Abstract
Background
A case of Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET) of the kidney in a 27-year-old woman is presented. Few cases are reported in the literature with a variable, nonspecific presentation and an aggressive behaviour. In our case, a radical nephrectomy with lymphadenectomy was performed and there was no residual or recurrent tumour at 24-month follow-up.
Methods
The surgical specimens were formalin-fixed and paraffin embedded. The sections were stained with routinary H&E. Immunohistochemistry was performed.
Results
The immunohistochemical evaluation revealed a diffuse CD99 positivity in the cytoplasm of the neoplastic cells. Pankeratin, cytokeratin AE1/AE3, vimentin, desmin, S100, cromogranin were negative. The clinical presentation and the macroscopic aspect, together with the histological pattern, the cytological characteristic and the cellular immunophenotype addressed the diagnosis towards primary PNET of kidney.
Conclusions
Since sometimes it is difficult to discriminate between PNET and Ewing's tumour, we reviewed the difficulties in differential diagnosis. These tumors have a common precursor but the stage of differentiation in which it is blocked is probably different. This could also explain their different biological behaviour and prognosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The peripheral Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET), firstly recognized by Arthur Purdy Stout in 1918, is a member of the family of "small round-cell tumors". Primitive renal localization is very rare. There are almost 50 cases reported in the literature, although it is difficult to estimate the exact number since often it has not been differentiated from Ewing's Sarcoma [1–13]. Renal PNET is more aggressive than in the other sites. It frequently arises during childhood or adolescence, having an aggressive clinical course towards metastatic disease and death. It often recurs locally and metastasises early to regional lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bone and bone marrow, resulting in a poor prognosis. The 5-year disease-free survival rate, for patients presenting well confined extra-skeletal PNET, is around 45–55% and cases with advanced disease at presentation have a median relapse-free survival of only 2 years [1].
Case presentation
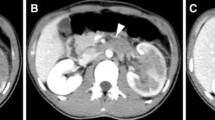
A 27-year-old woman was referred because of a mild left flank pain and haematuria. Ultrasonography identified a left renal mass homogeneously hyperechogenic in comparison with renal parenchyma. CT scan showed a 11 mm × 8 mm × 6 mm tumor replacing the upper half of the left kidney with extension into the renal vein. Chest x-ray was negative. Pathological stage after radical nephrectomy was T3aN0Mx.
The surgical specimens were formalin-fixed and paraffin embedded. The sections were stained with routinary H&E. Immunohistochemistry was performed using avidin biotin complex technique and diaminobenzidine as chromogen. The antibodies used included CD99 (Dako, M3601), pankeratin (Dako, M0821), cytokeratin AE1/AE3 (Dako, M3515), vimentin (Dako, M7010), desmin (Dako, M0760), S100 (Dako, Z0311), and chromogranin A (Dako, M0869), at suggested dilution. We performed also appropriate routinely positive and negative controls.
The tumor was multilobular, grey, glistening, focally hemorrhagic, surrounded by a capsule and with a sharp demarcation from the uninvolved kidney. Histologically, the tumor consisted of small round cells with round nuclei and scant cytoplasm. It presented different patterns, with cohesive lobules or rosettes and perivascular pseudo-rosettes or, in some areas, spindle cellular elements (fig. 1).
The immunohistochemical evaluation revealed a diffuse CD99 positivity in the cytoplasm of the neoplastic cells (fig. 2); tumoral cells were also visible in the vascular lumens (fig. 3). By contrast, pankeratin, cytokeratin AE1/AE3, vimentin, desmin, S100, cromogranin were negative.
The clinical presentation and the macroscopic aspect, together with the histological pattern, the cytological characteristic and the cellular immunophenotype addressed the diagnosis towards primary PNET of kidney. A bone scan did not reveal positive areas. Eight cycles of chemotherapy with Vincristine, Ifosfamide and Adriamycin, four cycles of Ifosfamide and VP16 and eight sittings of local radiotherapy were sequentially performed. Follow-up examinations with CT and bone scan failed to show residual or recurrent tumor after 24 months.
Conclusions
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor of the kidney is a rare entity. The few cases reported revealed a variable presentation and an aggressive behaviour. The distinction from other primary malignancies of the kidneys is crucial for prognosis. The differential diagnosis includes extra-osseous Ewing's sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Wilm's tumor, carcinoid, neuroblastoma, clear cell sarcoma of the kidney, lymphoma, the small cell variant of osteosarcoma, desmoplastic small round cell tumor and nephroblastoma [5].
The Homer-Wright type rosettes, commonly scarce of number or less defined in extra skeletal Ewing's sarcoma (ES), are a typical histological feature for PNET and can address the diagnosis although they can be found also in neuroblastoma [5]. To better address the diagnosis, an immunohistochemical analysis is necessary. In our case the presence of MIC-2 gene products, known also as CD99, 12E7, E2, 013 and HBA71, suggested a PNET diagnosis. Primitive neuroectodermal tumors only immunorreactive to CD99, even if uncommon, are reported in the literature [13]. The reactivity to vimentin, NSE and S-100 may facilitate the diagnosis but is not patognomonic, while CD 99 positivity is nowadays a clue for the diagnosis. Moreover cytogenetic studies (not performed in our case) demonstrated that PNET and Ewing's sarcoma can both be associated to a translocation of the long arms of chromosome 11 and 22, t(11;22)(q22;q12) [5]. Despite their genetic and antigenic similarity, many authors currently recognize PNET and extra-skeletal Ewing's sarcoma of the kidney as separate entities. It is also important to keep separate renal PNET and malignant rhabdomyosarcoma tumor (MRT). Weeks et al reported 8 cases suggestive for PNET but mimicking MRT [14]. Although renal PNET and MRT show similar clinico-pathological features, the latter usually occurs in very young children, having a more aggressive prognosis.
