Abstract
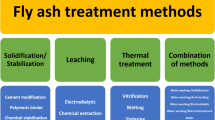
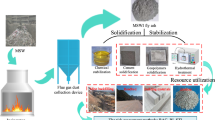
Incineration is widely adopted in municipal solid waste management, which produces large amounts of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash. The harmless treatment of MSWI fly ash requires the appropriate disposal of heavy metals and dioxins that are enriched in fly ash. This review summarizes recently developed harmless disposal methods for MSWI fly ash including solidification/stabilization, thermal treatment, and separation/extraction. In addition, we discuss heavy metal and dioxin fixation, and the removal capacity of fly ash via solidification/stabilization (including cement solidification, chemical stabilization, hydrothermal processes, and mechano-chemical methods), thermal treatment (including sintering, fuel-burning, or electric melting/vitrification), and separation/extraction (including water-washing, chemical reagent leaching, biological leaching, electrodialysis separation, chemical reagent extraction, and nanomaterials extraction). The advantages and disadvantages of different harmless treatment methods are compared and future research prospects and suggestions are summarized. This review provides general guidelines for the harmless treatment of MSWI fly ash in the future.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
27 August 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-021-00078-9
References
Das S, Lee S, Kumar P, et al. Solid waste management: scope and the challenge of sustainability. J Clean Prod. 2019;228:658–78.
Pujara Y, Pathak P, Sharma A, et al. Review on Indian Municipal Solid Waste Management practices for reduction of environmental impacts to achieve sustainable development goals. J Environ Manag. 2019;248:1–14.
National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2017. https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01. Accessed 20 Oct 2019.
Madon I, Drev D, Likar J. Long-term risk assessments comparing environmental performance of different types of sanitary landfills. Waste Manag. 2019;96:96–107.
Aracil C, Pedro H, Diego F, et al. Implementation of waste-to-energy options in landfill-dominated countries: Economic evaluation and GHG impact. Waste Manag. 2018;76:443–56.
Souza WDDM, Rodrigue WS, Filho MMSL, et al. Heavy metals uptake on Malpighia emarginata D.C. seed fiber microparticles: physicochemical characterization, modeling and application in landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2018;78:356–65.
Liu S, Xi B, Qiu Z, et al. Succession and diversity of microbial communities in landfills with depths and ages and its association with dissolved organic matter and heavy metals. Sci Total Environ. 2019;651:909–16.
Kumar SS, Kumar V, Kumar R, et al. Ferrous sulfate as an in-situ anodic coagulant for enhanced bioelectricity generation and COD removal from landfill leachate. Energy. 2019;176:570–81.
Fellner J, Lederer J, Purgar A, et al. Evaluation of resource recovery from waste incineration residues–the case of zinc. Waste Manag. 2015;37(3):95–103.
Makarichi L, Jutidamrongphan W, Techato K. The evolution of waste-to-energy incineration: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;91:812–21.
Ettouney RS, El-Rifai MA, El-Behairy SA. Control of thermally integrated incineration–waste heat recovery systems, a case study. Appl Therm Eng. 2005;25(8):1195–205.
Allegrini E, Vadenbo C, Boldrin A, et al. Life cycle assessment of resource recovery from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash. J Environ Manag. 2015;151:132–43.
Song J, Sun Y, Jin L. PESTEL analysis of the development of the waste-to-energy incineration industry in China. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2017;80:276–89.
IAWG (International ash working group). Municipal solid waste incinerator residues. Stud Environ Sci. 1997;67–68.
Boom AD, Degrez M. Belgian MSWI fly ashes and APC residues: a characterisation study. Waste Manag. 2012;32(6):1163–70.
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, et al. Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology: heavy metal toxicity and the. Environment. 2012;3:133–64.
Fei J, Min X, Wang Z, et al. Health and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in an antimony mining region: a case study from South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2017;24(35):27573–86.
Pan Y, Wu Z, Zhou J, et al. Chemical characteristics and risk assessment of typical municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash in China. J Hazard Mater. 2013;261(20):269–76.
Milbrath MO, Wenger Y, Chang CW, et al. Apparent half-lives of dioxins, furans, and polychlorinated biphenyls as a function of age, body fat, smoking status, and breast-feeding. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117(3):417–25.
Sun J, Hu J, Zhu G, et al. PCDD/Fs distribution characteristics and health risk assessment in fly ash discharged from MSWIs in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2017;139:83–8.
Pan Y, Yang L, Zhou J, et al. Characteristics of dioxins content in fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerators in China. Chemosphere. 2013;92(7):765–71.
Quina MJ, Bordado JC, Quinta-Ferreira RM. Treatment and use of air pollution control residues from MSW incineration: an overview. Waste Manag. 2008;28(11):2097–121.
