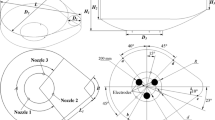
Abstract
Nowadays, in China, the bottom-blowing technique plays an important role in accelerating the molten bath stirring and promoting the metallurgical reactions in electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking. The innovations of bottom-blowing technologies in EAF steelmaking were reviewed. The optimized bottom-blowing arrangement in EAF based on the furnace structure and the position of electrodes was introduced, and the fluid flow characteristics of EAF molten bath with bottom-blowing were analyzed. Furthermore, bottom-blowing CO2 in EAF can facilitate the carbon–oxygen reaction reaching equilibrium and decrease the content of nitrogen in molten steel due to its special metallurgical properties. Pulsating bottom-blowing in EAF can effectively improve the molten bath stirring through the action of the unsteady bottom-blowing gas streams, which could make the fluid flow field more disorderly than the steady bottom-blowing. And submerged O2 injection with CO2 in EAF can noticeably strengthen the EAF molten bath stirring, increase the production efficiency and improve the molten steel quality.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.N. Toulouevski, I.Y. Zinurov, Innovation in electric arc furnaces, Springer, Berlin, 2010.
World Steel Association, Steel statistical yearbook 2017. https://www.worldsteel.org/zh/dam/jcr:3e275c73-6f11-4e7f-a5d8-23d9bc5c508f/Steel%2520Statistical%2520Yearbook%25202017_updated%2520version090518.pdf. Accessed November 2017.
L.Z. Yang, R. Zhu, G.H. Ma, High Temp. Mat. Pr-Isr. 35 (2016) 195–200.
L.Z. Yang, T. Jiang, G.H. Li, Y.F. Guo, High Temp. Mat. Pr-Isr. 36 (2017) 615–621.
H. Odenthal, A. Kemminger, F. Krause, L. Sankowski, N. Uebber, N. Vogl, Steel Res. Int. 89 (2018) 1700098.
G. Wei, R. Zhu, T. Cheng, K. Dong, L. Yang, X. Wu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 49 (2018) 361–374.
G.S. Wei, R. Zhu, T. Cheng, F. Zhao, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23 (2016) 997–1006.
C.L. He, R. Zhu, K. Dong, Y.Q. Qiu, K.M. Sun, G.L. Jiang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 38 (2011) 291–296.
M. Kirschen, R. Ehrengruber, K.M. Zettl, RHI Bulletin 5 (2016) No. 1, 8–13.
F. Liu, R. Zhu, K. Dong, X. Bao, S. Fan, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 2365–2373.
L.F. Li, M.F. Jiang, Z.Y. Duan, Steelmaking 12 (1996) No. 2, 49–52.
L.F. Li, M.F. Jiang, Res. Iron Steel 24 (1996) No. 3, 3–6.
B. Li, ISIJ Int. 40 (2000) 863–869.
G. Wei, R. Zhu, K. Dong, G. Ma, T. Cheng, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47 (2016) 3066–3079.
K. Dong, R. Zhu, W.J. Liu, Adv. Mater. Res. 361–363 (2012) 639–643.
H. Wang, R. Zhu, R.Z. Liu, D. Shou, G.J. Xie, S.L. Fan, Y.L. Gu, Industrial Heating 43 (2014) No. 2, 12–17.
G. Wei, R. Zhu, K. Dong, Z. Li, L. Yang, X. Wu, Ironmak. Steelmak. 45 (2018) 839–846.
G. Wei, R. Zhu, X. Wu, K. Dong, L. Yang, R. Liu, JOM 70 (2018) 969–976.
H. Wang, R. Zhu, X. Wang, Z. Li, Miner. Process. Extract. Metall.126 (2017) 47–53.
P. He, R.S. Zhang, K.W. Deng, J. Iron Steel Res. 8 (1988) No. S1, 107–113.
M.K. Cao, Shanghai Metals 20 (1998) No. 2, 34–37.
K. Dong, J.W. Li, C.F. Zhu, Ind. Heat. 40 (2011) No. 1, 60–62.
G. Brooks, G. Irons, D. Anghelina, in: 4th High Temperature Processing Symposium, Swinburne University of Technology, Hawthorn, Victoria, Australia, 2012, pp. 13–15.
J. Fu, S. Zhou, P. Wang, L. Di, J. Zhu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 17 (2001) 233–236.
Z.Z. Li, R. Zhu, R.Z. Liu, X.L. Wang, Iron and Steel 51 (2016) No. 9, 40–45.
N. Sumida, Y. Oguchi, T. Fujii, T. Fujimura, A. Ueda, Iron and Steel 19 (1984) No. 8, 66–70.
C. Yi, R. Zhu, B.Y. Chen, C.R. Wang, J.X. Ke, ISIJ Int. 49 (2009) 1694–1699.
G. Wei, R. Zhu, T. Cheng, K. Dong, L. Yang, T. Tang, X. Wu, ISIJ Int. 58 (2018) 842–851.
R. Zhu, G.S. Wei, T.P. Tang, Steelmaking 34 (2018) No. 1, 10–19.
G. Ma, L. Yang, R. Zhu, Z. Li, X. Wang, G. Wei, T. Cheng, in: Materials Science and Technology Conference and Exhibition 2016, Association for Iron and Steel Technology, AISTECH, 2016, pp. 555–563.
L.Z. Yang, R. Zhu, K. Dong, W.J. Liu, G.H. Ma, Adv. Mater. Res. 881–883 (2014) 1540–1544.
G. Ma, R. Zhu, K. Dong, Z. Li, R. Liu, G. Wei, Ironmak. Steelmak. 43 (2016) 594–599.
G.H. Ma, R. Zhu, R.Z. Liu, F.H. Liu, K. Dong, G.S. Wei, Industrial Heating 44 (2015) No. 2, 1–4.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their thanks for the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51734003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Gs., Zhu, R., Wang, Y. et al. Technological innovations of electric arc furnace bottom-blowing in China. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 26, 909–916 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0163-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0163-7