Abstract
Background
Essential oils extracted from aromatic plants exhibit important biological activities and have become increasingly important for scientific research. The essential oil extracted from Cinnamomum cassia Presl (CC-EO) has various functional properties, however, little information is available regarding the tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to investigate the chemical composition and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of the CC-EO.
Results
cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid (43.06%) and cinnamaldehyde (42.37%) were found to be the two major components of the CC-EO identified by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The inhibitory activities of CC-EO and its major constituents were further evaluated against mushroom tyrosinase. The results showed that CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde exhibited anti-tyrosinase activities with IC50 values of 6.16 ± 0.04 mg/mL and 4.04 ± 0.08 mg/mL, respectively. However, cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid did not show any anti-tyrosinase activity. The inhibition kinetics were analyzed by Lineweaver-Burk plots and second replots, which revealed that CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde were mixed-type inhibitors. The inhibition constants (Ki) for CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde were calculated to be 4.71 ± 0.09 mg/mL and 2.38 ± 0.09 mg/mL, respectively.
Conclusion
These results demonstrate that CC-EO and its major component, cinnamaldehyde, possess potent anti-tyrosinase activities and may be a good source for skin-whitening agents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Tyrosinase (monophenol, dihydroxyphenylalanine: oxygen oxidoreductase EC 1.14.18.1) is a multifunctional, copper-containing enzyme that is widely distributed in nature and is involved in melanogenesis. It catalyzes both the hydroxylation of L-tyrosine (monophenolase activity) and the oxidation of L-DOPA (diphenolase activity) to o-quinone, which induces the production of melanin pigments (Seo et al. 2003). Melanin formation is considered to be deleterious to color quality and results in a loss of nutritive and market values for plant-derived foods and beverages (Friedman 1996; Sánchez-Ferrer et al. 1995). In addition, excessive melanin accumulation leads to human skin disorders, such as melasma, freckles, age spots and malignant melanomas (Fitzpatrick et al. 1983). Furthermore, formation of neuromelanin in the mammalian brain may be related to neurodegeneration associated with Parkinson’s disease (Asanuma et al. 2003). Therefore, the development of safe and effective tyrosinase inhibitors has become important for improving food quality and preventing pigmentation disorders and other melanin-related human health issues (Seo et al. 2003). Additionally, tyrosinase inhibitors are supposed to have broad applications as cosmetics whitening agents (Dooley 1997). As plants are a rich source of bioactive chemicals that are mostly free from harmful side effects, interest in finding natural tyrosinase inhibitors in bioactive chemicals is also increasing. Some potent tyrosinase inhibitors, such as anisaldehyde, quercetin and recently dalenin have been isolated from various plants (Chen and Kubo 2002; Chiari et al. 2011; Kubo and Kinst-Hori 1998).
Cinnamomum cassia Presl is widely cultivated in China. The dried stem bark of C. cassia, i.e., cassia bark, is important not only as a food spice but is also considered to have medicinal properties, such as antimicrobial (Lee and Ahn 1998), antitumorigenic (Ka et al. 2003), anti-inflammatory (Lee et al. 2002) and antidiabetic properties (Verspohl et al. 2005). In addition, the methanol extract of twigs of C. cassia was found to possess tyrosinase inhibitory activity (Ngoc et al. 2009). It is known that plant essential oil (EO) has various functional properties, such as a pleasant aroma, insect and animal repellant, as well as inhibitory effects against microorganisms. Moreover, various products made from EO have been used in aromatherapy and may relax or stabilize some physical and psychological conditions (Matsuura et al. 2006). The anise oil and citrus essential oils have been reported to possess tyrosinase inhibitory activities (Kubo and Kinst-Hori 1998; Matsuura et al. 2006). The essential oil from the relative cinnamon species, C. zeylanicum Blume, has been reported to show anti-tyrosinase activity, and cinnamaldehyde was found to be mainly responsible for this inhibition effect (Marongiu et al. 2007). The C. cassia essential oil (CC-EO) has hypouricemic (Zhao et al. 2006) and antifungal activities (Zhao et al. 2006). A number of tyrosinase inhibitors from both natural and synthetic sources that inhibited monophenolase, diphenolase or both of these activities have been identified to date (Kim and Uyama 