Abstract
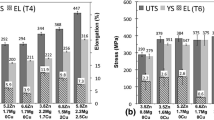
The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of different amounts of Mg on the microstructures of experimental and industrial 319 alloys. Thermal analysis was carried out for the various alloy compositions to determine the reactions corresponding to the formation of various phases. These phases were identified by examining the corresponding microstructures of the as-cast alloys. The results indicated that the addition of Mg leads to the segregation of the copper phase, resulting in the formation of the block-like form of the CuAl2 phase rather than its finer eutectic-like form. This makes it more difficult to dissolve the CuAl2 phase during solution heat treatment. It was also observed that the degree of modification achieved in the microstructures of the 319 alloys, irrespective of the alloy source, is greatly enhanced at 0.6 wt% Mg content. Addition of Mg also leads to the precipitation of the Al5Mg8Cu2Si6 phase, which normally precipitates after the CuAl2 phase. However, when the Mg level exceeds 0.4 wt%, the precipitation of the Al5Mg8Cu2Si6 phase also takes place in another reaction, before the precipitation of the CuAl2 phase. The morphology of the Al5Mg8Cu2Si6 phase in this case is script-like rather than the irregular-shaped particles normally observed. Tensile and impact properties of bars aged at different temperatures/times were reported as well.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.H. Samuel, P. Ouellet, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Effect of Mg and Sr Additions on the formation of intermetallics in Al-6 Wt Pct Si–3.5 Wt Pct Cu-(0.45) to (0.8) Wt Pct Fe 319–Type Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 29A, 2871–2884 (1998)
N. Roy, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, Porosity formation in Al-9%Si-3%Cu alloy systems: metallographic observations. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 27, 415–429 (1996)
A.M. Samuel, P. Ouellet, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Microstructural Interpretation of Thermal Analysis of Commercial 319 Al Alloy with Mg and Sr Additions. AFS Trans 105, 951–962 (1997)
J. Barresi, M.J. Kerr, H. Wang, M.J. Couper, Effect of magnesium, iron and cooling rate on mechanical properties of Al–7Si–Mg foundry alloys. AFS Trans. 117, 563–570 (2000)
C.H. Caceres, C.J. Davidson, J.R. Griffiths, Q.G. Wang, The effect of Mg on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of Al–Si–Mg casting alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30A, 2611–2618 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0301-8
Q.G. Wang, Microstructural effects on the tensile and fracture behavior of aluminum casting alloys A356/357. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34A, 2887–2899 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0189-7
Z. Ma, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Effect of Fe content and cooling rate on the impact toughness of cast 319 and 356 aluminum alloys. AFS Trans. 100, 657–666 (1992)
A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, Porosity factor in quality aluminum castings. AFS Trans 100, 657–666 (1992)
O. Elsebaie, F.H. Samuel, S.A. Alkahtani, H.W. Doty, Influence of metallurgical parameters on the impact toughness of near eutectic Al–Si alloys. Int. J. Metalcast. 102, 76–288 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0039-1
M.B. Durdjevic, B. Duric, A. Mitrasinoniv, J.H. Sokolowski, Modeling of casting processes parameters for the 3xx series of aluminum alloys using the silicon equivalency algorithm. Assoc. Metall. Eng. Serbia Mont. 9, 91–106 (2003)
J.A. Taylor, D.H. StJohn, L.H. Zheng, G.A. Edwards, J. Barresi, M.J. Couper, Solution treatment effects in Al–Si–Mg casting alloys: part 1—intermetallic phases. Aluminium Trans. 45, 95–110 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1080/13640461.2000.11819379
M. Kasprzak, W. Kasprzak, W.T. Kierkus, J.H. Sokolowski, Applications of High Frequency Induction Heating for the Metallurgical Simulation and Thermal Analysis of Industrial Light Metals Casting Processes, in Proceedings of Sessions & Symposia sponsored by the Extraction & Processing Division of TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 2002 TMS Annual Meeting, Seattle, Washington (USA), February 17–21, 2002, pp. 619–630
