Abstract
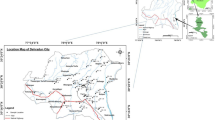
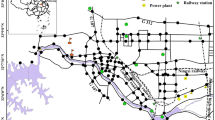
Road dust in industrial areas carries high levels of toxic heavy metals. Exposure to such polluted dust significantly affects the health of people residing in these areas, which is of major concern. The present study was taken up with an aim to highlight the magnitude and potential sources of accumulation of heavy metals in 32 road dust samples collected from six industrial areas of Hyderabad. Acid-digested sample solutions were analyzed by ICP-MS for Cu, Zn, Cr, Co, Pb, Ni, V, Zr, Ce, Y, and Hf. The road dusts exhibit significantly high mean metal levels which are much above their crustal abundances. The relative ordering of mean metal contents is Zr > Zn > Pb > Cr > Ce > Cu > V > Ni > Y > Co > Hf. Elevated pollution indices (I geo, EF, C i f, and C deg) reveal that the road dusts are pollution impacted showing varying degree of heavy metal contamination. Strong positive correlations exhibited by metal pairs Cu-Zn, Cr-Ni, Ce-V, Y-Ce, and Hf-Zr imply their origin from common anthropogenic sources. Principal component analysis grouped the metals according to the sources which contributed to their accumulation. The present study confirms to an intensive anthropogenic impact on the accumulation of heavy metals in the studied road dusts attributable mainly to strong influences of vehicular and industrial activity and partly to domestic and natural processes. The results obtained imply the need for further investigations to assess their ecological implications and human health risks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C. (2001). Trace elements in terrestrial environments. Biogeochemistry, bioavailability and risks of metals (2nd ed.p. 867). Berlin: Springer.
Ahmed, F., Bibi, M. H., & Ishiga, H. (2007). Environmental assessment of Dhaka city (Bangladesh) based on trace metal contents in road dusts. Environmental Geology, 51, 975–985.
Alloway, B. J., & Ayres, D. C. (1997). Chemical principles of environmental pollution (2nd ed.p. 395). London: Blackie academic and professional.
Balakrishna, S., & Raghava Rao, M. (1961). Pink and gray granites of Hyderabad. Current Science, 30, 264–274.
Balaram, V., & Rao, T. G. (2003). Rapid determination of REEs and other trace elements in geological samples by microwave acid digestion and ICP-MS. Atomic Spectroscopy, 24, 206–212.
Balaram, V., Kamala, C. T., Mathur, R., Rao, S., & Satyanarayanan, M. (2013). PGE in road dust/ top soil from major Indian cities: implications on human health and environment. In M. Ramkumar (Ed.), On a sustainable future of the earth’s natural resources (pp. 85–107) . Berlin: Springer Verlag.Springer Earth System Sciences
Banerjee, A. D. K. (2003). Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environmental Pollution, 123, 95–105.
Brown, H. S., Kaspertan, R. E., & Raymonds, S. (1990). Trace pollutants. In B. L. Turner, W. C. Clarke, R. W. Yates, J. F. Richards, J. T. Mathews, & W. B. Meyer (Eds.), The Earth as transformed by human action (pp. 437–455). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Buat-Menard, P., & Chesselet, R. (1979). Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 42, 398–411.
Charlesworth, S., Everett, M., McCarthy, R., Ordonez, A., & De Miguel, E. (2003). A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environment International, 29, 563–573.
De Miguel, E., Llamas, J. F., Chacon, E., Berg, T., Larssen, S., Royset, O., & Vadset, M. (1997). Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmospheric Environment, 31, 2733–2740.
Edwards, R., Lepp, N. W., & Jones, K. C. (1995). Other less abundant elements of potential significance. In B. J. Alloway (Ed.), Heavy metals in soils (2nd ed., pp. 307–352). London, U. K.: Blackie Academic/Chapman and Hall.
Fergusson, J. E. (1990). The heavy elements: chemistry, environmental impacts and health effects (p. 614). Oxford, U. K.: Pergamon press.
Gnaneshwar, P., & Sitaramayya, S. (1998). Petrochemistry and origin of archean granitic rocks of Hyderabad city. Indian Journal of Geology, 70, 249–264.
Goering, P. L., Fisher, B. R., & Fowler, B. A. (1991). The lanthanides. In E. Merian (Ed.), Metals and their compounds in the environment (p. 959). Weinheim: V.C.H.
Govil, P. K., Sorlie, J. E., Murthy, N. N., Sujatha, D., Reddy, G. L. N., Lund, R. K., Krishna, A. K., & Ram Mohan, K. (2008). Soil contamination of heavy metals in the Katedan Industrial Development Area, Hyderabad, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 140, 313–323.
Govindaraju, K. (1994). Compilation of working values and sample description for 383 geostandards. Geostandards Newsletter, 18 , 1–158.special issue
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
Helmers, E. (1996). Elements accompanying platinum emitted from automobile catalysts. Chemosphere, 33, 405–419.
Hjortenkrans, D. S. T., Bergback, B. G., & Haggerud, A. V. (2007). Metal emissions from brake linings and tires: case studies of Stockholme, Sweden, 1995 / 1998 and 2005. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 5224–5230.
IES (2008). Co-Benefits analysis of air pollution and GHG emissions for Hyderabad, India. Report prepared by Guttikunda, S. for Integrated Environmental Strategies, India Program, USEPA, Washington, D.C. http://www.epa.gov/ies/pdf/india
Jarvis, K. E., Parry, S. J., & Piper, J. M. (2001). Temporal and spatial studies of autocatalyst derived platinum, rhodium and palladium and selected vehicle derived trace elements in the environment. Environmental Science and Technology, 35, 1031–1036.
