Abstract
Background
Plant mitochondrial genomes are known for their complexity, and there is abundant evidence demonstrating that this organelle is important for plant sexual reproduction. Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) is a phenomenon caused by incompatibility between the nucleus and mitochondria that has been discovered in various plant species. As the exact sequence of steps leading to CMS has not yet been revealed, efforts should be made to elucidate the factors underlying the mechanism of this important trait for crop breeding.
Results
Two CMS mitochondrial genomes, LD-CMS, derived from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica (434,735 bp), and CW-CMS, derived from Oryza rufipogon Griff. (559,045 bp), were newly sequenced in this study. Compared to the previously sequenced Nipponbare (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica) mitochondrial genome, the presence of 54 out of 56 protein-encoding genes (including pseudo-genes), 22 tRNA genes (including pseudo-tRNAs), and three rRNA genes was conserved. Two other genes were not present in the CW-CMS mitochondrial genome, and one of them was present as part of the newly identified chimeric ORF, CW-orf307. At least 12 genomic recombination events were predicted between the LD-CMS mitochondrial genome and Nipponbare, and 15 between the CW-CMS genome and Nipponbare, and novel genetic structures were formed by these genomic rearrangements in the two CMS lines. At least one of the genomic rearrangements was completely unique to each CMS line and not present in 69 rice cultivars or 9 accessions of O. rufipogon.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate novel mitochondrial genomic rearrangements that are unique in CMS cytoplasm, and one of the genes that is unique in the CW mitochondrial genome, CW-orf307, appeared to be the candidate most likely responsible for the CW-CMS event. Genomic rearrangements were dynamic in the CMS lines in comparison with those of rice cultivars, suggesting that 'death' and possible 'birth' processes of the CMS genes occurred during the breeding history of rice.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
In contrast to the compact structure of the human mitochondrial genome (13 genes in approximately 17 kb), higher plant mitochondria are extremely complex in their constitution, and their process of evolution is enigmatic. In addition, although animal mitochondrial genomes are relatively conserved in size, from Homo sapiens to Mus musculus, the genomic content of plant mitochondria is highly divergent, ranging from an estimated 200 to 2,400 kb [1]. The conservation of simple circular mitochondrial DNA that is seen in animals is even in doubt in plants, and a number of studies have predicted that the genetic information of plant mitochondria is partitioned into subgenomes [2]. Finally, in addition to the 13 housekeeping genes also found in animals, plants contain numerous open reading flames (ORFs) with unknown functions as well as genes with known functions, such as ribosomal protein subunit-encoding genes, that are not observed in the animal genomes. Although most of these ORFs are considered to be non-functional and suppressed during development, some studies have reported that several ORFs are transcribed [3]. These mysteries of the mitochondria are certainly intriguing in view of the co-evolution of nuclear and mitochondrial genomes. To date, seven mitochondrial genomes have been sequenced from plant species: four from dicot species, Arabidopsis thaliana [4], Beta vulgaris [3, 5], Brassica napus [6], and Nicotiana tabacum [7], and three from monocot species, Oryza sativa [8, 9], Zea mays [10, 11], and Triticum aestivum [12]. These studies have shown that plant mitochondrial genomes are actually divergent in their non-coding sequences and even in their gene-coding regions; for instance, the presence of ribosomal protein subunit-encoding genes is known to be quite inconsistent among species [2, 13].
Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) is a maternally inherited male sterile trait, and a significant amount of evidence indicates that this phenomenon stems from alteration of the mitochondrial genome [14, 15]. In many cases, the product of the unique gene structure in the CMS mitochondrial genome, consisting of a chimeric structure of endogenous gene fragments and an alien sequence, has been demonstrated to be associated with the mitochondrial inner membrane [16–19]. Most of these mitochondrial CMS-associated genes (MCAG) are thought to form a pore within the membrane and, although the details of the mechanism from pore-forming to CMS occurrence have not been fully elucidated, it is speculated that MCAGs are responsible for CMS. Since CMS is often associated with cytoplasmic substitutions, such as successive backcrossing of distantly related strains, CMS is the key phenomenon that may shed some light on plant mitochondrial-nuclear interactions.
Studies of the CMS mitochondrial genomes in B. vulgaris [3] and Z. mays [11] revealed the presence of several large recombination events compared to normal cytoplasm. Satoh et al. [3] sequenced the Owen-CMS mitochondrial genome in sugar beet, and a comparison with the non-CMS mitochondria revealed the existence of several CMS-specific ORFs generated by the genomic rearrangements. PreSatp6 was later determined to be the best candidate for MCAG, and the gene products of PreSatp6 were localized in the mitochondrial inner membrane in the form of a homo-oligomer [18]. Allen et al. [11] sequenced five distinct mitochondrial genomes in maize and detected massive genomic recombinations among the lines. Even two of the normal cytoplasms which were sequenced, NA and NB, were significantly dissimilar to each other, and it was estimated that there were 16 genomic rearrangements between the lines. They reported that genome sizes of the lines ranged from 535,825 bp in CMS-T to 739,719 bp in CMS-C [11].
The 490,520-bp mitochondrial genome of rice (Oryza sativa L.) japonica cultivar Nipponbare was sequenced, and 53 protein-encoding genes, 17 tRNA genes, and 3 rRNA genes were predicted [8]. When the existence of the master circle was assumed, at least three large duplications (>10,000 bp) were found, and portions of plastid and nuclear sequences were frequently inserted, making the genome even more complex. The mitochondrial genome of the indica strain 93-11 was also assembled, and it was predicted to possess 491,515-bp nucleotides [9]. At the same time, the 490,673-bp mitochondrial genome was assembled for the strain PA64S carrying japonica cytoplasm. A total of 96 SNPs and 25 Indels were predicted between 93-11 and PA64S, but the differences in their overall genomic structures were rather conservative, in comparison to the report that the sequence arrangements of two normal cytoplasms from maize were never in parallel [11].
Based on this background, our intention was to determine whether the characteristics of CMS mitochondrial sequences of rice are comparable with those of maize or sugar beet. In rice, more than 60 types of CMS have been reported (see [20] or [21] for reviews); however, the mitochondrial sequence has not yet been revealed for any CMS rice. In this study, we employed two independent CMS lines, LD-CMS and CW-CMS, derived from the Burmese strain Lead rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica) and from the Chinese wild rice strain W1 (Oryza rufipogon Griff.), respectively. Using the Nipponbare mitochondrial sequence as a reference, we chose the high-throughput pyrosequencing method to gather information about the rice CMS mitochondrial genomes. A number of genomic rearrangement events were detected between the two CMS mitochondria in comparison with that of Nipponbare.