2005). These tyrosinase inhibitors include plant polyphenols and aldehydes, fungal metabolites, derivatives of natural compounds, and synthetics origins. The tyrosinase inhibitory constituents of the essential oil extracted from Cinnamomum cassia (Ngoc et al. 2009; Lee et al. 2002) and relative cinnamon species, C. zeylanicum (Marongiu et al. 2007) have been well documented. Cinnamaldehyde was found to be the major constitute of the essential oil. However, the inhibitory pattern of cinnamaldehyde isolated from C. cassia (Lee et al. 2002), C. zeylanicum (Marongiu et al. 2007), olive oil (Kubo and Kinst-Hori 1999) and the root of Pulsatilla cernua was rather controvesial. Cinnamaldehyde from C. cassia was a competitive tyrosinase inhibitor whereas those from C. zeylanicum, olive oil and and the root of Pulsatilla cernua was a noncompetitive tyrosinase inhibitor. Therefore, this study were to further investigate the chemical composition and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of the CC-EO, including identifying constituent compounds using GC-MS, determining IC50 values using inhibition kinetic analysis, and determining tyrosinase inhibitory patterns and inhibition constants using Lineweaver-Burk plots and second replots. In addition, the results were compared with those of the well-known tyrosinase inhibitor kojic acid.
Methods
Chemicals
Mushroom tyrosinase (EC 1.14.18.1; T7755), trans-cinnamaldehyde, cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid and kojic acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals Co. (St. Louis, MO, U.S.A). L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) was purchased from Merck Co. (Darmstadt, Germany). All other chemicals were reagent grade or higher.
Essential oils
The essential oil, which was obtained by steam distillation from the stem bark of C. cassia Presl, was purchased from Yangsen Biotech, Inc. (Taipei, Taiwan). The extraction procedure is according to previous study with slight modifications (Choi et al. 2001). Briefly, C. cassia stem bark was place into vessel and extracted by steam distillation for 4 hours. The vapors were cooled by a closed cooling system and the liquid were collected in a container. The oils floated towards the top while the water settled below and the essential oils were obtained by simply removing the oils which were separated.
Enzymatic assay of tyrosinase
Tyrosinase inhibitory activities of the CC-EO and its major constituents were determined by the tyrosinase-dependent L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) oxidation assay according to a slight modification of the method of Kubo and Kinst-Hori (1998). The substrate solution (0.84 mL of 0.89 mM L-DOPA in 16 mM sodium phosphate buffer, pH 6.8) was incubated at 25°C for 10 min. Following incubation, 0.03 mL of each sample solution and 0.03 mL of mushroom tyrosinase (1000 units/mL; T7755, Sigma, one unit = ΔOD280 of 0.001 per min at pH 6.5 at 25°C in 3 mL reaction mixture containing L-tyrosine) were added. The assay mixture in a total volume of 0.9 mL was immediately monitored for the formation of dopachrome by measuring the linear increase in optical density at 475 nm. Kojic acid, which is known to inhibit tyrosinase (Chen et al. 1991a), was used as a positive control. The inhibitory percentage of tyrosinase was calculated as follows: % inhibition = (1-B/A) × 100, where A = ΔOD475/min without tested sample and B = ΔOD475/min with tested sample. The 50% inhibition (IC50) of tyrosinase activity was calculated as the concentrations of the tested sample that inhibited 50% of tyrosinase activity under experimental conditions.
Kinetic analysis
The reaction mixture consisted of 0.3 mL of L-DOPA (0.75-3 mM) as a substrate, 0.54 mL of 25 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), 0.03 mL of mushroom tyrosinase (1000 units/ml) in 25 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), and 0.03 mL of each sample solution (0–12.50 mg/mL for CC-EO; 0–6.25 mg/mL for trans-cinnamaldehyde) in a total volume of 0.9 mL was assayed at 25°C, as described above. The inhibitory kinetics of each sample with tyrosinase were analyzed using Lineweaver-Burk plots. The reciprocal equation for a rapid equilibrium approach from the mixed-type noncompetitive inhibition can be expressed as eq 1 (Segel 1976). The Ki for CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde were calculated from the slope replots (eq 2). The αKi for CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde were calculated from the 1/v axis intercept replots (eq 3). Eq 1, ; eq 2, and eq 3, , where Ks is the dissociation constant of substrate (S) from enzyme-substrate complex (ES), Ki is the dissociation constant of inhibitor (I) from enzyme-inhibitor complex (EI), and αKi is the dissociation constant of inhibitor from enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complex (ESI).
