Abstract
Background
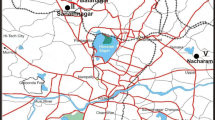
Meles River is one of the major Zn, Cr, Cu, Ni and Pb sources that enter Izmir inner Bay. However, the impacts of land uses on the river’s catchment basin has not been investigated before. The study aims to exhibit the impacts of various land uses located on the catchment basin of the river. Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni and Zn concentrations were determined to present the current situation. In addition, the correlation analyses were performed in order to identify the metals’ possible sources in the city.
Methods
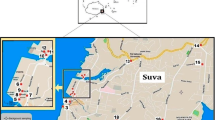
Soils and street dusts from the sites representing industrial, residential, and commercial areas and the roads in Meles River basin were sampled and heavy metal levels were determined by using the aqua regia digestion. The correlations among the analytical parameters and the factors loaded with clusters of parameters identified by Principal Component Analysis were used to describe the major sources of studied elements The contamination assessment was also done by using the geoaccumulation index (Igeo) and enrichment factor (EF) values.
Results
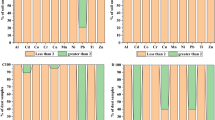
Ni concentrations (average 697 mg kg−1) in soils were higher than the levels in street dusts (average 548 mg kg−1). Dust samples contained 131 mg kg−1 Pb, 179 mg kg−1 Cr, 347 mg kg−1 Cu, and 241 mg kg−1 Zn, while the average values of these metals were detected in lower levels in soils. The average values were found as 114 mg kg−1, 125 mg kg−1, 143 mg kg−1, and 129 mg kg−1, for Pb, Cr, Cu and Zn, respectively. The main component of soil heavy metals was determined as geochemical background enriched with long-term industrial depositions. Similarly, industrial emissions were found to be the major influence on the heavy metal levels in street dusts.
Conclusions
Soil and street dust heavy metal levels are significantly affected by emissions from intense industrial activities and traffic emissions, and heavy metals are transported between these two matrices by exchanging masses between each other.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sansalone JJ, Buchberger SG. Partitioning and first flush of metals in urban roadway storm water. J Environ Eng. 1997;123(2):134–43.
Razo I, Carrizales L, Castro J, Diaz-Barriga F, Monroy M. Arsenic and heavy metal pollution of soil, water and sediments in a semi-arid cimate mining area in Mexico. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004;152(1–4):129–52.
Göber P, Dierkes C, Coldewey WG. Stormwater runoff concentration matrix for urban areas. J Contam Hydrol. 2007;91:26–42.
Duruibe JO, Ogwuegbu MOC, Egwurugwu JN. Heavy metal pollution and human biotoxic effects. Int J Phys Sci. 2007;2(5):112–8.
Elik A. Heavy metal accumulation in street dust samples in Sivas. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal. 2003;34(1–2):145–56.
Trujillo-Gonzalez JM, Torres-Mora M, Keesstra S, Brevik E, Jimenez-Ballesta R. Heavy metal accumulation related to population density in road dust samples taken from urban sites under different land uses. Sci Total Environ. 2016;533:636–42.
Fard RF, Naddafi K, Hassanvand MS, Khazaei M, Rahmani F. Trends of metal enrichment in deposited particulate matter at semi-arid area of Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2018;25:18737–51.
Chen TB, Zheng YM, Chen H, Wu H, Zhou J, Luo J, et al. Arsenic accumulation in soils for different land use types in Beijing (in Chinese). Geogr Res. 2005;24:229–35.
Kang JH, Lee SW, Cho KH, Ki SJ, Cha SM, Kim JH. Linking land-use type and stream water quality using spatial data of fecal indicator bacteria and heavy metals in the Yeongsan River basin. Water Res. 2010;44:4143–57.
Bail J, Yang Z, Cui B, Gao H, Ding Q. Some heavy metals distribution in wetland soils under different land use types along a typical plateu lake, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2010;106(2):344–8.