Results
Sequence assemblies and assessment of genomic arrangements in CW-CMS and LD-CMS mitochondrial genomes
The CW-CMS mitochondrial genome was assembled to 559,045-bp single circular sequences, whereas the LD-CMS mitochondrial genome was predicted to have 434,735 bp when the master circle was hypothesized. When compared with the previously assembled Nipponbare (490,669 bp), PA64S (490,673 bp), and 93-11 (491,515 bp) [9] genomes, the sequence length of the two CMS lines differed greatly (Table 1). Thus, we speculated that the predicted mitochondrial genomic organization of the CMS lines is quite inconsistent with that of the known cultivars. We plotted the syntenic regions via the bl2seq algorithm using the Nipponbare sequence, excluding three large (>10,000 bp) duplicated regions (Figure 1). When the entire Nipponbare sequence including duplicated regions (Nipponbare full-length) was plotted against its truncated version (Nipponbare w/o dup.), we detected the presence of three large redundant regions in the same positions where we deleted duplications. However, when we plotted the sequences from the two CMS lines to the same reference genome (Nipponbare w/o dup.), we found that the syntenic regions were largely discrepant in their genomic positions (Figure 1). In comparison with Nipponbare, which has three large duplications (>10,000 bp), we predicted five duplications in the CW-CMS genome and one in the LD-CMS genome (Table 1, Figure 1). This feature is consistent with the observation in maize mitochondrial comparative sequence analysis that the large duplications accounted for most of the genome size increases in mitochondria [11], and the largest genome (CW-CMS: 559,045 bp) outnumbered the smallest genome (LD-CMS: 434,735 bp) in large duplication events. The number of recombination events was at least 15-fold higher in the CW-CMS genome compared to Nipponbare and at least 12-fold higher in the LD-CMS genome. The hypothetical master circle of CMS mitochondrial genomes is displayed in Figure 2.
Comparison of nucleotide sequences in genic regions
We compared nucleotide sequences among five mitochondrial genomes: Nipponbare, PA64S, 93-11, and the two CMS lines. First, 56 protein-encoding genes (including pseudo-genes), 22 tRNA genes (including pseudo-tRNA), and three rRNA genes found in Nipponbare were searched in the other genomes (list in Additional file 1, Table 2, Table 3). Including genes of unknown functions and ribosomal protein subunits, the appearances of the majority of the genes were constant among the five genomes. An exception was found for two ORFs which were missing from the CW-CMS genome. Due to the N-terminal deletion, the orf152b found in Nipponbare was shortened to an ORF of 92 amino acids in the CW-CMS genome (Table 3, Figure 3). Only the N-terminus 294 bp sequences of orf288 were present in CW-CMS (CW-orf307), whereas the orf288-like sequence was present but elongated to an ORF encoding 310 amino acids with a recombination event at the sequence corresponding to its N-terminal region in the LD-CMS genome (LD-orf310, Figure 3).
Major changes in gene coding regions in the CMS lines. (A) Structure of orf152b. The deletion of nucleotides in the N-terminal region shortened the ORF to a length of 92 amino acids in the CW-CMS genome. (B) Structures of orf288. Nucleotide extension at the N-terminal region seen in the LD-CMS genome caused the generation of a novel ORF predicted to encode a 310-amino-acid polypeptide (L-orf310). The chimeric structure of partial orf288 for N-terminal peptides and sequences of unknown origin generated the CW-orf307 gene in the CW-CMS genome. (C) The 6,881-bp alien sequence insertion in the downstream region of atp6 in the LD-CMS genome.
We found four non-synonymous mutations in the CW-CMS genome (Table 2). Two point mutations caused a single amino acid change from arginine to glycine (R144G) in rps1 in the CW-CMS genome (Table 2). For rps2, two point mutations caused two amino acid changes, K183N and F184Y (Table 2). On the other hand, no amino acid changes were detected in the protein encoded by the LD-CMS genome in comparison to that of Nipponbare (Table 2), other than the 6-bp deletion in the pseudo-rps14 gene-like structure similarly observed in CW. The presence and the sequences of the electron chain subunit-encoding genes, nad, cob, cox, and atp, were completely conserved among the CMS lines and Nipponbare.
Evaluation of known SNPs in 93-11 vs PA64S
As the genomic arrangements of the CMS lines and the previously sequenced cultivars were quite divergent (Figure 1), alignment of the whole genomes to detect SNPs or InDels was difficult. Thus, we decided to analyze 96 SNPs, 25 InDels, and three segmental sequence variations (SSV) detected by comparing 93-11 and PA64S in the study by Tian et al. [9]. The genotypes in the sequence variations are summarized in Additional files 2 and 3. Of the non-redundant 70 SNPs, only 59 SNPs were detectable in the CW-CMS and LD-CMS genomes, due to genomic deletions (Additional file 2). All of the SNP genotypes in the CW-CMS and LD-CMS genomes were the same (Additional file 2). Approximately 57% of the SNP genotypes were the same as those shared by the two japonica genomes (designated j); 14.3% were shared with the indica strain 93-11, 8.3% with PA64S (p), 2.9% with SNPs shared by 93-11 and Nipponbare (9/n), and 1.4% were unique to the two CMS genomes.
Non-redundant InDels and SSVs were also surveyed and, in parallel to the SNPs, the genotypes of the two CMS lines were completely identical (Additional file 3). Approximately 81% of the genotypes in the CMS lines were equal to japonica type, whereas 14.8% were equal to 93-11 type. One InDel was highly variable, and we were able to distinguish all lines in this region except for the CMS lines (InDel 200488, Additional file 3). From the above results, the CMS genomes were rather close to japonica genomes when only the nucleotide sequences were taken into consideration. Overall, the sequence variations that we could detect between the two CMS lines encompassed: the elongation of orf288 into orf310 in the LD-CMS genome, whereas orf288 was lost from the CW-CMS genome; the absence of orf152b from the CW-CMS genome; and mutations in rps1 and rps2 (Figure 3, Additional file 2). Direct sequence comparison of the syntenic regions of the CW-CMS and LD-CMS mitochondrial genomes revealed 43 SNPs and InDels in total. Comparison of the syntenic regions of the CW-CMS and Nipponbare genome revealed 206 SNPs and IndDels, although it is possible in this case that some of these differences may result from the different sequencing technologies employed. Thus the two CMS genomes were relatively similar to one another in comparison to the other mitochondrial genomes. The phylogenetic relationship estimated from all SNPs of both genic and non-genic regions is displayed as a dendrogram in Additional file 4.