Sakai E, Miyahara S, Ohsawa S, et al. Hydration of fly ash cement. Cem Concr Res. 2005;35(6):1135–40.
Yu Q, Nagataki S, Lin J, et al. The leachability of heavy metals in hardened fly ash cement and cement-solidified fly ash. Cem Concr Res. 2005;35(6):1056–63.
Li X, Chen Q, Zhou Y, et al. Stabilization of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash using silica fume. Waste Manag. 2014;34(12):2494–504.
Sun Y, Watanabe N, Qiao W, et al. Polysulfide as a novel chemical agent to solidify/stabilize lead in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Chemosphere. 2010;81(1):120–6.
Jiang J, Wang J, Xu X, et al. Heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste incineration flyash using heavy metal chelating agents. J Hazard Mater. 2004;113(1):141–6.
Sukandar, Padmi T, Tanaka M et al. Chemical stabilization of medical waste fly ash using chelating agent and phosphates: heavy metals and ecotoxicity evaluation. Waste Manage. 2009;29(7):2065–70.
Li R, Li Y, Yang T, et al. A new integrated evaluation method of heavy metals pollution control during melting and sintering of MSWI fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2015;289:197–203.
Sobiecka E. Thermal and physicochemical technologies used in hospital incineration fly ash utilization before landfill in Poland. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2016;91(9):2457–61.
Wang X, Jin B, Xu B, et al. Melting characteristics during the vitrification of MSW incinerator fly ash by swirling melting treatment. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. 2017;19(1):483–95.
Ristić M, Milosević SD. Frenkel’s theory of sintering. Sci Sintering. 2006;38:7–11.
Li R, Wang L, Yang T, et al. Investigation of MSWI fly ash melting characteristic by DSC–DTA. Waste Manag. 2007;27(10):1383–92.
Wang Q, Tian S, Wang Q, et al. Melting characteristics during the vitrification of MSWI fly ash with a pilot-scale diesel oil furnace. J Hazard Mater. 2008;160(2):376–81.
Okada T, Suzuki M. Effect of ash circulation in gasification melting system on concentration and leachability of lead in melting furnace fly ash. J Environ Manag. 2013;130:347–53.
Wang Q, Yan J, Tu X, et al. Thermal treatment of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash using DC double arc argon plasma. Fuel. 2009;88(5):955–8.
Zhao P, Ni G, Jiang Y, et al. Destruction of inorganic municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash in a DC arc plasma furnace. J Hazard Mater. 2010;181(1):580–5.
Wang Q, Yan J, Chi Y, et al. Application of thermal plasma to vitrify fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerators. Chemosphere. 2010;78(5):626–30.
Tang J, Petranikova M, Ekberg C, et al. Mixer-settler system for the recovery of copper and zinc from MSWI fly ash leachates: an evaluation of a hydrometallurgical process. J Clean Prod. 2017;148:595–605.
Tang J, Steenari BM. Solvent extraction separation of copper and zinc from MSWI fly ash leachates. Waste Manag. 2015;44:147–54.
Li M, Xiang J, Hu S, et al. Characterization of solid residues from municipal solid waste incinerator. Fuel. 2004;83(10):1397–405.
Rendek E, Ducom G, Germain P. Influence of waste input and combustion technology on MSWI bottom ash quality. Waste Manag. 2007;27(10):1403–7.
Wang Y, Zhang X, Liao W, et al. Investigating impact of waste reuse on the sustainability of municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration industry using emergy approach: a case study from Sichuan province. China. Waste Manage. 2018;77:252–67.
Park K, Hyun J, Maken S, et al. Vitrification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash using brown’s gas. Energy Fuels. 2005;19(1):258–62.
Qiu Q, Jiang X, Lv G, et al. Adsorption of heavy metal ions using zeolite materials of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash modified by microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatment. Powder Technol. 2018;335:156–63.
Mu Y, Saffarzadeh A, Shimaoka T. Influence of ignition of waste fishbone on enhancing heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash. J Clean Prod. 2018;189:396–405.
Huber F, Blasenbauer D, Mallow O, et al. Thermal co-treatment of combustible hazardous waste and waste incineration fly ash in a rotary kiln. Waste Manag. 2016;58(58):181–90.
Kalmykova Y, Karlfeldt FK. Phosphorus recovery from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Waste Manag. 2013;33(6):1403–10.
Qiu Q, Jiang X, Chen Z, et al. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatment with soluble phosphate added for heavy metals solidification in MSWI fly ash. Energy Fuels. 2017;31(5):5222–32.
Bhatt AH, Priyadarshini S, Mohanakrishnan AA, et al. Physical, chemical, and geotechnical properties of coal fly ash: a global review. Case Stud Constr Mater. 2019;11:1–11.
