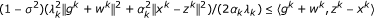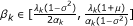Abstract
In this paper, a projective splitting method for solving a class of generalized mixed variational inequalities is considered in Hilbert spaces. We investigate a general iterative algorithm, which consists of a splitting proximal point step followed by a suitable orthogonal projection onto a hyperplane. Moreover, in our splitting algorithm, we only use the individual resolvent mapping (I + μ k ∂f)-1 and never work directly with the operator T +∂f, where μ k is a positive real number, T is a set-valued mapping and ∂f is the sub-differential of function f. We also prove the convergence of the algorithm for the case that T is a pseudomonotone set-valued mapping and f is a non-smooth convex function.
2000 Mathematics Subject Classification: 90C25; 49D45; 49D37.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Let X be a nonempty closed convex subset of a real Hilbert space H, T : X → 2H be a set-valued mapping and f : H → (- ∞, +∞] be a lower semi-continuous (l.s.c) proper convex function. We consider a generalized mixed variational inequality problem (GMVIP): find x* ∈ X such that there exists w* ∈ T(x*) satisfying

The GMVIP (1.1) has enormous applications in many areas such as mechanics, optimization, equilibrium, etc. For details, we refer to [1–3] and the references therein. It has therefore been widely studies by many authors recently. For example, by Rockafellar [4], Tseng [5], Xia and Huang [6] and the special case (f = 0) was studied by Crouzeix [7], Danniilidis and Hadjisavvas [8] and Yao [9].
A large variety of problems are special instances of the problem (1.1). For example, if T is the sub-differential of a finite-valued convex continuous function φ defined on Hilbert space H, then the problem (1.1) reduces to the following non-differentiable convex optimization problem:

Furthermore, if T is single-valued and f = 0, then the problem (1.1) reduces to the following classical variational inequality problem: find x* ∈ X such that, for all y ∈ X,

Many methods have been proposed to solve classical variational inequalities (1.2) in finite and infinite dimensional spaces. The simple one among these is the projection method which has been intensively studied by many authors (see, e.g., [10–14]). However, the classical projection method does not work for solving the GMVIP (1.1). Therefore, it is worth studying other implementable methods for solving the problem (1.1).
Algorithms that can be applied for solving the problem (1.1) or one of its variants are very numerous. For the case when T is maximal monotone, the most famous method is the proximal method (see, e.g., Rockafellar [4]). Splitting methods have also been studied to solve the problem (1.1). Here, the set-valued mapping T and ∂(f+ψ X ) play separate roles, where ψ X denotes the indicator function associated with X (i.e., ψ X (x) = 0 if x ∈ X and +∞ otherwise) and ∂(f + ψ X ) denotes the sub-differential of the convex function f + ψ X . The simplest splitting method is the forward-backward scheme (see, e.g., Tseng [5]), in which the iteration is given by

where {μ k } is a sequence of positive real numbers. Cohen [15] developed a general algorithm framework for solving the problem (1.1) in Hilbert space H, based on the so-called auxiliary problem principle. The corresponding method is a generalization of the forward-backward method. Due to the auxiliary problem principle Cohen [15], Salmon et al. [16] developed a bundle method for solving the problem (1.1).
For solving the GMVIP (1.1), some authors assumed that T is upper semi-continuous and mono-tone(or some other stronger conditions, e.g., strictly monotone, paramonotone, maximal monotone, strongly monotone). Moreover, their methods fail to provide convergence under weaker conditions than the monotonicity of T. So, it is a significant work that how to solve the problem (1.1) when T fails to be monotone. This is one of the main motivations of this paper.
On the other hand, the GMVIP (1.1) can be expressed as an inclusion form as follows: find x* ∈ X such that

Thus, the problem (1.1) is a special case of the following inclusion problem:

