Abstract
Commercial aluminum alloys corresponding to Al-Cu-Si family are commonly used in casting and molding process because their high castability. The main characteristics of these alloys are the excellent weight/strength relation in conjunction with wear and corrosion resistance. Additionally, the mechanical properties of these alloys could be enhanced by heat treatment.
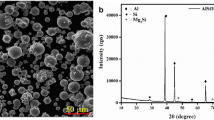
In Al A319 alloys, Cu and Mg are the main responsible to increase the mechanical properties after T6 heat treatment due to the precipitation of Al2Cu and Mg2Si and Al2CuMg phase [1]. Combined effects of Ni and Cu improve strength and hardness at relatively elevated temperature [2], Due to the low solubility of Ni in Al (0.04%), it has been reported the formation of FeAl9FeNi-type intermetallic, which is not totally dissolved with the typical solution treatments used in aluminum alloys [3]. Hayajneh et al., found that increasing amounts of intermetallic compounds Al3Ni, Al3(CuNi)2 and Al7Cu4Ni in Al-Cu alloy, the hardness increase [4].
The effect of Ni addition and solution treatment time on the microstructure and hardness of the Al A319 alloy are studied by Vickers microhardness (VHN), Rockwell B hardness (HRB), X Ray Diffraction (XRD), Optical Microscopy (OM), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tash M. a,b, Samuel F.H. a,*, Mucciardi F. c, Doty H.W. d. 2007. Effect of metallurgical parameters on the hardness and microstructural characterization of ascast and heat-treated 356 and 319 aluminum alloys. Materials Science and Engineering. 443. 185–201.
Miller W.S., Zhuang L., Bottema J., Wittebrood A.J. Smet P. D., Haszler A., Vieregge A. Recent developments in aluminum alloys for theautomotive industry. Materials Science and Engineering 280, 2000, pp.37–49.
Wessel J. K. Handbook of advanced materials: enabling new designs.Vol. 3. John Wiley & Sons; 2004, pp.185–193.
Hayajneh Mohammed T., Hassan Adel Mahamood, Jaradat Younis Mohammad. 2007. The Effect of Nickel Addition, Solution Treatment Temperature and Time on the Precipitation Hardening of (Al-Cu) Alloys. Jordan University of Science and Technology. 141. 1–5.
Sjolander Emma, Seifeddine Salem. 2010. The heat treatment of Al-Si-Cu-Mg casting alloys. Journal of Materials Processing Technology. XXX. 1–11.
Elsebaie O., Mohamed A.M.A., Samuel A.M., Samuel F.H., Al-Ahmari A.M.A. 2011. The role of alloying additives and aging treatment on impact behavior of 319 cast alloy. Materials and Design. 32. 3205–3220.
Tavitas-Medrano F.J, Grusleski J.E., Samuel F.H., Valtierra S., Doty H.W. 2008. Materials Effect of Mg and Sr-modification on the mechanical properties of 319-type aluminum cast alloys subjected to artificial aging. Materials Science and Engineering. 480. 356–364.
Tash M., Samuel F.H., Mucciardi F., Doty H.W., Valtierra S. 2006. Effect of metallurgical parameters on the machinability of heat-treated 356 and 319 aluminum alloys. Materials Science and Engineering. 434. 207–217.
Tibballs J. E., Horst J. A., Simensen C. J. 2001. Precipitation of αAl(Fe,Mn)Si from the melt. Journal of Materials Science. 36. 937–941.
Bray Jack W. 1990. Aluminum mill and Engineered wrought products. ASM International. ASM Handbook. Vol. 2, Properties and Selection: Non-ferrous alloys and Special-purpose materials. ASM International. USA. 165–166.
Zolotorevsky Vdim S., Belov Nicolai A., Glazoff Michael V. 2007. Alloying elements and dopants: Phase Diagrams. Elsevier. Casting Aluminum Alloys, vol. 1. Elsevier. Moscow, Pittsburgh. Russia-USA. 1–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medrano-Prieto, H.M., Garay-Reyes, C.G., Gómez-Esparza, C.D. et al. Influence of Solute Addition in the Microstructure and Hardness of the Al-Si-Cu Alloys. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1815, 92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2016.92
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2016.92