Shim YS, Rhee SW, Lee WK. Comparison of leaching characteristics of heavy metals from bottom and fly ashes in Korea and Japan. Waste Manag. 2005;25(5):473–80.
Gao X, Wang W, Ye T, et al. Utilization of washed MSWI fly ash as partial cement substitute with the addition of dithiocarbamic chelate. J Environ Manag. 2008;88(2):293–9.
Zhang H, Zhao Y, Qi J. Characterization of heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerators in Shanghai. Procces Saf Envrion. 2010;88(2):114–24.
Wang KS, Chiang KY, Lin KL, et al. Effects of a water-extraction process on heavy metal behavior in municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash. Hydrometallurgy. 2001;62(2):73–81.
Wan X, Wang W, Ye T, et al. A study on the chemical and mineralogical characterization of MSWI fly ash using a sequential extraction procedure. J Hazard Mater. 2006;134(1):197–201.
Li Q, Meng A, Jia J, et al. Investigation of heavy metal partitioning influenced by flue gas moisture and chlorine content during waste incineration. J Environ Sci China. 2010;22(5):760–8.
Kurashima K, Matsuda K, Kumagai S, et al. A combined kinetic and thermodynamic approach for interpreting the complex interactions during chloride volatilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste fly ash. Waste Manag. 2019;87:204–17.
Weibel G, Eggenberger U, Kulik D, et al. Extraction of heavy metals from MSWI fly ash using hydrochloric acid and sodium chloride solution. Waste Manag. 2018;76:457–71.
Xia Y, He P, Shao L, et al. Metal distribution characteristic of MSWI bottom ash in view of metal recovery. J Environ Sci China. 2017;52(2):178–89.
Luo H, Wu Y, Zhao A, et al. Hydrothermally synthesized porous materials from municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash and their interfacial interactions with chloroaromatic compounds. J Cleaner Prod. 2017;162:411–9.
Mizutani S, Yoshida T, Sakai S, et al. Release of metals from MSW I fly ash and availability in alkali condition. Waste Manag. 1996;16:537–44.
Tang J, Steenari B. Leaching optimization of municipal solid waste incineration ash for resource recovery: a case study of Cu. Zn Pb and Cd. Waste Manag. 2016;48(48):315–22.
Zhang Y, Cetin B, Likos WJ, et al. Impacts of pH on leaching potential of elements from MSW incineration fly ash. Fuel. 2016;184:815–25.
Trinh MM, Chang MB. Review on occurrence and behavior of PCDD/Fs and dl-PCBs in atmosphere of East Asia. Atmos Environ. 2018;180:23–36.
Cieplik MK, Vincent DJ, Jelena B, et al. Formation of dioxins from combustion micropollutants over MSWI fly ash. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40(4):1263–9.
Tang Z, Huang Q, Yang Y. PCDD/Fs in fly ash from waste incineration in china: a need for effective risk management. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47(11):5520–1.
Song S, Zhou X, Guo C, et al. Emission characteristics of polychlorinated, polybrominated and mixed polybrominated/chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs, PBDD/Fs, and PBCDD/Fs) from waste incineration and metallurgical processes in China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019;184:109608.
Barghi M, Choi S, Kwon H, et al. Influence of non-detect data-handling on toxic equivalency quantities of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs: a case study of major fish species purchased in Korea. Environ Pollut. 2016;214:532–8.
Liu Y, Liu Y. Novel incineration technology integrated with drying, pyrolysis, gasification, and combustion of MSW and ashes vitrification. Environ Sci Technol. 2005;39(10):3855–63.
Song GJ, Kim SH, Seo YC, et al. Dechlorination and destruction of PCDDs/PCDFs in fly ashes from municipal solid waste incinerators by low temperature thermal treatment. Chemosphere. 2008;71(2):248–57.
Chang Y, Fan W, Dai W, et al. Characteristics of PCDD/F content in fly ash discharged from municipal solid waste incinerators. J Hazard Mater. 2011;192(2):521–9.
Yasuhara AT. Katami Leaching behavior of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and furans from the fly ash and bottom ash of a municipal solid waste incinerator. Waste Manag. 2007;27(3):439–47.
Lundin L, Marklund S. Thermal degradation of PCDD/F, PCB and HCB in municipal solid waste ash. Chemosphere. 2007;67(3):474–81.
Liu G, Jiang X, Wang M, et al. Comparison of PCDD/F levels and profiles in fly ash samples from multiple industrial thermal sources. Chemosphere. 2015;133(1):68–74.
Ham SY, KimYJ Lee DH. Leaching characteristics of PCDDs/DFs and dioxin-like PCBs from landfills containing municipal solid waste and incineration residues. Chemosphere. 2008;70(9):1685–93.