Kaiser, H. F. (1960). The application of electronic computers to factor analysis. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 20, 141–151.
Kogel, J. E., Trivedi, N. C., Barker, J. M., & Krukowski, S. T. (2006). Industrial minerals and rocks: commodities, markets and uses (7th ed.p. 1548). Littleton, Colorado, USA: Society for Mining, Metallurgy and Exploration, Inc.
Krishna, A. K., & Govil, P. K. (2008). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around Manali industrial area, Chennai, Southern India. Environmental Geology, 54, 1465–1472.
Krishna, A. K., Satyanarayanan, M., & Govil, P. K. (2009). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: a case study from Patancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167, 366–373.
Lin, C. C., Chen, S. J., Huang, K. L., Hwang, W. I., Chang-Chien, G. P., & Lin, W. Y. (2005). Characteristics of metals in nano / ultrafine / fine/ coarse particles collected beside a heavily trafficked road. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 8113–8122.
Loska, K., Wiechula, D., & Korus, I. (2004). Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environment International, 30, 159–165.
Mathur, R., Balaram, V., Satyanarayanan, M., Sawant, S. S., & Ramesh, S. L. (2011). Anthropogenic platinum, palladium and rhodium concentrations in road dusts from Hyderabad city, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62, 1085–1098.
Muller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2, 108–118.
Muller, G. (1981). Die Schwermetallbelastung der sedimentation des Neckars und Seiner Nebenflusse : Eine Bestandsaufnahme. Chemiker-Zeitung, 6, 157–164.
Pacyna, E. G., Pacyna, J. M., Fudala, J., Strzelecka-Jastrzab, E., Hlawiczka, S., Panasiuk, D., Nitter, S., Pregger, T., Pfeiffer, H., & Friedrich, R. (2007). Current and future emissions of selected heavy metals to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in Europe. Atmospheric Environment, 41, 8557–8566.
Parekh, P. P., Khwaja, H. A., Khan, A. R., Naqvi, R. R., Malik, A., Khan, K. M., & Hussain, G. (2002). Lead content of petrol and diesel and its assessment in an urban environment. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 74, 255–262.
Reddy, M. V., Babu, K. S., Balaram, V., & Satyanarayanan, M. (2012). Assessment of the effects of municipal sewage, immersed idols and boating on the heavy metal and other elemental pollution of surface water of the eutrophic Hussainsagar lake, Hyderabad, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 1991–2000.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (2005). Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Science of the Total Environment, 33, 91–107.
Rodriguez, S., Xavier, Q., Alastuey, A., Viana, M., Alarcon, M., Mantilla, E., & Ruiz, C. R. (2004). Comparative PM10 - PM2.5 source contribution study at rural ,urban and industrial sites. PM episodes in eastern Spain. Science of the Total Environment, 328, 95–113.
Romic, M., & Romic, D. (2003). Heavy metal distribution in agricultural top soils in urban area, England. Environmental Geology, 43, 795–805.
Roy, P., Balaram, V., Kumar, A., Satyanarayanan, M., & Rao, T. G. (2007). New REE and trace element data on two kimberlitic reference materials by ICP-MS. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 31(3), 261–273.
Schaller, K. H. (1991). Zirconium. In E. Merian (Ed.), Metals and their compounds in the environment (pp. 1343–1348). Weinheim: VCH.
Shi, X., Chen, L., & Wang, J. (2013). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal pollution in street dusts of Xianyang city, NW China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69, 1973–1979.
Singh, A. K. (2011). Elemental chemistry and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in road dust from Dhanbad and Bokaro regions, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62, 1447–1459.
Stigliani, W. M., Doelman, P., Salomons, W., Schulin, R., Schmidt, G. R. B., & van der Zee, S. E. A. T. M. (1991). Chemical time bombs: predicting the unpredictable. Environment, 33, 26–30.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–627.
Taylor, S. R., & McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: its composition and evolution (p. 312). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Thorpe, A., & Harrison, R. M. (2008). Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: a review. Science of the Total Environment, 400, 270–282.
Wei, B., Jiang, F., Li, X., & Mu, S. (2010). Contamination levels assessment of potential toxic metals in road dust deposited in different types of urban environment. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61, 1187–1196.
WHO (2007). Health risks of heavy metals from long- range transboundary air pollution. Scherfigsvej 8 DK-2100, Copenhagen, Denmark: World Health Organization, Regional Office for Europe.
Wik, A., & Dave, G. (2009). Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment –a critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environmental Pollution, 157, 1–11.
Yongming, H., Peixuan, D., Junji, C., & Posmentier, E. S. (2006). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 355, 176–186.
Zereini, F., Wiseman, C., Beyer, J. M., Artelt, S., & Urban, H. (2001). Platinum, lead and cerium concentrations of street particulate matter (Frankfurt, Germany). Journal of Soils and Sediments, 1, 188–195.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Director, CSIR-National Geophysical Research Institute, Hyderabad, for his support and permission to publish this paper. The present study was carried out and funded by CSIR-NGRI institute project MLP-6201-28 (CM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathur, R., Balaram, V., Satyanarayanan, M. et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination of road dusts from industrial areas of Hyderabad, India. Environ Monit Assess 188, 514 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5496-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5496-8