GC-MS analysis
GC-MS analyses were carried out on a GCMS-QP-2010 plus Gas chromatograph Mass Spectrometer (Shimadzu, Japan) and GCMS-solution software (v. 2.50 SU3, Shimadzu, Japan). Compounds were separated on a Forte ID-BPX5 cross-linked 5% phenyl - 95% methyl polysiloxane (30 m × 0.25 mm i.d., film thickness 0.25 μ m) capillary column (SGE, AU). The column was maintained at 50°C for 5 min after injection then programmed at 5°C/min to 150°C, then programmed at 10°C/min to 300°C. The injection volume was 1.0 μl of pure essential oil, with a split ratio of 1:100. Helium was used as the carrier gas at a constant flow-rate of 1.0 ml/min. Injector, transfer line and ion-source temperatures were 250, 230 and 250°C, respectively. MS detection was performed with electron impact mode at 70 eV ionization energy and 60 μ A ionization current, by operating in the full-scan acquisition mode in the 40–350 amu range. Compounds were identified by comparing the retention times and retention indices of the chromatographic peaks with those of authentic reference standards run under the same conditions. Peak enrichment on co-injection with authentic reference compounds was also carried out. The comparison of the MS fragmentation pattern with those of pure compounds and mass spectrum database search was performed by using the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) MS spectral database (version 2005).
Statistical analysis
All the assays to determine enzyme activity (i.e., the tyrosinase inhibitory effect of CC-EO, trans-cinnamaldehyde, cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid and kojic acid and the enzyme kinetics) were conducted at least three times with three different sample preparations. All data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed using SPSS (SPSS Inc., U.S.A.). A one-way ANOVA and Scheffe test were used to determine the difference of means, and p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Chemical composition of CC-EO
The chemical composition of CC-EO was analyzed using GC-MS. The 16 constituent compounds identified, along with the retention times and Kovats indices, are listed in Table 1. Our results showed that the two major constituents of CC-EO were cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid (43.06%) and cinnamaldehyde (42.37%) and that the minor compounds were o-methoxycinnamaldehyde (5.11%), 1,2-dimethoxy-4-(3-methoxy-1-propenyl) benzene (2.05%), cinnamyl acetate (1.83%) and other compounds (1.25~0.16%) in the present study.
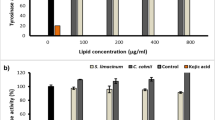
Effect of CC-EO, trans-cinnamaldehyde and cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid on the activity of mushroom tyrosinase
The effect of CC-EO, trans-cinnamaldehyde and cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid on the oxidation of L-DOPA catalyzed by mushroom tyrosinase as well as that of kojic acid which is a well-known tyrosinase inhibitor were studied. As shown in Figure 1, it was found that CC-EO and trans-cinnamaldehyde had potent inhibitory effects on the L-DOPA oxidase activity of mushroom tyrosinase in a dose-dependent manner. The results showed that trans-cinnamaldehyde had higher tyrosinase inhibitory activity than CC-EO. Based on the half-inhibition concentration (IC50) (Table 2), trans-cinnamaldehyde is approximately 1.5 times more effective than CC-EO. However, cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid had no inhibitory effects on the mushroom tyrosinase in this study (data not shown). Then, we had compared the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of the CC-EO with a well-known tyrosinase inhibitor, kojic acid. The IC50 value of the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of kojic acid was determined to be 0.22 mg/mL which was found to be significantly more pronounced than those of CC-EO (6.16 mg/mL) and trans-cinnamaldehyde (4.04 mg/mL). To obtain 80% tyrosinase inhibitory activity, the concentrations needed for CC-EO, trans-cinnamaldehyde, and kojic acid were 51.35, 16.65, and 0.96 mg/mL, respectively.
