Abstract
The present work demonstrates a validation of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) combining with ultra violet and visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy and quasi-elastic light scattering (QELS) analysis for characterization of silver sols synthesized in polymer matrices. Polymer matrix internal structure and polymer chemical nature actually controlled the sol size characteristics. It was shown that for precise analysis of nanoparticle size distribution these techniques should be used simultaneously. All applied methods were in good agreement for the characterization of size distribution of small particles (less than 60 nm) in the sols. Some deviations of the theoretical curves from the experimental ones were observed. The most probable cause is that nanoparticles were not entirely spherical in form.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The size of metal nanoparticles determines optical, catalytic, or biomedical properties of nanosystems and defines limits for applications [1–4]. Despite the increasing interest in the applications of functional nanoparticles, a comprehensive understanding of the formation of nanosystems as well as their precise characterization is still a challenge.
Techniques to detect and characterize nanoparticles fall into two categories: direct, or “real space,” and indirect, or “reciprocal space.” Direct techniques include transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and atomic force microscopy (AFM). These techniques can image nanoparticles, directly measure sizes, and infer shape information, but they are limited to studying only a few particles at a time. There are also significant issues surrounding the sample preparation for electron microscopy. In general, however, those techniques can be quite effective for obtaining basic information about a nanoparticle.
Indirect techniques for nanosystem characterization are absorption (ultra violet and visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy) and various scattering methods: quasi-elastic light scattering (QELS), X-rays, or neutron scattering. The techniques that become of greatest relevance to nanoscience are small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) [5, 6]. The advantage of those techniques is that they are able to characterize large numbers of nanoparticles and often do not require any particular sample preparation.
The main aim of the current research was to compare the data obtained by the complex of physical methods for evaluation of various indirect techniques for sol characterization.
Methods
The silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) were synthesized by reduction of the AgNO3 salt using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as reductant. The synthesis of Ag sols was carried out in situ into an aqueous solution of nonionic polymer dextran-graft-polyacrylamide and its anionic derivative [7–9].
The synthesis of AgNPs was performed at the polymer concentration corresponding to dilute polymer solutions.
NaBH4 was purchased from “Pharma” (Ukraine).
AgNO3 (Sigma Aldrich) was used without additional purification.
AgNP Synthesis
Reduction of Ag salt was performed at T = 60 °C. Molar ratio of AA monomers to Ag+ cations was equal to 5. The syntheses were carried out in polymer solutions prepared using deionized water. The pH value of aqueous solutions of nonionic polymer was 5.5 that corresponds to the pH of deionized water. pH value of aqueous solutions of anionic polymers was around 7.33.
Two milliliters of a 0.1 mol L−1 AgNO3 aqueous solution was added to 5 mL of aqueous polymer solution (c = 1.10−3 g cm−3) and stirred for 20 min. Then, 2 mL of 0.1 mol L−1 aqueous solution of NaBH4 was added. The final aqueous solution was stirred for 30 min. It turned reddish brown; thus, the formation of AgNPs was indicated.
Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
Multidetection size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) analysis of polymers was carried out by using an experimental setup consisting of a LC-10 AD Shimadzu pump (throughput 0.5 mL min−1; Nakagyo-ku, Kyoto, Japan), an automatic injector WISP 717+ from Waters (Milford, MA, USA), three coupled 30-cm Shodex OH-Pak columns (803HQ, 804HQ, and 806HQ; Munich, Germany), a multi-angle light scattering detector DAWN F from Wyatt Technology (Dernbach, Germany), and a differential refractometer R410 from Waters. Distilled water containing 0.1 M NaNO3 was used as eluent. Dilute polymer solutions (c = 1.10−3 g cm−3 < c* = 1/[η] (Table 1)) were prepared and injected. The intermolecular correlations were then negligible in the analysis of the light scattering measurements. To obtain gyration radii for macromolecules, static light scattering data was analyzed by Zimm method [10].
UV-vis Spectroscopy
UV-visible absorption spectra of silver sols were recorded by Varian Cary 50 scan UV-visible spectrophotometer (Palo Alto, CA, USA).
Quasi-Elastic Light Scattering (QELS)
DLS measurements were carried out using Zetasizer Nano ZS90 (Malvern Instruments Ltd., UK). The apparatus contains a 4-mW He-Ne laser with a wavelength of 632.8 nm, and the scattered light is detected at an angle of 60°.