Gene structures unique in CMS lines
Similar to the studies that reported CMS-specific gene structures in the CMS mitochondrial genome of other species [3, 11], we also found DNA rearrangements generating several CMS-specific structures. We previously identified a B-atp6-orf79-like structure in the LD-CMS mitochondrial genome, L-atp6-orf79 [22]. orf79 is the strongest MCAG candidate in BT-CMS rice [23–26]. Pyrosequencing enabled us to analyze the surrounding region of L-atp6-orf79 (Figure 3C). L-atp6-orf79 was on the long syntenic atp6 region with Nipponbare, but 6,881-bp alien sequences were inserted immediately after atp6 (Figure 3C). The insertion of 6,881 bp resulted in the generation of orf79. We have yet to determine the origin of the insertion sequences, but at least we were able to determine that the sequence was not present in Nipponbare, PA64S, 93-11, or the CW-CMS line. The L-atp6-orf79 transcripts are co-transcribed in the CMS line and the inter-genic region of the transcripts is cleaved by the action of the fertility restorer gene Rf1 [22]. The precise expression analysis of this L-atp6-orf79 locus was conducted in our previous study [22].
CW-CMS-specific genomic structures were found in the region around the rpl5 locus with exclusive genomic recombination involving the orf288 locus (Figure 4A). In Nipponbare, rpl5 was located upstream of atp1, 8.9 kb apart from it. In contrast, in the CW-CMS genome, the promoter region of rpl5 was substituted with other genomic regions by homologous recombination (Figure 4A). This recombination resulted in the insertion of nucleotides for 75 amino acids at the N-terminus of rps2, but the insertion was not considered to affect the rpl5 ORF structure because of the stop codon between partial rps2 and rpl5 (Figure 4B). Full-length rps2 was found in another location in the CW-CMS genome (data not shown).
Genomic structures around CW- orf307 and rpl5. (A) Large-scale genomic re-organization presumed to explain the evolution of the CW-orf307 region. Boxes of same colors indicate identical regions. (B) Schematic representation of the rpl5 locus in the CW-CMS mitochondrial genome. The A nucleotide in the TGA stop codon of partial rps2 inserted in the upstream region of rpl5 was equal to the A in the ATG start codon of rpl5. Thus, partial rps2 and rpl5 were not chimeric.
A rather interesting finding was the fate of the region around the atp1 locus because it was involved in the generation of the chimeric ORF gene, which was comprised of multiple recombination events (Figure 4A). The upstream region of atp1 was fused to a 294-bp sequence of orf288 corresponding to its N-terminal region (Figure 4A), and it was further followed by 1,369-bp unknown sequences and finally linked to the trnR region which is 26.0 kb away from atp1 in Nipponbare (Figure 4A). The 1,369-bp unknown sequence found in this locus was not found in the Nipponbare, PA64S, 93-11, or LD-CMS genomes, although some of its fragments showed 85% similarity to orf224 (Figure 5). As we stated previously, a part of orf288 was present in this region but the full-length copy was not present. The newly identified gene in this locus, possibly encoding a protein of 307 amino acids, was designated as CW-orf307. The structures of the rpl5 and CW-orf307 loci identified by pyrosequencing were verified by sequencing the lambda clones covering these regions (data not shown).
Sequence of CW- orf307. (A) Nucleotide sequence of the predicted coding region. (B) Amino acid sequence of the predicted protein. The region identical to orf288 is underlined. The region identical to cox2 is boxed within the orf288- homologous region. Indicated by broken lines are the regions similar to orf224.
Genomic structures unique in CMS lines
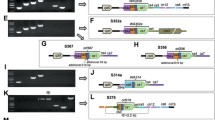
In order to evaluate the uniqueness of these genomic structures, distribution of the LD- and CW-specific structures and genes was surveyed in the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences (NIAS, Japan) global rice core collection consisting of 69 accessions of worldwide cultivars [27]. This rice collection retains 90% of RFLP alleles detected in about 300 accessions selected based on the passport data from the whole rice collection (about 30,000 accessions) maintained at the NIAS Genebank [28]. Nine wild rice strains (O. rufipogon), which had previously been reported to carry a CMS cytoplasm [29], were also included in this study, so that 78 accessions were tested in total. Six primers able to amplify the contig linkage regions (described precisely in the Methods) unique in the two CMS lines in comparison with Nipponbare were used to detect each amplicon by PCR. Table 4 summarizes the results of PCR amplification and accessions were categorized into 12 mitochondrial haplogroups (A to L). No amplicon was observed in any of the accessions using primer pairs CW_02 or LD_24 (Table 4). Thus, the genomic rearrangement detected by primer pair CW_02, which corresponds to the region between the atp1 and rrn26 or rps3 genes in CW-CMS (Figure 2), and the rearrangement detected by the primer pair LD_24, which corresponds to the region between cox1 and trnR in LD-CMS (Figure 2), were completely unique to each CMS line. The range of the proportion of the accessions with amplification by four other primer pairs (CW_19, LD_12, LD_29, LD_30) was 3.8 - 21.8%. Similar to the genomic structure detected by primer pair CW_02, CW-orf307 was solely present in the CW-CMS line (Table 4). Excluding two O. rufipogon accessions (W1086 and W1092, Additional file 5), the presence of the atp6-orf79 structure was completely linked with the amplification pattern of LD_12, as expected from the closeness of the two regions (Table 4). Lastly, distribution of the orf288- like gene in rice accessions was assessed, as the gene was not present in the CW-CMS genome (Figure 3, Table 4). Thirty-five accessions carried the orf288-like structure, whereas no amplification was observed in the other lines.
Expression analysis of genes involved in the recombination events
We investigated whether the genes involved in the recombination to generate the chimeric CW-orf307 locus were affected in terms of their expression patterns. As a result, cox1, orf284, orf165, atp1, cox2, trnR, rpl5, and rps2 were expressed in the CW-CMS calli (Additional file 6), whereas the orf224 transcripts were extensively reduced in the CW-CMS line (Additional file 6). Due to the recombination event with rps2, rpl5 probably acquired a new promoter and, as a result, transcript elongation of rpl5 occurred (Figure 4B, Additional file 6).
For CW-orf307, the regions that do not include partial orf288 were used as probes (probes 1-3, Figure 6). We detected a faint band in Taichung 65, the japonica nuclear donor for the CW-CMS line, using probe 1. The detection of this slight signal in Taichung 65 might have occurred via the orf224-like region in probe 1 and the two regions showing more than 85% identity with orf224 (Figure 5). On the other hand, we detected a CW-mitochondria-specific RNA expression using probes 2 and 3, suggesting that the downstream regions of CW-orf307 were co-transcribed (Figure 6). Although we checked to see if the presence of the gametophytic restorer gene, Rf17 for CW-CMS, would have any effects on the transcript regulation of CW-orf307 in anthers, no differences in transcript patterns were observed between a CMS line and a CW-restorer line, CWR, carrying Rf17 and CW-cytoplasm (Figure 6C).
Transcript detection around CW- orf307 locus by northern blot analysis. (A) C-terminus of CW-orf307 and the downstream sequences were probed. (B) Northern blot analysis of mitochondrial RNA extracted from calli using probes 1 to 3. atp6 was used as the internal control. (C) Northern blot using probe 1 to detect CW-orf307 transcript using the total RNA extracted from anthers at the tricellular pollen stage. R, CWR (The restorer line carrying Rf17 and CW cytoplasm); C, CW-CMS line; T, Taichung 65.
