Abstract
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a common cause of premature cardiovascular disease and is often undiagnosed in young people. Although the disease is diagnosed clinically by high LDL cholesterol levels and family history, to date there are no single internationally accepted criteria for the diagnosis of FH. Several genes have been shown to be involved in FH; yet determining the implications of the different mutations on the phenotype remains a hard task. The polygenetic nature of FH is being enhanced by the discovery of new genes that serve as modifiers. Nevertheless, the picture is still unclear and many unknown genes contributing to the phenotype are most likely involved. Because of this evolving polygenetic nature, the diagnosis of FH by genetic testing is hampered by its cost and effectiveness.
In this review, we reconsider the clinical versus genetic nomenclature of FH in the literature. After we describe each of the genetic causes of FH, we summarize the known correlation with phenotypic measures so far for each genetic defect. We then discuss studies from different populations on the genetic and clinical diagnoses of FH to draw helpful conclusions on cost-effectiveness and suggestions for diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
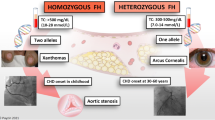
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) (MIM #143890) is a genetic disease characterized by elevated LDL-Cholesterol (LDL-C), which deposits in the tissues causing the external manifestations of the disease, namely tendinous xanthomas, xanthelasmas, and corneal arcus. More importantly, LDL-C deposits in blood vessels leading to premature cardiovascular disease [1, 2]. The patterns of inheritance of FH were first described by Khachadurian in Lebanon before the genes that contribute to the disease were known [3]. FH was defined as an autosomal dominant disease, with a clinical distinction based on phenotype severity of a "heterozygous" and a "homozygous" form, with serum LDL-C levels that are two times and four times the normal respectively [3]. The prevalence of the severe phenotype has been reported as 1 in a million in the general population, compared to the much more common mild form with a prevalence of 1 in 500 [1]. The prevalence has been reported to be ten times higher in certain populations with a presumed founder effect, such as the Lebanese, the French Canadians, and the South Afrikaners [1, 2]. A less common autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance was also described in some of the initial Lebanese families [3].
In 1986, the LDL receptor (LDLR) was discovered as the cause of Autosomal Dominant Hypercholesterolemia (ADH) [4]. It manifests a gene dosage effect such that the heterozygous and homozygous forms cause mild and severe phenotypes respectively. For years, ADH was thought of as a monogenetic disease. However, as more genotyping of FH patients was carried, patients with the phenotype but no LDLR mutation were discovered, and the search for other genes yielded the discovery of the Apolipoprotein B gene (ApoB) in 1987 [5], and the Proprotein Convertase Subtilin/Kexin 9 gene (PCSK9) in 2003 [6], as candidate genes in ADH. The Autosomal Recessive Hypercholesterolemia gene (ARH) was also discovered in 2001 [7]. These discoveries together fostered the idea of a polygenetic nature of FH.
Clinically, the severe phenotype is rarely missed with LDL-C levels that are four times higher than the normal and external manifestations since early childhood [3]. Additionally, family history is often informative of similar cases. The clinical diagnosis of the mild phenotype is much more challenging with external manifestations that might be absent or appear only in adulthood. LDL-C could also vary between upper normal levels to double the normal levels. Family history might not always be revealing. Early diagnosis of FH is crucial because the disease can be treated with lipid lowering therapy and lifestyle changes early on to prevent complications [1]. Failure to diagnose and treat FH leads to increased morbidity and mortality from premature cardiovascular disease [1, 8, 9].
Currently, FH can be diagnosed either clinically or genetically. The use of genetic terminologies to describe phenotypic presentations of the disease creates confusion in the literature. In this review, we set up a standard terminology for clinical and genetic descriptions of FH. We then describe the different molecular mechanisms that lead to FH and the known genotype-phenotype correlations. We finish by discussing the clinical versus genetic diagnosis of FH and by looking into worldwide models of genetic diagnosis and their mutation detection rates.
Terminology Used to Describe Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Clinicians still use the terms "homozygous" and "heterozygous" to describe a phenotypic presentation of FH. In Lebanon, severely affected patients are labeled as 'homozygous" based on clinical assessment and are referred for LDL apheresis therapy. Screening this population recently, we have shown that less than half of them are true homozygous for an LDLR mutation. The rest were either combined heterozygous for two different mutations, were heterozygous for one mutation, or had no detectable mutation [10]. Only few countries currently have national genetic screening programs for FH. Cholesterol levels together with other clinical indicators remain the most used method to diagnose familial hypercholesterolemia. In table 1, we suggest a distinction in the clinical versus genetic nomenclature of FH based on whether the phenotype or the genotype is being used for diagnosis.
For familial clustering of cases of elevated cholesterol levels, a clinical or a genetic assessment is done. A clinical assessment of the phenotype is difficult to categorize. It is inaccurate for the most of the cases since lipid levels represent a spectrum and since many non-genetic factors can affect lipid levels and disease manifestations. To simplify, we classify the clinical nomenclature into severe, mild, and paradoxical (Table 1). While mild and severe represent two clear ends of the spectrum, paradoxical cases are those that have a more confusing presentation. A genetic nomenclature on the other hand should be used only when genotyping of the four candidate genes has been made. Heterozygous, homozygous, or combined heterozygous mutations can thus be identified (Table 1). When no mutation is detected in a mild or severe clinically diagnosed FH case, the genetic cause is unknown. When no mutation is identified in a paradoxical case, non-familial hypercholesterolemia should be considered.
