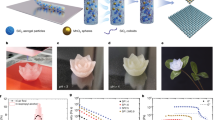
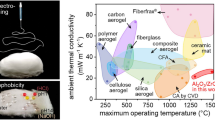
Abstract
Aerogels have the lowest thermal conductivity (< 0.2 W m−1 K−1) among known materials owing to the presence of pores, which constitute over 90% of the structure. Aerogels have mainly been commercialized for use as a thermal insulation material for building applications, such as walls and pipes. Herein, a silica aerogel thin film was fabricated by using a commercial and cost-effective HP inkjet printer. Next, silica aerogel ink was synthesized by mixing hydrophilic silica aerogel powder, solvent, and other organic additives. The thickness and pattern of the silica aerogel thin films were easily controlled by increasing the number of printing cycles and patterning by using a drawing software. The printed silica aerogel thin film had a smooth surface and thickness with well-distributed ink particles. Further, the aerogel had a unique structure comprising nanopores and nanonetworks. The thermal conductivity of the silica aerogel thin film was approximately 0.05 W m−1 K−1 at 30–300 °C. Inkjet printing of silica aerogels is expected to be a strong candidate for thermal insulating applications in micro-scale systems such as batteries and electronic chips.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parmenter, K. E., & Milstein, F. (1998). Mechanical properties of silica aerogels. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 223(3), 179–189.
Schmidt, M., & Schwertfeger, F. (1998). Applications for silica aerogel products. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 225, 364–368.
Lu, X., Arduini-Schuster, M. C., Kuhn, J., Nilsson, O., Fricke, J., & Pekala, R. W. (1992). Thermal conductivity of monolithic organic aerogels. Science, 255(5047), 971.
Fricke, J., & Tillotson, T. (1997). Aerogels: Production, characterization, and applications. Thin Solid Films, 297(1), 212–223.
Hrubesh, L. W. (1998). Aerogel applications. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 225, 335–342.
Hüsing, N., & Schubert, U. (1998). Aerogels—airy materials: Chemistry, structure, and properties. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 37(1–2), 22–45.
Soleimani Dorcheh, A., & Abbasi, M. H. (2008). Silica aerogel: Synthesis, properties and characterization. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 199(1), 10–26.
Tewari, P. H., Hunt, A. J., & Lofftus, K. D. (1985). Ambient-temperature supercritical drying of transparent silica aerogels. Materials Letters, 3(9), 363–367.
García-González, C. A., Camino-Rey, M. C., Alnaief, M., Zetzl, C., & Smirnova, I. (2012). Supercritical drying of aerogels using CO2: Effect of extraction time on the end material textural properties. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 66, 297–306.
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Wei, Y., & Zhang, X. (2015). Fast and one-pot synthesis of silica aerogels via a quasi-solvent-exchange-free ambient pressure drying process. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 218, 192–198.
Wang, Z., Dai, Z., Wu, J., Zhao, N., & Xu, J. (2013). Vacuum-dried robust bridged silsesquioxane aerogels. Advanced Materials, 25(32), 4494–4497.
Fenech, J., Viazzi, C., Ansart, F., & Bonino, J. P. (2010). Elaboration of sol-gel coatings from aerogels and xerogels of doped zirconia for TBC applications. Advanced Materials Research, 89–91, 184–189.
Liu, J., Fan, C., Shi, F., Yu, L., Huang, X., Hu, S., et al. (2016). Fabrication of Cs0.32WO3/SiO2 aerogel multilayer composite coating for thermal insulation applications. Materials Letters, 181, 140–143.
Tajiri, K., Igarashi, K., & Nishio, T. (1995). Effects of supercritical drying media on structure and properties of silica aerogel. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 186, 83–87.
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, X. (2016). Reversible superhydrophobic coatings on lifeless and biotic surfaces via dry-painting of aerogel microparticles. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 4(29), 11408–11415.
de Gans, B.-J., Duineveld, P. C., & Schubert, U. S. (2004). Inkjet printing of polymers: State of the art and future developments. Advanced Materials, 16(3), 203–2013.
Singh, M., Haverinen, H. M., Dhagat, P., & Jabbour, G. E. (2010). Inkjet printing—process and its applications. Advanced Materials, 22(6), 673–685.