Discussion
We obtained the entire mitochondrial genome sequences of two rice CMS lines of distinct origin. The master circle of the CW-CMS mitochondrial genome was predicted to contain 559,045 bp, whereas that of the LD-CMS genome had 434,735 bp. From a comparison with the recently assembled Nipponbare (japonica), PA64S (japonica), and 93-11 (indica) mitochondrial sequences [9], we found that the CMS genomes were exclusively rearranged (Figure 1). Based on the novel genomic rearrangements and unique ORFs discovered in this study, the mitochondrial haplogroups of the rice cultivars were divided into at least 12 groups (Table 4). It is highly likely that several mitochondrial genomic rearrangements occurred during rice breeding; apparently some rearrangements had deleted the CMS-specific genomic structures (Table 4). For instance, the strongest MCAG candidate of CW-CMS, CW-orf307, was absent from all of the other strains tested (Table 4, Additional file 5). The gene product of CW-orf307 was predicted to be strongly hydrophobic by SOSUI [30], which is consistent with the characteristics of previously known MCAG products [16–19]. Although we failed to detect a transcriptional alteration of CW-orf307 in the presence of Rf17, it is still possible that Rf17 could be related to translational regulation of CW-orf307. The presence of orf79 was observed in seven cultivars and in most of the O. rufipogon accessions that were previously reported to carry CMS cytoplasm [29], but orf79 was lost from the other cultivars presumably during rice breeding history (Table 4). The reason we speculate that orf79 was "lost" from majority of cultivars is because O. rufipogon genomes are generally considered as the ancestors of O. sativa cultivars.
The complete copies of orf152b and orf288 predicted in the Nipponbare genome were not present in the CW-CMS mitochondrial genome. Furthermore, a copy of orf224 was present in the CW-CMS genome, but its expression was unexpectedly suppressed (Additional file 6), possibly due to alteration of the transcriptional efficiency by the SNP 26 bp upstream of the initiation codon ATG or the two-nucleotide substitutions within the coding region (Table 2). As orf152b and orf288 were expressed in Nipponbare (S.F. and K.T. unpublished data), as was orf224 in this study (Additional file 6), we hypothesize that these ORFs are genes. Therefore, the genetic functions of orf152b, orf288, and orf224 were apparently missing or knocked down in the CW-CMS mitochondrial genome. Among these genes, the introduction of orf288 in the cultivars seemingly occurred during the rice breeding process. In fact, orf288 was present in only 35 accessions out of the 69 'core-collection' cultivars and in no accessions from O. rufipogon, indicating that the acquirement of orf288 at least had definitely occurred during the breeding history (Additional file 5). The absence of orf288 in approximately half of the cultivars indicates that this gene is obviously not necessary for pollen fertility. Thus the possibility that a loss of function of orf288 in the CW-CMS line is causing CMS is not likely, because again absence of orf288 apparently does not induce male sterility in such cultivars lacking orf288. Whether orf288 itself can be directly involved in CMS is still an open question, but it may be postulated that the presence of orf288 has contributed to the evolution of a new chimeric CMS gene as a segment of approximately 70 amino acids of orf288 is identical to cox2 (data not shown), persuading us that orf288 is a chimeric gene. Therefore, we conclude that compelling evidence of the 'death' of MCAG via genomic rearrangements during cultivation was demonstrated in this study and, contrarily, that the generation of genes such as orf288 may be part of the 'birth' process. The 'death' idea is also supported by the fact that the atp6-orf79- like structure was lost from a large proportion of the cultivars (Additional file 5).
The actual mechanism underlying the process of MCAG is considered to be substoichiometric shifting (SSS), which involves the idea that the copy numbers of multipartite mitochondrial genomic molecules (subgenomes) change over generations [31, 32]. Interactive recombinations between repeat regions within subgenomes create novel genomic rearrangements, and these novel subgenomes may be present in low copy numbers at first, but they can proliferate and become the majority in subsequent generations by SSS [33]. It has actually been proven that the knockdown of the homologue of the Escherichia coli mismatch repair component in tomato and tobacco unsuppressed the mitochondrial recombination events, and that it eventually caused artificial CMS possibly intermediated by SSS [34]. Therefore, quantitative measurement of the genomic rearrangements we found in the above experiments should provide us with a clearer picture of how the evolution of MCAG took place during rice breeding.
A CMS genome determination study of sugar beet reported a few CMS-specific chimeric structures, other than the best MCAG candidate, preSatp6 [3, 18]. Maize CMS sequencing detected one chimeric ORF other than MCAG T-urf13 in CMS-T; none were detected other than the best MCAG candidate orf77 in CMS-S; and none were detected in CMS-C under the 70-amino-acid cut-off criterion [11]. Whether this is meaningful or not, we found 480 ORFs in the Nipponbare genome, 591 in the CW-CMS genome, and 456 in the LD-CMS genome, using the same 70-amino-acid cut-off criterion. Out of the ones that were not present in Nipponbare, none except for the ones we listed (CW-orf307 and LD-orf79) contained a significant portion of the other known genes. Whether any one of these kinds of ORFs is actually related to CMS is still unknown, and it should be emphasized again that Nipponbare as well contains genes that were not described as related to known mitochondrial biological processes but are actually transcribed. The transcribed proportion of these predicted ORFs is undetermined but, based on our current knowledge, detection of any protein products of these genes has not yet been reported [35, 36].
On the other hand, the generation and maintenance of a novel chimeric ORF may be allowed by the presence of certain nuclear genes. Possible candidates of such nuclear-encoded genes are pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR)-motif containing genes as discussed below. PPRs are now undoubtedly considered to be involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation events, mostly in plant organelles [37–40]. In higher plant species 400 to 600 PPR genes are encoded, and there is concrete evidence demonstrating that orthologous PPR pairs exist between rice and Arabidopsis [39]. Most of the Rf genes (nuclear-encoded genes responsible for fertility restoration of CMS) identified to date have been demonstrated to encode a PPR protein [25, 41–48]. PPRs encoded by Rf genes (Rf-PPR) are exceptional because they are not conserved among the species [39]; they are curiously present as heavily duplicated clusters of Rf-PPR- like genes in the genome. This feature resembles that of diversifying selection acting on the evolution of the disease resistance R genes [49]. There have been a few implications that Rf-PPR s are actually positively selected [50, 51]. One perspective involves the expectation that some Rf-PPR-like genes may be responsible for preventing protein accumulations from certain predicted ORFs that are transcribed but untranslated [40]. There has been no concrete evidence demonstrating that the evolution of Rf-PPR s is related to the generation of novel ORFs in mitochondria; however, there certainly must be a selective constraint to the diversifying selection of the Rf-PPR s, in the same manner as there are pathogens restricting the evolution of the R genes. Our current study suggested that rice mitochondrial genomic rearrangement is an on-going event, and it seems quite reasonable to consider that frequent novel ORF generation as a consequence is the driving force of Rf-PPR diversification.
