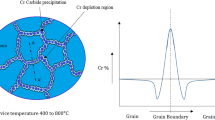
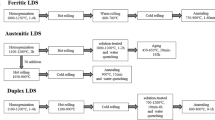
Abstract
In this manuscript, the latest developments pertaining to sensitization are discussed. Sensitization leads to intergranular corrosion and intergranular stress corrosion cracking. The advantages and disadvantages of conventional methods to combat sensitization are elaborated. Emerging/newer techniques such as grain boundary engineering, creation of orientation gradients, and high density of twinning to improve resistance to sensitization are also covered. Detection and monitoring of deleterious phase precipitation such as carbides, nitrides, and other intermetallic phases during operation necessitate making use of nondestructive testing (NDT) methods. Possible information that we get from NDT is for material characterization includes the size, shape, and location of a defect. Herein, the significant developments for monitoring and detection of phases concerning sensitization by NDT are discussed. These range from magnetic methods to ultrasonic techniques. The multi-physics approach is essential to fully utilize NDT to ensure/predict the lifetime of the components used in the industry. Further, proper selection of suitable NDT for defect detection can avert accidents, catastrophic failures, and economic losses due to corrosion degradation. For this, the corrosion engineer/corrosionist properly apply the suitable techniques (prevention, monitoring, and assessment) to address the issues of sensitization among the wide choice available.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kain V, Chandra K, Adhe KN, De PK (2004) Effect of cold work on low-temperature sensitization behaviour of austenitic stainless steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 334:115–132
Lozano-Perez S, Yamada T, Terachi T, Schröder M, English CA, Smith GDW, Grovenor CRM, Eyre BL (2009) Multi-scale characterization of stress corrosion cracking of cold-worked stainless steels and the influence of Cr content. Acta. Mater. 57:5361–5381
Gordon BM (2013) Corrosion and corrosion control in light water reactors. Jom. 65:1043–1056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-013-0658-4
Engelberg DL (2010) 2.06—intergranular corrosion. Shreir’s Corros. 2:810–827
Wang J, Shi W, Xiang S, Ballinger RG (2021) Study of the corrosion behaviour of sensitized 904L austenitic stainless steel in Cl- solution. Corros. Sci. 181:109234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.109234
Kumar S, Shahi AS, Sharma V, Malhotra D (2021) Effect of welding heat input and post-weld thermal aging on the sensitization and pitting corrosion behavior of AISI 304L stainless steel butt welds. J Mater Eng Perform. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05454-4
Singh R, Chowdhury SG, Das G, Singh PK, Chattoraj I (2012) Low temperature sensitization on the orthogonal surfaces of prior deformed AISI 304LN and aged at 673 K to 873 K (400 °C to 600 °C). Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 43:986–1003
Kain V (2011) Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) in stainless steels. In: Raja VS, Shoji T (eds) Stress Corrosion Cracking Theory and Practice, 1st edn. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge, pp 199–244
Kain V, Prasad RC, De PK (2002) Testing sensitization and predicting susceptibility to intergranular corrosion and intergranular stress corrosion cracking in austenitic stainless steels. Corrosion 58:15–37
Srinivasan N, Kain V, Birbilis N, Mani Krishna KV, Shekhawat S, Samajdar I (2015) Near boundary gradient zone and sensitization control in austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 100:544–555
Ramírez LM, Almanza E, Murr LE (2004) Effect of uniaxial deformation to 50% on the sensitization process in 316 stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 53:79–82
Alvarez C, Almanza E, Murr L (2005) Evaluation of the sensitization process in 304 stainless steel strained 50% by cold-rolling. J. Mater. Sci. 40:2965–2969
Singh R (2008) Influence of cold rolling on sensitization and intergranular stress corrosion cracking of AISI 304 aged at 500 °C. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 206:286–293
Jinlong LV, Hongyun L (2012) Influence of tensile pre-strain and sensitization on passive films in AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 135:973–978
Solomon N, Solomon I (2017) Effect of deformation-induced phase transformation on AISI 316 stainless steel corrosion resistance. Eng. Fail. Anal. 79:865–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.05.031
Zhang X, Tang J, Liu H, Gong J (2019) Effects of pre-strain on sensitization and interganular corrosion for 304 stainless steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 106:104179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.104179
Singh R, Chowdhury SG, Ravi Kumar B, Das SK, De PK, Chattoraj I (2007) The importance of grain size relative to grain boundary character on the sensitization of metastable austenitic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 57:185–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.04.017
