean and y v, with \( \left[\begin{array}{c}\hfill {\mathbf{a}}_{\mathrm{mean}}\hfill \\ {}\hfill {\mathbf{a}}_{\mathrm{v}}\hfill \end{array}\right]\sim \mathrm{N}\left(\mathbf{0},\left[\begin{array}{cc}\hfill {\sigma}_{{\mathrm{a}}_{\mathrm{mean}}}^2\hfill & \hfill {\sigma}_{{\mathrm{a}}_{\mathrm{mean}},\mathrm{a}\mathrm{v}}\hfill \\ {}\hfill {\sigma}_{{\mathrm{a}}_{\mathrm{mean}},\mathrm{a}\mathrm{v}}\hfill & \hfill {\sigma}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{v}}^2\hfill \end{array}\right]\otimes \mathbf{A}\right) \); and e and e v vectors of residuals, with \( \left[\begin{array}{c}\hfill {\mathbf{e}}_{\mathrm{mean}}\hfill \\ {}\hfill {\mathbf{e}}_{\mathrm{v}}\hfill \end{array}\right]\sim \mathrm{N}\left(\begin{array}{c}\hfill \mathbf{0}\hfill \\ {}\hfill \mathbf{0}\hfill \end{array},\left[\begin{array}{cc}\hfill {\mathbf{W}}^{*}{\upsigma}_{{\mathrm{e}}_{\mathrm{mean}}}^2\hfill & \hfill 0\hfill \\ {}\hfill 0\hfill & \hfill {\mathbf{W}}^{*}{\upsigma}_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{v}}^2\hfill \end{array}\right]\right) \), where W * is the weighting factor based on the number of litters the sow had. The conventional bivariate analysis has no permanent sow effect, since there is only a single observation per sow.
Estimation of residual variance of litter size
Estimation of residual variance was performed on the full data set. A Double Hierarchical Generalized Linear model (DHGLM) as presented by Rönnegård et al. [2] allows estimation of variance components of residual variance in ASReml 2.0 [69]. Felleki et al. [35] extended the model so that a bivariate linear mixed model can be used for the level (TNB) and the variance (TNB variation, varTNB) component of the model. In Rönnegård et al. [2], the response variable in the variance model was calculated as \( \log \left({\varphi}_i\right)= \log \left(\frac{e_i^2}{1-{h}_i}\right) \), where e 2 i is the squared residual from the level part of the model for observation i, and h i is the leverage, being the diagonal element of the hat matrix of y corresponding to observation i. A log link function was used, because \( \frac{e_i^2}{1-{h}_i} \) is χ 2-distributed with one degree of freedom. Felleki et al. [35] showed that instead of using a log link function, \( \log \left(\frac{e_i^2}{1-{h}_i}\right) \) can be linearized using the Taylor expansion of the first order by calculating the response variable \( {\psi}_i= \log \left({\widehat{\sigma}}_{e_i}^2\right)+\frac{\frac{e_i^2}{1-{h}_i}-{\widehat{\sigma}}_{e_i}^2}{{\widehat{\sigma}}_{e_i}^2} \). This enables using a bivariate linear mixed model, where \( {\widehat{\sigma}}_{e_i}^2 \) is the predicted residual variance for observation i and ψ is a vector with the response variable in the variance part of the model. Note that ψ i is a linearized working variable for log(φ i ). The DHGLM is then as follows:
where y is a vector of observations on TNB in the litter and ψ is a vector of response variables for the variance part of DHGLM; the residuals e and e v are assumed to be independent and normally distributed, but with heterogeneous variances across the observations; b and b v are vectors of fixed effects (parity of the sow and farm_year_season of the farrowing) on y and ψ; a and a v are vectors of random additive genetic effects on y and ψ, with \( \left[\begin{array}{c}\hfill \mathbf{a}\hfill \\ {}\hfill {\mathbf{a}}_{\mathrm{v}}\hfill \end{array}\right]\sim \mathrm{N}\left(\mathbf{0},\left[\begin{array}{cc}\hfill {\sigma}_{\mathrm{a}}^2\hfill & \hfill {\sigma}_{\mathrm{a},\mathrm{a}\mathrm{v}}\hfill \\ {}\hfill {\sigma}_{\mathrm{a},\mathrm{a}\mathrm{v}}\hfill & \hfill {\sigma}_{\mathrm{a}\mathrm{v}}^2\hfill \end{array}\right]\otimes \mathbf{A}\right) \); pe and pe v are vectors of random non-genetic permanent sow effects on y and ψ, with \( \left[\begin{array}{c}\hfill \mathbf{p}\mathbf{e}\hfill \\ {}\hfill \mathbf{p}{\mathbf{e}}_{\mathbf{v}}\hfill \end{array}\right]\sim \mathrm{N}\left(\mathbf{0},\left[\begin{array}{cc}\hfill {\upsigma}_{\mathrm{pe}}^2\hfill & \hfill {\upsigma}_{\mathrm{pe},\mathrm{p}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{v}}\hfill \\ {}\hfill {\upsigma}_{{\mathrm{pe},\mathrm{p}\mathrm{e}}_{\mathrm{v}}}\hfill & \hfill {\upsigma}_{\mathrm{pe}\mathrm{v}}^2\hfill \end{array}\right]\otimes \mathbf{I}\right) \); and e and e v vectors of residuals, with \( \left[\begin{array}{c}\hfill \mathbf{e}\hfill \\ {}\hfill {\mathbf{e}}_{\mathrm{v}}\hfill \end{array}\right]\sim \mathrm{N}\left(\begin{array}{c}\hfill \mathbf{0}\hfill \\ {}\hfill \mathbf{0}\hfill \end{array},\left[\begin{array}{cc}\hfill {\mathbf{W}}^{\hbox{-} 1}{\upsigma}_{\mathrm{e}}^2\hfill & \hfill 0\hfill \\ {}\hfill 0\hfill & \hfill {\mathbf{W}}_{\mathrm{v}}^{\hbox{-} 1}{\upsigma}_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{v}}^2\hfill \end{array}\right]\right) \), where \( \mathbf{W}=\mathrm{diag}\left( \exp {\left(\widehat{\boldsymbol{\uppsi}}\right)}^{-1}\right) \) and \( {\mathbf{W}}_{\mathrm{v}}=\mathrm{diag}\left(\frac{1-h}{2}\right) \) are expected reciprocals of the residual variance from the previous iteration, and σ 2e and σ 2ev are scaling variances, which are expected to be equal to 1 [12]. The predicted residual variances per observation \( \exp \left(\widehat{\boldsymbol{\uppsi}}\right) \) are based on the estimated fixed and random effects for ψ in the previous iteration of the algorithm. The method iterates the bivariate model a number of times until convergence, since the residual variance part (varTNB) depends on the level part (TNB) of the model and vice versa. In this study, 22 iterations were needed.
A DHGLM uses the log-transformed variance of the trait. To help with practical interpretation of the results, two measures will be used: Genetic Coefficient of Variation at standard deviation level and the heritability for residual variance. The Genetic Coefficient of Variation on standard deviation level (GCVSDe, a measure of ability to respond to selection) was applied to transform the estimates from the variance to the SD level. The GCVSDe is calculated as the genetic standard deviation in residual standard deviation divided by the mean residual standard deviation of the trait: \( {\mathrm{GCV}}_{\mathrm{SDe}}=\frac{\sigma_{\mathrm{av}}\left({\sigma}_{\mathrm{e}}\right)}{\overline{\sigma_{\mathrm{e}}}}\approx {\scriptscriptstyle \frac{1}{2}}{\sigma}_{\mathrm{av}} \), where σav is the genetic SD in residual variance. The GCVSDe shows the proportional change in residual SD, when the residual variance would be changed by one unit σav. This allows seeing the magnitude of potential response to selection in the SD of TNB. Note that in Hill and Mulder [1] the GCV was expressed at the level of the residual variance; the GCV at the level of residual variance is twice the GCVSDe. The literature on genetic analyses of residual variance defines also the heritability for residual variance at the level of the squared phenotype (h 2v ), which is equal to the genetic variance in residual variance as a proportion of the phenotypic variance of P2 and equals: h 2v = σ 2av /(2σ 4P + 3(σ 2av + σ 2pev )) [70]. The h 2v is a measure of reliability of EBV obtained on a single observation per animal; in contrast to classical heritability, it does not reflect the potential of the trait to respond to selection.