Choi K, Lee D. PCDD/DF in leachates from Korean MSW landfills. Chemosphere. 2006;63(8):1353–60.
Spence R. Designing of cement-based formula for solidification/stabilization of hazardous, radioactive, and mixed wastes. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. 2004;34(4):391–417.
Koo D, Sung H, Kim S, et al. Characteristics of cement solidification of metal hydroxide waste. Nucl Eng Technol. 2017;49(1):165–71.
Zhang R, Ren HQ, Ding LL, et al. Evaluating solidification characteristics of textile dyeing sludge with addition of portland cement and attapulgite. Appl Mech Mater. 2015;768:375–84.
Bayar S, Talinli I. Solidification/stabilization of hazardous waste sludge obtained from a chemical industry. Clean Technol Environ Policy. 2013;15(1):157–65.
Wang Z, Song Y. Adsorption properties of CFBC ash-cement pastes as compared with PCC fly ash-cement pastes. Int J Coal Sci Technol. 2016;3(1):62–7.
Petersen T, Valdenaire P, Pellenq R, et al. A reaction model for cement solidification: evolving the C–S–H packing density at the micrometer-scale. J Mech Phys Solids. 2018;118:58–73.
Nabajyoti S, Shigeru K, Toshinori K. Production of cement clinkers from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash. Waste Manag. 2007;27(9):1178–89.
Saeed KA, Kassim KA, Eisazadeh A. Interferences of cement based-solidification/stabilization and heavy metals: A review. Electron J Geotech Eng. 2012;17:2555–65.
Zhang J, Liu J, Li C, et al. Comparison of the fixation effects of heavy metals by cement rotary kiln co-processing and cement based solidification/stabilization. J Hazard Mater. 2009;165(1):1179–85.
Valls S, Vàzquez E. Leaching properties of stabilised/solidified cement-admixtures-sewage sludges systems. Waste Manag. 2002;22(1):37–45.
Conner JR, Hoeffner SL. A critical review of stabilization/solidification technology. Crit Rev Environ Control. 1998;28(4):397–462.
Lu H, Wei F, Tang J, et al. Leaching of metals from cement under simulated environmental conditions. J Environ Manag. 2016;169:319–27.
Li W, Sun Y, Huang Y, et al. Evaluation of chemical speciation and environmental risk levels of heavy metals during varied acid corrosion conditions for raw and solidified/stabilized MSWI fly ash. Waste Manag. 2019;87:407–16.
Gerven TV, Baelen DV, Dutré V, et al. Influence of carbonation and carbonation methods on leaching of metals from mortars. Cem Concr Res. 2004;34(1):149–56.
Zha X, Ning J, Saafi M, et al. Effect of supercritical carbonation on the strength and heavy metal retention of cement-solidified fly ash. Cem Concr Res. 2019;120:36–45.
Zha X, Wang H, Xie P, et al. Leaching resistance of hazardous waste cement solidification after accelerated carbonation. Cem Concr Compos. 2016;72:125–32.
Wen D, Zhang CY, Kong XM, et al. Mercury release from fly ashes and hydrated fly ash cement pastes. Atmos Environ. 2018;178:11–8.
His H, Wang L, Yu T. Effects of injected activated carbon and solidification treatment on the leachability of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from air pollution control residues of municipal waste incineration. Chemosphere. 2007;67(7):1394–402.
Hsi HC, Yu TH. Evaluation of the leachability of polychlorinated dibenzo–dioxins and dibenzofurans in raw and solidified air pollution control residues from municipal waste incinerators. Chemosphere. 2007;67(7):1434–43.
Wang MS, Wang LC, Chang-Chien GP. Distribution of polychlorinated dibenzo- p -dioxins and dibenzofurans in the landfill site for solidified monoliths of fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2006;133(1):177–82.
Yang Z, Tian S, Liu L, et al. Application of washed MSWI fly ash in cement composites: long-term environmental impacts. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2018;25(12):12127–38.
Bie R, Pei C, Song X, et al. Characteristics of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash with cement solidification treatment. J Energy Inst. 2016;89(4):704–12.
Colangelo F, Cioffi R, Montagnaro F, et al. Soluble salt removal from MSWI fly ash and its stabilization for safer disposal and recovery as road basement material. Waste Manag. 2012;32(6):1179–85.
Ding Z, Dong B, Xing F, et al. Cementing mechanism of potassium phosphate based magnesium phosphate cement. Ceram Int. 2012;38(8):6281–8.
Su Y, Yang J, Liu D, et al. Effects of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash on solidification/stabilization of Cd and Pb by magnesium potassium phosphate cement. J Environ Chem Eng. 2016;4(1):259–65.
Zhang N, Liu X, Sun H. Hydration characteristics of intermediate-calcium based cementitious materials from red mud and coal gangue. Chin J Mater Res. 2014;28(5):325–32.