Conclusion
We have shown that the mitochondrial genomes of the two CMS lines are greatly reorganized in comparison with that of Nipponbare. There appear to be a few genomic structures that are relevant to CMS, and finding these structures within rice cultivars and wild accessions provided us with the idea that genomic recombination events during rice breeding history diminished these unique genomic structures of CMS and, on the other hand, presumably gave rise to novel ORFs.
Methods
Plant materials
The origins of two independent rice CMS lines, LD-CMS and CW-CMS, were described in our previous studies [22, 52]. LD-CMS is derived from the Burmese cultivar Lead rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica) [53], and CW-CMS originates from the Chinese wild rice strain W1 (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) [54]. The nuclear donor maintainer line Taichung 65 (japonica) was used as the control for the RNA expression experiment. The development of a restorer line for CW-CMS, CWR, carrying the fertility restorer gene Rf17 which functions in a gametophytic manner [52], was described in our previous studies [52, 55]. The NIAS global rice core collection [27] was obtained from the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences Genebank (Tsukuba, Japan). O. rufipogon accessions were obtained from the National Institute of Genetics (Mishima, Japan).
Mitochondrial DNA extraction
Mitochondria were purified on sucrose gradients, as described by Tanaka et al. [56]. The DNeasy plant mini kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) was used to extract DNA from the mitochondrial fraction.
Sequence assembly
Pyrosequencing was conducted on the GS-FLX system (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) in TaKaRa-Bio (Otsu, Japan). We obtained 15,965,332-bp nucleotides for the CW-CMS genome and 15,020,464-bp nucleotides for the LD-CMS genome. Sequences were assembled to the average of 5,123-bp-long 824 contigs for the CW-CMS genome, and 4,966-bp-long 1,188 contigs for the LD-CMS genome, using the GS De Novo Assembler Software (Roche). The average sequence depth, which was defined as the sum of redundancies of each base divided by the length of the respective contig, was 41.74 for the CW-CMS genome and 44.75 for the LD-CMS genome. As many turning points and false linkages were considered, these contigs were manually assembled by the following criteria. (1) The depth of the bridging contigs had to be over 15, as bridging contigs with a depth under 15 often linked 'dead-end' contigs that were only linked to one another. Also, bridging contigs with a depth under 15 frequently linked fragments that were considered to be nuclear contaminants. (2) 'Dead-end' contigs were ignored. In addition, depth values of these 'dead-end' contigs (<15) were lower than those of non-dead-end contigs (>15). (3) Contigs that matched 100% with the Nipponbare or 93-11 nuclear genomic sequences were ignored as they were considered to be nuclear contaminants and, as in the case of 'dead-end' contigs, depth values of these contigs were always under 15. (4) Plasmid-like sequences, corresponding to B1, B2, B3, and B4 reported to be present in rice mitochondria [57, 58], were deposited to DDBJ (under accession nos. AB523794 to AB523802), but they were not analyzed in this study. Their characteristics will be presented elsewhere in detail.
These criteria left us with 19 contigs with an average length of 17,877 bp for the CW-CMS genome, and 24 contigs with an average length of 14,828 bp for the LD-CMS genome. Following these steps, the candidate linkage of the contigs was validated by PCR analysis (Additional file 7, and see Additional file 8 for the primer sets). Based on the linkage information of the contigs confirmed as well by PCR analysis (depicted in Additional files 9 and 10), master circles were developed for each genome by a 'parsimonious' method, so that each contig appeared at least once to construct the smallest genome. For the CW mitochondrial genome, there were eight alternative master circle patterns, and 64 patterns for the LD genome. In this paper, one pattern of the master circle was chosen for brevity of presentation (Additional file 11).
The BLASTN program in NCBI tools [59] was used to assign these contigs to the reference Nipponbare mitochondrial genome (DQ167400; described in [9]), and BLASTN was also used to eliminate nuclear genomic contaminations for the above criteria. Handling of the sequences was performed by Sequencher v4.2.2 software (Gene Codes Corporation, Ann Harbor, Minnesota). The Genomematcher v1.2 program [60] was used to plot the sequenced genomes with the reference Nipponbare genome by bl2seq. To avoid the possibility of detecting duplicated regions more than twice, the Nipponbare genome without large duplicated regions (>10,000 bp) synthesized for this study was referenced. Annotated sequences were deposited to DDBJ under accession nos. [DDBJ:AP011076] for CW-CMS and [DDBJ:AP011077] for LD-CMS.
Sequence comparison
Known mitochondrial genes in Nipponbare were BLASTN searched in the CW-CMS and LD-CMS genomes, and SNPs and Indels were detected. ORFs were attached to the newly sequenced genomes by the est2 genome program included in the EMBOSS v6.0.0 package [61]. Fifty-six protein-encoding genes (including pseudo-genes), 22 tRNA genes (including pseudo-tRNA) and three rRNA genes analyzed in this study are listed in Additional file 1. To obtain information for the genes that are not present in the Nipponbare genome, gene predictions were performed using the ORF Finder program [59] and Genemark.hmm for the Prokaryotes v2.4 program [62]. Six-frame-translation was performed using the getorf software included in the EMBOSS v6.0.0 package [61]. Since MCAG found in rice BT-CMS mitochondria genome encoded a protein of 79 amino acids, the ORFs predicted to encode peptides shorter than 70 amino acids were ignored.
Information on SNPs and InDels among Nipponbare, PA64S (DQ167807), and 93-11 (DQ167399) was obtained from the study by Tian et al. [9]. We considered it difficult to directly compare the pyrosequence data obtained in this study to that of the sequences obtained by shotgun sequencing in Tian et al. [9] because differences in sequence accuracies between the two strategies might be significant. Thus, instead, known SNPs and InDels in 93-11 vs PA64S [9] were surveyed in LD-CMS and CW-CMS genomes. Phylogenetic analyses of the mitochondrial genomes were performed using RAxML v 7.04 [63].
Construction and screening of the lambda library
The lambda library was constructed from total DNA isolated from the leaves of CWR, carrying CW cytoplasm, by the CTAB method [64]. DNA partially digested by Sau3A I (TaKaRa-Bio) was ligated into λGEM-11 Xho I half-site arms (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin) using Ligation high (TOYOBO, Osaka, Japan), and packaged using Gigapack III Gold packaging extract (Stratagene, La Jolla, California) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Lambda clones were screened using the probes synthesized from PCR and primer pairs 5'-AGTACCAAAAGCTGCCTCTG-3' and 5'-TTTCCCCCTCATCTTTTAGC-3' for the rpl5 region, and 5'-GCATGATGATCCGATAATC-3' and 5'-TAGGTTCGTTATCAGCGG-3' for the CW-orf307 region, respectively. Inserts in isolated clones were subcloned into pBluescript SK- after digestion by Bam HI, Sac I, Sal I, or Xba I (Takara-Bio, Otsu, Japan), and sequenced by the CEQ 8000 Genetic analysis system (Beckman Coulter, Fullerton, California). As a result of sequencing 20,513 bp, two mismatches were detected in comparison with pyrosequencing, thus the accuracy of pyrosequencing was estimated as 99.99%.