Using deregressed EBV for litter size and litter size variability
In this study, a large number of phenotypic observations for TNB were available, but much lower number of sows and boars was genotyped (see Genotypes below). In addition, the boars had only observations through their daughters’, sisters’ and mothers’ performance. The use of deregressed EBV of animals instead of their phenotype is expected to give more reliable results in genome-wide association study; since accounting for offspring and parents information increases the power of the GWAS [71]. Therefore, for the optimal use of the entire data in the GWAS, the estimated breeding values (EBV) obtained with DHGLM were deregressed. The deregressed EBV were used as y-variables in the GWAS (see below).
The EBV were deregressed following the methodology of Garrick et al. [72]. First, the parent average was subtracted from an individual’s EBV to avoid double counting because of various information sources and complex family structure. Thus, the sow’s (or boar’s) deregressed EBV contained only the information on own and progeny performance. Second, for calculation of deregressed EBV the reliability of EBV was required. Reliability was calculated following the equation [69]:
where si is the standard error reported for the EBV of the ith individual; fi is the inbreeding coefficient of the ith individual; 1 + f1 is the diagonal element of the additive genetic relationship matrix and σ 2 a is the additive genetic variance. Finally, Garrick et al. [72] showed that deregressed EBV have heterogeneous variances, which can be accounted for using weights (w). The weight was estimated based on the reliability of calculated deregressed EBV.
Deregressed EBV were obtained based on EBV from two univariate analyses of the traits TNB and varTNB using the results from the final iteration of the DHGLM (see Estimation of residual variance). The EBV from univariate analysis were used to avoid EBV for one trait to be affected by the other trait in the bivariate analysis. The deregressed EBV obtained with the DHGLM for TNB, were also compared with those from the conventional bivariate analysis. The correlation between deregressed EBV for TNB from both methods was 0.988.
Genotypes
Genotypes were available for 2,679 Large White sows and 426 boars. All animals were genotyped with the Illumina PorcineSNP60 Beadchip. Samples of blood, hair and ear punches used to extract DNA were collected in the process of routine procedure within the breeding program and as such did not require an approval from Animal Care and Use Committee. Quality control removed SNPs with GenCall score <0.15, minor allele frequency <0.01, as well as SNPs from the sex chromosome (low number of animals had sex chromosome genotyped) or with unknown position on build 10.2. After quality control, 40,969 out of 64,232 genotyped SNPs remained in the data set. In addition, animals were removed from the data set if their call rate was <95 % and if pedigree or genotype led to many Mendelian inconsistencies [73].
The deregressed EBV for litter size variability have overall low reliabilities, due to the low heritability of that trait. To maintain a sufficient number of genotyped animals for the genome-wide association study (GWAS), a threshold of 0.05 was used as an acceptable reliability of the deregressed EBV of the animal. Nonetheless, this caused a difference in number of animals used in GWAS for TNB and varTNB. Subsequently, 2,351 animals remained in the set with litter size observations and 2,067 in the set for residual variance of litter size.
