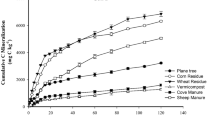
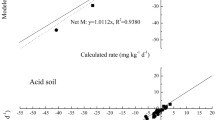
Abstract
Maintaining soil health and soil organic carbon (SOC) restoration through residue addition could serve as waste recycling and nutrient supplying technique. Published articles demonstrated that carbon (C)/nitrogen (N)/phosphorus (P)/sulphur (S) ratio of stable humus is 10000:833:200:143. However, higher C/N ratio of crop residues and deficiency of N, P and S in soils affects SOC mineralization and humus formation. This research aimed to assess proper NPS doses to hasten the humus formation either from soil native C or incorporated residues. Total four different NPS doses with or without crop residue (wheat straw) amendment comprised eight different treatments, and the experiment was conducted in soils belonging to different taxonomic orders (viz. Inceptisol, Ultisol and Vertisol). Six different kinetic models were used to assess the parameters related to C mineralization kinetics. Results revealed that the residue amended treatments had significantly higher C mineralization throughout the incubation period compared to treatments devoid of residue. Among kinetic models, two phase exponential association fitted better with time-series C mineralization data obtained across the treatments and soils. With double and quadruple nutrient doses, higher rates of C mineralization were observed. With the quadruple nutrient doses, C mineralization from added residue was 77% in Vertisol, 74% in Ultisol and 54% in Inceptisol, whereas the optimum dose had 47%, 42% and 45% of residue C mineralized, respectively. C mineralization quotient (CminQ) also increased due to higher NPS doses. Hence, optimum nutrient dose is essential for conversion of the added labile residues to stable form; also, decomposition can be hastened by nutrient addition. In conservation agriculture, the addition of nutrients following stoichiometric values will accelerate the residue decomposition and help in stubble management. However, higher nutrient doses over and above the stoichiometric values cause rapid efflux of added C and can repudiate the purpose of residue addition to soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernal MP, Sanchez-Monedero MA, Paredes C, Roig A (1998) Carbon mineralization from organic wastes at different composting stages during their incubation with soil. Agril Ecosyst Environ 69:175–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-8809(98)00106-6
Bhattacharyya R, Kundu S, Ved-Prakash GHS (2008) Sustainability under combined application of mineral and organic fertilizers in a rainfed soybean-wheat system of the Indian Himalayas. Eur J Agron 28:32–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2007.04.006
Bol R, Poirier N, Balesdent J, Gleixner G (2009) Molecular turnover time of soil organic matter in particle-size fractions of an arable soil. Rapid Commun Mass Spectro 23:2551–2558. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.4124
Bonde TA, Lindberg T (1988) Nitrogen mineralization kinetics in soil during long-term aerobic laboratory incubations. A Case Study J Environ Qual 17:414–417. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1988.00472425001700030011x
Broadbent FE (1986) Empirical modeling of soil nitrogen mineralization. Soil Sci 141:208–213
Bruce AM, Metting FB, Rice C (2007) Soil carbon sequestration. Clim Change 80:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9174-7
Burney JA, Davis SJ, Lobell DB (2010) Greenhouse gas mitigation by agricultural intensification. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:12052–12057. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914216107
Campbell CA, Bowren KE, Schnitzer M, Zenter RP, Townley-Smith L (1991) Effect of crop rotations and fertilization on soil organic matter and some biochemical properties of a thick Black Chernozem. Can J Soil Sci 71:377–387. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjss91-036
Chandran P, Ray SK, Bhattacharyya T, Srivastava P, Krishnan P, Pal DK (2005) Lateritic soils of Kerala, India: their mineralogy, genesis, and taxonomy. Aust J Soil Res 43:839–852. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR04128
Chen R, Senbayram M, Blagodatsky S, Myachina O, Dittert K, Lin X, Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2014) Soil C and N availability determine the priming effect: microbial N mining and stoichiometric decomposition theories. Glob Change Biol 20:2356–2367. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12475