Rodriguez et al postulated that these two renal neoplasms share a common undifferentiated precursor to explain their similarity and we agree with these Authors [12]. Indeed, the hypothesis that tumors arise from stem cells (SCs) as a consequence of a maturative arrest is now growing [15]. SCs are present in almost all tissues and may originate different cellular lineages by the multi-step process named "differentiation". The role of SCs in tumorigenesis was clearly demonstrated in a number of carcinogenic models showing that solid and haematopoietic cancers could arise from tissue-specific SCs [16–19]. In agreement with Sell and Pierce, we retain that the degree of malignancy of a carcinoma depends by the stage in which SCs differentiation stopped during carcinogenesis [19]. In particular, since PNET, Ewing's tumour and MRT have a similar morphology, our hypothesis is that the mesenchimal stem precursor of these tumors is the same, but the stage of differentiation in which it is blocked is different. This could explain why sometimes it is difficult to discriminate between these tumors, notwithstanding they present a different biological behaviour.
References
Casella R, Moch H, Rochlitz C, et al: Metastatic primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney in adults. Eur Urol. 2001, 39: 613-617. 10.1159/000052514.
Cuesta Alcala JA, Solchaga Martinez A, Caballero Martinez MC, et al: Primary neuroectodermal tumor (PNET)of the kidney:26 cases. Current status of its diagnosis and treatment. Arch Esp Urol. 2001, 54: 1081-1093.
Dogra PN, Goel A, Kumar R, et al: Extra-osseous Ewing's Sarcoma of the kidney. Urol Int. 2002, 69: 150-152. 10.1159/000065566.
Friedrichs N, Vorreuther R, Poremba C, et al: Primitive neuroectodermal tumor in the differential diagnosis of malignant kidney tumors. Pathol Res Pract. 2002, 198: 563-569.
Gonsulen G, Ergin M, Paydas S, et al: Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney: a rare entity. Int Urol Nephrol. 2001, 33: 449-451. 10.1023/A:1019511205650.
Jimenez RE, Folpe AL, Lapham RL, et al: Primary Ewing's Sarcoma/Primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney. A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 11 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002, 26: 320-327. 10.1097/00000478-200203000-00005.
Karnes RJ, Gettman MT, Anderson PM, et al: Primitive neuroectodermal tumor (extraskeletal Ewing's Sarcoma) of the kidney with vena caval tumor thrombus. J Urol. 2000, 164: 772-10.1097/00005392-200009010-00036.
Kuroda M, Urano M, Abe M, et al: Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney. Pathol Int. 2000, 50: 967-972. 10.1046/j.1440-1827.2000.01147.x.
Lam JS, Hensle TW, et al: Organ-confined Primitive Neuroectodermal tumor arising from the kidney. J Pediatr Surger. 2003, 38: 619-621. 10.1053/jpsu.2003.50135.
Premalata CS, Gayathri DV, et al: Primitive Neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney. A report of two cases diagnosed by fine needle aspiration cytology. Acta Cytol. 2003, 47: 475-479.
Ranadive NU, Urmi C, Kumar M: Primary primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) of the kidney: a case report. Arch Esp Urol. 1999, 52: 190-192.
Rodriguez-Galindo C, Marina NM, Fletcher BD, et al: Is primitive neuroectodermal tumor of kidney a distinct entity?. Cancer. 1997, 79: 2243-2250. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19970601)79:11<2243::AID-CNCR24>3.3.CO;2-1.
Thomas JC, Sebek BA, Krishnamurthi V: Primitive Neuroectodermal tumor of the kidney with inferior cava and atrial tumor thrombus. J Urol. 2002, 168: 1486-1487. 10.1097/00005392-200210010-00045.
Weeks DA, Beckwith JB, Mierau GW, Zuppan CW: Renal neoplasms mimicking rhabdoid tumor of kidney. A report from the National Wilms' Tumor Study Pathology Center. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991, 15: 1042-54.
Reya T, Morrison JS, Clarke MF, et al: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001, 414: 105-111. 10.1038/35102167.
Andrews PW: From teratocarcinomas to embryonic stem cells. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977, 357: 405-417. 10.1098/rstb.2002.1058.
Novikoff PM, Yam A: Stem cells and rat liver carcinogenesis: contributions of confocal and electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1998, 46: 613-626.
Pathak S: Organ- and tissue-specific stem cells and carcinogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22: 1353-1356.
Sell S, Pierce GB: Maturation arrest of stem cell differentiation in a common pathway for the cellular origin of teratocarcinomas and epithelial cancers. Lab Invest. 1994, 70: 6-22.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/4/3/prepub
Acknowledgements
Written consent was obtained from the patient for publication of the patient's details
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
None declared.
Authors' contribution
All authors contributed.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under an open access license. Please check the 'Copyright Information' section either on this page or in the PDF for details of this license and what re-use is permitted. If your intended use exceeds what is permitted by the license or if you are unable to locate the licence and re-use information, please contact the Rights and Permissions team.
About this article
Cite this article
Pomara, G., Cappello, F., Cuttano, M.G. et al. Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET) of the kidney: a case report. BMC Cancer 4, 3 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-4-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-4-3