Abstract
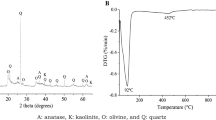
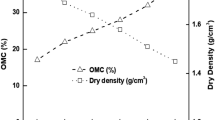
Toxic tannery wastewater(s) (TWW) pose(s) a great risk to the environment. This study explores the potential of mitigating the harmful effects of TWW through sedimentation using clinoptiolite in the presence of various anionic, cationic and non-ionic flocculants with different molecular weights and charge densities followed by encapsulation in a brick structure for stability. Compressive strength (CS), size reduction after firing (SRAF), water absorption (WA) and colouring parameters of bricks were determined. X-Ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM)–energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analyses were conducted on brick bodies. Kinetic leaching experiments were conducted for possible heavy metal release from the bricks. Bricks containing 10 wt% leather waste and 5 wt% clinoptiolite sintered at 800 °C instead of 920 °C possessed similar properties to the standard brick (SB).












Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
26 July 2017
An erratum to this article has been published.
References
WORLD BANK GROUP: Tanning and leather finishing, pollution prevention and abatement handbook, effective (1998)
Ayalew, A.: Cleaner production options for solid waste management in the leather industry. M.Sc. Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa (2005)
Abreu, M.A., Toffoli, S.M.: Characterization of a chromium-rich tannery waste and its potential use in ceramics. Ceram Int. 35, 2225–2234 (2009)
Ozgunay, H., Colak, S., Mutlu, M.M., Akyuz, F.: Characterization of leather industry wastes. Polish J of Environ Stud. 16, 867–873 (2007)
Kolomaznik, K., Barinova, M., Vaskova, H.: Chromium VI issue in leather waste—a technology for the processing of used leather goods and potential of Raman spectroscopy in chromium traces detection. MACOS. 6, 447–455 (2012)
Wang, Y.S., Pan, Z.Y., Lang, J.M., Xu, J.M., Zheng, Y.G.: Bioleaching of chromium from tannery sludge by indigenous Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.005
Sharaf, S.A.A., Gasmeleed, G.A., Musa, A.E.: Extraction of chromium six from chrome shavings. JFPI. 2, 21–26 (2013)
Fernandes, H.R., Ferreira, J.M.F.: Recycling of chromium-rich leather ashes in porcelain tiles production. J Eur Cer Soc. 27, 4657–4663 (2007)
Swarnalatha, S., Srinivasulu, T., Srimurali, M., Sekaran, G.: Safe disposal of toxic chrome buffing dust generated from leather industries. J Hazard Mater. 150, 290–299 (2008)
Sekaran, G., Shanmugasundaram, K., Mariappan, M.: Characterization and utilization of buffing dust generated by the leather industry. J Hazard Mater. B63, 53–68 (1998)
Sekaran, G., Swarnalatha, S., Srinivasulu, T.: Solid waste management in leather sector. IJDMT. 1, 47–52 (2007)
Kanaragaj, J., Velappan, K.C., Chandra Babu, N.K., Sadulla, S.: Solid waste generation in the leather industry and its utilization for cleaner environment—a review. J Sci Ind Res. 65, 541–548 (2006)
Paul, H., Antunes, A.P.M., Covington, A.D., Evans, P., Phillips, P.S.: Utilising tannery waste as a protein source for poultry feed. In: Towards zero solid waste: Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Solid Waste Technology and Management, Philadelphia, PA, USA. The Journal of Solid Waste Technology and Management, 10–13. (2013). ISSN 1091–8043
Famielec, S., Wieczorec-Ciurowa, K.: Waste from leather industry—threats to the environment. CzT. 1-Ch, 43–48 (2011)
Sreeram, K.J., Ramasami, T.: Sustaining tanning process through conservation, recovery and better utilization of chromium. Resour Conserv Recy. 38, 185–212 (2003)
de Souza e Silva, P.T., de Mello, N.T., Menezes Duarte, M.M., Conceiçao, M., Montenegro, B.S.M., Araujo, A.N., de Barros Neto, B., Lins da Silva, V.: Extraction and recovery of chromium from electroplating sludge. J Hazard Mater. B128, 39–43 (2006)
Kurniawan, T.A., Chan, G.Y.S., Loa, W.-H., Babel, S.: Physico–chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem Eng J. 118, 83–98 (2006)
Haydar, S., Aziz, J.A.: Characterization and treatability studies of tannery wastewater using chemically enhanced primary treatment (CEPT)—a case study of Siddiq leather works. J Hazard Mater. 163, 1076–1083 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.074