Molecular Pathways of Familial Hypercholesterolemia
The Molecular Pathway for the Uptake and Degradation of LDL-C by the Cell
The pathway was first described by Brown and Goldstein in 1986 [4]. LDL in the blood has Apolipoprotein B-100 (ApoB-100) on its surface. The LDL receptor (LDLR) is a glycoprotein found on the surface of hepatocytes and binds ApoB-100 of the LDL-C. A clathrin-coated pit is formed and both receptor and LDL-C ligand are taken into an endosome with other proteins via interactions involving the LDLR adaptor protein 1 (LDLRAP1). After dissociation of the ligand-receptor complex, LDLR is recycled to the cell membrane, while free cholesterol is used inside the cell. PCSK9 serves as a post-transcriptional LDLR inhibitor. It is secreted outside the cell and inhibits LDLR through cell surface interactions. Evidence also suggests an intracellular pathway of PCSK9-mediated LDLR inhibition, however the exact mechanism is yet to be elucidated [11]. Nuclear regulation of LDLR production includes two pathways. First, the binding of a Steroid Response Element Binding Protein (SREBP) to a Steroid Response Element (SRE) on the DNA stimulates the transcription of the LDLR in response to decreased intracellular cholesterol [11]. This pathway is activated during treatment with HMG-CoA Reductase inhibitors. The second player in LDLR regulation is another sterol-mediated nuclear receptor LXR, which was recently shown to induce the transcription of IDOL (Inducible Degrader of the LDLR). As its name implies, IDOL triggers ubiquitinization of the LDLR targeting it for degradation [12]. (Figure 1) This pathway ensures proper uptake of LDL-C from the blood. Any defect in this pathway results in improper uptake and high LDL-C in the blood leading to the clinical manifestations of FH.
Molecular Pathways of Disease in Familial Hypercholesterolemia (1) The LDL receptor on the surface of hepatocytes binds ApoB-100 of the LDL particle forming a complex. (2) A clathrin-coated pit is formed and the ligand-receptor complex is endocytosed via interactions involving the LDLR Adaptor Protein 1 (LDLRAP1). (3) Inside the hepatocyte, the complex dissociates, the LDLR recycles to the cell membrane, (4) and free cholesterol is used inside the cell. (5) PCSK9 serves as a post-transcriptional inhibitor of LDLR. It is secreted and inhibits LDLR through cell-surface interactions. (6) The presence of an intracellular pathway for PCSK9-mediated LDLR inhibition is still a subject of controversy. (7) In response to decreased cholesterol such as during treatment with statins, Steroid Response Element Binding Protein (SREBP) binds to the Steroid Response Element (SRE) on the DNA and induces the transcription of the LDLR. (8) The sterol-responsive nuclear receptor LXR on the other hand responds to increased intracellular cholesterol inducing the transcription of IDOL, a recently discovered molecule that induces the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the LDLR. Clouds in the figure refer to genes in which mutations have been associated with increased LDL-C levels.
LDLR
A mutation in LDLR (MIM#s 606945, 143890) is by far the most common cause of ADH. Null alleles produce no LDL receptors. Other alleles produce defective LDL receptors. A defective LDLR does not localize to the nuclear membrane, does not properly bind the LDL-C particle, or fails to internalize into the cell after binding [4]. The LDLR gene is located on 19p13 and is 45 kb long [13]. It is composed of 18 exons that code for an 860 amino acid long peptide. The LDLR protein has different domains including a signal peptide, a ligand-binding domain, an epidermal growth factor-precursor like domain, as well as O-linked sugars, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains [14, 15]. Mutations are widely distributed along all domains of the LDLR protein and hence can result in different types of dysfunction. (Table 2) Since the discovery of the LDLR in the mid 1980s, the number of mutations has been continuously increasing. Currently, the University College of London database for the LDLR sequence variants lists more than 1700 hits [16, 17]. Among them are nonsense substitutions or large deletions that result in absent or truncated LDLR, missense mutations that result in dysfunctional receptor, or silent mutations and other polymorphisms that do not significantly affect the function of the receptor. Many LDLR mutations are population specific, and many populations have a number of mutations that leads to the phenotype. In 1987, a nonsense mutation in exon 14 of the LDLR leading to a truncated receptor was discovered in Lebanese families and named the "Lebanese allele" [18]. This allele has always been associated with the Christian-Lebanese and people with Arab ancestry in the West [19, 20]. Not until recently did our team study LDLR mutations in Lebanon and show that the Lebanese allele accounts to no more than 45% of the clinically homozygous FH patients [10]. A recent study from Tunisia shows that only 5 LDLR mutations are specific for the population with one of them accounting to 29.67% of cases [21]. Another example comes from Quebec where more than 90% of the heterozygous FH patients have one of eleven LDLR mutations [22].
