Abstract.
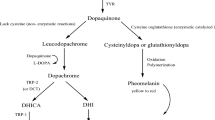
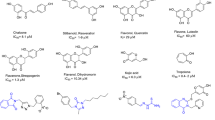
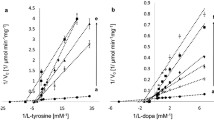
Tyrosinase is known to be a key enzyme in melanin biosynthesis, involved in determining the color of mammalian skin and hair. Various dermatological disorders, such as melasma, age spots and sites of actinic damage, arise from the accumulation of an excessive level of epidermal pigmentation. In addition, unfavorable enzymatic browning of plant-derived foods by tyrosinase causes a decrease in nutritional quality and economic loss of food products. The inadequacy of current conventional techniques to prevent tyrosinase action encourages us to seek new potent tyrosinase inhibitors. This article overviews the various inhibitors obtained from natural and synthetic sources with their industrial importance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 9 February 2005; received after revision 4 April 2005; accepted 14 April 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, YJ., Uyama, H. Tyrosinase inhibitors from natural and synthetic sources: structure, inhibition mechanism and perspective for the future. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 1707–1723 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5054-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5054-y