Inhibition type of CC-EO and trans-cinnamaldehyde on the activity of mushroom tyrosinase
The kinetic behaviors of CC-EO, on the mushroom tyrosinase for the oxidation of L-DOPA were first studied. Under the experimental conditions, the Michaelis constant (K m ) and maximum velocity (Vmax) of the L-DOPA oxidation reaction catalyzed by the tyrosinase (30 units) were 0.80 mM and 0.469 ΔOD475/min, respectively. The inhibitory kinetics of CC-EO were analyzed using Lineweaver-Burk double reciprocal plots as shown in Figure 2A. The five lines, obtained from the uninhibited enzyme and from four different concentrations of CC-EO, intersected to the left of the 1/v axis above the 1/S axis. Increased concentrations of CC-EO resulted in decreased Vmax and an increased K m . These results indicate that CC-EO exhibited mixed-I type inhibition for the oxidation of L-DOPA catalyzed by mushroom tyrosinase. Similar results were obtained with trans-cinnamaldehyde (Figure 3A), showing that it was also a mixed-I type inhibitor for the enzyme. The dissociation constants for inhibitor binding with the free enzyme and the enzyme-substrate complex, Ki and αKi, were obtained from the double-reciprocal plots and the replots of the slope and the vertical intercept versus the concentration of CC-EO (Figure 2B, 2C) or trans-cinnamaldehyde (Figure 3B, 3C), respectively. The obtained values are summarized in Table 2.
Determination of inhibition type and inhibition constants of C. cassia essential oil. (A) Lineweaver-Burk plots of mushroom tyrosinase and L-DOPA without (●) and with [(○) 1.56 mg/mL, (▼) 3.12 mg/mL, (△) 6.25 mg/mL and (■) 12.50 mg/mL] essential oil from C. cassia. (B) and (C) represent expressions of Ki and αKi, respectively.
Determination of inhibition type and inhibition constants of trans- cinnamaldehyde. (A) Lineweaver-Burk plots of mushroom tyrosinase and L-DOPA without (●) and with [(○) 0.78 mg/mL, (▼) 1.56 mg/mL, (△) 3.12 mg/mL and (■) 6.25 mg/mL] trans-cinnamaldehyde. (B) and (C) represent expressions of Ki and αKi, respectively.
Discussion
The essential oil extracted by steam distillation from the stem bark of C. cassia Presl was quantitatively analyzed by GC-MS. cis-2-Methoxycinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde were determined as the major compounds of the oil (43.06% and 42.37%, respectively). For comparison, a previous study reported that cinnamaldehyde (92.2%) was the most plentiful constituent in the C. cassia essential oil (Giordani et al. 2006). Different extraction processes and assay methods could have contributed to differences in cinnamaldehyde levels of C. cassia essential oils (Dugoua et al. 2007). Cinnamaldehyde (77.1%) was also found to be the major constituent of volatile oil of the bark of C. zeylanicum (Marongiu et al. 2007). Several studies have demonstrated that cinnamaldehyde has antimicrobial (Ooi et al. 2006), antimutagenic (Shaughnessy et al. 2001), antitumorigenic (Ka et al. 2003) and immunomodulatory activities (Koh et al. 1998); furthermore, cinnamaldehyde is considered to possess tyrosinase-inhibitory effects with IC50 values from 0.52~0.97 mM (Lee 2002; Lee et al. 2000; Ngoc et al. 2009). Lee (2002) reported that 2-methoxycinnamic acid that had been isolated from Pulsatilla cernua root was a potent noncompetitive inhibitor of mushroom tyrosinase with an IC50 value of 0.34 mM. In addition, benzaldehyde, one of the flavor compounds characterized in anise oil, showed potent tyrosinase inhibitory activity with an IC50 of 0.82 mM (Kubo and Kinst-Hori 1998). Because the CC-EO contained major in cinnamaldehyde and cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid, and trace readings of benzaldehyde, however, there is no report directly evaluating the tyrosinase inhibitory activities of CC-EO.