Apo B-100
Apolipoprotein B-100 (ApoB-100) is a protein component of the LDL particle. It is found on 2p24-p23. The gene is made up of 29 exons spanning ~43 Kb and encoding two main isoforms, ApoB-48 and ApoB-100. In Familial Defective Apolipoprotein B (MIM #s 107730, 144010), LDL-C fails to bind to its ligand and remains high in the circulation [5]. There is a limited number of mutations in ApoB-100 that can cause the FH phenotype. The Arg3500Gln variant is the most famous [23]. It is common in Europe accounting to 2-5% of the FH phenotype [24]. Another variant at the same position (Arg3500Trp) is common in the Chinese population [25]. As a cause of ADH, ApoB-100 is relatively uncommon compared to LDLR mutations. (Table 2)
PCSK9
The Proprotein Convertase Subtilin/Kexin Type 9 gene (PCSK9; MIM# 607786) spanning 3.6 Kb on 1p32 emerged as a third locus involved in ADH, with the discovery in 2003 of two disease-causing mutations in the French population [6]. The gene spans ~25 Kb, and the 695 aa protein is encoded by twelve exons. PCSK9 binds to the Epidermal Growth Factor-Like Repeat A (EGF-A) domain of the LDLR inducing its degradation. Reduced LDLR levels could thus lead to hypercholesterolemia. Over the past seven years, PCSK9 has been heavily investigated in many populations with FH, and the databases currently list 161 sequence variants distributed along all twelve exons of the gene [14, 15]. (Table 2) PCSK9 mutations can affect the phenotype in different ways. Gain of function mutations are rare and are associated with decreased LDLR on the surface and a severe phenotype of FH [6]. Loss of function mutations on the other hand are associated with decreased cholesterol levels [26]. Moreover, many SNPs exist in PCSK9 and affect cholesterol regulation differently in different populations. As a cause of ADH, PCSK9 is rare compared to LDLR and ApoB-100; however, large numbers of PCSK9 polymorphisms are associated with cholesterol levels in population studies [27]. Recent studies are focusing on the potential of PCSK9-inhibiting compounds as a therapeutic target for dyslipidemias [28–30].
ARH
Since the initial observations on the mode of inheritance of FH, an autosomal recessive pattern has been noted [3]. In 2001, Autosomal Recessive Hypercholesterolemia (ARH) was found to be caused by mutations in the LDL Receptor Adaptor Protein 1 (LDLRAP1) also referred to as the ARH gene [7]. The gene is mapped to 1p36-35 [31] spanning ~25 Kb with 9 exons coding for a 308 aa protein. In ARH, the internalization of the ligand-receptor complex cannot occur and all the LDL receptors accumulate on the cell membrane. ARH is extremely rare compared to ADH, and the number of patients described to have defects in the ARH gene does not exceed 100 [32]. ARH was initially described in Sardinian and Lebanese families, but later found in American, Iranian, Japanese, Mexican, Asian, Indian, English, Turkish, and Syrian families [32–34].
Genotype Phenotype Correlations
LDLR mutations show a gene dosage effect, and a classical presentation of homozygous versus heterozygous FH patients has been documented. However, with the advances in sequencing strategies it became clear that LDLR mutations did not describe it all. Many patients with severe or moderate phenotypes did not carry any LDLR mutation. Later studies showed Familial Defective ApoB[5], ARH[7], and more recently PCSK9[6] as possible explanations for an LDLR defect-negative FH phenotype.
LDLR
Table 2 shows phenotype comparisons between the four different genes involved in FH. In general, the classical ADH patients with LDLR mutations have the worst phenotype with the highest lipid levels and the least response to lipid-lowering therapy. Homozygotes usually necessitate LDL apheresis therapy otherwise they die of cardiovascular events as young as adolescence. Heterozygotes have moderately elevated lipid levels, external manifestations by adulthood or not at all, and premature cardiovascular disease [1, 8, 9].
ApoB-100
ApoB-100 mutations show incomplete penetrance, so patients with Familial Ligand-Defective Apolipoprotein B show in general a less severe phenotype than FH patients with LDLR mutations [24]. Still in many instances however, heterozygous ApoB defective patients can be clinically indistinguishable from heterozygous LDLR mutation patients. It was estimated that at least 2-5% of FH patients in lipid clinics are due to ApoB-100 mutations [24]. Considering ApoB-100 mutations is particularly important in populations where it is known to be common, namely European and North American [24], and less important in populations where it is rarely reported such as Arabs and Middle Easterns [35].
ARH
ARH also shows some phenotypic differences from the classical LDLR mutants. Patients have lower lipid levels, traditionally observed to be somewhere between the levels seen in heterozygous and homozygous ADH patients. However, this does not always hold true, and there seems to be a great variability of the phenotype between patients in ARH, even within the same family [36]. A report of LDL kinetic studies on one patient with Turkish decent harboring an ARH mutation showed that the LDL catabolic rate was delayed up to three-fold, making the patient indistinguishable from patients with homozygous LDLR mutations [37]. In general, ARH patients show a better response to lipid-lowering therapy than the ADH patients, and they rarely require LDL apheresis [38]. Some studies also reported increased HDL levels in ARH compared to ADH. The incidence of cardiovascular events in ARH also tends to be delayed and they rarely have any in adolescence [36]. Most importantly in FH is the family history. LDLRAP1 mutations should always be suspected in patients who are products of consanguineous marriages, in typical populations, and with an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
PCSK9
The discovery of PCSK9 has added a lot to the phenotypic understanding of FH. We have established earlier that gain of function mutations in this gene cause hypercholesterolemia and loss of function mutations cause hypocholesterolemia, and that the gene is greatly polymorphic with population differences. This has established PCSK9 as a modifier gene in FH, which causes the significant phenotypic variability even in patients carrying the same LDLR mutation [39]. Many studies have looked at the presence of PCSK9 sequence variants on top of LDLR mutations [39–41]. For some combined mutants, the phenotype is as severe as that of homozygous LDLR mutants [27].
The Diagnostic Gap in FH
Still many clinically diagnosed FH patients fail to show any mutation in these four genes. This diagnostic gap is observed in most clinically diagnosed FH cohorts who are screened for mutations. Canadians have studied this diagnostic gap in Ontario and showed that exon-by-exon sequencing analysis (EBESA) diagnosed only two thirds the FH patients [42]. Using the Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) technique to detect copy number variations (CNVs) [43], they could detect an abnormality in two thirds of the remaining gap, reducing it from 30% to 10% [42]. Their findings suggested that heterozygous LDLR CNV's are associated with more severe phenotypes and they are usually missed in EBESA [22]. Another major explanation of the diagnostic gap is the presence of mutations in other unknown novel genes that are involved in cholesterol metabolism. More mapping studies to look for novel genes involved in FH are needed to fill the diagnostic gap.