SAXS experiments were carried out on an instrument with a high-intensity microfocus rotating Cu anode X-ray generator in the Laboratory for Advanced Studies of Membrane Proteins (Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Dolgoprudniy, Russia), using a standard transmission configuration. An X-ray wavelength of λ = 1.54 Å was used, resulting in a momentum transfer Q in the range of 0.007–0.2 Å−1, where Q = (4π/λ) sin(θ/2) and θ is the scattering angle. The samples studied were placed in borosilicate capillaries of 1.5 mm diameter and 0.01 mm wall thickness (W. Muller, Berlin, Germany). Water was used as a buffer sample. Center of beam line and conversation channel to value of module q-vector was done using silver behenate [11].
Results and Discussion
The main characteristics of the polymers used as the matrices for in situ AgNP syntheses are drawn in Table 1, where I = M w/M n, the polydispersity index; R g, the radius of gyration; and A, the chemical charge fraction of polyelectrolytes obtained by alkaline hydrolysis of polyacrylamide.
SEC analysis indicates that polymer samples possess relatively low polydispersity index and display in aqueous solution rather large radii of gyration in agreement with their high average molecular weights. The peculiarities of the molecular structure of the copolymers dextran-graft-polyacrylamide (D-g-PAA) were discussed in [12–14]. These copolymers are star-like polymers, consisting of a compact dextran core and long polyacrylamide arms. As it was previously reported, the branched polymers, due to their more compact internal structure, have higher local concentration of functional groups with respect to their linear analogues [13, 14] that is why they are more efficient matrices for nanosystem fabrication [15].
D-g-PAA copolymer was transformed into polyelectrolyte, referred as D-g-PAA(PE) by alkaline hydrolysis. The process of D-g-PAA hydrolysis was not attended by irrelevant processes (breaking or cross-linking of the macromolecules) [14].
It is evident that saponified polymers contain two types of functional groups: carbamide and carboxylate ones. The pH value of the solutions was equal to 7.33 after the D-g-PAA(PE) sample dissolved in bi-distilled water. Thus, carboxylate groups of polymer were partially hydrolyzed in such conditions. Obviously, the nucleation process occurring just after reductant addition differs for silver ions interacting with carbamide or carboxylate moiety. That could lead to a different size distribution for nanoparticles synthesized in branched nonionic and polyelectrolyte polymer matrices.
In situ syntheses of AgNPs into dilute aqueous solutions of both uncharged (nonionic) and polyelectrolyte branched polymer matrices resulted in rather stable colloids. Our previous attempts to synthesize the stable colloid in anionic linear PAA matrices were not successful; some precipitation has been observed [15].
The sols were studied using indirect technique for nanosystem characterization, namely UV-vis spectroscopy and two scattering methods: QELS and SAXS.
UV-vis Spectroscopy
Surface plasmon resonance peak with well-defined shoulders were observed in UV-vis spectra of Ag sols (Fig. 1). For AgNPs (nanosystems-sols) synthesized in D-g-PAA and D-g-PAA(PE), further sol 1 and sol 2, respectively, the extinction maxima were observed at 392 and 386 (Fig. 1a, b, curve 1, peak 1) and shoulders on the plasmon bands at 432 and 451 (Fig. 1a, b, curve 1, peak 2). Such result could be explained by the existence of two size fractions of AgNPs. Experimental extinction curves have been fitted by Lorenz multiple peak fit (OriginLab 9.1) (see Fig. 1a, b; curve 2, 3). In light scattering theory, the most famous theory is likely to be the one published by Gustav Mie in 1908. This theory describes the quasi-elastic interaction between an electromagnetic plane wave and a homogeneous sphere defined by its (arbitrary) diameter and its (arbitrary) complex refractive index. It allows to calculate scattered fields outside the sphere, internal fields, phase relations, and various cross sections. Peaks 1 and peaks 2 have been approximated using MieLab software for spherical homogeneous particles. The algorithm of mathematical analysis and source code are described in detail in [16]. The best fits are represented in Fig. 2. Deviation of theoretical curve takes place for both samples. For both sols, the additional maximum on the theoretical curves (marked as “scattering” on peaks 2) was observed for the second maximum (Fig. 2b–d). These peaks can correspond to scattering contribution to extinction spectra. Absence of this phenomenon on the experimental spectrum for sol 1 and on the Lorenz fit (Fig. 1a) can be explained by overlap of scattering maxima with the peak 1 at the similar wavelength (384 and 386 nm, respectively). A phase retardation of scattering contribution appeared to be more significant for the case of sol 2 (Fig. 2d). It may be related to the presence of the fraction of larger particles in sol 2 in comparison with sol 1. As the result, the shoulder on the experimental spectrum corresponded to scattering could be observed in the range of 380 nm (Fig. 1b). Parameters of Mie approximation, namely sphere size and polydispersity, are represented in Table 2.
