Abstract
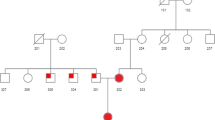
Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia (ARH) is characterized by elevated LDL serum levels, xanthomatosis, and premature coronary artery disease. Three loci have been described for this condition (1p35, 15q25-q26 and 13q). Recently, the responsible gene at the 1p35 locus, encoding an LDL receptor adaptor protein (ARH) has been identified. We studied a Mexican ARH family with two affected siblings. Sequence analysis of the ARH gene (1p35 locus) revealed that the affected siblings are homozygous for a novel mutation (IVS4+2T>G) affecting the donor splice site in intron 4, whereas both the parents and an unaffected sister are heterozygous for this mutation. The IVS4+2T>G mutation results in a major alternative transcript derived from a cryptic splice site, which carries an in-frame deletion of 78 nucleotides in the mature mRNA. The translation of this mRNA yields a mutant protein product (ARH-26) lacking 26 amino acids, resulting in the loss of β-strands β6 and β7 from the PTB domain. This is the first case where a naturally occurring mutant with an altered PTB domain has been identified.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Salinas CA (2001) Hipercolesterolemia familiar. Revista de Investigación Clínica 53:254–265
Aguilar-Salinas CA, Barrett PHR, Kelber J, Delmez J, Schonfeld G (1995) Physiologic mechanism of action of lovastatin in nephrotic syndrome. J Lipid Res 36:188–199
Al-Kateb H, Bahring S, Hoffmann K, Strauch K, Busjahn A, Nurnberg G, Jouma M, Bautz EK, Dresel HA, Luft FC (2002) Mutation in the ARH gene and a chromosome 13q locus influence cholesterol levels in a new form of digenic-recessive familial hypercholesterolemia. Circ Res 90:951–958
Al-Kateb H, Bautz EK, Luft FC, Bahring S (2003) A splice mutation in a Syrian autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia family causes a two-nucleotide deletion of mRNA. Circ Res 93(5):e49–e50
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arca M, Zuliani G, Wilund K, Campagna F, Fellin R, Bertolini S, Calandra S, Ricci G, Glorioso N, Maioli M, Pintus P, Carru C, Cossu F, Cohen J, Hobbs HH (2002) Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolaemia in Sardinia, Italy, and mutations in ARH: a clinical and molecular genetic analysis. Lancet 359:841–847
Buffone GJ, Darlington GJ (1985) Isolation of DNA from biological specimens without extraction with phenol. Clin Chem 31:164–165
Carson M (1997) Ribbons. Methods Enzymol 277:493–505
Cartegni L, Chew SL, Krainer AR (2002) Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat Rev Genet 3:285–298
Ciccarese M, Pacifico A, Tonolo G, Pintus P, Nikoshkov A, Zuliani G, Fellin R, Luthman H, Maioli M (2000) A new locus for autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia maps to human chromosome 15q25-q26. Am J Hum Genet 66:453–460
Cohen JC, Kimmel M, Polanski A, Hobbs HH (2003) Molecular mechanisms of autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. Curr Opin Lipidol 14:121–127
Eden ER, Naoumova RP, Burden JJ, McCarthy MI, Soutar AK (2001) Use of homozygosity mapping to identify a region on chromosome 1 bearing a defective gene that causes autosomal recessive homozygous hypercholesterolemia in two unrelated families. Am J Hum Genet 68:653–660
Eden ER, Patel DD, Sun XM, Burden JJ, Themis M, Edwards M, Lee P, Neuwirth C, Naoumova RP, Soutar AK (2002) Restoration of LDL receptor function in cells from patients with autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia by retroviral expression of ARH1. J Clin Invest 110:1695–1702
Friedewald WT, Levy IR, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoproteins cholesterol in plasma without the use of the ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:449–502
Garcia CK, Wilund K, Arca M, Zuliani G, Fellin R, Maioli M, Calandra S, Bertolini S, Cossu F, Grishin N, Barnes R, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH (2001) Autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia caused by mutations in a putative LDL receptor adaptor protein. Science 292:1394–1398
Gibrat JF, Madej T, Bryant SH (1996) Surprising similarities in structure comparison. Curr Opin Struct Biol 6:377–385
Grundy SM (1991) George Lyman Duff memorial lecture. Multifactorial etiology of hypercholesterolemia. Implications for prevention of coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb 11:1619–1635
Harada-Shiba M, Takagi A, Miyamoto Y, Tsushima M, Ikeda Y, Yokoyama S, Yamamoto A (2003) Clinical features and genetic analysis of autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:2541–2547
Havekes L, de Wit E, Leuven JG, Klasen E, Utermann G, Weber W, Beisiegel U (1986) Apolipoprotein E3-Leiden. A new variant of human apolipoprotein E associated with familial type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Hum Genet 73:157–163
Hixson JE, Vernier DT (1990) Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res 31:545–548
Jones C, Hammer RE, Li WP, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH, Herz J (2003) Normal sorting but defective endocytosis of the low density lipoprotein receptor in mice with autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem 278:29024–29030
Khachadurian AK, Uthman SM (1973) Experiences with the homozygous cases of familial hypercholesterolemia. A report of 52 patients. Nutr Metab 15:132–140
Maquat LE (1996) Defects in RNA splicing and the consequence of shortened translational reading frames. Am J Hum Genet 59:279–286
Mishra SK, Watkins SC, Traub LM (2002) The autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia (ARH) protein interfaces directly with the clathrin-coat machinery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16099–16104
Nagai M, Meerloo T, Takeda T, Farquhar MG (2003) The adaptor protein ARH escorts megalin to and through endosomes. Mol Biol Cell 4:4984–4996
Nakai K, Sakamoto H (1994) Construction of a novel database containing aberrant splicing mutations of mammalian genes. Gene 141:171–177
Roca X, Sachidanandam R, Krainer AR (2003) Intrinsic differences between authentic and cryptic 5’ splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res 31:6321–6333
Rohlmann A, Gotthardt M, Hammer RE, Herz J (1998) Inducible inactivation of hepatic LRP gene by cre-mediated recombination confirms role of LRP in clearance of chylomicron remnants. J Clin Invest 101:689–695
Sali A, Blundell T (1993) Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234:779–815
Sander C, Schneider R (1991) Database of homology-derived protein structures and the structural meaning of sequence alignment. Proteins 9:56–68
Shapiro MB, Senapathy P (1987) RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 15:7155–7174
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Wilund KR, Yi M, Campagna F, Arca M, Zuliani G, Fellin R, Ho YK, Garcia JV, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC (2002) Molecular mechanisms of autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. Hum Mol Genet 11:3019–3030
Zuliani G, Arca M, Signore A, Bader G, Fazio S, Chianelli M, Bellosta S, Campagna F, Montali A, Maioli M, Pacifico A, Ricci G, Fellin R (1999) Characterization of a new form of inherited hypercholesterolemia: familial recessive hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:802–809
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the family who participated in this study. This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) (30774-M), Dirección General de Asuntos del Personal Académico, UNAM (IN217501) and Fundación Miguel Alemán (Mexico). A.H.-V. and L.R.-O. were supported by a fellowship from CONACyT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canizales-Quinteros, S., Aguilar-Salinas, C.A., Huertas-Vázquez, A. et al. A novel ARH splice site mutation in a Mexican kindred with autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia. Hum Genet 116, 114–120 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1192-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1192-9