where A and B are set-valued operators on real Hilbert space H.
The algorithms for solving the inclusion (1.4) have an extensive literature. The simplest one among these is the splitting method. All splitting methods can be essentially divided into three classes: Douglas/Peaceman-Rachford class (see, e.g., [17, 18]), the double-backward class (see, e.g., [19]), and the forward-backward class (see, e.g., [20, 21]). Therefore, one natural problem is whether the splitting method can be developed for solving (1.1). This is another main motivation of this paper.
In this paper, we provide a projective splitting method for solving the GMVIP (1.1) in Hilbert spaces. Our iterative algorithm consists of two steps. The first step of the algorithm in generating a hyperplane separating z k from the solution set of problem (1.1). The second step is then to project z k onto this hyperplane (with some relaxation factor). We first prove that the sequences {xk} and {zk} are weakly convergent. We also prove that the weak limit point of {xk} is the same as the weak limit point of {zk}. Moreover, we obtain that the weak limit point of these sequences is a solution of the problem (1.1) under the conditions that the set-valued mapping T is pseudomonotone with respect to f and the function f is convex.
2 Preliminaries
For a convex function f : H → (-∞, +∞], let domf = {x ∈ H : f(x) < ∞} denote its effective domain, and let

denote its sub-differential.
Suppose that X ⊂ H is a nonempty closed convex subset and

is the distance from z to X. Let P X [z] denote the projection of z onto X, that is, P X [z] satisfies the condition

The following well-known properties of the projection operator will be used later in this paper.
Proposition 2.1. [22] Let X be a nonempty closed convex subset in H, the following properties hold:
-
(i)
〈x - y, x - P X [x]〉 ≥ 0, for all x ∈ H and y ∈ X;
-
(ii)
〈P X [x] - x, y - P X [x]〉 ≥ 0, for all x ∈ H and y ∈ X;
-
(iii)
||P X [x] - P X [y]|| ≤ ||x - y||, for all x, y ∈ H.
Definition 2.1. Let X be a nonempty subset of a Hilbert space H, and let f : X → (-∞, +∞] a function. A set-valued mapping T : X → 2H is said to be
-
(i)
monotone if

-
(ii)
pseudomonotone with respect to f if for any x, y ∈ X, u ∈ T(x), v ∈ T(y),
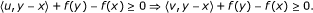
We will use the following Lemmas.
Lemma 2.1. [23] Let D be a nonempty convex set of a topological vector space E and let ϕ : D × D → ℝ∪{+∞} be a function such that
-
(i)
for each v ∈ D, u → ϕ(v, u) is upper semi-continuous on each nonempty compact subset of D;
-
(ii)
for each nonempty finite set {v1, · · ·, v m } ⊂ D and for each
 , max1≤i≤mϕ(v
i
, u) ≥ 0;
, max1≤i≤mϕ(v
i
, u) ≥ 0; -
(iii)
there exists a nonempty compact convex subset D0 of D and a nonempty compact subset K of D such that, for each u ∈ D\K, there is v ∈ co(D0 ∪ {u}) with ϕ(v, u) < 0.
Then, there exists  such that
such that  for all v ∈ D.
for all v ∈ D.
Lemma 2.2. [24, p. 119] Let X, Y be two topological spaces, W : X × Y → ℝ be an upper semi-continuous function, and G : X → 2Y be upper semi-continuous at x0 such that G(x0) is compact. Then, the marginal function V defined on X by

is upper semi-continuous at x0.
Lemma 2.3. [25] Let σ ∈ [0, 1) and  . If v = u+ξ, where ||ξ||2 ≤ σ2(||u||2+||v||2), then
. If v = u+ξ, where ||ξ||2 ≤ σ2(||u||2+||v||2), then
-
(i)
〈u, v〉 ≥ (||u||2 + ||v||2)(1 - σ2)/2;
-
(ii)
(1 - μ)||v|| ≤ (1 - σ2)||u|| ≤ (1 + μ)||v||.
3 Projective splitting method
ψ X : H → (- ∞, +∞] be the indicator function associated with X. Choose three positive sequences {λ k > 0}, {α k } ∈ (0, 2) and {ρ k } ∈ (0, 2). Select a fixed relative error tolerance σ ∈ [0, 1). We first describe a new projective splitting algorithm for the GMVIP (1.1), and then give some preliminary results on the algorithm.
Algorithm 3.1.
Step 0. (Initiation) Select initial z0 ∈ X. Set k = 0.
Step 1. (Splitting proximal step) Find xk ∈ X such that


where the residue ξk ∈ H is required to satisfy the following condition:

Step 2. (Projection step) If gk + wk = 0, then STOP; otherwise, take

Step 3. Set  .
.
Step 4. Let k = k + 1 and return to Step 1.
In this paper, we focus our attention on obtaining general conditions ensuring the convergence of {zk}k∈Nand {xk}k∈Ntoward a solution of problem (1.1), under the following hypotheses on the parameters:


To motivate Algorithm 3.1, we note that (3.1) implies xk = (I + λ
k
∂f)-1(zk + λ
k
ξ
k
), and that the operator (I + λ
k
∂f)-1 is everywhere defined and single-valued. Rearranging (3.1) and (3.2), one has  and
and  . Algorithm 3.1 is a true splitting method for problem (1.1), in that it only uses the individual resolvent mapping (I + λ
k
∂f)-1, and never works directly with the operator ∂f + T. The existence of xk ∈ X and wk ∈ T(xk) such that (3.1)-(3.2) will be proved in the following Theorem 3.1.
. Algorithm 3.1 is a true splitting method for problem (1.1), in that it only uses the individual resolvent mapping (I + λ
k
∂f)-1, and never works directly with the operator ∂f + T. The existence of xk ∈ X and wk ∈ T(xk) such that (3.1)-(3.2) will be proved in the following Theorem 3.1.
Substituting (3.1) into (3.2) and simplifying, we obtain

This method is the so-called inexact hybrid proximal algorithm for solving problem (1.1). Obvious that problem (3.7) is solved only approximately and the residue ξk ∈ H satisfying (3.3). There are at least two reasons for dealing with the proximal algorithm (3.7). First, it is generally impossible to find an exact value for xk given by (3.1) and (3.2). Particularly when T is nonlinear; second, it is clearly inefficient to spend too much effort on the computation of a given iterate zk when only the limit of the sequence {xk} has the desired properties.
It is easy to see that (3.4) is a projection step because it can be written as  , where P
K
: H → K is the orthogonal projection operator onto the half-space K = {z ∈ H : 〈gk + wk, z - xk〉 ≤ 0}. In fact, by (3.4) we have
, where P
K
: H → K is the orthogonal projection operator onto the half-space K = {z ∈ H : 〈gk + wk, z - xk〉 ≤ 0}. In fact, by (3.4) we have  . Then for each y ∈ K, we deduce that
. Then for each y ∈ K, we deduce that

By Proposition 2.1, we know that  . By pseudomonotonicity of T with respect to f and Theorem 4.1(ii) below, the hyperplane K separates the current iterate zk from the set S = {x ∈ H : 0 ∈ ∂f(x) + T(x)}. Thus, in Algorithm 3.1, the splitting proximal iteration is used to construct this separation hyperplane, the next iterate zk+1is then obtained by a trivial projection of zk, which is not expensive at all from a numerical point of view.
. By pseudomonotonicity of T with respect to f and Theorem 4.1(ii) below, the hyperplane K separates the current iterate zk from the set S = {x ∈ H : 0 ∈ ∂f(x) + T(x)}. Thus, in Algorithm 3.1, the splitting proximal iteration is used to construct this separation hyperplane, the next iterate zk+1is then obtained by a trivial projection of zk, which is not expensive at all from a numerical point of view.
Now, we will prove that the sequence {xk} is well defined and so is the sequence {zk}. Note that if xk satisfies (3.1)-(3.2) together with (3.3), with σ = 0, then xk always satisfies these conditions with any σ ∈ [0, 1). Since σ = 0 also implies that the error term ξk vanishes, existence of xk for ξk = 0 is enough to ensure the existence of ξk ≠ 0. So in the following theorem 3.1, we assume that ξk = 0.
Theorem 3.1. Let X be a nonempty closed convex subset of a Hilbert space H, and let f : X → (- ∞, + ∞] be a l.s.c proper convex function. Assume that T : X → 2H is pseudomonotone with respect to f and upper semi-continuous from the weak topology to the weak topology with weakly compact convex values. If the parameter α k , λ k > 0 and solution set of problem (1.1) is nonempty, then for each given zk ∈ X, there exist xk ∈ X and wk ∈ T(xk) satisfying (3.1)-(3.2).
Proof. For each given zk ∈ X and ξk = 0, it follows from (3.1) and (3.2) that,

where gk ∈ ∂[f + ψ X ](xk) and wk ∈ T (xk). (3.8) is equivalent to the following inequality:

So we consider the following variational inequality problem: find xk ∈ X such that for each y ∈ X,

For the sake of simplicity, we rewrite the problem (3.9) as follows: find  such that
such that