Liu X, Zhao X, Yin H, et al. Intermediate-calcium based cementitious materials prepared by MSWI fly ash and other solid wastes: hydration characteristics and heavy metals solidification behavior. J Hazard Mater. 2018;349:262–71.
Huang K, Fan X, Gan M, et al. Use of municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash in alkali activated slag cement. In: Li B et al, editors. Characterization of minerals, metals, and materials. Cham: Springer; 2019. p 401–10.
Bournonville B, Nzihou A, Sharrock P, et al. Stabilisation of heavy metal containing dusts by reaction with phosphoric acid: study of the reactivity of fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2004;116(1):65–74.
Piantone P, Bodenan F, Derie R, et al. Monitoring the stabilization of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by phosphation: mineralogical and balance approach. Waste Manag. 2003;23(3):225–43.
Quina MJ, Bordado JC, Quintaferreira RM. Chemical stabilization of air pollution control residues from municipal solid waste incineration. J Hazard Mater. 2010;179(1):382–92.
Mu Y, Saffarzadeh A, Shimaoka T. Feasibility of using natural fishbone apatite on removal of Pb from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash. Proc Environ Sci. 2016;31:345–50.
Wang H, Fan X, Wang Y, et al. Comparative leaching of six toxic metals from raw and chemically stabilized MSWI fly ash using citric acid. J Environ Manag. 2018;208:15–23.
Rodella N, Bosio A, Dalipi R, et al. Waste silica sources as heavy metal stabilizers for municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Arab J Chem. 2017;10(S2):3676–81.
Yuan W, Xu W, Wu Z, et al. Mechanochemical treatment of Cr(VI) contaminated soil using a sodium sulfide coupled solidification/stabilization process. Chemosphere. 2018;212:540–7.
Zhao Y, Song L, Li G. Chemical stabilization of MSW incinerator fly ashes. J Hazard Mater. 2002;95(1):47–63.
Lundtorp K, Jensen DL, SRensen MA, et al. Treatment of waste incinerator air-pollution-control residues with FeSO4: concept and product characterisation. Waste Manag Res. 2002;20(1):69–79.
Huang WJ, Lo JS. Synthesis and efficiency of a new chemical fixation agent for stabilizing MSWI fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2004;112(1):79–86.
Ecke H, Sakanankura H, Matsuto T, et al. State-of-the-art treatment processes for municipal solid waste incineration residues in Japan. Waste Manag Res. 2010;18(1):41–51.
Çelik Z, Gülfen M, Aydın AO. Synthesis of a novel dithiooxamide–formaldehyde resin and its application to the adsorption and separation of silver ions. J Hazard Mater. 2010;174(1):556–62.
Liu S, Guo Y, Yang H, et al. Synthesis of a water-soluble thiourea-formaldehyde (WTF) resin and its application to immobilize the heavy metal in MSWI fly ash. J Environ Manag. 2016;182:328–34.
Sakanakura H. Formation and durability of dithiocarbamic metals in stabilized air pollution control residue from municipal solid waste incineration and melting processes. Environ Sci Technol. 2007;41(5):1717–22.
Wang FH, Zhao B, Zhang F, et al. A novel heavy metal chelating agent sixthio guanidine acid for in situ remediation of soils contaminated with multielements: its synthesis, solidification, biodegradability, and leachability. J Soils Sedime. 2016;16(2):371–81.
Wang F, Zhang F, Chen Y, et al. A comparative study on the heavy metal solidification/stabilization performance of four chemical solidifying agents in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2015;300:451–8.
Eighmy TT, Crannell BS, Butler LG, et al. Heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste combustion dry scrubber residue using soluble phosphate. Environ Sci Technol. 1997;31(11):3330–8.
Hyks J, Astrup TF, Christensen TH. Long-term leaching from MSWI air-pollution-control residues: leaching characterization and modeling. J Hazard Mater. 2009;162(1):80–91.
Jiri H, Thomas A, Christensen TH. Influence of test conditions on solubility controlled leaching predictions from air-pollution-control residues. Waste Manag Res J Int Solid Wastes Public Clean Assoc ISWA. 2007;25(5):457–66.
Ma QY, Traina SJ, Logan T, et al. In situ lead immobilization by apatite. Environ Sci Technol. 1993;27(9):1803–10.
Crannell BS, Eighmy TT, Krzanowski JE, et al. Heavy metal stabilization in municipal solid waste combustion bottom ash using soluble phosphate. Waste Manag. 2000;20(2):135–48.
Hong K, Tokunaga S, Kajiuchi T. Extraction of heavy metals from MSW incinerator fly ashes by chelating agents. J Hazard Mater. 2000;75(1):57–73.