Cole CV, Duxbury J, Freney J, Heinemeyer O, Minami K, Mosier A, Paustian K, Rosenberg N, Sampson N, Sauerbeck D, Zhao Q (1997) Global estimates of potential mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions by agriculture. Nutr Cycl Agroecosystems 49:221–228. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009731711346
Cooper J, Baranski M, Stewart G, Nobel-de Lange M, Bàrberi P, Fließbach A, Peigné J, Berner A, Brock C, Casagrande M, Crowley O (2016) Shallow non-inversion tillage in organic farming maintains crop yields and increases soil C stocks: a meta-analysis. Agron Sustain Dev 36:22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-016-0354-1
Cooper JM, Burton D, Daniell TJ, Griffiths BS, Zebarth BJ (2011) Carbon min-eralization kinetics and soil biological characteristics as influenced by manure addition in soil incubated at a range of temperatures. Eur J Soil Biol 47:392–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2011.07.010
Dodor DE, Amanor YJ, Asamoah-Bediako A, MacCarthy DS, Dovie DBK (2019) Kinetics of carbon mineralization and sequestration of sole and/or co-amended biochar and cattle manure in a sandy soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2019.1671443
Dossa EL, Khouma M, Diedhiou I, Sene M, Kizito F, Badiane AN, Samba SAN, Dick RP (2009) Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus mineralization potential of semiarid Sahelin soils amended with native shrub residues. Geoderma 148:251–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2008.10.009
FAO (2017) Soil organic carbon: the hidden potential. Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy, pp. 77.
Gan HY, Schoning I, Schall P, Ammer C, Scrump M (2020) Soil organic matter mineralization as driven by nutrient stoichiometry in soils under differently managed forest stands. Front Forest Global Change 3:99. https://doi.org/10.3389/ffgc.2020.00099
Gerzabek MH, Pichlmayer F, Kirchmann H, Haberhauer G (1997) The response of soil organic matter to manure amendments in a long-term experiment at Ultuna, Sweden. Eur J Soil Sci 48:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1997.tb00547.x
Gulde S, Chung H, Amelung W, Chang C, Six J (2008) Soil carbon saturation controls labile and stable carbon pool dynamics. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:605–612. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2007.0251
Haddaway NR, Hedlund K, Jackson LE, Kätterer T, Lugato E, Thomsen IK, Jørgensen HB, Isberg PE (2016) How does tillage intensity affect soil organic carbon? A systematic review protocol. Environ Evid 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13750-017-0108-9
Hayes MHB, Mingelgrin U (1991) Interactions between small organic chemicals and soil colloidal constituents. In: Bolt GH, De Boodt ME Hayes MHB, McBride MB (ed). Interactions at the soil colloid-soil solution interface. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht Boston London, pp 323407
Heitkotter J, Niebuhr J, Heinze S, Marschner B (2017) Patterns of nitrogen and citric acid induced changes in C-turnover and enzyme activities are different in topsoil and subsoils of a sandy Cambisol. Geoderma 292:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.01.017
Himes FL (1998) Nitrogen, sulphur and phosphorus and the sequestration of carbon. Soil Processes Carbon Cycle. CRC Press Boca Raton, FL, pp 315–319
Huggins DR, Buyanovsky GA, Wagner GH, Brown JR, Darmody RG, Peck TR, Lesoing GW, Vanotti MB, Bundy LG (1998) Soil organic C in the tall grass prairie-derived region of the corn belt: effects of long-term crop management. Soil till Res 47:219–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-1987(98)00108-1
Jackson ML (1973) Soil chemical analysis-advanced course: A manual of methods useful for instruction and research in soil chemistry, physical chemistry of soils, soil fertility, and soil genesis. Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Janzen HH, Campbell CA, Brandt SA, Lafond GP, Townley-Smith L (1992) Light-fraction organic matter in soils from long-term crop rotations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:1799–1806. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1992.03615995005600060025x
Jones CA (1984) Estimation of an active fraction of soil nitrogen. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 15:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103628409367451