Expression analysis
Mitochondrial RNA was extracted from calli using the typical phenol/chloroform RNA isolation method. For anthers at the tricellular pollen stage, total RNA was extracted using the same method. Mitochondrial RNA (2.5 μg) was electrophoresed on 1% agarose gel after denaturation by formamide treatment and transferred to a nylon membrane. Primers used to design probes for northern hybridization are listed in Additional file 1.
Abbreviations
- CMS:
-
cytoplasmic male sterility
- InDel:
-
insertion/deletion
- MCAG:
-
Mitochondrial cytoplasmic male sterility associated gene
- PPR:
-
pentatricopeptide repeat
- Rf:
-
restorer of fertility
- SNP:
-
single nucleotide polymorphism
- SSV:
-
segmental sequence variation.
References
McCauley DE, Olson MS: Do recent findings in plant mitochondrial molecular and population genetics have implications for the study of gynodioecy and cytonuclear conflict?. Evolution. 2008, 62: 1013-1025. 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00363.x.
Kubo T, Newton KJ: Angiosperm mitochondrial genomes and mutations. Mitochondrion. 2008, 8: 5-14. 10.1016/j.mito.2007.10.006.
Satoh M, Kubo T, Nishizawa S, Estiati A, Itchoda N, Mikami T: The cytoplasmic male-sterile type and normal type mitochondrial genomes of sugar beet share the same complement of genes of known function but differ in the content of expressed ORFs. Mol Genet Genomics. 2004, 272: 247-256. 10.1007/s00438-004-1058-9.
Unseld M, Marienfeld JR, Brandt P, Brennicke A: The mitochondrial genome of Arabidopsis thaliana contains 57 genes in 366,924 nucleotides. Nat Genet. 1997, 15: 57-61. 10.1038/ng0197-57.
Kubo T, Nishizawa S, Sugawara A, Itchoda N, Estiati A, Mikami T: The complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) reveals a novel gene for tRNA(Cys)(GCA). Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28: 2571-2576. 10.1093/nar/28.13.2571.
Handa H: The complete nucleotide sequence and RNA editing content of the mitochondrial genome of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): comparative analysis of the mitochondrial genomes of rapeseed and Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31: 5907-5916. 10.1093/nar/gkg795.
Sugiyama Y, Watase Y, Nagase M, Makita N, Yagura S, Hirai A, Sugiura M: The complete nucleotide sequence and multipartite organization of the tobacco mitochondrial genome: comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in higher plants. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005, 272: 603-615. 10.1007/s00438-004-1075-8.
Notsu Y, Masood S, Nishikawa T, Kubo N, Akiduki G, Nakazono M, Hirai A, Kadowaki K: The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa L.) mitochondrial genome: frequent DNA sequence acquisition and loss during the evolution of flowering plants. Mol Genet Genomics. 2002, 268: 434-445. 10.1007/s00438-002-0767-1.
Tian X, Zheng J, Hu S, Yu J: The rice mitochondrial genomes and their variations. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140: 401-410. 10.1104/pp.105.070060.
Clifton SW, Minx P, Fauron CM, Gibson M, Allen JO, Sun H, Thompson M, Barbazuk WB, Kanuganti S, Tayloe C: Sequence and comparative analysis of the maize NB mitochondrial genome. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136: 3486-3503. 10.1104/pp.104.044602.
Allen JO, Fauron CM, Minx P, Roark L, Oddiraju S, Lin GN, Meyer L, Sun H, Kim K, Wang C: Comparisons among two fertile and three male-sterile mitochondrial genomes of maize. Genetics. 2007, 177: 1173-1192. 10.1534/genetics.107.073312.
Ogihara Y, Yamazaki Y, Murai K, Kanno A, Terachi T, Shiina T, Miyashita N, Nasuda S, Nakamura C, Mori N: Structural dynamics of cereal mitochondrial genomes as revealed by complete nucleotide sequencing of the wheat mitochondrial genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33: 6235-6250. 10.1093/nar/gki925.
Kubo T, Mikami T: Organization and variation of angiosperm mitochondrial genome. Physiol Plant. 2007, 129: 6-13. 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2006.00768.x.
Schnable PS, Wise RP: The molecular basis of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3: 175-180. 10.1016/S1360-1385(98)01235-7.
Hanson MR, Bentolila S: Interactions of mitochondrial and nuclear genes that affect male gametophyte development. Plant Cell. 2004, 16: S154-169. 10.1105/tpc.015966.
Hack E, Lin C, Yang H, Horner HT: T-URF 13 Protein from Mitochondria of Texas Male-Sterile Maize (Zea mays L.): Its Purification and Submitochondrial Localization, and Immunogold Labeling in Anther Tapetum during Microsporogenesis. Plant Physiol. 1991, 95: 861-870. 10.1104/pp.95.3.861.
Nivison HT, Sutton CA, Wilson RK, Hanson MR: Sequencing, processing, and localization of the petunia CMS-associated mitochondrial protein. Plant J. 1994, 5: 613-623. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.1994.00613.x.
Yamamoto MP, Kubo T, Mikami T: The 5'-leader sequence of sugar beet mitochondrial atp6 encodes a novel polypeptide that is characteristic of Owen cytoplasmic male sterility. Mol Genet Genomics. 2005, 273: 342-349. 10.1007/s00438-005-1140-y.
Yamamoto MP, Shinada H, Onodera Y, Komaki C, Mikami T, Kubo T: A male sterility-associated mitochondrial protein in wild beets causes pollen disruption in transgenic plants. Plant J. 2008, 54: 1027-1036. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03473.x.
Kinoshita T: Gene symbols and information on male sterility. Rice Genet Newsl. 1997, 14: 13-22.
Virmani SS: Heterosis and hybrid rice breeding. Monograph on Theor Appl Genet. 1994, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 22: 1-189.
Itabashi E, Kazama T, Toriyama K: Characterization of cytoplasmic male sterility of rice with Lead Rice cytoplasm in comparison with that with Chinsurah Boro II cytoplasm. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28: 233-239. 10.1007/s00299-008-0625-7.
Iwabuchi M, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K: Processing followed by complete editing of an altered mitochondrial atp6 RNA restores fertility of cytoplasmic male sterile rice. EMBO J. 1993, 12: 1437-1446.