Mushroom tyrosinase has been widely used as a target enzyme in screening and characterizing potential tyrosinase inhibitors. Because the inhibition mode depends on the structures of both the substrate and inhibitor, L-DOPA has been used as the substrate in this study. Therefore, the activity studied in this paper was the o-diphenolase inhibitory activity of mushroom tyrosinase. The results showed that CC-EO and its major constituent, cinnamaldehyde, showed a dose-dependent anti-tyrosinase effect, however no activity was observed for the other major constituent, cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid. Because CC-EO contains 42.37% of cinnamaldehyde, it is suggested that cinnamaldehyde is responsible for the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of CC-EO. Although pure cis-2-methoxycinnamic acid had no tyrosinase inhibitory activity in our study, Lee (2002) reported that 2-methoxycinnamic acid that had been isolated from Pulsatilla cernua root was a potent noncompetitive inhibitor of mushroom tyrosinase with an IC50 value of 0.34 mM. The discrepancy of these results may be due to different assay methods or inhibitor purity. The methanolic extracts of C. cassia or the bark essential oil from the different cinnamon species obtained using different extraction techniques such as supercritical CO2 fluid extraction have been reported to exert anti-tyrosinase activity (Marongiu et al. 2007; Ngoc et al. 2009). However, the extraction methods or plant species mentioned in these studies are different from the present paper. Moreover, the biological activities of plant extracts and essential oils are contributed to their bioactive components which may be affected by seasons, geographical origin, harvest time, agronomic practices and extraction methods (Fiocco et al. 2011). Kojic acid, a fungal secondary metabolic product produced by species of Aspergillus and Penicillium, was shown to inhibit mushroom tyrosinase activity (Chen et al. 1991b). Kojic acid has been extensively used as a medical agent for the treatment of a number of different skin disorders associated with hyperpigmentation. To reach a similar degree of tyrosinase inhibitory effect, the concentration required for CC-EO or its major constituent, cinnamaldehyde, was significantly higher than that required for kojic acid. Although the anti-tyrosinase abilities of the CC-EO and its major constituent, cinnamaldehyde, were significantly less than that of kojic acid, it was evident that they did have potent tyrosinase inhibitory activity.
Kinetic analyses confirmed that both CC-EO and trans-cinnamaldehyde were regarded as mixed-I type inhibitors for the enzyme with L-DOPA as the substrate. This result implies that CC-EO and trans-cinnamaldehyde affected the affinity of the enzyme for L-DOPA but did not bind at the active site (Webb 1963). Furthermore, the behavior of mixed-I type inhibition indicated that CC-EO and trans-cinnamaldehyde could bind, not only with the free enzyme, but also with the enzyme-substrate complex. As shown in Table 2, the determined values showed that the Ki value for trans-cinnamaldehyde was approximately 2 times lower than that of CC-EO. In other words, trans-cinnamaldehyde had a more effective binding capacity for the enzyme than CC-EO. Additionally, the value of αKi was almost 4 times as great as Ki for the oxidation of L-DOPA, indicating that the affinity of the inhibitor, CC-EO or trans-cinnamaldehyde, for a free enzyme is stronger than that of inhibitor for the enzyme–substrate complex. Lee et al. (2000) reported that trans-cinnamaldehyde isolated from the bark of C. cassia exhibited competitive inhibition for L-DOPA oxidation by mushroom tyrosinase, while Lee (2002) reported that cinnamaldehyde isolated from the root of P. cernua was a noncompetitive tyrosinase inhibitor. However, different enzyme preparation and assay methods or inhibitor purities could have contributed to these differences in enzyme inhibitory kinetics (Chen et al. 1991b).
Recently, safe tyrosinase inhibitors have become important for their potential applications in improving food quality and preventing pigmentation disorders and other melanin-related human health issues (Fitzpatrick et al. 1983; Seo et al. 2003). Furthermore, safe tyrosinase inhibitors are important in cosmetics for skin whitening effects. C. cassia has been safely used for many years by humans as a flavoring agent and a traditional medicinal herb. According to the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA), Cinnamomum spp., including common and cassia cinnamon, are generally recognized as safe (GRAS) when used in amounts commonly found in food (Dugoua et al. 2007). Furthermore, cinnamaldehyde and benzaldehyde, which are found in CC-EO, are also GRAS (Kubo and Kinst-Hori 1999). Thus, it is expected that CC-EO and its major constituent, cinnamaldehyde, may be a safe and viable source of skin-whitening agents.