Statistical analyses used for GWAS–Bayesian Variable Selection method
Multi-SNP genome-wide association was performed using a Bayesian Variable Selection method [74], which estimates the effect of all markers simultaneously. The analysis was performed in Bayz [75]. The fitted model was:
where y is an n-vector of deregressed EBV for the litter size or its variation on n animals; μ is an n-vector equal to the mean; X b is a matrix with dimensions n by p, where p SNPs are coded as 0, 1, 2 copies of specific allele vector; and β is a p-vector with the markers effects fitted as random effects; e is an n-vector of weighted random residual effects assumed to be normally distributed N(0, σ 2e W t ), where W t is a diagonal matrix with wt1,…,wtn elements. On the marker effect, the Bernoulli distribution was applied:
where the first distribution refers to the null distribution and it is assumed that the SNPs have small effect (\( {\sigma}_{g_0}^2 \)); the second distribution refers to the SNPs that are assumed to have a large effect, which explain a large part of variance (\( {\sigma}_{g_1}^2 \)) of the analyzed traits. In this study a relatively strict prior was selected of π1 = 0.001, meaning that on average only 1 in 1,000 SNPs will be in the second distribution in each cycle. This allowed only ~41 SNPs per cycle to have a large effect on the traits. To secure that all the SNPs were used, 500,000 MCMC cycles were performed. Selecting a stringent prior provides a more precise distinction between SNPs with large and small effects on the trait [76, 77].
A Metropolis-Hastings sampler was applied to get good convergence which was assessed by visual inspection of the trace and with Gelman and Rubin’s convergence diagnostic based on deviance [78] using the R package CODA [79].
The GWAS was also repeated with a less strict prior of 0.005 and a larger step in the Metropolis-Hastings sampler (0.004 instead of 0.003), which yielded the same results as the analysis with prior of 0.001.
Identification of significant SNPs
The Bayes Factor (BF) was calculated for each SNP to determine the significant associations:
where π1 and π0 are the prior probabilities and \( {\widehat{p}}_i \) is the posterior probability of the fraction of times the SNP was in the distribution with large effect. Following the definitions of Kass and Raftery [80], the SNPs with BF > 30 are described as “very strong” association and with BF > 150 as “decisive”. The variance explained by significant SNP was estimated as a fraction of the total genetic variance explained by all SNPs. The candidate gene search was performed with software BIOMART available in Ensembl Sscrofa 10.2 [81] by entering position of a SNP.
Availability of supporting data
The dataset used in this study is available upon request. Contact Egbert Knol by e-mail: Egbert.Knol@topigsnorsvin.com. Furthermore, the SNPs detected within this study are submitted to an open access animal QTL database – Pig QTL database (http://www.animalgenome.org/QTLdb/pig.html).
References
Hill WG, Mulder HA. Genetic analysis of environmental variation. Genet Res Camb. 2010;92:381.
Rönnegård L, Felleki M, Fikse F, Mulder HA, Strandberg E. Genetic heterogeneity of residual variance-estimation of variance components using double hierarchical generalized linear models. Genet Sel Evol. 2010;42:1–10.
Rönnegård L, Valdar W. Recent developments in statistical methods for detecting genetic loci affecting phenotypic variability. BMC Genet. 2012;13:63.
Cao Y, Maxwell TJ, Wei P. A Family-Based Joint Test for Mean and Variance Heterogeneity for Quantitative Traits. Ann Hum Genet. 2015;79:46–56.
Mackay TFC, Lyman RF. Drosophila bristles and the nature of quantitative genetic variation. Philos T Roy Soc B. 2005;360:1513–27.
Ibáñez-Escriche N, Varona L, Sorensen D, Noguera JL. A study of heterogeneity of environmental variance for slaughter weight in pigs. Animal. 2008;2:19–26.
Sell-Kubiak E, Wang S, Knol EF, Mulder HA. Genetic analysis of within-litter variation in piglets’ birth weight using genomic or pedigree relationship matrices. J Anim Sci. 2015;93:1471–80.
Sell-Kubiak E, Bijma P, Knol EF, Mulder HA. Comparison of methods to study uniformity of traits: application to birth weight in pigs. J Anim Sci. 2015;93:900–11.
Sonesson AK, Ødegård J, Rönnegård L. Genetic heterogeneity of within-family variance of body weight in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Genet Sel Evol. 2013;45:41.
Rönnegård L, Felleki M, Fikse W, Mulder HA, Stransberg E. Variance component and breeding value estimation for genetic heterogeneity of residual variance in Swedish Holstein dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci. 2013;96:2627–36.
Vandenplas J, Bastin C, Gengler N, Mulder H. Genetic variance in micro-environmental sensitivity for milk and milk quality in Walloon Holstein cattle. J Dairy Sci. 2013;96:5977–90.