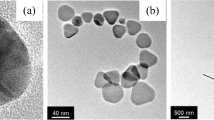
Some deviations of the theoretical curves from the experimental ones were observed (Fig. 2). The most probable cause is that nanoparticles were not entirely spherical in form, as described in the theoretical model. But the average diameters of AgNPs estimated from the theoretical curves proved to be very close to the ones evaluated from TEM images in our previous work [13].
QELS Analysis
Regularized inverse Laplace transform of experimental correlation functions was performed using MathLab code rilt.m (inserted graphs in Fig. 3) [17]. Hydrodynamic radii of particle scatter have been reached from Stokes-Einstein equation:
where k—Boltzmann constant, T—absolute temperature, η—viscosity, and D—diffusion coefficient.
The results of analysis are represented in Fig. 3. Intensity-weighted distributions for both nanosystems have a complicated multimodal shape. The existence of 10–20-Å nanoparticles in sol 1 (peak 1, Fig. 3a) and 7–15 Å in sol 2 (peak 1, Fig. 3b) is evident. The fractions of larger AgNPs of 100–150 Å (peaks 2; Fig. 3a, b) and the aggregates of 200–1000 Å (peaks 3; Fig. 3a, b) are observed in both sols. Statistical analysis of distribution curves is represented in Table 3.
The peaks in the range of 200–1000 Å can correspond to the aggregates of AgNPs as well as to the macromolecules of polymer matrices (Table 1). QELS results are in good agreement with the UV-vis results excluding the peak of AgNP aggregates and macromolecules.
SAXS Data Analysis
The small-angle X-ray scattering curves for sol 1 and sol 2 are represented in Fig. 4. Curves were normalized on sample transmission; scattering from buffer sample (water) was subtracted.
For the analysis of experimental data, the following methods were used: Guinier plot, size distribution function plot, and fitting of the obtained scattering curves. For Guinier plot and for the size distribution function plot, the PRIMUS program from the software package ATSAS was applied [18, 19]. Experimental curve fitting was provided using SASVIEW program [20].
The gyration radii (R g) of AgNPs in sol 1 and sol 2 were determined using Guinier plot. The influence of structure factor was taken into account. The results of analysis are drawn in Table 4. The third column (Table 4) is shown for evaluation of applicability of Guinier approximation.
This function depends both on the particle’s geometry, expressing numerically the set of distances joining the volume elements within a particle, and on a particle’s inner inhomogeneity distribution.
For size distribution function analysis, the program PRIMUS of the software package ATSAS was used. The results are represented in Fig. 5a, b for sol 1 and sol 2, respectively. The gyration radius as well as the particle size maximum in both sols are shown in Table 5.
Here, R max is the largest distance between the volume elements within a particle.
Figure 6a, b represents the results of fitting the experimental scattering curves for sol 1 and sol 2, respectively. Sphere model function with polydispersity as a model fitting function was used. Scattering intensity formula for sphere model function is
where scale is a volume fraction, V is the volume of the scatterer, R is the radius of the sphere, bkg is the background level, and Δρ is the contrast [21].
The resulting particle size with a comparison with results obtained by other methods is shown in Table 6.
Some fitting inaccuracies occurred on Fig. 6a, b in the range of small q values. It can be caused by the interaction between scattering particles in the aggregates. The fit model does not take it into account. However, the dimensions obtained after the fitting of SAXS results are in good agreement with the size characteristics derived by other methods. This fact indicates the correction of the fit model.