Ma W, Chen D, Pan M, et al. Performance of chemical chelating agent stabilization and cement solidification on heavy metals in MSWI fly ash: a comparative study. J Environ Manag. 2019;247:169–77.
Jing Z, Ran X, Jin F, et al. Hydrothermal solidification of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash with slag addition. Waste Manag. 2010;30(8):1521–7.
Bayuseno AP, Schmahl WW, Mullejans T. Hydrothermal processing of MSWI fly ash-towards new stable minerals and fixation of heavy metals. J Hazard Mater. 2009;167(1):250–9.
Gong B, Deng Y, Yang Y, et al. Effects of microwave-assisted thermal treatment on the fate of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Energy Fuels. 2017;31(11):12446–54.
Xie JL, Hu Y, Chen D, et al. Hydrothermal treatment of MSWI fly ash for simultaneous dioxins decomposition and heavy metal stabilization. Front Environ Sci Eng China. 2010;4(1):108–15.
Hu Y, Zhang P, Chen D, et al. Hydrothermal treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash for dioxin decomposition. J Hazard Mater. 2012;207:79–85.
Gilman JJ. Mechanochemistry. Science. 1996;274(5284):65.
Do J, Friscic T. Mechanochemistry: a force of synthesis. ACS Cent Sci. 2017;3(1):13–9.
Montinaro S, Concas A, Pisu M, et al. Immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soils through ball milling with and without additives. Chem Eng J. 2008;142(3):271–84.
Nomura Y, Fujiwara K, Terada A, et al. Prevention of lead leaching from fly ashes by mechanochemical treatment. Waste Manag. 2010;30(7):1290–5.
Li M, Sun C, Gau S, et al. Effects of wet ball milling on lead stabilization and particle size variation in municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2010;174(1):586–91.
Chen Z, Lu S, Mao Q, et al. Suppressing heavy metal leaching through ball milling of fly ash. Energies. 2016;9(524):1–13.
Yoshiharu M, Norie T, Maki T, et al. Calcium-promoted catalytic degradation of PCDDs, PCDFs, and coplanar PCBs under a mild wet process. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40(6):1849–54.
Lu S, Huang J, Zheng P, et al. Ball milling 2,4,6-trichlorophenol with calcium oxide: dechlorination experiment and mechanism considerations. Chem Eng J. 2012;195–196(7):62–8.
Wang Z, Huang J, Xu F, et al. Mechanochemical destruction of pentachloronitrobenzene with reactive iron powder. J Hazard Mater. 2011;198(2):275–81.
Chen Z, Tang M, Lu S, et al. Evolution of PCDD/F-signatures during mechanochemical degradation in municipal solid waste incineration filter ash. Chemosphere. 2018;208:176–84.
Chen Z, Mao Q, Lu S, et al. Dioxins degradation and reformation during mechanochemical treatment. Chemosphere. 2017;180:130–40.
Yang GCC, Chuang T, Huang C. Achieving zero waste of municipal incinerator fly ash by melting in electric arc furnaces while steelmaking. Waste Manag. 2017;62:160–8.
Yang J, Xiao B, Boccaccini AR. Preparation of low melting temperature glass–ceramics from municipal waste incineration fly ash. Fuel. 2009;88(7):1275–80.
Lindberg D, Molin C, Hupa M. Thermal treatment of solid residues from WtE units: a review. Waste Manag. 2015;37(3):82–94.
Liu Y, Zheng L, Li X, et al. SEM/EDS and XRD characterization of raw and washed MSWI fly ash sintered at different temperatures. J Hazard Mater. 2009;162(1):161–73.
Karamanov A, Aloisi M, Pelino M. Sintering behaviour of a glass obtained from MSWI ash. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2005;25(9):1531–40.
Chou S, Lo S, Hsieh C, et al. Sintering of MSWI fly ash by microwave energy. J Hazard Mater. 2009;163(1):357–62.
Min Y, Liu C, Shi P, et al. Effects of the addition of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash on the behavior of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and furans in the iron ore sintering process. Waste Manag. 2018;77:287–93.
Bingham PA, Hand RJ. Vitrification of toxic wastes: a brief review. Br Ceram Trans. 2006;105(1):21–31.
Colombo P, Brusatin G, Bernardo E, et al. Inertization and reuse of waste materials by vitrification and fabrication of glass-based products. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci. 2003;7(3):225–39.
Shi WJ, Kong LX, Bai J, et al. Effect of CaO/Fe2O3 on fusion behaviors of coal ash at high temperatures. Fuel Process Technol. 2018;181:18–24.
Wang ZG, Kong LX, Bai J, et al. Effect of vanadium and nickel on iron-rich ash fusion characteristics. Fuel. 2019;246:491–9.
Qiang Z, Liu H, Qian Y, et al. The influence of phosphorus on ash fusion temperature of sludge and coal. Fuel Process Technol. 2013;110(110):218–26.