Conclusions
In summary, our findings demonstrate that the CC-EO and its major component, cinnamaldehyde, possess potent inhibitory activity against the diphenolase activity of tyrosinase. A study of the kinetics for the inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase showed that the CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde are mixed-type inhibitors for the enzyme with L-DOPA as the substrate. Both CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde are generally recognized as safe (GRAS). Therefore, CC-EO and cinnamaldehyde may be suggested as a safe and as a good source of skin-whitening agents for pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications.
References
Asanuma M, Miyazaki I, Ogawa N: Dopamine- or L-DOPA-induced neurotoxicity: the role of dopamine quinone formation and tyrosinase in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 2003, 5: 165–176. 10.1007/BF03033137
Chen JS, Wei CI, Marshall MR: Inhibition mechanism of kojic acid on polyphenol oxidase. J Agric Food Chem 1991, 39: 1897–1901. 10.1021/jf00011a001
Chen JS, Wei C, Rolle RS, Otwell WS, Balaban MO, Marshall MR: Inhibitory effect of kojic acid on some plant and crustacean polyphenol oxidases. J Agric Food Chem 1991, 39: 1396–1401. 10.1021/jf00008a008
Chen QX, Kubo I: Kinetics of mushroom tyrosinase inhibition by quercetin. J Agric Food Chem 2002, 50: 4108–4112. 10.1021/jf011378z
Chiari ME, Vera DM, Palacios SM, Carpinella MC: Tyrosinase inhibitory activity of a 6-isoprenoid-substituted flavanone isolated from Dalea elegans . Bioorg Med Chem 2011, 19: 3474–3482. 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.04.025
Choi J, Lee KT, Ka H, Jung WT, Jung HJ, Park HJ: Constituents of the essential oil of the Cinnamomum cassia stem bark and the biological properties. Arch Pharm Res 2001, 24: 418–423. 10.1007/BF02975187
Dooley T: Topical skin depigmentation agents. J Dermatolog Treat 1997, 8: 275–283. 10.3109/09546639709160535
Dugoua JJ, Seely D, Perri D, Cooley K, Forelli T, Mills E, Koren G: From type 2 diabetes to antioxidant activity: a systematic review of the safety and efficacy of common and cassia cinnamon bark. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2007, 85: 837–847. 10.1139/Y07-080
Fiocco D, Fiorentino D, Frabboni L, Benvenuti S, Orlandini G, Pellati F, Gallone A: Lavender and peppermint essential oils as effective mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: a basic study. Flavour Fragr J 2011, 26: 441–446. 10.1002/ffj.2072
Fitzpatrick TB, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Freedberg IM, Austen KF: Updates: dermatology in general medicine. In Vitiligo: ethology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Edited by: Mosher DB, Pathak MA, Fitzpatrick TB. New York: Mcgraw-Hill; 1983.
Friedman M: Food browning and its prevention: an overview. J Agric Food Chem 1996, 44: 631–653. 10.1021/jf950394r
Giordani R, Regli P, Kaloustian J, Portugal H: Potentiation of antifungal activity of amphotericin B by essential oil from Cinnamomum cassia . Phytother Res 2006, 20: 58–61. 10.1002/ptr.1803
Ka H, Park HJ, Jung HJ, Choi JW, Cho KS, Ha J, Lee KT: Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett 2003, 196: 143–152. 10.1016/S0304-3835(03)00238-6
Kim YJ, Uyama H: Tyrosinase inhibitors from natural and synthetic sources: structure, inhibition mechanism and perspective for the future. Cell Mol Life Sci 2005, 62: 1707–1723. 10.1007/s00018-005-5054-y
Koh WS, Yoon SY, Kwon BM, Jeong TC, Nam KS, Han MY: Cinnamaldehyde inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and modulates T-cell differentiation. Int J Immunopharmacol 1998, 20: 643–660. 10.1016/S0192-0561(98)00064-2
Kubo I, Kinst-Hori I: Tyrosinase inhibitors from anise oil. J Agric Food Chem 1998, 46: 1268–1271. 10.1021/jf9708958
Kubo I, Kinst-Hori I: Tyrosinase inhibitory activity of the olive oil flavor compounds. J Agric Food Chem 1999, 47: 4574–4578. 10.1021/jf990165v
Lee HS: Tyrosinase inhibitors of Pulsatilla cernua root-derived materials. J Agric Food Chem 2002, 50: 1400–1403. 10.1021/jf011230f
Lee HS, Ahn YJ: Growth-inhibiting effects of Cinnamomum cassia bark-derived materials on human intestinal bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 1998, 46: 8–12. 10.1021/jf970548y
Lee HS, Kim BS, Kim MK: Suppression effect of Cinnamomum cassia bark-derived component on nitric oxide synthase. J Agric Food Chem 2002, 50: 7700–7703. 10.1021/jf020751f
Lee SE, Kim MK, Lee SG, Ahn YJ, Lee HS: Inhibitory effects of Cinnamomum cassia bark-derived materials on mushroom tyrosinase. Food Sci Biotechnol 2000, 9: 330–333.