For each fixed k, define ϕ : X × X → (- ∞, + ∞] by

Since T is upper semi-continuous from the weak topology to weak topology with weakly compact values, by Lemma 2.2, we know that the mapping V(x) = supw∈T(x)〈w, y - x〉 is upper semi-continuous from the weak topology to weak topology. Noting that f is a l.s.c convex function, for each y ∈ X, the function x α ϕ(y, x) is weakly upper semi-continuous on X. We now claim that ϕ(y, x) satisfies condition (ii) of Lemma 2.1. If it is not, then there exists a finite subset {y1, y2, · · ·, ym} of X and  (δ
i
≥ 0, i = 1, 2, · · ·, m with
(δ
i
≥ 0, i = 1, 2, · · ·, m with  ) such that ϕ(yi, x) < 0 for all i = 1, 2, · · ·, m. Thus,
) such that ϕ(yi, x) < 0 for all i = 1, 2, · · ·, m. Thus,

and so

By the convexity of f, we get

which is a contradiction. Hence, condition (ii) of Lemma 2.1 holds.
Now, let  be a solution of problem (1.1). Then, there exists
be a solution of problem (1.1). Then, there exists  such that
such that

By the pseudomonotonicity of T with respect to f, for all x ∈ X,

and so

On the other hand, we have

We consider the following equation in ℝ:

It is obviously that equation (3.12) has only one positive solution  . If the real number x > r, we have
. If the real number x > r, we have

Thus, when  , we obtain
, we obtain

Let

Then,  and X0 are both weakly compact convex subsets of Hilbert space H. By (3.11) and (3.13), we deduce that for each x ∈ X\X0, there exists a
and X0 are both weakly compact convex subsets of Hilbert space H. By (3.11) and (3.13), we deduce that for each x ∈ X\X0, there exists a  such that
such that  . Hence, all conditions of Lemma 2.1 are satisfied. Now, Lemma 2.1 implies that there exists a
. Hence, all conditions of Lemma 2.1 are satisfied. Now, Lemma 2.1 implies that there exists a  such that
such that  for all y ∈ X. That is,
for all y ∈ X. That is,

Therefore,  is a solution of the problem (3.9). By the assumptions on T, we know that there exists wk ∈ T(xk) such that
is a solution of the problem (3.9). By the assumptions on T, we know that there exists wk ∈ T(xk) such that

Thus, xk ∈ X and wk ∈ T(xk) such that (3.1) and (3.2) hold. This completes the proof.
4 Preliminary results for iterative sequence
In what follows, we adopt the following assumptions (A1)-(A4):
(A1) The solution set S of the problem (1.1) is nonempty (see, for example, [24]).
(A2) f : H → (- ∞, + ∞] is a proper convex l.s.c function with X ⊂ int(domf).
(A3) T : X → 2H is a pseudomonotone set-valued mapping with respect to f on X and upper semi-continuous from the weak topology to the weak topology with weakly compact convex values.
(A4) A fixed relative error tolerance σ ∈ [0, 1). Three positive sequences {λ k }, {ρ k } satisfy (3.5),(3.6) and α k ∈ (0, 2).
Remark 4.1. Since f is a proper convex l.s.c function, f is also weakly l.s.c and continuous over int(dom f)(see [26]).
Remark 4.2. It is obviously that monotone mapping is pseudomonotone with respect to a function f, but the converse is not true in general as illustrated by the following set-valued mapping that satisfies (A3).
EXAMPLE 4.1. Let H = ℝ, T : ℝ → 2ℝ be a set-valued mapping defined by:

Define f(x) = x, ∀x ∈ ℝ. We have the following conclusions:
-
(1)
T is upper semi-continuous with compact convex values.
-
(2)
T is not a monotone mapping. For example, let x = 2,
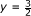 ,
, 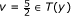 and u = 2 ∈ T(x), we have 〈v - u, y - x〉 < 0.
and u = 2 ∈ T(x), we have 〈v - u, y - x〉 < 0. -
(3)
T is pseudomonotone mapping with respect to f. In fact, ∀x, y ∈ ℝ and ∀u ∈ T(x), if 〈u, y - x〉 + f(y) - f(x) ≥ 0, we have 〈u, y - x〉 + x - y ≥ 0. So, if y > x, we obtain that 〈v, y - x〉 ≥ y - x > 0 for all v ≥ 1. By the definition of T, we have 〈v, y - x〉 + f(y) - f(x) ≥ 0, for all v ∈ T(y). If y < x, 〈u, y - x〉 + x - y ≥ 0 implies that u ≤ 1. Since u ∈ T(x), we have x ≤ 1 and then y < 1. By the definition of T, we deduce that v = T(y) = 1 and then 〈v, y - x〉 +x - y ≥ 0, for all v ∈ T(y). That is 〈v, y - x〉 + f(y) - f(x) ≥ 0, ∀v ∈ T(y). If y = x, we always have 〈v, y - x〉 + f(y) - f(x) ≥ 0, for all v ∈ T(y). So, we conclude that T is a pseudomonotone mapping with respect to f.
Now, we give some preliminary results for the iterative sequence generated by Algorithm 3.1 in a Hilbert space H. First, we state some useful estimates that are direct consequences of the Lemma 2.3.
Theorem 4.1 Under (3.1)-(3.4), if  , then we have:
, then we have:
-
(i)
λ k (1 - μ)||gk + wk|| ≤ (1 - σ2)α k ||xk - zk|| ≤ λ k (1 + μ)||gk + wk||;
-
(ii)
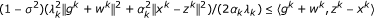
;
-
(iii)
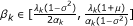
.
Proof. We apply Lemma 2.3 to v = gk + wk, u = α k (zk - xk)/λ k to get (i) and (ii). For (iii), using first Cauchy-Schwarz inequality and then (i), we get

On the other hand, (ii) implies that

this leads to (iii).
Remark 4.4. Suppose that gk + wk = 0 in Step 2. As -wk ∈ ∂f(xk), this implies that

That is, xk is a solution of problem (1.1). On the other hand, assuming gk + wk ≠ 0, Theorem 4.1(ii) yields 〈gk + wk, zk - xk〉 > 0. By the pseudomonotonicity of T with respect to f, it is easy to see that for all x* ∈ S (S denotes the solution set of problem (1.1)),

Using the fact that gk ∈ ∂f(xk), we deduce

Thus, the hyperplane {z ∈ H : 〈gk + wk, z - xk〉 = 0} strictly separates zk from S. The latter is the geometric motivation for the projection step (3.4).
Theorem 4.2. Suppose that x* ∈ S and the sequence {ρ k } satisfy (3.6), then

and so the sequence {||x* - zk||2} is convergent (not necessarily to 0). Moreover,

Proof. By Step 3, we have

It follows from (4.1) and x* ∈ S that

Since  , by Proposition 2.1(ii), we deduce that
, by Proposition 2.1(ii), we deduce that

So

By (3.6), we obtain that

Thus, the sequence {||x* - zk||2} is convergent. Let L∞ be the limit of {||x* - zk||2}.
Now, we prove that (4.3) holds. It follows from (3.6) and (4.2) that

(4.4) implies that

and then  holds. On the other hand,
holds. On the other hand,  , so that we obtain
, so that we obtain  . This completes the proof.
. This completes the proof.
Theorem 4.3. Suppose that assumption (A4) holds, then there exists some constant ζ > 0 such that

Proof. By Theorem 4.1(ii), we have

Since λ k ∈ [λ1, λ2] and α k ∈ (0, 2),

This completes the proof.
Theorem 4.4. Suppose that assumption (A4) holds, then

Proof. It follows from (3.4) and (4.5) that, for all k for which gk + wk ≠ 0,

which clearly also holds for k satisfying gk + wk = 0. By (4.3) and (4.7), we have

This completes the proof.
5 Convergence analysis
We now study the convergence of Algorithm 3.1.
Theorem 5.1. Suppose that the sequence {xk} generated by Algorithm 3.1 is finite. Then, the last term is a solution of the problem (1.1).
Proof. If the sequence is finite, then it must stop at Step 2 for some xk. In this case, we have gk + wk = 0. By Remark 4.4, we know that xk ∈ X is a solution of problem (1.1). This completes the proof.
From now on, we assume that the sequence {xk} generated by Algorithm 3.1 is infinite and so is the sequence {zk}.
Theorem 5.2. Let {xk} and {zk} be sequences generated by Algorithm 3.1 under assumptions (A1)-(A4). Then, {xk} and {zk} are bounded. Moreover, {xk} and {zk} have the same weak accumulation points.
Proof. It follows from Theorem 4.2 that the sequence {zk} is bounded. Using Theorem 4.4 and Theorem 4.1(i), we know that