Kell DB (2012) Large-scale sequestration of atmospheric carbon via plant roots in natural and agricultural ecosystems: why and how. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:1589–1597. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2011.0244
Kimble JM, Follett RF, Cole CV (1998). The potential of US cropland to sequester carbon and mitigate the greenhouse effect. CRC Press pp - 144
King AE, Ali GA, Gillespie AW, Wagner-Riddle C (2020) Soil organic matter as catalyst of crop resource capture. Front Environ Sci 8:50. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2020.00050
Kirkby CA, Kirkegaard JA, Richardson AE, Wade LJ, Blanchard C, Batten G (2011) Stable soil organic matter: a comparison of C: N: P: S ratios in Australian and other world soils. Geoderma 163:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.04.010
Kirkby CA, Richardson AE, Wade LJ, Batten GD, Blanchard C, Kirkegaard JA (2013) Carbon-nutrient stoichiometry to increase soil carbon sequestration. Soil Biol Biochem 60:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.01.011
Kirkby CA, Richardson AE, Wade LJ, Passioura JB, Batten GD, Blanchard C, Kirkegaard JA (2014) Nutrient availability limits carbon sequestration in arable soils. Soil Biol Biochem 68:402–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.09.032
Laban P, Metternicht G, Davies J (2018). Soil Biodiversity and Soil Organic Carbon: Keeping Drylands Alive. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.CH.2018.03.en
Lal R (2004) Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 304:1623–1627. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097396
Lal R (2008) Carbon sequestration. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:815–830. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2007.2185
Mackenzie F, Lerman A (1993) C, N, P, S global biogeochemical cycles and modelling of global change. In: Wollast R, Mackenzie F, Chou L (ed) Interactions of C, N, P and S Biogeochemical Cycles and Global Change. Publisher Springer-Verlag, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-76064-8_18
Mangalassery S, Mooney SJ, Sparkes DL, Fraser WT, Sjögersten S (2015) Impacts of zero tillage on soil enzyme activities, microbial characteristics and organic matter functional chemistry in temperate soils. Eur J Soil Biol 68:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2015.03.001
McGrath VB, Blakeney AB, Batten GD (1997) Fructan to nitrogen ratio as an indicator of nutrient stress in wheat crops. New Phytol 136:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00712.x
Mohanty S, Nayak AK, Kumar A, Tripathi R, Shahid M, Bhattacharyya P, Raja R, Panda BB (2013) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization kinetics in soil of rice-rice system under long term application of chemical fertilizers and farmyard manure. Eur J Soil Biol 58:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2013.07.004
Molina JAE, Clap CE, Larson WE (1980) Potentially mineralizable nitrogen in soil: the simple exponential model does not apply to the first 12 weeks of incubation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:442–443. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400020054x
Morowitz HJ (1968) Energy Flow in Biology: Biological Organization as a Problem in Thermal Physics. Academic Press, New York
Nater EA, Jalenski NA (2014) Temperate region soils. Ref Module Earth Systems Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.09069-2
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1983) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In: Page, AL (Ed), Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 - Chemical and Microbiological Properties. ASA-SSSA, pp 539–579. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed.c29
Ni X, Yang W, Tan B, Li H, He J, Xu L, Wu F (2016) Forest gaps slow the sequestration of soil organic matter: a humification experiment with six foliar litters in an alpine forest. Sci Rep 6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19744
Pal DK (2017) Cracking Clay Soils (Vertisols): Pedology, Mineralogy and Taxonomy. In: Pal DK (ed) A Treatise of Indian and Tropical Soils. Springer, Cham, pp 9–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49439 -5_2
Pal DK, Bhattacharyya T, Srivastava P, Chandran P, Ray SK (2009) Soils of the Indo-Gangetic plains: their historical perspective and management. Curr Sci 96:1193–1202