Mulder HA, Rönnegård L, Fikse WF, Veerkamp RF, Strandberg E. Estimation of genetic variance for macro-and micro-environmental sensitivity using double hierarchical generalized linear models. Genet Sel Evol. 2013;45:23.
Shen X, Pettersson M, Rönnegård L, Carlborg Ö. Inheritance beyond plain heritability: variance-controlling genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002839.
Nelson RM, Pettersson ME, Li X, Carlborg Ö. Variance Heterogeneity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Expression Data: Trans-Regulation and Epistasis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e79507.
Paré G, Cook NR, Ridker PM, Chasman DI. On the use of variance per genotype as a tool to identify quantitative trait interaction effects: a report from the Women’s Genome Health Study. PLoS Genet. 2010;6:e1000981.
Struchalin MV, Dehghan A, Witteman JCM, Van Duijn C, Aulchenko YS. Variance heterogeneity analysis for detection of potentially interacting genetic loci: method and its limitations. BMC Genet. 2010;11:92.
Geiler-Samerotte K, Bauer C, Li S, Ziv N, Gresham D, Siegal M. The details in the distributions: why and how to study phenotypic variability. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2013;24:752–9.
Ordas B, Malvar RA, Hill WG. Genetic variation and quantitative trait loci associated with developmental stability and the environmental correlation between traits in maize. Genet Res. 2008;90:385–95.
Perry GML, Nehrke KW, Bushinsky DA, Reid R, Lewandowski KL, Hueber P, et al. Sex modifies genetic effects on residual variance in urinary calcium excretion in rat (Rattus norvegicus). Genetics. 2012;191:1003–13.
Mulder HA, Crump R, Calus MPL, Veerkamp R. Unraveling the genetic architecture of environmental variance of somatic cell score using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism and cow data from experimental farms. J Dairy Sci. 2013;96:7306–17.
Yang J, Loos RJF, Powell JE, Medland SE, Speliotes EK, Chasman DI, et al. FTO genotype is associated with phenotypic variability of body mass index. Nature. 2012;490:267–72.
Queitsch C, Sangster TA, Lindquist S. Hsp90 as a capacitor of phenotypic variation. Nature. 2002;417:618–24.
Rutherford S, Hirate Y, Swalla BJ. The Hsp90 capacitor, developmental remodeling, and evolution: the robustness of gene networks and the curious evolvability of metamorphosis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol. 2007;42:355–72.
Sangster TA, Bahrami A, Wilczek A, Watanabe E, Schellenberg K, McLellan C, et al. Phenotypic diversity and altered environmental plasticity in Arabidopsis thaliana with reduced Hsp90 levels. PLoS One. 2007;2:e648.
Pig QTL data base. http://www.animalgenome.org/QTLdb/pig.html.
Rutherford KMD, Baxter EM, D’Eath RB, Turner SP, Arnott G, Roehe R, et al. The welfare implications of large litter size in the domestic pig I: biological factors. Anim Welf. 2013;22:199–218.
Zurbrigg K. Sow shoulder lesions: Risk factors and treatment effects on an Ontario farm. J Anim Sci. 2006;84(9):2509–14.
Herskin MS, Bonde MK, Jørgensen E, Jensen KH. Decubital shoulder ulcers in sows: a review of classification, pain and welfare consequences. Animal. 2011;5(5):757–66.
Merks JWM, Mathur PK, Knol EF. New phenotypes for new breeding goals in pigs. Animal. 2012;6(4):535–43.
Beaulieu AD, Aalhus JL, Williams NH, Patience JF. Impact of piglet birth weight, birth order, and litter size on subsequent growth performance, carcass quality, muscle composition, and eating quality of pork. J Anim Sci. 2010;88(8):2767–78.
Rehfeldt C, Nissen PM, Kuhn G, Vestergaard M, Ender K, Oksbjerg N. Effects of maternal nutrition and porcine growth hormone (pGH) treatment during gestation on endocrine and metabolic factors in sows, fetuses and pigs, skeletal muscle development, and postnatal growth. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2004;27:267–85.