Variability of the Phenotype
FH is a disease that shows great phenotypic variability [44]. The polygenetic nature of the disease is being enhanced with the discovery of more modifier genes, which explains a large part of this phenotypic variability. In our cohort of Lebanese FH patients, we identified many heterozygotes for the Lebanese allele mutation in the LDLR, yet having normal lipid levels on no therapy [10]. So far we have been referring to the phenotype of FH patients in terms of lipid levels only. However, other phenotypic measures in this population include onset of hypercholesterolemia, onset and degree of atherosclerosis, cardiovascular measurements such as aortic stenosis, carotid plaques, and intima-media thickness, cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and response to lipid-lowering therapy among others. All these phenotypic measures are the result of not only lipid levels, but also a combination of genetic, metabolic, and environmental factors. People carrying the same mutation can have different lipid levels, and certain populations have moderate phenotypic expression of apparently severe mutations [21, 45]. The type of LDLR mutation has been shown to correlate with the response to statin therapy [46]. Polymorphisms in lipid modifier genes, such as apolipoproteins, particularly ApoE, can significantly affect the FH phenotype [47]. Conventional risk factors for atherosclerosis such as smoking, diet, hypertension, and diabetes are also additive in FH [48, 49]. The levels of lipoprotein (a) have been correlated with atherosclerosis and could also explain a variable phenotype or a paradoxical case of FH [50].
The Clinical Diagnosis of Familial Hypercholesterolemia
The Three Sets of Clinical Criteria for the Diagnosis of FH
Early diagnosis of heterozygous FH allows for prompt treatment and prevention of morbidity and mortality from premature cardiovascular disease. Tremendous efforts have been made to improve the early diagnosis of this population, yet, there is no single internationally accepted set of criteria for the clinical diagnosis of FH. There are three sets of statistically and genetically validated criteria however that are most commonly used: the Dutch [51], the UK [52], and the US [53] criteria. (Table 3) The US MEDPED developed two sets of criteria distinguishing between the general population and close relatives of known FH patients. Criteria differ in each group due to the statistical component of a pre-determined probability. The statistical criteria developed are based solely on lipid levels and age, and they are highly sensitive and specific [53]. (Table 3) The Simon Broome Register Group in the UK as well as the MEDPED group in the Netherlands developed their criteria by classifying definite, probable, and possible diagnoses of FH. Unlike the US criteria, which used only lipid levels, the UK and Dutch criteria use family history, personal history, and physical signs in addition to the cholesterol levels [51, 52].
Advantages and Disadvantages of Clinical Diagnosis
Although the above clinical criteria for diagnosis might be helpful in diagnosing relatives of known FH patients, they are not accurate in diagnosing index cases in the general population. They are very helpful though in avoiding the informal assessment of patients, which is very often a weak predictor of FH. The advantage of clinical criteria is also their low cost as they depend solely on history taking, physical exam, blood lipid profile testing, and possibly noninvasive cardiovascular testing. Clinical diagnosis will fail to distinguish between the classical FH due to LDLR mutations and the other genetic causes of FH such as ApoB-100, ARH, and PCSK9, or even non-familial hypercholesterolemia such as secondary hypercholesterolemia, sitosterolemia, and others. More importantly, clinical diagnosis could miss a considerable proportion of the FH patients, particularly those with a mild phenotype and the pediatric population in whom the phenotype has not appeared yet. Very often, a myocardial infarction is the first presenting sign in many FH patients. Finally, clinical diagnosis will not allow for understanding known genotype phenotype correlations such as the better response to statin therapy in ApoB-100 and ARH compared to LDLR mutations.
The Genetic Diagnosis of Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Importance of a DNA Diagnosis
Genetic testing may give a definite diagnosis of FH if a pathological mutation were detected [54]. Early and definite diagnosis of FH has large benefits since it allows for cholesterol lowering and risk prevention [54]. DNA diagnosis is particularly important in equivocal cases where lipid levels are mild with no clear external manifestations and with a family history of premature coronary artery disease. These comprise the majority of the cases of FH. In the extreme case, a patient with an LDLR mutation might have LDL-C levels that fall within the normal range. We have pinpointed few of these cases in the Lebanese cohort. Although there is no evidence that suggests that the mutation by itself poses an independent risk for cardiovascular disease, identifying such a mutation is clinically important since the patient can develop high LDL-C levels at any point in life and be missed. Finding a known pathogenic mutation might prompt the clinician to screen more frequently for hypercholesterolemia. This concept is most useful in pediatrics where lipid levels might not be high enough to make a diagnosis, although genetic testing in the pediatric population remains a subject of controversy [55]. A recent Cochrane review established the efficiency and short-term safety of lipid-lowering therapy in children with FH [56]. Hence, an accurate and early diagnosis might allow for treatment early on to prevent cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality.