Kolli S, Javaheri V, Kömi J, Porter D (2019) On the role of grain size and carbon content on the sensitization and desensitization behavior of 301 austenitic stainless steel. Metals. https://doi.org/10.3390/met9111193
Kavner A, Devine TM (1997) Effect of grain boundary orientation on the sensitization of austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 32:1555–1562
Pradhan SK, Prithiv TS, Mandal S (2017) Through-thickness microstructural evolution during grain boundary engineering type thermomechanical processing and its implication on sensitization behavior in austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 134:134–142
Kaithwas CK, Bhuyan P, Pradhan SK, Mandal S (2018) Microstructure evolution during low-strain thermo-mechanical processing and its repercussion on intergranular corrosion in alloy 600H. Mater. Charact. 145:582–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.09.019
Fujii T, Tohgo K, Mori Y, Shimamura Y (2018) Crystallography of intergranular corrosion in sensitized austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 144:219–226
Almanza E, Murr LE (2000) A comparison of sensitization kinetics in 304 and 316 stainless steels. J. Mater. Sci. 35:3181–3188
Jinlong L, Hongyun L (2014) Temperature dependence of sensitization on tensile pre-strained AISI 304 stainless steels. J. Alloys Compd. 588:509–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.048
Srinivasan N, Kain V, Birbilis N, Kumar BS, Gandhi MN, Sivaprasad PV, Chai G, Lodh A, Ahmedabadi PM, Samajdar I (2016) Plastic deformation and corrosion in austenitic stainless steel: a novel approach through microtexture and infrared spectroscopy. Corros. Sci. 111:404–413
Wasnik DN, Kain V, Samajdar I, Verlinden B, De PK (2002) Resistance to sensitization and intergranular corrosion through extreme randomization of grain boundaries. Acta. Mater. 50:4587–4601
Shimada M, Kokawa H, Wang ZJ, Sato YS, Karibe I (2002) Optimization of grain boundary character distribution for intergranular corrosion resistant 304 stainless steel by twin-induced grain boundary engineering. Acta. Mater. 50:2331–2341
Srinivasan N, Kumaran SS, Venkateswarlu D (2018) Effects of in-grain misorientation developments in sensitization of 304 L austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Res. Express. 6:016551. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae802
Lai CL, Tsay LW, Kai W, Chen C (2010) The effects of cold rolling and sensitisation on hydrogen embrittlement of AISI 304L welds. Corros. Sci. 52:1187–1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2009.11.029
Wang Y, Wu X, Li X, Wu W, Gong J (2019) Combined effects of prior plastic deformation and sensitization on hydrogen embrittlement of 304 austenitic stainless steel. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 44:7014–7031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.01.122
Ghosh S, Kain V, Ray A, Roy H, Sivaprasad S, Tarafder S, Ray KK (2009) Deterioration in fracture toughness of 304LN austenitic stainless steel due to sensitization. Metall Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 40:2938–2949
Li S-X, He Y-N, Yu S-R, Zhang P-Y (2013) Evaluation of the effect of grain size on chromium carbide precipitation and intergranular corrosion of 316L stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 66:211–216
Taiwade RV, Shukla R, Vashishtha H, Ingle AV, Dayal RK (2013) Effect of grain size on degree of sensitization of chrome-manganese stainless steel. ISIJ Int. 53:2206–2212. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.53.2206
Pradhan SK, Bhuyan P, Mandal S (2018) Individual and synergistic influences of microstructural features on intergranular corrosion behavior in extra-low carbon type 304L austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 139:319–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.05.014
Jinlong L, Zhuqing W (2019) Sensitization evaluation of the AISI 2205 duplex stainless steel by the IQ value in EBSD technique. Eng. Fail. Anal. 105:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENGFAILANAL.2019.07.001
Barr CM, Thomas S, Hart JL, Harlow W, Anber E, Taheri ML (2018) Tracking the evolution of intergranular corrosion through twin-related domains in grain boundary networks. Npj Mater. Degrad. 2:14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-018-0032-7
Chen AY, Hu WF, Wang D, Zhu YK, Wang P, Yang JH, Wang XY, Gu JF, Lu J (2017) Improving the intergranular corrosion resistance of austenitic stainless steel by high density twinned structure. Scr. Mater. 130:264–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2016.11.032
Zhang R, Qiu Y, Qi Y, Birbilis N (2018) A closer inspection of a grain boundary immune to intergranular corrosion in a sensitised Al-Mg alloy. Corros Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.01.009
Maurotto A, Tsivoulas D, Gu Y, Burke MG (2017) Effects of machining abuse on the surface properties of AISI 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 151:35–44