Table 6 joins all parameters obtained from SAXS analysis.
SAXS analysis demonstrates monomodal scatterer size distribution in both sols in contrast to QELS and UV-vis spectroscopy, where multimodal particle size distribution is observed. Such contradiction may be caused by the ability of QELS and UV-vis to register large particles or aggregates within the range 300–600 Å. SAXS data analysis is accurate in the limited q-range value, 0.02 Å−1 < q <0.4 Å−1. Thus, large particles and aggregates are “invisible” for the q values we used.
Size parameters of the nanoparticles estimated correctly by UV-vis, QELS, and SAXS have been marked by italic font within Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5. These values appeared to be close for all techniques. Three different indirect methods also reveal the similar difference in size distribution in nanosystems synthesized in nonionic and anionic branched polymer matrices. The reason for such distinction is the various chemical nature of the polymer template affecting on the nucleation process in the process of nanoparticle formation.
The TEM investigation of silver sols has shown that most AgNPs synthesized in the solution of nonionic branched polymer matrices D-g-PAA had sizes in the range of 8–15 nm. The small number of aggregates was observed too. Silver sols synthesized in branched anionic polymer matrices D-g-PAA(PE) along with NPs have a size of 10–15 nm, i.e., the same as in the sols synthesized in the nonionic polymer matrix. Nanoparticles with a size of 2–5 nm and some large aggregates were observed.
Thus, the present work confirmed the validation of UV-vis spectroscopy and scattering methods for accurate investigation of sols. But UV-vis and SASX are limited for characterization of polydispersed nanosystems and should be used in combination with QELS or TEM.
Conclusions
The present study proved the efficiency of using branched nonionic and anionic polymers as matrices for the stable silver sols preparation. It was demonstrated that the chemical nature of polymer matrix (uncharged or charged) and the polymer internal structure affect the nanoparticles’ actual control on the sol size characteristics and nanoparticle size distribution in the nanosystems. The analysis of the silver sols was performed using UV-vis spectroscopy, QELS, and SAXS. All methods used were in good agreement for the characterization of size distribution of small particles (less than 60 nm) in the sols. The polydispersity estimated by various methods was comparable. It was shown that for precise analysis of sols synthesized in polymer matrices all these techniques should be used simultaneously. It should be noted that nanoparticle aggregates and macromolecules of the polymer matrix can be characterized only by QELS.
References
Nejad A, Unnithan A, Sasikala A, Samarikhalaj M, Thomas R, Jeong Y, Nasseri S, Murugesan P, Wu D, Park C, Kim C (2015) Mussel-inspired electrospun nanofibers functionalized with size-controlled silver nanoparticles for wound dressing application. Appl Mater Interfaces 7:12176–12183
Zille A, Fernandes M, Francesko A, Tzanov T, Fernandes M, Oliveira F, Almeida F, Amorim T, Carneiro N, Esteves M, Souto A (2015) Size and aging effects on antimicrobial efficiency of silver nanoparticles coated on polyamide fabrics activated by atmospheric DBD plasma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:13731–13744
Sharma H, Vendamani V, Pathak A, Tiwari A (2015) Fraxinus paxiana bark mediated photosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their size modulation using swift heavy ion irradiation. Radiat Phys Chem 117:184–190
Raghavendra U, Basanagouda M, Thipperudrappa J (2015) Investigation of role of silver nanoparticles on spectroscopic properties of biologically active coumarin dyes 4PTMBC and 1IPMBC. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 150:350–359
Schwamberger A, Roo B, Jacob D, Dillemans L, Bruegemann L, Seo J, Locquet J. Combining SAXS and DLS for simultaneous measurements and time-resolved monitoring of nanoparticle synthesis. Nucl Instrum Meth B. 2015;343:116–122
Yang G, Chang V-S, Hallinan D Jr (2015) A convenient phase transfer protocol to functionalize gold nanoparticles with short alkylamine ligands. J Colloid Interface Sci 460:164–172
Kutsevol N, Bezugla T, Bezuglyi M, Rawiso M (2012) Branched dextran-graft-polyacrylamide copolymers as perspective materials for nanotechnology. Macromol Symp 1:82–90
