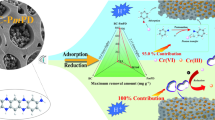
Abstract
Hierarchical CuO–ZnO/SiO2 (CZS) nanofibrous membranes are designed and fabricated to remove Congo red and 4-nitrophenol two common small molecular pollutants in water. The electrospun SiO2 fibrous membrane is serves as the substrate for hydrothermal depositing CuO–ZnO nanosheets. The CZS nanofibrous membrane shows good adsorption characteristics for Congo red due to the hierarchical morphology and the adsorption kinetics where isotherm follows the pseudo-second-order model and Langmuir model, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacity for Congo red is 141.8 mg/g. Moreover, the membrane exhibits excellent catalytic reduction activity for 4-nitrophenol under mild conditions and over 96% of the pollutants are degraded within 90 s. The CZS nanofibrous membrane has promising prospects in applications in water treatment and environmental protection because of the good flexibility, easy fabrication, excellent adsorption, and catalytic activity.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thavasi V, Singh G, Ramakrishna S. Electrospun nanofibers in energy and environmental applications. Energy Environ Sci 2008;1:205.
Lellis B, Fávaro-Polonio CZ, Pamphile JA, Polonio JC. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol Res Innov 2019;3:275.
Sharma B, Tiwari S, Bisht N, Tewari L. Eco-friendly bioprocess using agar plug immobilized Penicillium crustosum PWWS-6 biomass for treatment of wastewater contaminated with toxic Congo red dye for use in agriculture. Ind Crops Prod 2021;170:113755.
Wang Y-L, Dai Y-M, Tsai M-H. Highly efficient and recyclable Fe3C/Au@NG catalyst for 4-nitrophenol reduction. Catal Commun 2021;149:106251.
Nodehi R, Shayesteh H, Kelishami AR. Enhanced adsorption of congo red using cationic surfactant functionalized zeolite particles. Microchem J 2020;153:104281.
Xiong S-W, Yu Y, Wang P, Liu M, Chen S-H, Yin X-Z, Wang L-X, Wang H. Growth of AgBr/Ag3PO4 heterojunction on chitosan fibers for degrading organic pollutants. Adv Fiber Mater 2020;2:246.
Hasan MM, Shenashen MA, Hasan MN, Znad H, Salman MS, Awual MR. Natural biodegradable polymeric bioadsorbents for efficient cationic dye encapsulation from wastewater. J Mol Liq 2021;323:114587.
Zhao J, Liu H, Xue P, Tian S, Sun S, Lv X. Highly-efficient PVDF adsorptive membrane filtration based on chitosan@CNTs-COOH simultaneous removal of anionic and cationic dyes. Carbohydr Polym 2021;274:118664.
Bhatia P, Nath M. Green synthesis of p-NiO/n-ZnO nanocomposites: excellent adsorbent for removal of congo red and efficient catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol present in wastewater. J Water Process Eng 2020;33:101017.
Brião GV, Jahn SL, Foletto EL, Dotto GL. Highly efficient and reusable mesoporous zeolite synthetized from a biopolymer for cationic dyes adsorption. Colloids Surf A 2018;556:43.
Shohr M, Abd-Elhamid AI, El-Shanshory AA, Soliman HMA. Adsorption of cationic dyes onto chemically modified activated carbon: kinetics and thermodynamic study. J Mol Liq 2022;346:118227.
Nasrollahzadeh M, Shafiei N, Eslamipanah M, Fakhri P, Jaleh B, Orooji Y, Varma RS. Preparation of Au nanoparticles by Q switched laser ablation and their application in 4-nitrophenol reduction. Clean Technol Environ Policy 2020;22:1715.
Ameen F, Dawoud T, AlNadhari S. Ecofriendly and low-cost synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles from Acremonium potronii for the photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Environ Res 2021;202:111700.
Coşkuner FB. The role of catalyst support on activity of copper oxide nanoparticles for reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Adv Powder Technol 2020;31:3845.
Chen Y, Wang L, Sun H, Zhang D, Zhao Y, Chen L. Self-assembling TiO2 on aminated graphene based on adsorption and catalysis to treat organic dyes. Appl Surf Sci 2021;539:147889.
Hua W, Zhang T, Ding S, Wang X. A novel cost-effective PAN/CNS nanofibrous membranes with rich carboxyl groups for high efficient adsorption of Lanthanum(III) ions. Sep Purif Technol 2021;259:118216.
Song J, Sun G, Yu J, Si Y, Ding B. Construction of ternary Ag@ZnO/TiO2 fibrous membranes with hierarchical nanostructures and mechanical flexibility for water purification. Ceram Int 2020;46:468.
Wan M, Zhao H, Wang Z, Zou X, Zhao Y, Sun L. Fabrication of Ag modified SiO2 electrospun nanofibrous membranes as ultrasensitive and high stable SERS substrates for multiple analytes detection. Colloid Interface Sci Commun 2021;42:100428.