Srinivasan N, Sunil Kumar B, Kain V, Birbilis N, Joshi SS, Sivaprasad PV, Chai G, Durgaprasad A, Bhattacharya S, Samajdar I (2018) Defining the post-machined sub-surface in austenitic stainless steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 49:2281–2292
Lyon KN, Marrow TJ, Lyon SB (2015) Influence of milling on the development of stress corrosion cracks in austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 218:32–37
Ghosh S, Rana VPS, Kain V, Mittal V, Baveja SK (2011) Role of residual stresses induced by industrial fabrication on stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 32:3823–3831
Kumar PS, Acharyya SG, Rao SVR, Kapoor K (2017) Distinguishing effect of buffing vs. grinding, milling and turning operations on the chloride induced SCC susceptibility of 304L austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 687:193–199
Acharyya SG, Khandelwal A, Kain V, Kumar A, Samajdar I (2012) Surface working of 304L stainless steel: impact on microstructure, electrochemical behavior and SCC resistance. Mater. Charact. 72:68–76
Wang S, Hu Y, Fang K, Zhang W, Wang X (2017) Effect of surface machining on the corrosion behaviour of 316 austenitic stainless steel in simulated PWR water. Corros. Sci. 126:104–120
Suresh G, Parida PK, Bandi S, Ningshen S (2019) Effect of carbon content on the low temperature sensitization of 304L SS and its corrosion resistance in simulated ground water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 226:184–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.01.019
Kolli S, Javaheri V, Ohligschläger T, Kömi J, Porter D (2020) The importance of steel chemistry and thermal history on the sensitization behavior in austenitic stainless steels: experimental and modeling assessment. Mater. Today Commun. 24:101088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2020.101088
Pardo A, Merino MC, Carboneras M, Viejo F, Arrabal R, Munoz J (2006) Influence of Cu and Sn content in the corrosion of AISI 304 and 316 stainless steels in H2SO4. Corros. Sci. 48:1075–1092
Farahat AIZ, El-Bitar TA (2010) Effect of Nb, Ti and cold deformation on microstructure and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steels. Mat. Sci. Eng. A. 527:3662–3669
Advani AH, Atteridge DG, Murr LE (1991) Solution annealing effects on sensitization of 316 stainless steels. Scripta. Metallurgica Mater. 25:2221–2226
Thorvaldsson T, Dunlop G (1983) Grain boundary Cr-depleted zones in Ti and Nb stabilized austenitic stainless steels. J. Mater. Sci. 18:793–803
Kim JK, Kim YH, Lee BH, Kim KY (2011) New findings on intergranular corrosion mechanism of stabilized stainless steels. Electrochim. Acta. 56:1701–1710
Zhang B, Ma X (2019) A review—pitting corrosion initiation investigated by TEM. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35:1455–1465
Verlinden B, Driver J, Samajdar I, Doherty RD (2007) Thermo Mechanical Processing of Metallic Materials, 1st edn. Pergamon Materials Series, Great Briton
Watanabe Y, Kain V, Tonozuka T, Shoji T, Kondo T, Masuyama F (2000) Effect of Ce addition on the sensitization properties of stainless steels. Scripta. Mater. 42:307–312
Jeon S, Haeng D, Kim H, Park Y (2015) Effect of Ce addition on the precipitation of deleterious phases and the associated intergranular corrosion resistance of 27Cr–7Ni hyper duplex stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 90:313–322
Watanabe T (1984) Approach to grain boundary design for strong and ductile polycrystals. Res. Mech. 11:47–84
Watanabe T (2011) Grain boundary engineering: historical perspective and future prospects. J. Mater. Sci. 46:4095–4115
Jones R, Randle V (2010) Sensitisation behaviour of grain boundary engineered austenitic stainless steel. Mat. Sci. Eng. A. 527:4275–4280
Owen G, Randle V (2006) On the role of iterative processing in grain boundary engineering. Scripta. Mater. 55:959–962
Engelberg DL, Newman RC, Marrow TJ (2008) Effect of thermomechanical process history on grain boundary control in an austenitic stainless steel. Scripta. Mater. 59:554–557
Engelberg DL, Humphreys FJ, Marrow TJ (2008) The influence of low-strain thermo-mechanical processing on grain boundary network characteristics in type 304 austenitic stainless steel. J. Microsc. 230:435–444
Michiuchi M, Kokawa H, Wang ZJ, Sato YS, Sakai K (2006) Twin-induced grain boundary engineering for 316 austenitic stainless steel. Acta Mater. 54:5179–5184
Johnson OK, Schuh CA (2013) The uncorrelated triple junction distribution function: towards grain boundary network design. Acta Mater. 61:2863–2873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2013.01.025
Tsurekawa S, Nakamichi S, Watanabe T (2006) Correlation of grain boundary connectivity with grain boundary character distribution in austenitic stainless steel. Acta Mater. 54:3617–3626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2006.03.048
Rahimi S, Engelberg DL, Marrow TJ (2010) Characterisation of grain boundary cluster compactness in austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 26:670–675