Parton WJ, Schimel DS, Cole CV, Ojima DS (1987) Analysis of factors controlling soil organic matter levels in Great Plains grasslands. Soil Sci Soc Am J 51:1173–1179
Paustian K, Lehmann J, Ogle S, Reay D, Robertson GP, Smith P (2016) Climate-smart soils. Nature 532:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17174
Paustian K, Larson E, Kent J, Marx E, Swan A (2019) Soil C sequestration as a biological negative emission strategy. Front Clim 1:8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fclim.2019.00008
Qayyum MF, Steffens D, Reisenauer HP, Schubert S (2012) Kinetics of carbon mineralization of biochars compared with wheat straw in three soils. J Environ Qual 41:1210–1220. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2011.0058
Rakesh S, Sarkar D, Sinha AK, Mukhopadhyay P, Danish S, Fahad S, Datta R (2021) Carbon Mineralization Rates and Kinetics of Surface-Applied and Incorporated Rice and Maize Residues in Entisol and Inceptisol Soil Types. Sustainability 13:7212
Raphael JP, Calonego JC, Milori DMB, Rosolem CA (2016) Soil organic matter in crop rotations under no-till. Soil till Res 155:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2015.07.020
Ribeiro HM, Fangueiro D, Alves F, Vasconcelos E, Coutinho J, Bol R, Cabral F (2010) Carbon-mineralization kinetics in an organically managed CambicArenosol amended with organic fertilizers. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 173:39–45.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15222624
Riffaldi R, Saviozzi A, Levi-Minzi R (1996) Carbon mineralization kinetics as influenced by soil properties. Biol Fertil Soils 22:293–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334572
Rumpel C (2008) Does burning of harvesting residues increase soil carbon storage. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 8:44–51
Saha M, Das M, Sarkar A (2021) Distinct nature of soil organic carbon pools and indices under nineteen years of rice based crop diversification switched over from uncultivated land in eastern plateau region of India. Soil till Res 207:104856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104856
Sanderman J, Hengl T, Fiske GJ (2017) Soil carbon debt of 12000 years of human land use. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114:9575–9580. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1706103114
Sarkar A, Saha M, Saha JK, Vassanda Coumar M, Mandal A, Patra AK (2021) Comparative assessment of P adsorption, release kinetics, enzymatic activities of weathered fly ash amended texturally different soils. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03196-3
Saviozzi A, Vanni G, Cardelli R (2014) Carbon mineralization kinetics in soils under urban environment. Appl Soil Ecol 73:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.08.007
Seyfried MS, Rao PSC (1988) Kinetics of nitrogen mineralization in Costa Rican soils: Model evaluation and pretreatment effects. Plant Soil 106:159–169
Sistla SA, Schimel JP (2012) Stoichiometric flexibility as a regulator of carbon and nutrient cycling in terrestrial ecosystems under change. New Phytol 196:68–78
Six J, Conant RT, Paul EA, Paustian K (2002) Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant Soil 241:155–176
Soil Survey Staff (2014) Keys to soil taxonomy, 12thedn. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington, p 360
Solomon D, Lehmann J, Zech W (2000) Land use effects on soil organic matter properties of chromic luvisols in semi-arid northern Tanzania: carbon, nitrogen, lignin and carbohydrates. Agric Ecosyst Environ 78:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(99)00126-7
Soon YK (1998) Crop residue and fertilizer management effects on some biological and chemical properties of a Dark Grey Solod. Can J Soil Sci 78:707–713
Srinivasa Rao C, Lal R, Prasad JVNS, Gopinath KA, Singh R, Jakkula VS, Sahrawat KL, Venkateswarlu B, Sikka AK, Virmani SM (2015) Potential and challenges of rainfed farming in India. In: Sparks DL (Eds), Adv Agron pp. 113–181
Stanford G, Smith SJ (1972) Nitrogen mineralization potentials of soils. Soil SciSoc Am J 36:465–472
Stella T, Mouratiadou I, Gaiser T, Berg-Mohnicke M, Wallor E, Ewert F, Nendel C (2019) Estimating the contribution of crop residues to soil organic carbon conservation. Environ Res Lett 14:094008
Venkateswarlu B (2011) Rainfed agriculture in India: issues in technology development and transfer. Model training course on “impact of climate change in rainfed agriculture and adaptation strategies” November, 22–29.