Miao YE, Wang R, Chen D, Liu Z, Liu T. Electrospun self-standing membrane of hierarchical SiO2@gamma-AlOOH (boehmite) core/sheath fibers for water remediation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2012;4:5353.
Chen S, Du J, Shen L, Chen W. In situ decoration of Ag nanoparticles on hierarchical TiO2 nanowire nanofibers with enhanced catalytic activity used for the removal of 4-nitrophenol. J Phys Chem Solids 2021;149:109784.
Chen H, Wageh S, Al-Ghamdi AA, Wang H, Yu J, Jiang C. Hierarchical C/NiO-ZnO nanocomposite fibers with enhanced adsorption capacity for Congo red. J Colloid Interface Sci 2019;537:736.
Noothongkaew S, Thumthan O, An K-S. UV-Photodetectors based on CuO/ZnO nanocomposites. Mater Lett 2018;233:318.
Prajapati AK, Mondal MK. Novel green strategy for CuO-ZnO-C nanocomposites fabrication using marigold (Tagetes spp.) flower petals extract with and without CTAB treatment for adsorption of Cr(VI) and Congo red dye. J Environ Manag 2021;290:112615.
Pirzada T, Arvidson SA, Saquing CD, Shah SS, Khan SA. Hybrid silica-PVA nanofibers via sol-gel electrospinning. Langmuir 2012;28:5834.
Bharathi P, Harish S, Archana J, Navaneethan M, Ponnusamy S, Muthamizhchelvan C, Shimomura M, Hayakawa Y. Enhanced charge transfer and separation of hierarchical CuO/ZnO composites: the synergistic effect of photocatalysis for the mineralization of organic pollutant in water. Appl Surf Sci 2019;484:884.
Zhang X, He X, Kang Z, Cui M, Yang D-P, Luque R. Waste eggshell-derived dual-functional CuO/ZnO/eggshell nanocomposites: (Photo)catalytic reduction and bacterial inactivation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2019;7:15762.
Zheng Y, Liu J, Cheng B, You W, Ho W, Tang H. Hierarchical porous Al2O3@ZnO core-shell microfibres with excellent adsorption affinity for Congo red molecule. Appl Surf Sci 2019;473:251.
Shaislamov U, Krishnamoorthy K, Kim SJ, Abidov A, Allabergenov B, Kim S, Choi S, Suresh R, Ahmed WM, Lee H-J. Highly stable hierarchical p-CuO/ZnO nanorod/nanobranch photoelectrode for efficient solar energy conversion. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2016;41:2253.
Kim C, Ngoc BTN, Yang KS, Kojima M, Kim YA, Kim YJ, Endo M, Yang SC. Self-sustained thin webs consisting of porous carbon nanofibers for supercapacitors via the electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile solutions containing zinc chloride. Adv Mater 2007;19:2341.
Lei C, Pi M, Xu D, Jiang C, Cheng B. Fabrication of hierarchical porous ZnO-Al2O3 microspheres with enhanced adsorption performance. Appl Surf Sci 2017;426:360.
Wang J, Guo X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification, physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020;258:127279.
Wang M, Li X, Zhang T, Deng L, Li P, Wang X, Hsiao BS. Eco-friendly poly(acrylic acid)-sodium alginate nanofibrous hydrogel: a multifunctional platform for superior removal of Cu(II) and sustainable catalytic applications. Colloids Surf A 2018;558:228.
Malwal D, Gopinath P. Efficient adsorption and antibacterial properties of electrospun CuO-ZnO composite nanofibers for water remediation. J Hazard Mater 2017;321:611.
Wang Y, Ding W, Jiao X, Chen D. Electrospun flexible self-standing silica/mesoporous alumina core–shell fibrous membranes as adsorbents toward Congo red. RSC Adv 2014;4:30790.
Peng C, Zhang J, Xiong Z, Zhao B, Liu P. Fabrication of porous hollow γ-Al2O3 nanofibers by facile electrospinning and its application for water remediation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 2015;215:133.
He X, Yang D, Zhang X, Liu M, Kang Z, Lin C, Jia N, Luque R. Waste eggshell membrane-templated CuO-ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced adsorption, catalysis and antibacterial properties for water purification. Chem Eng J 2019;369:621.
Liu J, Li J, Jian P, Jian R. Intriguing hierarchical Co@NC microflowers in situ assembled by nanoneedles: towards enhanced reduction of nitroaromatic compounds via interfacial synergistic catalysis. J Hazardous Mater 2021;403:123987.
Sahu K, Singh J, Mohapatra S. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water by copper oxide nanosheets. Opt Mater 2019;93:58.
Abay AK, Chen X, Kuo D-H. Highly efficient noble metal free copper nickel oxysulfide nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol, methyl blue, and rhodamine-B organic pollutants. New J Chem 2017;41:5628.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 51903044) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant number 2232020D-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Liu, K., Wang, D. et al. Hierarchical CuO–ZnO/SiO2 Fibrous Membranes for Efficient Removal of Congo Red and 4-Nitrophenol from Water. Adv. Fiber Mater. 4, 1069–1080 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00142-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00142-x