Nielsen B, Su G, Lund MS, Madsen P. Selection for increased number of piglets at d 5 after farrowing has increased litter size and reduced piglet mortality. J Anim Sci. 2013;91:2575–82.
Kapell DNRG, Ashworth CJ, Knap PW, Roehe R. Genetic parameters for piglet survival, litter size and birth weight or its variation within litter in sire and dam lines using Bayesian analysis. Livest Sci. 2011;115:215–24.
Sorensen D, Waagepetersen R. Normal linear models with genetically structured residual variance heterogeneity: a case study. Genet Res. 2003;82:207–22.
Felleki M, Lee D, Lee Y, Gilmour AR, Rönnegård L. Estimation of breeding values for mean and dispersion, their variance and correlation using double hierarchical generalized linear models. Genet Res Camb. 2012;94:307–17.
Yang J, Manolio TA, Pasquale LR, Boerwinkle E, Caporaso N, Cunningham JM, et al. Genome partitioning of genetic variation for complex traits using common SNPs. Nat Genet. 2011;43(6):519–25.
Roehe R, Kennedy BW. Estimation of genetic parameters for litter size in Canadian Yorkshire and Landrace swine with each parity of farrowing treated as a different trait. J Anim Sci. 1995;73:2959–70.
Hanenberg E, Knol EF, Merks JWM. Estimates of genetic parameters for reproduction traits at different parities in Dutch Landrace pigs. Livest Prod Sci. 2001;69:179–86.
Crump R, Haley C, Thompson R, Mercer J. Individual animal model estimates of genetic parameters for performance test traits of male and female Landrace pigs tested in a commercial nucleus herd. Anim Sci. 1997;65:275–83.
Mulder HA, Bijma P, Hill WG. Prediction of breeding values and selection responses with genetic heterogeneity of environmental variance. Genetics. 2007;175:1895–910.
Yang Y, Christensen OF, Sorensen D. Use of genomic models to study genetic control of environmental variance. Genet Res (Camb). 2011;93(2):125–38.
Onteru SK, Fan B, Du Z, Garrick DJ, Stalder KJ, Rothschild MF. A whole-genome association study for pig reproductive traits. Anim Genet. 2012;43:18–26.
Onteru SK, Fan B, Nikkilä MT, Garrick DJ, Stalder KJ, Rothschild MF. Whole-genome association analyses for lifetime reproductive traits in the pig. J Anim Sci. 2011;89:988–95.
Cassady JP, Johnson RK, Pomp D, Rohrer GA, Van Vleck LD, Spiegel EK, et al. Identification of quantitative trait loci affecting reproduction in pigs. J Anim Sci. 2001;79:623–33.
Schneider JF, Rempel LA, Rohrer GA. Genome-wide association study of swine farrowing traits. Part I: Genetic and genomic parameter estimates. J Anim Sci American Society of Animal Science. 2012;90:3353–9.
Guo Y, Lee GJ, Archibald AL, Haley CS. Quantitative trait loci for production traits in pigs: a combined analysis of two Meishan × Large White populations. Anim Genet. 2008;39:486–95.
Scarlett D-JG, Herst PM, Berridge MV. Multiple proteins with single activities or a single protein with multiple activities: the conundrum of cell surface NADH oxidoreductases. BBA-Bioenergetics. 1708;2005:108–19.
Schneider JF, Nonneman DJ, Wiedmann RT, Vallet JL, Rohrer GA. Genomewide association and identification of candidate genes for ovulation rate in swine. J Anim Sci. 2014;92:3792–803.
Hadari YR, Eisenstein M, Zakut R, Zick Y, 平林淳. Galectin-8: on the Road from Structure to Function. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. FCCA (Forum: Carbohydrates Coming of Age). 1997;9:103–12.
Rönnegård L, Valdar W. Detecting major genetic loci controlling phenotypic variability in experimental crosses. Genetics. 2011;188:435–47.
Nikolaev AY, Li M, Puskas N, Qin J, Gu W. Parc: a cytoplasmic anchor for p53. Cell. 2003;112:29–40.
