Abstract
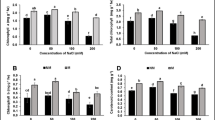
Stressful environment such as drought and salinity affects the plant growth and development. This research was conducted to find out growth and photosynthetic threshold values in Orychophragmus violaceus (L.) O. E. Schulz for an appropriate regime to dilute the salted water. O. violaceus was subjected to different treatments of NaCl (NC2.5: 2.5, NC5: 5, NC10: 10) g L−1, Na2SO4 (NS2.5: 2.5, NS5: 5, NS10: 10) g L−1, and mixture of salts (MS1: 2.5 NaCl + 10 Na2SO4; MS2: 10 NaCl + 2.5 Na2SO4; MS3: 5 NaCl + 5 Na2SO4) g L−1 and 0 as control followed by re-watering. Relative performance of stomatal conductivity and photosynthetic activity was found to have significantly affected plant growth under high-concentration salts levels at NC10, NS10, MS1, and MS2, respectively. Growth parameters were stable under slight (NC2.5 and NS2.5) to moderate stress (NC5, NS5, and MS3) conditions due to fact that photosynthetic activities were partially maintained under stimulated carbonic anhydrase activity. Consequently, the increase in net photosynthetic rate was noted under moderate stress condition which was 44.13, 37.07, and 43.01%, respectively. However, O. violaceus was found as salt tolerant up to moderate stress level, and all growth and physiological parameters were recovered during re-watering phases. Relatively, better recovery noticed in net photosynthetic rate under moderate stress levels, and values were 55.62, 65.46, and 50.82%, respectively. Hence, it is suggested that salinity effect in plants could be reduced by re-watering, based on plant physiological characteristics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas T et al (2014) Evaluation of different Okra genotypes for salt tolerance. IJPES 4:23–30
Ashraf M, Foolad M (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Azevedo-Neto ADD, Prisco JT, Enéas-Filho J, Lacerda CFD, Silva JV, Costa PHAD, Gomes-Filho E (2004) Effects of salt stress on plant growth, stomatal response and solute accumulation of different maize genotypes. Braz J Plant Physiol 16:31–38
Bhatt MJ, Patel AD, Bhatti PM, Pandey AN (2008) Effect of soil salinity on growth, water status and nutrient accumulation in seedlings of Ziziphus mauritiana (Rhamnaceae). J FruitOrnam Plant Res 16:383–401
Chartzoulakis K, Loupassaki M, Bertaki M, Androulakis I (2002a) Effects of NaCl salinity on growth, ion content and CO2 assimilation rate of six olive cultivars. Sci Hortic Amst 96:235–247
Chartzoulakis K, Patakas A, Kofidis G, Bosabalidis A, Nastou A (2002b) Water stress affects leaf anatomy, gas exchange, water relations and growth of two avocado cultivars. Sci Hortic Amst 95:39–50
Chaves M, Flexas J, Pinheiro C (2009) Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann Bot Lond 103:551–560
Chen W, Hou Z, Wu L, Liang Y, Wei C (2010) Evaluating salinity distribution in soil irrigated with saline water in arid regions of northwest China. Agr Water Manag 97:2001–2008
Cornic G (2000) Drought stress inhibits photosynthesis by decreasing stomatal aperture—not by affecting ATP synthesis. Trends Plant Sci 5:187–188
Dudley LM, Ben-Gal A, Shani U (2008) Influence of plant, soil, and water on the leaching fraction. Vadose Zone J 7:420–425
Flexas J et al (2009) Photosynthesis limitations during water stress acclimation and recovery in the drought-adapted Vitis hybrid Richter-110 (V. berlandieri × V. rupestris). J Exp Bot 60:2361–2377
Flowers T, Yeo A (1995) Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: where next? Funct Plant Biol 22:875–884
Galle A, Florez-Sarasa I, Tomas M, Pou A, Medrano H, Ribas-Carbo M, Flexas J (2009) The role of mesophyll conductance during water stress and recovery in tobacco (Nicotiana sylvestris): acclimation or limitation? J Exp Bot 60:2379–2390
Hajiaghaei-Kamrani M, Hosseinniya H (2013) Effect of salinity on nutrient uptake in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) in hydroponic system. IJAPP 4:2729–2733
Hayat S, Ali B, Hasan SA, Ahmad A (2007) Effect of 28-homobrassinolide on salinity-induced changes in Brassica juncea. Turk J Biol 31:141–146
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circ Calif Agric Exp Stn 347:357–359
Hu L, Wang Z, Huang B (2009) Photosynthetic responses of bermudagrass to drought stress associated with stomatal and metabolic limitations. Crop Sci 49:1902–1909