Liu Z, Zhang T, Zhang J, et al. Ash fusion characteristics of bamboo, wood and coal. Energy. 2018;161:517–22.
Sakai SI, Hiraoka M. Municipal solid waste incinerator residue recycling by thermal processes. Waste Manag. 2000;20(2):249–58.
Yue Y, Zhang J, Sun F, et al. Heavy metal leaching and distribution in glass products from the co-melting treatment of electroplating sludge and MSWI fly ash. J Environ Manag. 2019;232:226–35.
Okada T, Tomikawa H. Leaching characteristics of lead from melting furnace fly ash generated by melting of incineration fly ash. J Environ Manag. 2012;110:207–14.
Rendek E, Ducom G, Germain P. Carbon dioxide sequestration in municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) bottom ash. J Hazard Mater. 2006;128(1):73–9.
Nilsson M, Andreas L, Lagerkvist A. Effect of accelerated carbonation and zero valent iron on metal leaching from bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2016;51(51):97–104.
Ni P, Xiong Z, Tian C, et al. Influence of carbonation under oxy-fuel combustion flue gas on the leachability of heavy metals in MSWI fly ash. Waste Manag. 2017;67:171–80.
Ma W, Fang Y, Chen D, et al. Volatilization and leaching behavior of heavy metals in MSW incineration fly ash in a DC arc plasma furnace. Fuel. 2017;210:145–53.
Karoly Z, Mohai I, Toth M, et al. Production of glass–ceramics from fly ash using arc plasma. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2007;27(2):1721–5.
Čarnogurská M, Lázár M, Puškár M, et al. Measurement and evaluation of properties of MSW fly ash treated by plasma. Measurement. 2015;62:155–61.
Zhou Y, Yan P, Cheng Z, et al. Application of non-thermal plasmas on toxic removal of dioxin-contained fly ash. Powder Technol. 2003;135:345–53.
Ren Y, Li X, Yu L, et al. Degradation of PCDD/Fs in Fly Ash by Vortex-shaped Gliding Arc Plasma. Plasma Chem Plasma Process. 2013;33(1):293–305.
Luo H, Cheng Y, He D, et al. Review of leaching behavior of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) ash. Sci Total Environ. 2019;668:90–103.
Ferreira C, RibeiroAB, Ottosen LM. Possible applications for municipal solid waste fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2003;96(2):201–216.
Wang X, Li A, Zhang Z. The effects of water washing on cement-based stabilization of MWSI fly ash. Proc Environ Sci. 2016;31:440–6.
Nowak B, Pessl A, Aschenmrenner P, et al. Heavy metal removal from municipal solid waste fly ash by chlorination and thermal treatment. J Hazard Mater. 2010;179(1):323–31.
Jiang Y, Xi B, Li X, et al. Effect of water-extraction on characteristics of melting and solidification of fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerator. J Hazard Mater. 2009;161(2):871–7.
Yang Z, Tian S, Ji R, et al. Effect of water-washing on the co-removal of chlorine and heavy metals in air pollution control residue from MSW incineration. Waste Manag. 2017;68:221–31.
Yang R, Liao WP, Wu PH. Basic characteristics of leachate produced by various washing processes for MSWI ashes in Taiwan. J Environ Manag. 2012;104(16):67–76.
Chen X, Bi Y, Zhang H, et al. Chlorides removal and control through water-washing process on MSWI fly ash. Proc Environ Sci. 2016;31:560–6.
Bayuseno AP, Schmahl WW. Characterization of MSWI fly ash through mineralogy and water extraction. Resour Conserv Recycl. 2011;55(5):524–34.
Chiang KY, Hu YH. Water washing effects on metals emission reduction during municipal solid waste incinerator (MSWI) fly ash melting process. Waste Manag. 2010;30(5):831–8.
Huang K, Inoue K, Harada H, et al. Leaching behavior of heavy metals with hydrochloric acid from fly ash generated in municipal waste incineration plants. Trans Nonferr Met Soc China. 2011;21(6):1422–7.
Nordmark D, Lagerkvist A. Controlling the mobility of chromium and molybdenum in MSWI fly ash in a washing process. Waste Manage. 2018;76:727–33.
Fedje KK, Ekberg C, Skarnemark G, et al. Removal of hazardous metals from MSW fly ash—an evaluation of ash leaching methods. J Hazard Mater. 2010;173(1):310–7.
Zhang HY, Ma GX. Leaching of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash using sulfuric acid. Appl Mech Mater. 2012;249–250:922–6.
Zhang HY, Ma GX. Leaching of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash using nitric acid. Appl Mech Mater. 2012;249–250:918–21.