Due to the paucity of data on genotype phenotype correlations, clinical diagnosis will miss a large percentage of FH patients. It is currently estimated that only 15 to 20% of patients with FH are actually diagnosed [57, 58]. A study on 643 Danish probands could not even find a single phenotypic characteristic to predict the existence of a mutation [59]. A more recent study on 696 possible FH patients in Portugal showed that genetic diagnosis for cardiovascular risk stratification was superior to clinical diagnosis using the Simon Broome criteria [60]. Not only does finding a mutation allow for early diagnosis and treatment, but it also has prognostic value. Different mutations can dictate different directions of management, such as the poorer response to lipid-lowering therapy with certain LDLR mutations [46]. The identity of the gene involved, dictates some aspects of the phenotype as we already established in the genotype-phenotype correlations. Although still not completely understood, such correlations can potentially aid the clinician to decide on how aggressive the treatment strategy will be. The effect of the different LDLR mutations on the response to statins was studied in a limited number of small-scale studies in which several showed statistically significant correlations [46]. Nevertheless, such pharmacogenetic variability should be studied in large randomized control trials, which is a little bit challenging in the presence of a huge number of mutations in the LDLR.
Finally, the phenotypic expression of the FH mutation may skip generations. This can occur for instance due to the presence of modifier genes that can decrease LDL-C levels or due to epigenetic factors that might also modulate the phenotype. In such cases, genetic testing may have a prognostic significance for succeeding generations. For this reason, discovery of a known pathogenic mutation in an individual with normal LDL-C levels prompts the clinician to screen other family members who might have undiagnosed hypercholesterolemia.
Population Screening
In 1997, the WHO clearly established the benefits of a DNA test for the diagnosis of FH and re-assured that it is cost-effective [61]. However, with the evolving polygenetic nature of the disease, several studies showed that genetic diagnosis is hampered by the high cost, and genetic screening for the population at large failed to show cost-effectiveness due to the polygenetic nature of the disease [62]. Nevertheless, for certain populations where one or few known mutations cause the disease, and where the prevalence of FH is higher than the general population, population screening might be a good strategy. However, until genetic epidemiology studies are conducted on these populations, it will be hard to comment. Another limitation of genetic population screening for FH is the variability of the phenotype [44] and the paucity of data in genotype phenotype correlations. Moreover, the phenotype is affected by many non-genetic factors as mentioned earlier [47–49]. A recent meta-analysis showed a benefit for population screening of children ages 1 to 9 years using serum lipid levels and suggested that this strategy might be helpful in identifying new cases in two generations, the children and their parents [63].
Cascade Screening
Cascade screening is another strategy that proved to be cost-effective in genetic testing for FH. In cascade screening, an index patient is diagnosed initially clinically through one of the clinical criteria listed in Table 3. A DNA test confirms the mutation in the index patient. Screening for the same mutation is undertaken in first degree relatives to look for new cases. New confirmed cases from the relatives are treated as new index cases and their first degree relatives are screened. The first successful model of national genetic cascade screening programs came from the Netherlands, which started in 1994 [64–66]. Norway also had successful results with their program started in 2003 [67, 68]. A large percentage of the relatives screened ended up having definite FH, and many of them were not on any therapy at the time of diagnosis. Other countries that are starting to follow similar strategies include Spain [69, 70], Australia and New Zealand [71, 72], and Wales [73, 74]. Table 4 summarizes mutation detection rates in these genetic cascade screening programs as reported in the most recent literature. It also lists mutation detection rates in clinically diagnosed cohorts of patients from these countries [70, 72, 74, 75] and others such as Denmark [76, 77]. Mutation detection rates differ based on the original clinical diagnosis of the cohort and on the mutation detection method. Various mutation detection methods are used in different countries, including direct sequencing [66], arrays [70], or Denaturing High Performance Liquid Chromatography (DHPLC) and melting analysis [78, 79]. Most screening strategies cover the LDLR and apoB-100 genes. An more novel screening strategy has been implemented in Iceland whereby ancestors of FH probands were traced and the oldest in each family lineage was screened for the common LDLR Icelandic mutation, I4T +2C [80]. This genealogical tracing might be superior to the conventional first-degree relative approach in founder populations.
Implementation Issues
Although cascade testing is a successful and cost-effective model for early diagnosis and treatment of FH, its implementation carries many considerations. Currently there is no study that could genetically identify the cause of 100% of a clinically diagnosed FH population, and a large part of that is due to the polygenetic nature of the disease. This complicates DNA testing and necessitates the development of clear national guidelines that provide step-by-step criteria for screening for particular genes, based on previous genotype data on the population. Such a national system would necessitate an infrastructure to accommodate it, including education and training, specialized clinics, outreach, etc. A genetic testing program also carries with it ethical considerations, psychological implications, and insurance coverage issues [81].
The Lipids or the Genes?
Familial Hypercholesterolemia has been historically diagnosed and described based on lipid levels and family history. LDL-C levels also were the major determinant of the phenotype. The advances in genetic testing have added a different perspective to the disease. Not only does genetic diagnosis provide a more accurate and early diagnosis of FH, but it also provides information about the phenotype and the prognosis that could not be known from lipid levels alone. It also allows for the identification of more silent cases in the population, decreasing the incidence of premature cardiovascular disease. Although proven cost-effective, the move from lipids to genes is challenging and will require huge efforts from researchers and public health systems.
Conclusions
-
Familial Hypercholesterolemia is caused by mutations in LDLR, ApoB-100, PCSK9, and LDLRAP1.
-
The terms homozygous and heterozygous refer to a definite genotype of a patient with FH, while the phenotype is a variable spectrum that could potentially be described as mild, severe, or paradoxical.
-
The majority of people with FH have a mild phenotype, are undiagnosed and untreated, and ultimately develop premature cardiovascular disease.
-
FH is a polygenetic disease with known and unknown genes. It demonstrates a large variability in the phenotype not only due to the polygenetic nature, but also due to non-genetic factors.
-
A DNA diagnosis for FH is the only definite diagnosis for the disease.