Chu, W. S., Kim, M. S., Jang, K. H., Song, J. H., Rodrigue, H., Chun, D. M., et al. (2016). From design for manufacturing (DFM) to manufacturing for design (MFD) via hybrid manufacturing and smart factory: A review and perspective of paradigm shift. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, Green Technology, 3(2), 209–222.
Kang, H. S., Lee, J. Y., Choi, S., Kim, H., Park, J. H., Son, J. Y., et al. (2016). Smart manufacturing: Past research, present findings, and future directions. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 3(1), 111–128.
Lee, J., Kim, H.-C., Choi, J.-W., & Lee, I. H. (2017). A review on 3D printed smart devices for 4D printing. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 4(3), 373–383.
Chu, W.-S., Kim, C.-S., Lee, H.-T., Choi, J.-O., Park, J.-I., Song, J.-H., et al. (2014). Hybrid manufacturing in micro/nano scale: A review. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 1(1), 75–92.
Shin, D.-G., Kim, T.-H., & Kim, D.-E. (2017). Review of 4D printing materials and their properties. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 4(3), 349–357.
Kang, M., & Kang, K.-T. (2018). Flexible 2-Layer paper printed circuit board fabricated by inkjet printing for 3-D origami electronics. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 5(3), 421–426.
Liu, X., Tarn, T.-J., Huang, F., & Fan, J. (2015). Recent advances in inkjet printing synthesis of functional metal oxides. Particuology, 19, 1–13.
Li, Y., Lan, L., Sun, S., Lin, Z., Gao, P., Song, W., et al. (2017). All inkjet-printed metal oxide thin-film transistor array with good stability and uniformity using surface-energy patterns. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 9(9), 8194–8200.
Rieu, M., Camara, M., Tournier, G., Viricelle, J.-P., Pijolat, C., de Rooij, N. F., et al. (2016). Fully inkjet printed SnO2 gas sensor on plastic substrate. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 236, 1091–1097.
Delannoy, P. E., Riou, B., Brousse, T., Le Bideau, J., Guyomard, D., & Lestriez, B. (2015). Ink-jet printed porous composite LiFePO4 electrode from aqueous suspension for microbatteries. Journal of Power Sources, 287, 261–268.
Jung, S., Sou, A., Banger, K., Ko, D.-H., Chow, P. C. Y., McNeill, C. R., et al. (2014). All inkjet-printed, all-air-processed solar cells. Advanced Energy Materials, 4(14), 1400432.
He, S., Huang, Y., Chen, G., Feng, M., Dai, H., Yuan, B., et al. (2019). Effect of heat treatment on hydrophobic silica aerogel. Journal of Hazardous materials, 362, 294–302.
Han, G. D., Neoh, K. C., Bae, K., Choi, H. J., Park, S. W., Son, J.-W., et al. (2016). Fabrication of lanthanum strontium cobalt ferrite (LSCF) cathodes for high performance solid oxide fuel cells using a low price commercial inkjet printer. Journal of Power Sources, 306, 503–509.
Han, G. D., Choi, H. J., Bae, K., Choi, H. R., Jang, D. Y., & Shim, J. H. (2017). Fabrication of lanthanum strontium cobalt ferrite–gadolinium-doped ceria composite cathodes using a low-price inkjet printer. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 9(45), 39347–39356.
Kim, J. H., Feldman, A., & Novotny, D. (1999). Application of the three omega thermal conductivity measurement method to a film on a substrate of finite thickness. Journal of Applied Physics, 86(7), 3959–3963.
Wang, H., & Sen, M. (2009). Analysis of the 3-omega method for thermal conductivity measurement. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 52(7–8), 2102–2109.
Kaul, P. B., Day, K. A., & Abramson, A. R. (2007). Application of the three omega method for the thermal conductivity measurement of polyaniline. Journal of Applied Physics, 101, 083507.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Hydrogen Energy Innovation Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT(MSIT)) (No. NRF-2019M3E6A1064697) and Korea Electric Power Corporation (Grant No. R17XA05-57).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koo, J., Kim, J.W., Kim, M. et al. Inkjet Printing of Silica Aerogel for Fabrication of 2-D Patterned Thermal Insulation Layers. Int. J. of Precis. Eng. and Manuf.-Green Tech. 8, 445–451 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00189-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40684-020-00189-4