Skaar JR, Florens L, Tsutsumi T, Arai T, Tron A, Swanson SK, et al. PARC and CUL7 form atypical cullin RING ligase complexes. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2006–14.
Surget S, Khoury MPBJ. Uncovering the role of p53 splice variants in human malignancy: a clinical perspective. Onco Targets Ther. 2013;7:57–68.
GeneCards. http://www.genecards.org.
Van Wijk R, Ovelgönne JH, De Koning E, Jaarsveld K, Van Rijn J, Wiegant FAC. Mild step-down heating causes increased levels of HSP68 and of HSP84 mRNA and enhances thermotolerance. Int J Hyperther. 1994;10:115–25.
Huang H, Lee W, Lin J, Huang H, Jian S, Mao SJT, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of porcine cDNA encoding a 90-kDa heat shock protein and its expression following hyperthermia. Gene. 1999;226:307–15.
Zhang X, Mosser DM. Macrophage activation by endogenous danger signals. J Pathol. 2008;214:161–78.
Fujisawa K, Asahara H, Okamoto K, Aono H, Hasunuma T, Kobata T, et al. Therapeutic effect of the anti-Fas antibody on arthritis in HTLV-1 tax transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1996;98:271.
Lund AA, Rhoads DM, Lund AL, Cerny RL, Elthon TE. In vivo modifications of the maize mitochondrial small heat stress protein, HSP22. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:29924–9.
Debat V, Milton CC, Rutherford S, Klingenberg CP, Hoffmann AA. Hsp90 and the quantitative variation of wing shape in Drosophila melanogaster. Evolution (N Y). 2006;60:2529–38.
Takahashi KH, Rako L, Takano-Shimizu T, Hoffmann AA, Lee SF. Effects of small Hsp genes on developmental stability and microenvironmental canalization. BMC Evol Biol. 2010;10:284.
Cimpean AM, Raica M, Encica S, Cornea R, Bocan V. Immunohistochemical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF), and its receptors (VEGFR1, 2) in normal and pathologic conditions of the human thymus. Ann Anat. 2008;190:238–45.
Woolard J, Wang W-Y, Bevan HS, Qiu Y, Morbidelli L, Pritchard-Jones RO, et al. VEGF165b, an Inhibitory Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Splice Variant Mechanism of Action, In vivo Effect On Angiogenesis and Endogenous Protein Expression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7822–35.
Spötter A, Distl O. Genetic approaches to the improvement of fertility traits in the pig. Vet J. 2006;172:234–47.
Dekkers JCM, Mathur PK, Knol EF. Genetic improvement of the pig. Genet pig. 2011;16:390–425.
Tomiyama M, Takagi T, Suzuki K, Kubo S. Evaluation of genetic trends and determination of the optimal number of cumulative records of parity required in reproductive traits in a Large White pig population. Anim Sci J. 2011;82:621–6.
Vidović V, Štrbac L, Višnjić V, Punoš D, Šević R, Krnjajić J, et al. Genetic trend for certain traits in pigs using different selection criteria. Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2012;45:274–9.
Taylor G, Hermesch S, Roese G. Breeds of pigs: Large White. Primefact 62. New South Wales Department of Primary Industries: Orange, New South Wales, Australia. 2005.
Gilmour AR, Gogel BJ, Cullis BR, Thompson R. ASReml user guide release 2.0. . Hemel Hempstead, UK: VSN Int. Ltd.; 2006.
Sae-Lim P, Kause A, Janhunen M, Vehviläinen H, Koskinen H, Gjerde B, et al. Genetic (co) variance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) body weight and its uniformity across production environments. Genet Sel Evol. 2015;47:46.
Ostersen T, Christensen OF, Henryon M, Nielsen B, Su G, Madsen P. Deregressed EBV as the response variable yield more reliable genomic predictions than traditional EBV in pure-bred pigs. Genet Sel Evol. 2011;43:38.
Garrick DJ, Taylor JF, Fernando RL. Deregressing estimated breeding values and weighting information for genomic regression analyses. Genet Sel Evol. 2009;41:44.