and so

By the boundedness of the sequence {zk}, we obtain that the sequence {xk} is bounded. Moreover, (5.1) implies that the two sequences {xk} and {zk} have the same weak accumulation points. This completes the proof.
Theorem 5.3. Suppose that assumptions (A1)-(A4) hold. Then, every weak accumulation point of the sequence {xk} generated by Algorithm 3.1 is a solution of problem (1.1). Moreover, every weak accumulation point of the sequence {zk} generated by Algorithm 3.1 is also a solution of problem (1.1)
Proof. Let  be a weak accumulation point of {xk}, we can extract a subsequence that weakly converges to
be a weak accumulation point of {xk}, we can extract a subsequence that weakly converges to  . Without loss of generality, let us suppose that
. Without loss of generality, let us suppose that  . It is obvious that
. It is obvious that  . By (5.1), we have
. By (5.1), we have  .
.
Now, we prove each weak accumulation point of {xk} is a solution of the problem (1.1). By  and gk ∈ ∂f(xk), we deduce that for each y ∈ X,
and gk ∈ ∂f(xk), we deduce that for each y ∈ X,

where wk ∈ T(xk). It follows that

By Theorem 4.1(iii) and (A4), we have

For each fixed y ∈ X, (5.3) implies that

It follows from (5.4), (4.3) and the boundedness of {xk} that

On the other hand, by assumptions (A2) and (A3), Lemma 2.2 implies that V(x): = supw∈T(x)[〈w, y - x〉 + f(y) - f(x)] is a weak upper semi-continuous function. Using the fact  (weakly), we have
(weakly), we have

and so

By (5.2), (5.5) and (5.6),

Using assumption (A3), we know that there exists  such that
such that

That is,  is a solution of problem (1.1). This completes the proof.
is a solution of problem (1.1). This completes the proof.
The following uniqueness argument just given closely follows the one of Martinet [27] (also see Rockafellar [4]), but we give the proof for the convenience of the reader.
Theorem 5.4. Suppose that assumptions (A1)-(A4) hold. Then, the sequence {zk} generated by Algorithm 3.1 has a unique weak accumulation point, thus, {zk} is weakly convergent and so does the sequence {xk}.
Proof. For each x* ∈ S, it follows from Theorem 4.2 that the sequence {||zk - x*||2} converges (not necessarily to 0). Now, we prove that the sequence {zk} has a unique weak accumulation point and so does the sequence {xk}. Existence of weak accumulation points of {zk} follows from Theorem 5.2. Let  and
and  be two weak accumulation points of {zk} and
be two weak accumulation points of {zk} and  ,
,  be two subsequences of {zk} that weakly converge to
be two subsequences of {zk} that weakly converge to  ,
,  respectively. By Theorem 5.3, we know that
respectively. By Theorem 5.3, we know that  ,
,  . Then, the sequences
. Then, the sequences  and
and  are convergent. Let
are convergent. Let  ,
,  and
and  . Then,
. Then,

and

Take limit in (5.7) as j → ∞ and (5.8) as i → ∞, observing that the inner products in the right hand sides of (5.7) and (5.8) converge to 0 because  ,
,  are weak limits of
are weak limits of  ,
,  respectively, and get, using the definitions of ξ, η, γ,
respectively, and get, using the definitions of ξ, η, γ,