Hu H et al (2011) Carbonic anhydrases are upstream regulators of CO2-controlled stomatal movements in guard cells. Nat Cell Biol 13:734
Jaleel CA, Gopi R, Manivannan P, Gomathinayagam M, Sridharan R, Panneerselvam R (2008) Antioxidant potential and indole alkaloid profile variations with water deficits along different parts of two varieties of Catharanthus roseus. Colloid Surf B 62:312–318
Kalapos T (1994) Leaf water potential-leaf water deficit relationship for ten species of a semiarid grassland community. Plant Soil 160:105–112
Karlberg L, Ben-Gal A, Jansson P-E, Shani U (2006) Modelling transpiration and growth in salinity-stressed tomato under different climatic conditions. Ecol Model 190:15–40
Lee G, Carrow RN, Duncan RR (2005) Growth and water relation responses to salinity stress in halophytic seashore paspalum ecotypes. Sci Hortic Amst 104:221–236
Memon SA, Hou X, Wang LJ (2010) Morphological analysis of salt stress respose of pak choi. EJEAFChe 9:248–254
Munira S, Hossain M, Zakaria M, Ahmed J, Islam M (2015) Evaluation of potato varieties against salinity stress in Bangladesh. IJPSS 6:73–81
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Nadeem SM, Zahir ZA, Naveed M, Arshad M, Shahzad S (2006) Variation in growth and ion uptake of maize due to inoculation with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria under salt stress. Soil Environ 25:78–84
Nurfitri I, Maniam GP, Hindryawati N, Yusoff MM, Ganesan S (2013) Potential of feedstock and catalysts from waste in biodiesel preparation: a review. Energ Convers Manag 74:395–402
Shahid MA, Pervez MA, Balal RM, Ahmad R, Ayyub CM, Abbas T, Akhtar N (2011) Salt stress effects on some morphological and physiological characteristics of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). Soil Environ 30:66–73
Siddiqui ZS, Khan MA, Kim B-G, Huang J-S, Kwon T-R (2008) Physiological responses of Brassica napus genotypes to combined drought and salt stress. Plant Stress 2:78–83
Tavallali V, Rahemi M, Maftoun M, Panahi B, Karimi S, Ramezanian A, Vaezpour M (2009) Zinc influence and salt stress on photosynthesis, water relations, and carbonic anhydrase activity in pistachio. Sci Hortic Amst 123:272–279
Wang R, Kang Y, Wan S, Hu W, Liu S, Liu S (2011) Salt distribution and the growth of cotton under different drip irrigation regimes in a saline area. Agr Water Manag 100:58–69
Wilbur KM, Anderson NG (1948) Electrometric and colorimetric determination of carbonic anhydrase. J Biol Chem 176:147–154
Wu Y, Xing D (2012) Effect of bicarbonate treatment on photosynthetic assimilation of inorganic carbon in two plant species of Moraceae. Photosynthetica 50:587–594
Wu Y, Wu X, Li P, Zhao Y, Li X, Zhao X (2005) Comparison of photosynthetic activity of Orychophragmus violaceus and oil-seed rape. Photosynthetica 43:299–302
Wu Y, Li P, Zhao Y, Wang J, Wu X (2007) Study on photosynthetic characteristics of Orychophragmus violaceus related to shade-tolerance. Sci Hortic Amst 113:173–176
Wu Y, Shi Q, Wang K, Li P, Xing D, Zhu Y, Song Y (2011) An electrochemical approach coupled with Sb microelectrode to determine the activities of carbonic anhydrase in the plant leaves. In: Zeng D (ed) Future intelligent information systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 87–94
Xing D, Wu Y (2012) Photosynthetic response of three climber plant species to osmotic stress induced by polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1659–1668
Yousfi N, Sihem N, Ramzi A, Abdelly C (2016) Growth, photosynthesis and water relations as affected by different drought regimes and subsequent recovery in Medicago laciniata (L.) populations. J Plant Biol 59:33–43
Zhang L, Clarke M, Steven M, Jaggard K (2011) Spatial patterns of wilting in sugar beet as an indicator for precision irrigation. Precis Agric 12:296–316
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31301243), the national key basic research program (973) special projects (2013CB956701), the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javed, Q., Wu, Y., Xing, D. et al. Salt-induced effects on growth and photosynthetic traits of Orychophragmus violaceus and its restoration through re-watering. Braz. J. Bot 41, 29–41 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-017-0432-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-017-0432-x