Song, Z., Willians, C.J., Edyvean, R.G.J.: Treatment of tannery wastewater by chemical coagulation. Desalination. 164, 249–259 (2004)
Haydar, S., Aziz, J.A.: Coagulation–flocculation studies of tannery wastewater using combination of alum with cationic and anionic polymers. J Hazard Mater. 168, 1035–1040 (2009)
Zhao, Y.Q., Bache, D.H.: Integrated effects of applied pressure, time, and polymer doses on alum sludge dewatering behaviour. Waste Manag. 22, 813–819 (2002)
Zeng, Y., Yang, C., Zhang, J., Pu, W.: Feasibility investigation of oily wastewater treatment by combination of zinc and PAM in coagulation/flocculation. J Hazard Mater. 147, 991–996 (2007)
Fu, F., Wang, Q.: Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag. 92, 407–418 (2011)
Ibrahimi, M.M., Sayyadi, A.S.: Application of natural and modified zeolites in removing heavy metal cations from aqueous media: an overview of including parameters affecting the process. Int J Geo Earth Env Sc. 3, 1–7 (2015) ISSN: 2348-0254
Golomeova, M., Zendelska, A., Blazev, K., Krstev, B., Golomeov, B.: Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using clinoptilolite and stilbite. IJERT. 3, 1029–1035 (2014) ISSN: 2278-0181
Hansson, A.: Mechanism of zeolite activity in biogas co-digestion. M.Sc. Thesis, Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology, Institue of Technology, Linköping University, Sweden (2011)
Gorimbo, Joshua: Effect of the homoionic form of clinoptilolite on Ni2+ adsorption isotherms: a thermodynamic study. M.Sc. Thesis, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg (2011)
http://www.geo.wvu.edu/~lang/Geol484/Zeolites.pdf (2016). Accessed 17.10.16
Halimoon, N., Yin, R.G.S.: Removal of heavy metals from textile wastewater using zeolite. Environment Asia. 3, 124–130 (2010)
Koprivanac, N., Cerjan-Stefanović, Š., Papić, S., Meteš, A., Kušić, H.: Removal of the Cu(II) complex dyes from wastewater with natural zeolite. In: Zeolite '02 (6th International Conference on the Occurrence, Properties and Utilization of Natural Zeolites), Tessaloniki, Greece, 3–7 June (2002)
Kanawade, S.M.: Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by using natural zeolites as adsorbent. IJESTA. 01, 30–38 (2015)
Erdem, E., Karapinar, N., Donat, R.: The removal of heavy metal cations by natural zeolites. J Colloid Interface Sci. 280, 309–314 (2004)
Shaheen, S.M., Derbalah, A.S., Moghanm, F.S.: Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by zeolite in competitive sorption system. IJESD. 3, (2012)
Zhang, P., Ding, W., Zhang, Y., Dai, K., Liu, W.: Heavy metal ions removal from water using modified zeolite. J Chem Pharm Res. 6, 507–514 (2014)
Khachatryan, Sh.V.: Heavy metal adsorption by armenian natural zeolite from natural aqueous solutions. In: Proceedings of the Yerevan State University, Chemistry and Biology, № 2, 31–35, (2014)
Motsi, T., Rowson, N.A., Simmons, M.J.H.: Kinetic studies of the removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by natural zeolite. Int J Miner Process. 101, 42–49 (2011)
TS EN 771-1:2011+A1: Specification for masonry units—Part 1: clay masonry units Turkish Standards Institute, Ankara, Turkey (2015)
TSE 4790: Turkish Standard Test Method for Common Bricks and Roofing Tile Clays. Turkish Standards Institute, Ankara (1986)
ASTM C67-92 a: Standard test methods of sampling and testing brick and structural clay tile. Philadelphia, USA: American Society of testing and materials 1916 Race street PA 19103–1187 (1992)
TS EN ISO 10545-16: Ceramic tiles—Part 16: determination of small colour differences, Turkey (2012)
Hunter, R.S., Harold, R.W.: The Measurement of Appearance, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York (1987)
HunterLab: Hunter L, a, b color scale. Insight on Color. 8, 1–4 (2008) downloaded from http://www.hunterlab.com/appnotes/an08_96a.pdf
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original article revised.
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0113-z.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köseoglu, K., Cengizler, H., İsrail, L.İ. et al. Tannery wastewater sediments produced by clinoptiolite/polyacrylamide-aided flocculation as a clay additive in brick making. J Aust Ceram Soc 53, 719–731 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0085-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0085-z