From (5.9) and (5.10), we get ξ - η = γ = η - ξ, which implies γ = 0, i.e.,  . It follows that all weak accumulation points of {zk} coincide, i.e., {zk} is weakly convergent. This completes the proof.
. It follows that all weak accumulation points of {zk} coincide, i.e., {zk} is weakly convergent. This completes the proof.
References
Cohen G: Nash equilibria: gradient and decomposition algorithms. Large Scale Syst 1987, 12: 173–184.
Konnov I: A combined relaxation method for a class of nonlinear variational inequalities. Optimization 2002, 51: 127–143. 10.1080/02331930211990
Panagiotopoulos P, Stavroulakis G: New types of variational principles based on the notion of quasidifferentiablity. Acta Mech 1994, 94: 171–194.
Rockafellar RT: Monotone operators and the proximal point algorithm. SIAM J Control Optim 1976, 14: 877–898. 10.1137/0314056
Tseng P: Applications of a splitting algorithm to decomposition in convex programming and variational inequalities. SIAM J Control Optim 1991, 29: 119–138. 10.1137/0329006
Xia FQ, Huang NJ: A projected subgradient method for solving generalized mixed variational inequalities. Oper Res Lett 2008, 36: 637–642. 10.1016/j.orl.2008.03.007
Crouzeix JP: Pseudomonotone variational inequality problems: existence of solutions. Math Program 1997, 78: 305–314.
Danniilidis A, Hadjisavvas N: Coercivity conditions and variational inequalities. Math Program 1999, 86: 433–438. 10.1007/s101070050097
Yao JC: Multivalued variational inequalities with K-pseudomonotone operators. J Optim Theory Appl 1994, 83: 391–403. 10.1007/BF02190064
Facchinei F, Pang JS: Finite Dimensional Variational Inequalities and Complementarity Problems. Springer-Verlag, New York; 2003.
He YR: A new double projection algorithm for variational inequalities. J Comput Appl Math 2006, 185: 166–173. 10.1016/j.cam.2005.01.031
Harker PT, Pang JS: Finite dimensional variational inequality and nonlinear complementarity problems: a survey of theory, algorithms and applications. Math Programm 1990, 48: 161–220. 10.1007/BF01582255
Marcotte P: Application of Khobotov's algorithm to variational inequalities and network equilibrium. Inf Syst Oper Res 1991, 29: 258–270.
Solodov MV, Svaiter BF: A new projection method for variational inequality problems. SIAM J Control Optim 1999, 37: 765–776. 10.1137/S0363012997317475
Cohen G: Auxiliary problem principle extended to variational inequalities. J Optim Theory Appl 1988, 49: 325–333.
Salmon G, Strodiot JJ, Nguyen VH: A bundle method for solving variational inequalities. SIAM J Optim 2004, 14: 869–893. 10.1137/S1052623401384096
Eckstein J, Bertsekas DP: On the Douglas-Rachford splitting method and the proximal point algorithm for maximal monotone operators. Math Program 1992, 55: 293–318. 10.1007/BF01581204
Lions PL, Mercier B: Splitting algorithms for the sum of two nonlinear operators. SIAM J Numer Anal 1979, 16: 964–979. 10.1137/0716071
Bauschke HH, Combettes PL, Reich S: The asymptotic behavior of the composition of two resolvents. Nonlinear Anal 2005, 60: 283–301.
Gabay D: Applications of the method of multipliers to variational inequalities. In Augmented Lagrangian Methods: Applications to the Solution of Boundary Value Problems. Volume Chap IX. Edited by: Fortin M, Glowinski R. North-Holland, Amsterdam; 1983:299–340.
Tseng P: A modified forward-backward splitting method for maximal monotone mapping. SIAM J Control Optim 2000, 38: 431–446. 10.1137/S0363012998338806
Polyak BT: Introduction to Optimization. Optimization Software, New York; 1987.
Ding XP, Tan KK: A minimax inequality with application to the existence of equilibrium point and fixed point theorems. Colloquium Math 1992, 63: 233–247.
Aubin JP, Ekeland I: Applied Nonlinear Analysis. Wiley, New York; 1984.
Solodov MV, Svaiter BF: A unified framework for some inexact proximal point algorithms. Numer Funct Anal Optim 2001, 22: 1013–1035. 10.1081/NFA-100108320
Ekeland I, Temam R: Convex Analysis and Variational Inequalities. North-Holland, Amsterdam; 1976.
Martinet B: Régularisation d'inéquations variationelles par approximations successives. Rev Francaise Informat Recherche Opérationnelle 1970, 4: 154–158.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Professor Kun-Quan Lan and the referees for their valuable comments and suggestions leading to the improvement of this paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (10671135), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20105134120002), the Application Foundation Fund of Sichuan Technology Department of China (2010JY0121), the NSF of Sichuan Education Department of China (09ZA091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
Both authors contributed equally to this work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Fq., Zou, Yz. A projective splitting algorithm for solving generalized mixed variational inequalities. J Inequal Appl 2011, 27 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1029-242X-2011-27
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1029-242X-2011-27






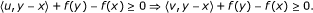
 , max1≤i≤mϕ(v
i
, u) ≥ 0;
, max1≤i≤mϕ(v
i
, u) ≥ 0;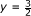 ,
, 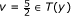 and u = 2 ∈ T(x), we have 〈v - u, y - x〉 < 0.
and u = 2 ∈ T(x), we have 〈v - u, y - x〉 < 0.