Kang D, Son J, Yoo Y, et al. Heavy-metal reduction and solidification in municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash using water, NaOH, KOH, and NH4OH in combination with CO2 uptake procedure. Chem Eng J. 2020;380:1–11.
Henric L, Karin Karlfeldt F, Britt-Marie S. Leaching for recovery of copper from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: influence of ash properties and metal speciation. Waste Manag Res. 2014;32(8):755–62.
Ke Y, Li P, Wei P, et al. Characteristics of heavy metals leaching from MSWI fly ashes in sequential scrubbing processes. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. 2018;20(1):604–13.
Tomonori I, Akane N, Masafumi T, et al. Bioleaching of metal from municipal waste incineration fly ash using a mixed culture of sulfur-oxidizing and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Chemosphere. 2005;60(8):1087–94.
Mulligan CN, Mahtab K, Gibbs BF. Bioleaching of heavy metals from a low-grade mining ore using Aspergillus niger. J Hazard Mater. 2004;110(1–3):77–84.
Krebs W, Bachofen R, Brandl H. Growth stimulation of sulfur oxidizing bacteria for optimization of metal leaching efficiency of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Hydrometallurgy. 2001;59(2):283–90.
Xu TJ, Ramanathan T, Ting YP. Bioleaching of incineration fly ash by Aspergillus niger—precipitation of metallic salt crystals and morphological alteration of the fungus. Biotechnol Rep. 2014;3:8–14.
Wang Q, Yang J, Wang Q, et al. Effects of water-washing pretreatment on bioleaching of heavy metals from municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash. J Hazard Mater. 2009;162(2):812–8.
Ramanathan T, Ting YP. Alkaline bioleaching of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by autochthonous extremophiles. Chemosphere. 2016;160:54–61.
Funari V, Mäkinen J, Salminen L, et al. Metal removal from Municipal Solid Waste Incineration fly ash: a comparison between chemical leaching and bioleaching. Waste Manag. 2016;60:397–406.
Ferreira C, Jensen P, Ottosen L, et al. Removal of selected heavy metals from MSW fly ash by the electrodialytic process. Eng Geol. 2005;77(3):339–47.
Kirkelund GM, Jensen PE. Electrodialytic treatment of Greenlandic municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Waste Manage. 2018;80:241–51.
Chen W, Kirkelund GM, Jensen PE, et al. Comparison of different MSWI fly ash treatment processes on the thermal behavior of As, Cr, Pb and Zn in the ash. Waste Manag. 2017;24(27):21591–600.
Chen W, Kirkelund GM, Jensen PE, et al. Electrodialytic extraction of Cr from water-washed MSWI fly ash by changing pH and redox conditions. Waste Manag. 2018;71:215–23.
Andrés-Mañas JA, Ruiz-Aguirre A, Acién FG, et al. Assessment of a pilot system for seawater desalination based on vacuum multi-effect membrane distillation with enhanced heat recovery. Desalination. 2018;443:110–21.
Hamieh BM, Beckman JR. Seawater desalination using Dewvaporation technique: theoretical development and design evolution. Desalination. 2006;195(1):1–13.
Yue D, Xu Y, Mahar R, et al. Laboratory-scale experiments applied to the design of a two-stage submerged combustion evaporation system. Waste Manag. 2007;27(5):704–10.
Tang J, Su M, Zhang H, et al. Assessment of copper and zinc recovery from MSWI fly ash in Guangzhou based on a hydrometallurgical process. Waste Manag. 2018;76:225–33.
Tang J, Yimen R, Petranikova M, et al. Comparative study of the application of traditional and novel extractants for the separation of metals from MSWI fly ash leachates. J Clean Prod. 2018;172:143–54.
Wu YW, Pang H, Liu Y, et al. Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions by novel-nanomaterials: a review. Environ Pollut. 2019;246:608–20.
Xing L, Yang L, Zhang C, et al. Porous Fe2O3 microcubes derived from metal organic frameworks for efficient elimination of organic pollutants and heavy metal ions. Chem Eng J. 2017;336:241–52.
Tang J, Su M, Wu Q, et al. Highly efficient recovery and clean-up of four heavy metals from MSWI fly ash by integrating leaching, selective extraction and adsorption. J Clean Prod. 2019;234:139–49.
Ng VMH, Hui H, Zhou K, et al. Correction: recent progress in layered transition metal carbides and/or nitrides (MXenes) and their composites: synthesis and applications. J Mater Chem A. 2017;5(18):3039–68.
Zou Y, Wang P, Wen Y, et al. Synergistic immobilization of UO22+ by novel graphitic carbon nitride @ layered double hydroxide nanocomposites from wastewater. Chem Eng J. 2017;330:573–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ma, Z., Fang, Z. et al. Review of harmless treatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2, 1–25 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-020-00033-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42768-020-00033-0