Kamani H, Ashrafi SD, Isazadeh S, Jaafari J, Hoseini M, Mostafapour FK, et al. Heavy metal contamination in street dusts with various land uses in Zahedan, Iran. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2015;94:382–6.
Christoforidis A, Stamatis N. Heavy metal contamination in street dust and roadside soil along the major national road in Kavala’s region, Greece. Geoderma. 2009;151:257–63.
Guney M, Onay TT, Copty NK. 2010. Impact of overland traffic on heavy metal levels in highway dust and soils of Istanbul, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess. 2010;161:101–10.
Dassenakis M, Scoullos M, Foufa E, Krasakpoulou E, Pavlivdou A, Kloukinitou M. Effects of multiple source pollution on a small Mediterrenean river. Appl Geochem. 1998;13:197–211.
TurkStat. Population of provinces by years, 2000–2017. In Republic of Turkey, Prime Ministry Turkish Statistical Institute. http://www.turkstat.gov.tr. Accessed Dec 15 2018.
Muezzinoğlu A, Çizmecioglu S. Deposition of heavy metals in a Mediterrenean climate area. Atmos Res. 2006;81:1–16.
Akinci G, Guven ED, Keles US. Assessing pollution in Izmir Bay from rivers in western Turkey:heavy metals. Environ Sci Process Imp. 2013;15:2252–62.
Kilicaslan C, Özkan B. From past to extant Meles River. ZKÜ J Bartın Forestry Faculty. 2006;8(9):51–9.
ESBAS. Aegean Free Zone Development&Operating C.O. Document. http://www.esbas.com.tr/en/why-esbas. Accessed Nov 2018.
Nal S. Sustainable transport in city-regions:the case of Izmir city region. A thesis submitted to the graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences of Middle East Technical University. 2008, Ankara.
Caliskanelli P, Ozuysal M, Tanyel S, Yayla N. Comparison of different capacity models for traffic circles. Transport. 2010;24(4):257–64.
Chen M, Ma LQ. Comparison of three aqua regia digestion methods for twenty Florida soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 2001;65:491–9.
Soylak M, Turkoglu O. Trace metal accumulation caused by traffic in agricultural soil near a motorway in Kayseri-Turkey. J Trace Microprobe Techn. 1999;17(2):209–17.
Müller M. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of Rhine River. Geojournal. 1969;2:108–18.
Kara M, Dumanoglu Y, Altıok H, Elbir T, Odabası M, Bayram A. Spatial distribution and source identiification of trace elements in topsoil from heavily industrialized region, Aliaga, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess. 2014;186:6017–38.
Tarcan G, Akinci G, Danışman MA. Assessment of the pollution from tannery effluents upon waters and soils in and around Kula vicinity, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010;213:199–210.
Wedepohl KH. The composition of the continental crust, Ingerson lecture. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1995;59(7):1217–32.
Yatkin S, Bayram A. Investigation of chemical compositions of urban, industrial, agricultural, and rural top-soils in Izmir, Turkey. Clean Soil Air Water. 2011;39(6):522–9.
Kaiser HF. The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educ Psychol Meas. 1960;20:141–51.
Mahanta MJ, Bhattacharyya KG. Total concentrations, fractionation and mobility of heavy metals in soils of urban area of Guwahati, India. Environ Monit Assess. 2011;173:221–40.
Shi G, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi C, et al. Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and rodside dust in Shangai, China. Environ Pollut. 2008;156:251–60.
Yaylalı-Abanuz G. Heavy metal contamination of surface soil around Gebze industrial area, Turkey. Microchem J. 2011;99:82–92.
Wu S, Peng S, Zhang X, Wu D, Zhang T, Zhou S, et al. Levels and health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban soils in Dongguan, China. J Geochem Explor. 2015;148:71–8.
Ordonez A, Loredo J, Miguel ED, Charlesworth S. Distribution of heavy metals in street dusts and soils of an industrial city in northern Spain. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2003;44:160–70.