-
Cascade genetic screening for FH is cost-effective and should be adopted by national healthcare programs.
Authors' Information
AF is an MD and a post-doctoral research fellow in Cardiogenetics at the American University of Beirut. GN is an Associate Professor of Biochemistry and Director of the Congenital Heart Disease Genetic Program (CHDGP) at the American University of Beirut.
Abbreviations
- LDL:
-
Low Density Lipoprotein
- MEDPED:
-
Make Early Diagnosis to Prevent Early Deaths.
References
Goldstein J, Hobbs H, Brown M: Familial Hypercholesterolemia. The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease. Edited by: Scriver C, Baudet A, Sly W, Valle D. 2001, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2863-2913.
Khachadurian AK: Clinical features, diagnosis and frequency of familial hypercholesterolemia. Contributions to infusion therapy. 1988, 23: 26-32.
Khachadurian AK: The Inheritance of Essential Familial Hypercholesterolemia. The American journal of medicine. 1964, 37: 402-7. 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90196-2.
Brown M, Goldstein J: A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986, 232: 34-47. 10.1126/science.3513311.
Innerarity TL, Weisgraber KH, Arnold KS: Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: low density lipoproteins with abnormal receptor binding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1987, 84: 6919-23. 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6919.
Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabès JP: Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nature genetics. 2003, 34: 154-6. 10.1038/ng1161.
Garcia CK, Wilund K, Arca M: Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia caused by mutations in a putative LDL receptor adaptor protein. Science. 2001, 292: 1394-8. 10.1126/science.1060458.
Slack J: Risks of ischaemic heart-disease in familial hyperlipoproteinaemic states. Lancet. 1969, 2: 1380-2.
Scientific Steering Committee on behalf of the Simon Broome Register Group: Risk of fatal coronary heart disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia. BMJ. 1991, 303: 893-896.
Fahed AC, Safa RM, Haddad FF: Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in Lebanon: A genotype/phenotype correlation. Molecular genetics and metabolism. 2011, 102: 181-188. 10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.11.006.
Costet P, Krempf M, Cariou B: PCSK9 and LDL cholesterol: unraveling the target to design the bullet. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2008, 33: 426-434. 10.1016/j.tibs.2008.06.005.
Zelcer N, Hong C, Boyadjian R: LXR Regulates Cholesterol Uptake through Idol-dependent Ubiquitination of the LDL Receptor. Science. 2009, 325: 100-104. 10.1126/science.1168974.
Südhof TC, Goldstein JL, Brown MS, Russell DW: The LDL receptor gene: a mosaic of exons shared with different proteins. Science. 1985, 228: 815-22. 10.1126/science.2988123.
Russell DW, Schneider WJ, Yamamoto T: Domain map of the LDL receptor: sequence homology with the epidermal growth factor precursor. Cell. 1984, 37: 577-85. 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90388-X.
Cumings RD, Kornfeld S, Schneider WJ: Biosynthesis of N- and O-linked oligosaccharides of the low density lipoprotein receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1983, 258: 15261-73.
Leigh SEA, Foster AH, Whittall RA, Hubbart CS, Humphries SE: Update and analysis of the University College London low density lipoprotein receptor familial hypercholesterolemia database. Annals of human genetics. 2008, 72: 485-98. 10.1111/j.1469-1809.2008.00436.x.
University College London Low Density Lipoprotein Familial Hypercholesterolemia Database. Accessed 15 January 2011, [http://www.ucl.ac.uk/ldlr]
Lehrman MA, Schneider WJ, Brown MS: The Lebanese allele at the low density lipoprotein receptor locus. Nonsense mutation produces truncated receptor that is retained in endoplasmic reticulum. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1987, 262: 401-10.
Oppenheim A, Friedlander Y, Dann EJ: Hypercholesterolemia in five Israeli Christian-Arab kindreds is caused by the "Lebanese" allele at the low density lipoprotein receptor gene locus and by an additional independent major factor. Human genetics. 1991, 88: 75-84. 10.1007/BF00204933.
Alberto FL, Figueiredo MS, Zago MA, Araújo AG, Dos-Santos JE: The Lebanese mutation as an important cause of familial hypercholesterolemia in Brazil. Brazilian journal of medical and biological research. 1999, 32: 739-45. 10.1590/S0100-879X1999000600009.
Jelassi A, Slimani A, Jguirim I: Moderate phenotypic expression of familial hypercholesterolemia in Tunisia. Clinical Chimica Acta. 2010, 411: 735-738. 10.1016/j.cca.2010.02.008.
Hegele RA: Genetic susceptibility to heart disease in Canada: lessons from patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Genome/National Research Council Canada. 2006, 49: 1343-50.
Soria LF, Ludwig EH, Clarke HR: Association between a specific apolipoprotein B mutation and familial defective apolipoprotein B-100. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1989, 86: 587-91. 10.1073/pnas.86.2.587.
Myant NB: Familial defective apolipoprotein B-100: a review, including some comparisons with familial hypercholesterolaemia. Atherosclerosis. 1993, 104: 1-18. 10.1016/0021-9150(93)90171-P.
Tai DY, Pan JP, Lee-Chen GJ: Identification and haplotype analysis of apolipoprotein B-100 Arg3500-->Trp mutation in hyperlipidemic Chinese. Clinical chemistry. 1998, 44: 1659-65.
Cohen J, Pertsemlidis A, Kotowski IK: Low LDL cholesterol in individuals of African descent resulting from frequent nonsense mutations in PCSK9. Nature genetics. 2005, 37: 161-5. 10.1038/ng1509.
