Abstract
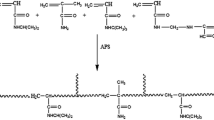
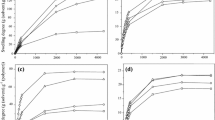
In the present study, hydrogels were prepared by free radical polymerization in water–dioxane mixture with fixed molar ratio (25 mol%) of N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) and varying remaining molar concentrations of N-tert-butylacrylamide (NTBA) and acrylamide (AAm). The structure of the resultant hydrogels was studied by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques. The thermal properties of the hydrogels were analyzed by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) methods. DSC thermograms were used for the quantitative determination of free, interfacial and bound water contents. The result showed that the free and interfacial water contents increased with increase in the hydrophilic AAm content, and the bound water content increased with hydrophobic NTBA content in the hydrogels. Swelling behavior of the hydrogels was evaluated at different temperatures. The percentage swelling and diffusion kinetic parameters (network structure constant, type of diffusion and diffusion constant) were calculated for all samples. The diffusion was found to be Fickian type for copolymer having equimolar concentrations of NTBA and AAm and non-Fickian type for others. Diffusion coefficients of the hydrogels were found to be increased with increasing temperature. In addition, poly(NIPAM-co-NTBA-co-AAm) hydrogels were used in concentration separation process for BSA solution. The result showed that the copolymer with equimolar NTBA and AAm contents has high separation efficiency with good thermoresponsive behavior among all copolymers.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mu B, Wang T, Wu Z, Shi H, Xue D, Liu P (2011) Fabrication of functional block copolymer grafted supermagnetic nanoparticles for targeted and controlled drug delivery. Coll Surf A 75:163–168
Kumara A, Srivastavaa A, Galaevb IY, Mattiasson B (2007) Smart polymers: physical forms and bioengineering applications. Prog Polym Sci 32:1205–1237
Chunyue P, Quigde L, Dian YU, Yanping R, Nianqian W, Xingcui L (2008) Swelling and drug releasing properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) thermosensitive copolymeric gels. Front Chem China 3:314–319
Ayano E, Kanazawa H (2006) Aqueous chromatography system using temperature-responsive polymer-modified stationary phases. J Sep Sci 29:738–749
Hirokawa Y, Tanaka T (1984) Volume phase transition in a nonionic gel. J Chem Phys 81:6379–6380
Zuang YF, Chen LW, Zhu ZQ, Yang H (2000) Preparation and separation function of N-isopropylacrylamide copolymer hydrogels. Poly Adv Technol 11:192–197
Han J, Park CH, Ruan R (1995) Concentrating alkaline serine protease, subtilisin using a temperature sensitive hydrogel. Biotechnol Lett 17:851–852
Park CH, Avila IO (1992) Concentrating cellulose from fermented broth using a temperature sensitive hydrogel. Biotechnol Prog 8:521–526
Kayaman N, Kazan D, Erarslan A, Okay O, Baysal BM (1998) Structure and protein separation efficiency of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gels: effect of synthesis conditions. J Appl Polym Sci 67:805–814
Zhuang Y, Wang G, Yang H, Zhu Z, Fu J, Song W, Zhao H (2005) Radiation polymerization and concentration separation of P(NIPA-co-AMPS) hydrogels. Polym Int 54:617–621
Yildiz B, Isik B, Ki M (2002) Synthesis and characterization of thermoresponsive isopropylacrylamide–acrylamide hydrogels. Eur Polym J 48:1343–1347
Demirel G, Özçetin G, Turan E, ÇayKara T (2005) pH/Temperature-sensitive imprinted ionic poly(N-tert-butylacrylamide-co-acrylamide/maleic acid) hydrogels for bovine serum albumin. Macromol Biosci 5:1032–1037
Rochev YU, O’Halloran D, Gorelova T, Gilcreest V, Selenzneva I, Gavrilyuk B, Gorelov A (2004) Rationalising the design of polymeric thermoresponsive biomaterials. J Mater Sci Mater Med 15:513–517
Ni C, Zhu XX (2004) Synthesis and swelling behavior of thermosensitive hydrogels based on N-substituted acrylamides and sodium acrylate. Eur Polym J 40:1075–1080
Save NS, Jassal M, Agrawal AK (2003) Stimuli sensitive copolymer poly(N-tert-butylacrylamide–ran-acrylamide): processing into thin films and their translational behavior. Polymer 44:7979–7988