Akagi H, Sakamoto M, Shinjyo C, Shimada H, Fujimura T: A unique sequence located downstream from the rice mitochondrial atp6 may cause male sterility. Curr Genet. 1994, 25: 52-58. 10.1007/BF00712968.
Wang Z, Zou Y, Li X, Zhang Q, Chen L, Wu H, Su D, Chen Y, Guo J, Luo D: Cytoplasmic male sterility of rice with boro II cytoplasm is caused by a cytotoxic peptide and is restored by two related PPR motif genes via distinct modes of mRNA silencing. Plant Cell. 2006, 18: 676-687. 10.1105/tpc.105.038240.
Kazama T, Nakamura T, Watanabe M, Sugita M, Toriyama K: Suppression mechanism of mitochondrial ORF79 accumulation by Rf1 protein in BT-type cytoplasmic male sterile rice. Plant J. 2008, 55: 619-628. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03529.x.
Kojima Y, Ebana K, Fukuoka S, Nagamine T, Kawase M: Development of an RFLP-based rice diversity research set of germplasm. Breed Sci. 2005, 55: 431-440. 10.1270/jsbbs.55.431.
National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences Genebank Global Rice Collection. [http://www.gene.affrc.go.jp/databases-core_collections_wr_en.php]
Shinjo C, Ishimine U, Motomura K: Identification of male strile cytoplasms and fertility restoring genes by seed fertility of F1 hybrids between male strlie and their restore lines of rice. Jpn J Breed. 1982, 32: 126-in Japanese
SOSUI. [http://bp.nuap.nagoya-u.ac.jp/sosui/]
Small ID, Isaac PG, Leaver CJ: Stoichiometric differences in DNA molecules containing the atpA gene suggest mechanisms for the generation of mitochondrial genome diversity in maize. EMBO J. 1987, 6: 865-869.
Small I, Suffolk R, Leaver CJ: Evolution of plant mitochondrial genomes via substoichiometric intermediates. Cell. 1989, 58: 69-76. 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90403-0.
Janska H, Sarria R, Woloszynska M, Arrieta-Montiel M, Mackenzie SA: Stoichiometric shifts in the common bean mitochondrial genome leading to male sterility and spontaneous reversion to fertility. Plant Cell. 1998, 10: 1163-1180. 10.1105/tpc.10.7.1163.
Sandhu AP, Abdelnoor RV, Mackenzie SA: Transgenic induction of mitochondrial rearrangements for cytoplasmic male sterility in crop plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007, 104: 1766-1770. 10.1073/pnas.0609344104.
Huang S, Taylor NL, Narsai R, Eubel H, Whelan J, Millar AH: Experimental analysis of the rice mitochondrial proteome, its biogenesis, and heterogeneity. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149: 719-734. 10.1104/pp.108.131300.
Huang S, Taylor NL, Whelan J, Millar AH: Refining the definition of plant mitochondrial presequences through analysis of sorting signals, N-terminal modifications, and cleavage motifs. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150: 1272-1285. 10.1104/pp.109.137885.
Small ID, Peeters N: The PPR motif - a TPR-related motif prevalent in plant organellar proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000, 25: 46-47. 10.1016/S0968-0004(99)01520-0.
Lurin C, Andres C, Aubourg S, Bellaoui M, Bitton F, Bruyere C, Caboche M, Debast C, Gualberto J, Hoffmann B: Genome-wide analysis of Arabidopsis pentatricopeptide repeat proteins reveals their essential role in organelle biogenesis. Plant Cell. 2004, 16: 2089-2103. 10.1105/tpc.104.022236.
O'Toole N, Hattori M, Andres C, Iida K, Lurin C, Schmitz-Linneweber C, Sugita M, Small I: On the expansion of the pentatricopeptide repeat gene family in plants. Mol Biol Evol. 2008, 25: 1120-1128. 10.1093/molbev/msn057.
Schmitz-Linneweber C, Small I: Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins: a socket set for organelle gene expression. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13: 663-670. 10.1016/j.tplants.2008.10.001.
Bentolila S, Alfonso AA, Hanson MR: A pentatricopeptide repeat-containing gene restores fertility to cytoplasmic male-sterile plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002, 99: 10887-10892. 10.1073/pnas.102301599.
Desloire S, Gherbi H, Laloui W, Marhadour S, Clouet V, Cattolico L, Falentin C, Giancola S, Renard M, Budar F: Identification of the fertility restoration locus, Rfo, in radish, as a member of the pentatricopeptide-repeat protein family. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4: 588-594. 10.1038/sj.embor.embor848.
Koizuka N, Imai R, Fujimoto H, Hayakawa T, Kimura Y, Kohno-Murase J, Sakai T, Kawasaki S, Imamura J: Genetic characterization of a pentatricopeptide repeat protein gene, orf687, that restores fertility in the cytoplasmic male-sterile Kosena radish. Plant J. 2003, 34: 407-415. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01735.x.
Brown GG, Formanova N, Jin H, Wargachuk R, Dendy C, Patil P, Laforest M, Zhang J, Cheung WY, Landry BS: The radish Rfo restorer gene of Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility encodes a protein with multiple pentatricopeptide repeats. Plant J. 2003, 35: 262-272. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01799.x.
Kazama T, Toriyama K: A pentatricopeptide repeat-containing gene that promotes the processing of aberrant atp6 RNA of cytoplasmic male-sterile rice. FEBS Lett. 2003, 544: 99-102. 10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00480-0.
Komori T, Ohta S, Murai N, Takakura Y, Kuraya Y, Suzuki S, Hiei Y, Imaseki H, Nitta N: Map-based cloning of a fertility restorer gene, Rf-1, in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J. 2004, 37: 315-325. 10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01961.x.
Akagi H, Nakamura A, Yokozeki-Misono Y, Inagaki A, Takahashi H, Mori K, Fujimura T: Positional cloning of the rice Rf-1 gene, a restorer of BT-type cytoplasmic male sterility that encodes a mitochondria-targeting PPR protein. Theor Appl Genet. 2004, 108: 1449-1457. 10.1007/s00122-004-1591-2.
Klein RR, Klein PE, Mullet JE, Minx P, Rooney WL, Schertz KF: Fertility restorer locus Rf1 [corrected] of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein not present in the colinear region of rice chromosome 12. Theor Appl Genet. 2005, 111: 994-1012. 10.1007/s00122-005-2011-y.
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC: Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res. 1998, 8: 1113-1130.
Geddy R, Brown GG: Genes encoding pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) proteins are not conserved in location in plant genomes and may be subject to diversifying selection. BMC Genomics. 2007, 8: 130-10.1186/1471-2164-8-130.
Kato H, Tezuka K, Feng YY, Kawamoto T, Takahashi H, Mori K, Akagi H: Structural diversity and evolution of the Rf-1 locus in the genus Oryza. Heredity. 2007, 99: 516-524. 10.1038/sj.hdy.6801026.