Calus MPL, Mulder HA, Bastiaansen JWM. Identification of Mendelian inconsistencies between SNP and pedigree information of sibs. Genet Sel Evol. 2011;43:34.
George EI, McCulloch RE. Variable selection via Gibbs sampling. J Am Stat Assoc. 1993;88:881–9.
Heuven HCM, Janss LLG. Bayesian multi-QTL mapping for growth curve parameters. BMC Proc. BioMed Central Ltd. 2010. p. S12.
Van Den Berg I, Fritz S, Boichard D. QTL fine mapping with Bayes C (pi): a simulation study. Genet Sel Evol. 2013;45:10.1186.
Duijvesteijn N, Veltmaat JM, Knol EF, Harlizius B. High-resolution association mapping of number of teats in pigs reveals regions controlling vertebral development. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:542.
Gelman A, Rubin DB. Inference from iterative simulation using multiple sequences. Stat Sci. 1992;7:457–72.
Plummer M, Best N, Cowles K, Vines K. CODA: Convergence diagnosis and output analysis for MCMC. R news. 2006;6:7–11.
Kass RE, Raftery AE. Bayes factors. J Am Stat Assoc. 1995;90:773–95.
Ensembl Sscrofa 10.2 . http://www.ensembl.org.
Mulder HA, Visscher J, F J. Estimating the purebred-crossbred genetic correlation for uniformity of eggshell color in laying hens. 2015.
Weller JI. Quantitative trait loci analysis in animals. Wallingford, U.K.: CABI Publishing; 2009.
Hernandez SC, Finlayson HA, Ashworth CJ, Haley CS, Archibald AL. A genome-wide linkage analysis for reproductive traits in F2 Large White × Meishan cross gilts. Anim Genet. 2014;45:191–7.
Bidanel J-P, Milan D, Iannuccelli N, Amigues Y, Boscher M-Y, Bourgeois F, et al. Detection of quantitative trait loci for growth and fatness in pigs. Genet Sel Evol. 2001;33:289–310.
Sanchez M-P, Riquet J, Iannuccelli N, Gogue J, Billon Y, Demeure O, et al. Effects of quantitative trait loci on chromosomes 1, 2, 4, and 7 on growth, carcass, and meat quality traits in backcross Meishan × Large White pigs. J Anim Sci. 2006;84:526–37.
Ai H, Ren J, Zhang Z, Ma J, Guo Y, Yang B, et al. Detection of quantitative trait loci for growth-and fatness-related traits in a large-scale White Duroc × Erhualian intercross pig population. Anim Genet. 2012;43:383–91.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Dutch Science Council (NWO) and part of the study was coordinated by the Dutch Technology Foundation (STW). This research was also supported by Breed4Food, a public-private partnership in the domain of animal breeding and genomics and Topigs Norsvin (Vught, The Netherlands). Data for this study were provided by Topigs Norsvin (Beuningen, The Netherlands). The authors would like to thank Mario Calus and Johan van Arendonk for valuable comments during writing of this manuscript. Ewa Sell-Kubiak also thanks Susan Wijga, Juanma Herrero-Medrano and Mirte Bosse for helpful discussions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interest
EFK, ND and MSL are employees of Topigs Norsvin Research Center, a research institute closely related to one of the funders (Topigs Norsvin). Topigs Norsvin had a role in the study design, data collection, and preparation of the manuscript. The authors declare that the results are presented in full and as such present no conflict of interest.
Authors’ contributions
ESK, EFK, PB and HAM participated in the design of the study and writing of the paper. ESK was responsible for editing the data, conducting the statistical analyses, preparing figures and tables, and writing the paper. ND and MSL were involved in statistical analysis and writing the paper. LJ was a discussion partner (especially with respect to the Bayesian analysis) and involved in writing the paper. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Sell-Kubiak, E., Duijvesteijn, N., Lopes, M.S. et al. Genome-wide association study reveals novel loci for litter size and its variability in a Large White pig population. BMC Genomics 16, 1049 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2273-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2273-y