Abifadel M, Rabes JP, Devillers M: Mutations and Polymorphisms in the Proprotein Convertase Subtilin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) Gene in Cholesterol Metabolism and Disease. Human Mutation. 2009, 30: 520-529. 10.1002/humu.20882.
Seidah NG: PCSK9 as a therapeutic target for dyslipidemia. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. 2009, 13: 19-28. 10.1517/14728220802600715.
Marian AJ: PCSK9 as a therapeutic target in atherosclerosis. Current Atherosclerosis Reports. 2010, 12: 151-4. 10.1007/s11883-010-0099-2.
Duff CJ, Hooper NM: PCSK9: an emerging target for treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets. 2011, 15 (2): 157-68. 10.1517/14728222.2011.547480. Epub 2011 Jan 5
Eden ER, Naoumova RP, Burden JJ: Use of homozygosity mapping to identify a region on chromosome 1 bearing a defective gene that causes autosomal recessive homozygous hypercholesterolemia in two unrelated families. American Journal of Human Genetics. 2001, 68: 653-60. 10.1086/318795.
Soutar AK, Naoumova RP, Traub LM: Genetics, clinical phenotype, and molecular cell biology of autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2003, 23: 1963-70. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000094410.66558.9A.
Canizales-Quinteros S, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Huertas-Vasquez A: A novel ARH splice site mutation in a Mexican kindred with autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. Human Genetics. 2005, 116: 114-20. 10.1007/s00439-004-1192-9.
Harada K, Miyamoto Y, Morisaki H: A novel Thr56Met mutation of the autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia gene associated with hypercholesterolemia. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis. 2010, 17: 131-40.
Sabbagh AS, Daher RT, Otrock ZK: ApoB-100 R3500Q mutation in the Lebanese population: prevalence and historical review of the literature. Molecular biology reports. 2007, 34: 267-70. 10.1007/s11033-006-9041-7.
Pisciotta L, Priore Olivia C, Pes GM: Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia (ARH) and homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH): a phenotypic comparison. Atherosclerosis. 2006, 188: 398-405. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.11.016.
Tietge UJ, Genschel J, Schmidt HH: A Q136Stop Mutation in the ARH gene causing autosomal recessive hypercholesterolaemia with severely delayed LDL catabolism. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2003, 253: 582-583. 10.1046/j.1365-2796.2003.01139.x.
Naoumova RP, Neuwirth C, Lee P: Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolaemia: long-term follow up and response to treatment. Atherosclerosis. 2004, 174: 165-72. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.01.020.
Abifadel M, Rabès JP, Jambart S: The molecular basis of familial hypercholesterolemia in Lebanon: spectrum of LDLR mutations and role of PCSK9 as a modifier gene. Human Mutation. 2009, 30: E682-91. 10.1002/humu.21002.
Allard D, Amsellem S, Abifadel M: Novel mutations of the PCSK9 gene cause variable phenotype of autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Human Mutation. 2005, 26: 497-10.1002/humu.9383.
Pisciotta L, Priore Olivia C, Cefalu AB: Additive effect of mutations in LDLR and PCSK9 genes on the phenotype of familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2006, 186: 433-40. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.08.015.
Wang J, Ban MR, Hegele RA: Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification of LDLR enhances molecular diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia. Journal of Lipid Research. 2005, 46: 366-72.
Sellner LN, Taylor GR: MLPA and MAPH: new techniques for detection of gene deletions. Human Mutation. 2004, 23: 413-9. 10.1002/humu.20035.
Jansen AC, van Wissen S, Defesche JC: Phenotypic variability in familial hypercholesterolaemia: an update. Current Opinion in Lipidology. 2002, 13: 165-71. 10.1097/00041433-200204000-00008.
Slimane MN, Lestavel S, Sun X: Fh-Souassi: a founder frameshift mutation in exon 10 of the LDL-receptor gene, associated with a mild phenotype in Tunisian families. Atherosclerosis. 2001, 154: 557-65. 10.1016/S0021-9150(00)00572-4.
Choumerianou DM, Dedoussis GVZ: Familial hypercholesterolemia and response to statin therapy according to LDLR genetic background. Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine: CCLM/FESCC. 2005, 43: 793-801. 10.1515/CCLM.2005.134.
Dedoussis GVZ: Apolipoprotein polymorphisms and familial hypercholesterolemia. Pharmacogenomics. 2007, 8: 1179-89. 10.2217/14622416.8.9.1179.
Austin MA, Hutter CM, Zimmern RL, Humphries S: Familial hypercholesterolemia and coronary heart disease: a HuGE association review. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2004, 160: 421-9. 10.1093/aje/kwh237.
Jansen AC, van Aalst-Cohen ES, Tanck MW: The contribution of classical risk factors to cardiovascular disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia: data in 2400 patients. Journal of Internal Medicine. 2004, 256: 482-90. 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01405.x.
Clarke A: Commentary: Lipoprotein (a) and atherosclerosis. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2011, 40 (2): 478-9. 10.1093/ije/dyr015. Epub 2011 Feb 17
Civeira F: Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2004, 173: 55-68. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2003.11.010.
Scientific Steering Committee on behalf of the Simon Broome Register Group: Risk of fatal coronary heart disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia. BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 1991, 303: 893-6.
Williams RR, Hunt SC, Schumacher MC: Diagnosing heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia using new practical criteria validated by molecular genetics. American Journal of Cardiology. 1993, 72: 171-6. 10.1016/0002-9149(93)90155-6.
Nicholls P, Young I, Lyttle K: Screening for familial hypercholesterolaemia. Early identification and treatment of patients is important. BMJ. 2001, 322: 1062-10.1136/bmj.322.7293.1062.