W. Bonfield, B.K. Dutta, Precipitation hardening in an Al–Cu–Si–Mg alloy at 130 to 220 °C. J. Mater. Sci. 11, 1661–1666 (1976)
D. Yang, Role of Magnesium Addition on the Occurrence of Incipient Melting in Experimental and Commercial Al-Si-Cu Alloys and its Influence on the Alloy Microstructure and Tensile Properties. Master’s Thesis, Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Chicoutimi, Canada, 2006, pp. 57–116
J. Gauthier, P.R. Louchez, F.H. Samuel, Heat treatment of 319.2 aluminium automotive alloy: part 1, solution heat treatment. Cast Metals 8, 91–114 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1080/09534962.1995.11819197
J. Gauthier, P.R. Louchez, and F.H. Samuel, Heat treatment of 319.2 aluminium automotive alloy: part 2, aging behavior. Cast Metals 8, 107–114 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1080/09534962.1995.11819198
S. Shivkumar, C. Keller, D. Apelian, Aging behavior in cast Al–Si–Mg alloys. AFS Trans 98, 905–911 (1990)
F.H. Samuel, Incipient melting of Al5Mg8Si6Cu2 and CuAl2 intermetallics in unmodified and strontium-modified Al–Si–Cu–Mg (319) alloys during solution heat treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 2283–2297 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004383203476
M. Tash, F.H. Samuel, F. Mucciardi, H.W. Doty, Effect of metallurgical parameters on the hardness and microstructural characterization of as-cast and heat-treated 356 and 319 aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 443, 185–201 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2006.08.054
E. Rincon, H.F. Lopez, M.M. Cisneros, H. Mancha, Temperature effects on the tensile properties of cast and heat treated aluminum alloy A319. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 519, 128–140 (2009)
J. Hernandez-Sandoval, M.H. Abdelaziz, E.A. Elsharkawi, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, Change of tensile properties with aging time and temperature in Al–Si–Cu–Mg 354 cast alloys with/without minor addition of Ni and/or Zr. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021 (2021)
M. Shayan, B. Eghbali, B. Niroumand, Synthesis and characterization of AA2024-SiO2 nanocomposites through the vortex method. Inter. Metalcast. 15, 1427–1440 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00574-y
Ç. Bolat, İC. Akgün, A. Gökşenli, Effect of aging heat treatment on compressive characteristics of bimodal aluminum syntactic foams produced by cold chamber die casting. Int. J. Metalcast. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00629-0
M. Salarvand, S.M.A. Boutorabi, M. Pourgharibshahi, M. Tamizifar, Effect of cooling rate on the microstructure and mechanical properties of high-zinc AA 5182 Aluminum wrought alloy cast by the ablation green sand mold casting process. Inter. Metalcast. 15, 1464–1475 (2021)
L. Bäckerud, G. Chai, J. Tamminen, Solidification Characteristics of Aluminum Alloys, vol. 2: Foundry Alloys (AFS/Skanaluminium, Des Plaines, IL, 1990), p. 71–84
A.M.A. Mohamed, F.H. Samuel, A Review on the Heat Treatment of Al-Si-Cu/Mg Casting Alloys, in Heat Treatment: Conventional and Novel Applications (InTech publications, 2012), p. 229
M.A. Moustafa, C. Lepage, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Metallographic observations on phase precipitation in strontium-modified Al-11.7% si alloys: role of alloying elements. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 15, 609–626 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/13640461.2003.11819547
M.F. Ibrahim, Effects of magnesium content and aging conditions on the impact toughness of 319-type Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloys. Master’s Thesis (Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Chicoutimi, Canada, 2010) p. 105–161
F.J. Tavitas-Medrano, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, On the enhancement of the impact toughness of A319 alloys: role of Mg content and melt treatment. Int. J. Metalcast. 11, 536–551 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0098-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed, A.M.A., Ibrahim, M.F., Samuel, E. et al. Assessment of the Effect of Mg Addition on the Solidification Behavior, Tensile and Impact Properties of Al–Si–Cu Cast Alloys. Inter Metalcast 17, 82–108 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00786-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00786-w