Karim Z, Qureshi BA. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soil of Karachi, Pakistan. Hum Ecol Risk Assess. 2014;20(3):658–67.
Guvenç N, Alagha O, Tuncel G. Investigation of multi-element composition in Antalya, Turkey. Environ Int. 2003;29(5):631–40.
Official Gazette. Regulation of the Quality of Gasoline and Diesel Fuel, Official Gazette No: 25489. Ankara: Ministry of Environment and Forestry; 2004.
Mehr MR, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Shariifi R, Lahijanzadeh A, Kermani M. Distribution, source identification and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in urban areas of Isfahan province, Iran. J Afr Earth Sci. 2017;132:16–26.
Alloway BJ. Heavy metals in soils (Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability. 3rd ed. Springer Netherlands:Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht; 2013.
Arslan H. Heavy metals in street dust in Bursa, Turkey. J Trace Microprobe Techn. 2001;19(3):439–45.
Lu X, Wang L, Lei K, Huang J, Zhai Y. Contamination assessment of coppe, lead, zinc, manganese and nickel in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater. 2009;161:1058–62.
Al-Khashman O. Heavy metal distribution in dust, street dust and soils from the work place in Karak industrial estate, Jordan. Atmos Environ. 2004;38:6803–12.
Akhter MS, Madany IM. Heavy metals in street and hose dust in Bahrain. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1993;66:111–9.
Chen T, Zheng Y, Lei M, Huang Z, Wu H, Chen H, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chemosphere. 2005;60:542–51.
Fleming GA, Parle PJH. Heavy metals in soils, herbage and vegetation from an industrialized area west of Dublin-city. Ir J Agric Res. 1977;16:35–48.
El-Hasan T, Batarseh M, Al-Omari H, Ziadat A, El-Alali A, Al-Naser F, et al. The distribution of heavy metals in urban street dusts of Karak City, Jordan. Soil Sediment Contam. 2006;15(4):357–65.
Kumar M, Furumai H, Kurisu F, Kasuga I. Tracing source and distribution of heavy metals in road dust, soil and soakaway sediment through speciation and isotopic fingerprinting. Geoderma. 2013;211-212:8–17.
Shi G, Chen Z, Bi C, Li Y, Teng J, Wang L, et al. Comprehensive assessment of toxic metals in urban and suburban street deposited sediments (SDSs) in the biggest metropolitan area of China. Environ Pollut. 2010;158(3):694–703.
Zhu W, Bian B, Li L. Heavy metal contamination of road-deposited sediments in a medium size city of China. Environ Monit Assess. 2008;147:171–81.
Young TM, Heeraman DA, Sirin G, Ashbaug LL. Resuspension of soil as a source of airborne lead near industrial facilities and highways. Environ Sci Technol. 2002;36:2484–90.
Adachi K, Tainosho Y. Characterization of heavy metal particles embedded in tire dust. Environ Int. 2004;30(8):1009–17.
Kabata-Pendias A. Trace elements in soils and plants. Third ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2000. p. 413.
Batjargal T, Otgonjargal E, Baek K, Yang JS. Assessment of metals contamination of soils in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. J Hazard Mater. 2010;184(1–3):872–6.
Ma J, Singhirunnusorn W. Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface dusts of Maha sarakham municipality. Procedia Soc Behav Sci. 2012;50(1):280–93.
Councell TB, Duckenfield KU, Landa ER, Callender E. Tire-wear particles as a source of zinc to the environment. Environ Sci Technol. 2004;38(15):4206–14.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Dr. Gorkem Akinci for her expertise and assistance throughout all aspects of my study. I also would like to thank Dr. Aylin Alin for her comments that greatly improved the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the self-incomes of Dokuz Eylul University-Solid Wastes and Soil Pollution Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guven, E.D. Heavy metal contamination in street dusts and soils under different land uses in a major river basin in an urbanized zone of Aegean region, Turkey. J Environ Health Sci Engineer 17, 917–930 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00408-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00408-4