Newman TB, Garber AM: Cholesterol screening in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2000, 105: 637-638. 10.1542/peds.105.3.637.
Vuorio A, Kuoppala J, Kovanen PT: Statins for children with familial hypercholesterolemia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2010, 7: CD006401-
Datta BN, McDowell IFW, Rees A: Integrating provision of specialist lipid services with cascade testing for familial hypercholesterolaemia. Current Opinion in Lipidology. 2010, 21: 366-371. 10.1097/MOL.0b013e32833c14e2.
Leren TP: Cascade genetic screening for familial hypercholesterolemia. Clinical Genetics. 2004, 66: 483-487. 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2004.00320.x.
Nybo M, Brusgaard K, Hansen AB: No certain predictors for mutation status in a Danish cohort with familial hypercholesterolemia: a descriptive study. Clinical biochemistry. 2007, 40: 1347-52. 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2007.09.012.
Alves AC, Medeiros AM, Francisco V: Molecular diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia: an important tool for cardiovascular risk stratification. Portugese Journal of Cardiology. 2010, 29: 907-21.
Familial Hypercholesterolemia. A Report of a WHO consultation Part I. Paris. 1997
Defesche JC, Kastelein JJ: Molecular epidemiology of familial hypercholesterolaemia. Lancet. 1998, 352: 1643-4.
Wald DS, Bestwick JP, Wald NJ: Child-parent screening for familial hypercholesterolaemia: screening strategy based on a meta-analysis. BMJ. 2007, 335: 599-10.1136/bmj.39300.616076.55.
Umans-Eckenhausen MA, Defesche JC, Sijrbrands EJ: Review of first 5 years of screening for familial hypercholesterolaemia in the Netherlands. Lancet. 2001, 357: 165-8. 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03587-X.
Wonderling D, Umans-Eckenhausen MA, Marks D: Cost-effectiveness analysis of the genetic screening program for familial hypercholesterolemia in The Netherlands. Seminars in vascular medicine. 2004, 4: 97-104.
Defesche JC: Defining the challenges of FH Screening for familial hypercholesterolemia. Journal of Clinical Lipidology. 2010, 4: 338-341. 10.1016/j.jacl.2010.08.022.
Leren TP, Manshaus T, Skovholt U: Application of molecular genetics for diagnosing familial hypercholesterolemia in Norway: results from a family-based screening program. Seminars in vascular medicine. 2004, 4: 75-85.
Leren TP, Finborud TH, Manshaus TE: Diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia in general practice using clinical diagnostic criteria or genetic testing as part of cascade genetic screening. Community Genetics. 2008, 11: 26-35. 10.1159/000111637.
Pocovi M, Civeira F, Alonso R: Familial hypercholesterolemia in Spain: case-finding program, clinical and genetic aspects. Seminars in Vascular Medicine. 2004, 4: 67-74.
Civeira F, Ros E, Jarauta E: Comparison of Genetic Versus Clinical Diagnosis in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. The American Journal of Cardiology. 2008, 102: 1187-93. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.06.056.
The Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Familial Hypercholesterolemia 2010. Accessed 15 January 2011, [http://www.csanz.edu.au/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=EOvAvk2jApc%3d&tabid=148]
Muir LA, George PM, Laurie AD: Preventing cardiovascular disease: a review of the effectiveness of identifying the people with familial hypercholesterolaemia in New Zealand. New Zealand Medical Journal. 2010, 123: 97-102.
Wales Familial Hypercholesterolemia Testing Service. Accessed 15 January 2011, [http://www.fhwales.co.uk]
Taylor A, Wang D, Patel K: Mutation detection rate and spectrum in familial hypercholesterolaemia patients in the UK pilot cascade project. Clinical Genetics. 2010, 77: 572-580.
Lombardi MP, Redeker EJ, van Gent DH: Molecular genetic testing for familial hypercholesterolemia in the Netherlands: a stepwise screening strategy enhances the mutation detection rate. Genetic Testing. 2006, 10: 77-84. 10.1089/gte.2006.10.77.
Brusgaard K, Jordan P, Hansen H: Molecular genetic analysis of 1053 Danish individuals with clinical signs of familial hypercholesterolemia. Clinical Genetics. 2006, 69: 277-283. 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00585.x.
Damgaard D, Larsen ML, Nissen PH: The relationship of molecular genetic to clinical diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia in a Danish population. Atherosclerosis. 2005, 180: 155-160. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.12.001.
Laurie AD, George PM: Evaluation of high-resolution melting analysis for screening the LDL receptor gene. Clinical Biochemistry. 2009, 42: 528-535. 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.11.015.
Laurie AD, Scott RS, George PM: Genetic screening of patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH): a New Zealand perspective. Atherosclerosis Supplements. 2004, 5: 13-15.
Thorsson B, Sigurdsson G, Gudnason V: Systematic Family Screening for Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Iceland. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis and Vascular Biology. 2003, 23: 335-338. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000051874.51341.8C.
Hadfield SG, Humphries SE: Implementation of cascade testing for the detection of familial hypercholesterolaemia. Current Opinion in Lipidology. 2005, 16: 428-433. 10.1097/01.mol.0000174152.76554.d6.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Theresa Farhat for her assistance in designing Figure 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
AF and GN reviewed the literature and wrote different sections of the manuscript equally. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Fahed, A.C., Nemer, G.M. Familial Hypercholesterolemia: The Lipids or the Genes?. Nutr Metab (Lond) 8, 23 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-8-23
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-8-23