Marongiu B, Piras A, Porcedda S, Tuveri E, Sanjust E, Meli M, Sollai F, Zucca P, Rescigno A: Supercritical CO 2 extract of Cinnamomum zeylanicum : chemical characterization and antityrosinase activity. J Agric Food Chem 2007, 55: 10022–10027. 10.1021/jf071938f
Matsuura R, Ukeda H, Sawamura M: Tyrosinase inhibitory activity of citrus essential oils. J Agric Food Chem 2006, 54: 2309–2313. 10.1021/jf051682i
Ngoc TM, Lee I, Ha DT, Kim H, Min B, Bae K: Tyrosinase-inhibitory constituents from the twigs of Cinnamomum cassia . J Nat Prod 2009, 72: 1205–1208. 10.1021/np900031q
Ooi LS, Li Y, Kam SL, Wang H, Wong EY, Ooi VE: Antimicrobial activities of cinnamon oil and cinnamaldehyde from the Chinese medicinal herb Cinnamomum cassia Blume. Am J Chin Med 2006, 34: 511–522. 10.1142/S0192415X06004041
Sánchez-Ferrer A, Rodríguez-López JN, García-Cánovas F, García-Carmona F: Tyrosinase: a comprehensive review of its mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1995, 1247: 1–11. 10.1016/0167-4838(94)00204-T
Segel IH: Biochemical calculations. 2nd edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1976.
Seo SY, Sharma VK, Sharma N: Mushroom tyrosinase: recent prospects. J Agric Food Chem 2003, 51: 2837–2853. 10.1021/jf020826f
Shaughnessy DT, Setzer RW, DeMarini DM: The antimutagenic effect of vanillin and cinnamaldehyde on spontaneous mutation in Salmonella TA104 is due to a reduction in mutations at GC but not AT sites. Mutat Res 2001, 480–481: 55–69.
Verspohl EJ, Bauer K, Neddermann E: Antidiabetic effect of Cinnamomum cassia and Cinnamomum zeylanicum in vivo and in vitro . Phytother Res 2005, 19: 203–206. 10.1002/ptr.1643
Webb JL: Enzyme and metabolic inhibitors. New York: Academic Press; 1963.
Zhao X, Zhu JX, Mo SF, Pan Y, Kong LD: Effects of cassia oil on serum and hepatic uric acid levels in oxonate-induced mice and xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activities in mouse liver. J Ethnopharmacol 2006, 103: 357–365. 10.1016/j.jep.2005.08.040
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for financial support from the National Science Council of the Republic of China awarded to Dr. S.-T. Chou (NSC98-2313-B-126-004-MY3) and Dr. Y. Shih (NSC-98-2113-M-126-005-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
C-TC, YS and S-TC conceived and designed the experiments, and drafted the manuscript. W-LC carried out the enzymatic assay, kinetic assay and statistical analysis. J-CH conducted the GC-MS analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, CT., Chang, WL., Hsu, JC. et al. Chemical composition and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil. Bot Stud 54, 10 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1999-3110-54-10
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1999-3110-54-10