Walkley A, Black CA (1934) Estimation of organic carbon by chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Warren Raffa D, Bogdanski A, Tittonell P (2015) How does crop residue removal affect soil organic carbon and yield? A hierarchical analysis of management and environmental factors. Biomass Bioenergy 81:345–355
Wei X, Hu Y, Peng P, Zhu Z, Atere CT, O’Donnell AG, Wu J, Ge T (2017) Effect of P stoichiometry on the abundance of nitrogen-cycle genes in phosphorus-limited paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 53:767–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-017-1221-1
Wei X, Zhu Z, Liu Y, Luo Y, Deng Y, Xu X, Liu S, Richter A, Shibistova O, Guggenberger G, Wu J (2020) C: N: P stoichiometry regulates soil organic carbon mineralization and concomitant shifts in microbial community composition in paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 56:1093–1107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-020-01468-7
Wei X, Zhu Z, Wei L, Wu J, Ge T (2019) Biogeochemical cycles of key elements in the paddy-rice rhizosphere: microbial mechanisms and coupling processes. Rhizosphere 10:100145
Wiesmeier M, Poeplau C, Sierra CA, Maier H, Fruhaauf C, Hubner R, Kuhnel A, Sporlein P, Geub U, Hangen E, Schiling B, von Lutzow M, Kogel-Knabner I (2016) Projected loss of soil organic carbon in temperate agricultural soils in the 21st century: effects of climate change and carbon input trends. Sci Rep 6:32525. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32525
Wu X, Wang J, Shen L, Wu X, Amanze C, Zeng W (2021) Effect of bamboo sphere amendment on the organic matter decomposition and humification of food waste composting. Waste Manage 133:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.07.030
Xu Y, Ding F, Gao X, Wang Y, Li M, Wang J (2019) Mineralization of plant residues and native soil carbon as affected by soil fertility and residue type. J Soil Sediment 19:1407–1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2152-7
Yazdanpanah N, Mahmoodabadi M, Cerda A (2016) The impact of organic amendments on soil hydrology, structure and microbial respiration in semiarid lands. Geoderma 266:58–65
Zhu Z, Ge T, Luo Y, Liu S, Xu X, Tong C, Shibistova O, Guggenberger G, Wu J (2018) Microbial stoichiometric flexibility regulates rice straw mineralization and its priming effect in paddy soil. Soil Biol Biochem 121:67–76
Zibilske LM (1994) Carbon mineralization. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties, 5, pp.835–863
Zou XM, Ruan HH, Fu Y, Yang XD, Sha LQ (2005) Estimating soil labile organic carbon and potential turnover rates using a sequential fumigation–incubation procedure. Soil Biol Biochem 37:1923–1928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.02.028
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to express their sincere thanks and gratitude to Director and all scientific staff of Indian Institute of Soil Science, Bhopal and Indian Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, Dehradun. This research was conducted with the financial help of Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Trisha Roy contributed to experiment conceptualization; investigation; methodology; data curation; formal analysis; and roles/writing of original draft. Ashis Kumar Biswas contributed to experiment visualization; supervision; resources; and writing, review and editing. Abhijit Sarkar contributed to formal analysis; data curation; kinetics calculations; and roles/writing of original draft. Pramod Jha contributed to supervision; methodology; and writing, review and editing. N.K. Sharma contributed to writing, review and editing. P.K. Mishra contributed to resources facilitation of the study. Ashok Kumar Patra contributed to resources and writing, review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, T., Biswas, A.K., Sarkar, A. et al. Impact of Varied Levels of N, P, and S Stoichiometry on C Mineralization from three Contrasting Soils with or Without Wheat Straw Amendment: a Laboratory Study. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22, 501–514 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00664-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00664-0