Bezuglyi M, Kutsevol N, Rawiso M, Bezugla T (2012) Water-soluble branched copolymers dextran-polyacrylamide and their anionic derivates as matrices for metal nanoparticles in-situ synthesis. Chemik 66:862–867
Kutsevol N, Chumachenko V, Rawiso M, Shkodich V, Stoyanov O (2015) Star-shaped dextran-polyacrylamide polymers: prospects of use in nanotechnologies. J Struct Chem 56:959–966
Zimm BH (1948) Apparatus and methods for measurement and interpretation of the angular variation of light scattering; preliminary results on polystyrene solution. J Chem Phys 16:1093–1099
Nyam-Osor M, Soloviov DV, Kovalev YS, Zhigunov A, Rogachev AV, Ivankov OI, Erhan RV, Kuklin AI (2012) Silver behenate and silver stearate powders for calibration of SAS instruments. J Phys Conf Ser 351(1):012024
Kutsevol N, Guenet JM, Melnyk N, Sarazin D, Rochas C (2006) Solution properties of dextran-polyacrylamide graft copolymers. Polymer 47:2061–2068
Kutsevol N, Bezuglyi M, Bezugla T (2014) Features of the intramolecular structure of branched polymer systems in solution. J Struct Chem 55:575–587
Kutsevol N, Bezuglyi M, Rawiso M (2014) Bezugla T: star-like dextran-graft-(polyacrylamide-co-polyacrylic acid) Copolymers. Macromol Symp 335:12–16
Chumachenko V, Kutsevol N, Rawiso M, Schmutz M, Blanck C (2014) In situ formation of silver nanoparticles in linear and branched polyelectrolyte matrices using various reducing agent. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:164
Peña-Rodríguez O, Pérez P, Pal U (2011) MieLab: a software tool to perform calculations on the scattering of electromagnetic waves by multilayered spheres. Int J Spectrosc 2011:10
Marino LG (2004) Regularized inverse Laplace transform., http://www.mathworks.com. Accessed 10 Dec 2004
Konarev PV, Volkov VV, Sokolova AV, Koch MHJ, Svergun DI (2003) PRIMUS: a windows PC-based system for small-angle scattering data analysis. J Appl Crystallogr 36(5):1277–1282
Petoukhov MV, Franke D, Shkumatov AV, Tria G, Kikhney AG, Gajda M, Gorba C, Mertens HDT, Konarev PV, Svergun DI (2012) New developments in the ATSAS program package for small-angle scattering data analysis. J Appl Crystallogr 45(2):342–350
SasView software. http://www.sasview.org. Accessed date November 2012.
Svergun DI, Feigin LA (1987) Structure analysis by small-angle x-ray and neutron scattering. Plenum Press, New York
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support of this work by the MIPT “5Top100” program of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation. This work benefitted from SasView software, originally developed by the DANSE project under NSF award DMR-0520547.
The authors are grateful to Dr. Michel Rawiso from Institute Charles Sadron (Strasbourg, France) for polymer sample characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ Contributions
VC and NK carried out the polymer and nanoparticle synthesis, polymer characterization, UV-vis study, and QELS and UV-vis data analysis. AM performed the QELS experiment. DS performed the SAXS experiment and data analysis. LB and AK have discussed the summary results. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ Information
LB is Academician of the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) of Ukraine, PhD, and Dr. Phys.-Math. degree holder, Professor, and the Head of the Department of Molecular Physics at the Physics Department of Kiev National Taras Shevchenko University. NK is the principal researcher, PhD and Dr. Chem. Sci. degree holder, and Deputy Dean for Science of the Faculty of Chemistry of Kiev National Taras Shevchenko University. VC is a PhD student at the Faculty of Chemistry of Kiev National Taras Shevchenko National University. DS is a PhD in physics, responsible for Small Angle Neutron Spectrometer YuMO at Joint Institute for Nuclear Research and a researcher at the Institute for Safety Problems of Nuclear Power Plants NAS of Ukraine and at Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. AK is a PhD in physics, the Head of small angle scattering group at Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, and principal researcher at Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Bulavin, L., Kutsevol, N., Chumachenko, V. et al. SAXS Combined with UV-vis Spectroscopy and QELS: Accurate Characterization of Silver Sols Synthesized in Polymer Matrices. Nanoscale Res Lett 11, 35 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1230-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1230-2