Fujii S, Toriyama K: Molecular mapping of the fertility restorer gene for ms-CW-type cytoplasmic male sterility of rice. Theor Appl Genet. 2005, 111: 696-701. 10.1007/s00122-005-2054-0.
Watanabe Y: Establishment of cytoplasmic and genetic male-sterile lines by means of Indica-Japonica cross. Oryza Cuttack. 1971, 8 (Suppl2): 9-16.
Katsuo K, Mizushima U: Studies on the cytoplasmic difference among rice varieties, Oryza sativa L. 1. On the fertility of hybrids obtained reciprocally between cultivated and wild varieties. Japan J Breed. 1958, 8: 1-5.
Toriyama K, Hinata K: Anther culture application to breeding of a restorer for a male-sterile cytoplasm of wild rice [ms-CW]. Japan J Breed. 1987, 37: 469-473.
Tanaka N, Fujita M, Handa H, Murayama S, Uemura M, Kawamura Y, Mitsui T, Mikami S, Tozawa Y, Yoshinaga T: Proteomics of the rice cell: systematic identification of the protein populations in subcellular compartments. Mol Genet Genomics. 2004, 271: 566-576. 10.1007/s00438-004-1002-z.
Kanazawa A, Sakamoto W, Nakagahra M, Kadowaki K, Tsutsumi N, Tano S: Distribution and quantitative variation of mitochondrial plasmid-like DNAs in cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Jpn J Genet. 1992, 67: 309-319. 10.1266/jjg.67.309.
Miyata S, Kanazawa A, Tsutsumi N, Sano Y, Hirai A: Polymorphic distribution and molecular diversification of mitochondrial plasmid-like DNAs in the genus Oryza. Jpn J Genet. 1995, 70: 601-614. 10.1266/jjg.70.601.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Tools/]
Ohtsubo Y, Ikeda-Ohtsubo W, Nagata Y, Tsuda M: A graphical user interface for DNA sequence comparison. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008, 9: 376-10.1186/1471-2105-9-376.
European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. [http://emboss.sourceforge.net/index.html]
Genemark.hmm for the Prokaryotes v2.4. [http://opal.biology.gatech.edu/GeneMark/gmhmm2_prok.cgi]
Stamatakis A: RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinfomatics. 2008, 22: 2688-10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446.
Murray MG, Thompson WF: Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980, 8: 4321-4325. 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Special Research on Priority Areas (No. 18075002) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture, Japan and partly supported by the program for promotion of Basic and Applied Researches for Innovations in Bio-oriented Industry (BRAIN). We thank Ms. Yukiko Ikeda for her excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authors' contributions
SF designed the study, carried out the experiments, performed sequence analysis, and drafted the manuscript. TK and MY participated in the experiments. KT conceived and supervised the work and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
12864_2009_2803_MOESM2_ESM.XLS
Additional file 2: Comparison of SNP genotypes among japonica mitochondrial genomes Nipponbare, PA64S, and indica 93-11. Nucleotide positions in 93-11 are displayed. Genotypes in CMS are: j, japonica type; 9, 93-11 type; n, Nipponbare type; p, PA64S type; cms, CMS specific; -, no syntenic region present in the CMS lines. SNPs in the genic regions are given in the last column. (XLS 24 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM3_ESM.XLS
Additional file 3: Comparison of InDel and segmental sequence variation (SSV) genotypes among japonica mitochondrial genomes Nipponbare, PA64S, and indica 93-11. Nucleotide positions in 93-11 are displayed. Genotypes are: j, japonica type; 9, 93-11 type; n, Nipponbare type; p, PA64S type; c, CMS specific. Sequence variations in the genic regions are given in the last column. *Nipponbare vs 93-11 InDels detected in the genomic study by Tian et al. (2006) [9]. Nucleotide positions in 93-11 are indicated. **Only CW-CMS and LD-CMS genomes retained the same sequences in this region, and other genomes possessed different sequences. (XLS 18 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM4_ESM.PDF
Additional file 4: Phylogenetic relationship of the five rice mitochondrial genomes. All of the sequence variations were used to generate the maximum-likelihood inference-based dendrogram. Bar indicates the rate of nucleotide substitution per site. (PDF 64 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM5_ESM.XLS
Additional file 5: PCR amplification of the CMS unique genomic structure and genes. PCR amplification positive (+) and negative (-) in each rice core-collection accession for each primer pair. * Refer to Figure 2, Additional files 8 and 11 for information on the primers. ** Refer to [28] for details. (XLS 37 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM6_ESM.PDF
Additional file 6: Transcript detection of genes involved in the evolution of the CW- orf307 locus. Transcripts were detected by northern blot analysis using mitochondrial RNA extracted from calli. Genes involved in the rpl5 region (orf165, orf284, cox1, pseudo-rps14, rpl5, and rps2) and genes involved in CW-orf307 (atp1, orf288, orf224, cox2, and trnR). C-terminal region of rps2 was probed to avoid detecting partial rps2 present in the rpl5 locus. Also, C-terminal orf288, orf224, and cox2 were probed to avoid detecting the fragments in the CW-orf307 transcript. The transcript abundance of atp6 was used as the internal control, and the atp6 transcript level reflected the ribosomal RNA band intensities detected by ethidium bromide staining. R, CWR (The restorer line carrying Rf17 and CW cytoplasm); C, CW-CMS line; T, Taichung 65. (PDF 843 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM7_ESM.PDF
Additional file 7: Validation of contig linkage by PCR analysis. Lane numbers refer to primer pairs in Additional file 8. (PDF 389 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM8_ESM.XLS
Additional file 8: Information on the primers used for the PCR analysis to validate the linkage between the contigs. Information on the primers used for the PCR analysis in Additional file 7. (XLS 22 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM9_ESM.PDF
Additional file 9: Possible linkage of the contigs validated by PCR analysis for the CW-CMS mitochondrial genome. Numbers within the arrows indicate the contig accession numbers, whereas numbers above indicate the sequence depth of each contig. The yellow color indicates the contigs that appear twice in our master circle, and the blue color indicates the contigs that appear three times. Capital letters represent contig linkages. (PDF 208 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM10_ESM.PDF
Additional file 10: Possible linkages of the contigs validated by PCR analysis for the LD-CMS mitochondrial genome. See the legend for Additional file 9 for descriptions. (PDF 260 KB)
12864_2009_2803_MOESM11_ESM.XLS
Additional file 11: Order and position of the contigs aligned in the master circles. Sequences in this order were deposited to DDBJ (CW-CMS, AP011076; LD-CMS, AP011077). (XLS 23 KB)
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, S., Kazama, T., Yamada, M. et al. Discovery of global genomic re-organization based on comparison of two newly sequenced rice mitochondrial genomes with cytoplasmic male sterility-related genes. BMC Genomics 11, 209 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-209
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-11-209