Ozturk V, Okay O (2002) Temperature sensitive poly(N-t-butylacrylamide-co-acrylamide) hydrogels: synthesis and swelling behavior. Polymer 43:5017–5026
Thomas W (1964) Acrylamide polymers In: Bikales NM (ed) Encyclopedia of polymer science and technology, vol 1, Wiley Int Sci, NY, p 177–179
Van Dyke JD, Kasperski KL (1993) Thermogravimetric study of polyacrylamide with evolved gas analysis. J Polym Sci Part A Polym Chem 31:1807–1823
Katime I, Díaz de Apodaca E, Mendizábal E, Puig JE (2000) Acrylic acid/methyl methacrylate hydrogels. I. Effect of composition on mechanical and thermodynamic properties. J Mac Sci Part A 37:307–321
Huglin MB, Rehab MM, Zakaria MB (1986) Thermodynamic interaction in copolymeric hydrogels. Macromolecules 19:2986–2991
Li W, Xue F, Cheng R (2005) States of water in partially swollen poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Polymer 46:12026–12031
Davis TP, Huglin MB, Yip DCF (1988) Properties of poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) hydrogels crosslinked with ethyleneglycol dimethacrylate. Polymer 29:701–706
Abraham AA, Sen AK (2010) Thermal and swelling studies of hydrophobically modified poly(acrylamide) hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 117:2795–2802
Kim SJ, Park SJ, Kim SI (2003) Synthesis and characteristics of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels composed of poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). React Funct Polym 55:61–67
Isreachvilli JN (1992) Special interaction: hydrogen-bonding, hydrophobic and hydrophilic interaction. In: Intermolecular and surface forces, Academic Press, NY, p 151–167
Tanford C (1980) The structure of water. In: The hydrophobic effect: formation of micelles and biological membranes, 2nd edn. Wiley, USA, p 29–41
Berens AR, Hopfenberg HB (1978) Diffusion and relaxation in glassy polymer powders: 2. Separation of diffusion and relaxation parameters. Polymer 19:489–496
Buckley JD, Berger MJ (1962) The swelling of polymer system in solvents. II. Mathematics of diffusion. J Polym Sci 56:175–188
Peppas NA, Franson NM (1983) The swelling interface number as a criterion for prediction of diffusional solute release mechanisms in swellable polymers. J Polym Sci Phys Ed 21:983–997
Bajpai SK, Singh S (2006) Analysis of swelling behavior of poly(methacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) hydrogels and effect of synthesis conditions on the water uptake. React Funct Polym 66:431–440
Bajpai SK (2000) Poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone)-polyacrylamide hydrogels as extraction solvents. Iran Polym J 9:19–27
Kabra BG, Gehrke SH, Hwang ST, Ritschel WA (1991) Modification of the dynamic swelling behavior of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) in water. J Appl Polym Sci 42:2409–2416
Katime I, Novoa R, Díaz de Apodaca E, Mendizábal E, Puig JE (1999) Theophylline release from poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) hydrogels. Polym Test 18:559–566
Kardag E, Saraydin D (2002) Swelling of superabsorbent acrylamide–sodium acrylate hydrogels prepared using multifunctional crosslinkers. Turk J Chem 26:863–875
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Central Instrumentation Facility (CIF) at Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, established in 2006, and the Technical Education Quality Improvement Programme (TEQIP) funded by World Bank for the State of the Art Instrumentation Facility. The authors also acknowledge the financial support from the Central Coir Research Institute (CCRI), Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) (Government of India), Alappuzha, Kerala, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shekhar, S., Mukherjee, M. & Sen, A.K. Synthesis, characterization and protein separation efficiency of N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-tertiary butylacrylamide-co-acrylamide-based hydrogels. Iran Polym J 21, 895–905 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-012-0094-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13726-012-0094-2