Raveendra S, Kanjarala AK, Paranjape H, Mishra SK, Mishra S, Delannay L, Samajdar I, Vanhoutte P (2011) Strain mode dependence of deformation texture developments:microstructural origin. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 42A:2113–2124
Srinivasan N, Kain V, Samajdar I, Krishna KVM, Sivaprasad PV (2017) Plane strain compression testing of Sanicro 28 by channel-die compression test: a direct microstructural observation. Mater. Today Proc. 4:9888–9892
Hong Y, Zhou C, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Zheng J, Chen X, An B (2018) Formation of strain-induced martensite in selective laser melting austenitic stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.10.121
Conde A, García I, De Damborenea JJ (2001) Pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel after laser surface melting in argon and nitrogen atmospheres. Corros. Sci. 43:817–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(00)00114-1
Kwok CT, Man HC, Cheng FT (1998) Cavitation erosion and pitting corrosion of laser surface melted stainless steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 99:295–304
Mudali UK, Dayal RK, Goswami GL (1995) Desensitisation of austenitic stainless steels using laser surface melting. Surf. Eng. 11:331–336. https://doi.org/10.1179/sur.1995.11.4.331
Parvathavarthini N, Subbarao RV, Kumar S, Dayal RK, Khatak HS (2001) Elimination of intergranular corrosion susceptibility of cold-worked and sensitized AISI 316 SS by laser surface melting. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 10:5–13. https://doi.org/10.1361/105994901770345277
Mudali UK, Pujar MG, Dayal RK (1998) Effects of laser surface melting on the pitting resistance of sensitized nitrogen-bearing type 316L stainless steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 7:214–220. https://doi.org/10.1361/105994998770347945
Stewart J, Williams DEE (1992) The initiation of pitting corrosion on austenitic stainless steel: on the role and importance of sulphide inclusions. Corros. Sci. 33:457–474
Hong Y, Zhou C, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Zheng J, Chen X, An B (2019) Formation of strain-induced martensite in selective laser melting austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 740–741:420–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.10.121
De Assis KS, Rocha AC, Margarit-Mattos ICP, Serra FAS, Mattos OR (2013) Practical aspects on the use of on-site double loop electrochemical potentiodynamic reactivation technique (DL-EPR) for duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 74:250–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2013.04.050
Bose A, De PK (1987) An EPR study on the influence of prior cold work on the degree of sensitization of AISI 304 stainless steel. Corrosion 43:624–631
De Tiedra P, Martín Ó, López M, San-Juan M (2011) Use of EPR test to study the degree of sensitization in resistance spot welding joints of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 53:1563–1570
Momeni M, Moayed MH, Davoodi A (2010) Tuning DOS measuring parameters based on double-loop EPR in H2SO4 containing KSCN by Taguchi method. Corros. Sci. 52:2653–2660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.04.015
Kauss N, Heyn A, Halle T, Rosemann P (2019) Detection of sensitisation on aged lean duplex stainless steel with different electrochemical methods. Electrochim. Acta. 317:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.05.081
Pujar MG, Parvathavarthini N, Dayal RK, Thirunavukkarasu S (2009) Assessment of intergranular corrosion (IGC) in 316 (N) stainless steel using electrochemical noise (EN) technique. Corros. Sci. 51(8):1707–1713
Kikuchi H, Sumimoto T, Kamada Y, Kobayashi S (2013) Magnetic NDE for sensitization of Inconel 600 alloy. J. Magn. 18:348–351. https://doi.org/10.4283/JMAG.2013.18.3.348
Xu J, Wu X, Han EH (2013) Acoustic emission response of sensitized 304 stainless steel during intergranular corrosion and stress corrosion cracking. Corros. Sci. 73:262–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2013.04.014
Ortiz N, Curiel FF, López VH, Ruiz A (2013) Evaluation of the intergranular corrosion susceptibility of UNS S31803 duplex stainless steel with thermoelectric power measurements. Corros. Sci. 69:236–244
Takaya S, Suzuki T, Matsumoto Y, Demachi K, Uesaka M (2004) Estimation of stress corrosion cracking sensitivity of type 304 stainless steel by magnetic force microscope. J. Nucl. Mater. 327:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2004.01.016
Yanliang H, Kinsella B, Becker T (2008) Sensitisation identification of stainless steel to intergranular stress corrosion cracking by atomic force microscopy. Mater. Lett. 62:1863–1866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2007.10.040
Číhal V (1980) A potentiokinetic reactivation method for predicting the I.C.C. and I.G.S.C.C. sensitivity of stainless steels and alloys. Corros. Sci. 20:737–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-938x(80)90054-2
Cihal V, Stefec R, Shoji T, Watanabe T, Kain V (2004) Electrochemical potentiodynamic reactivation: development and applications of the EPR test. Key. Eng. Mat. 261–263:855–864
Majidi AP, Streicher MA (1984) The double loop reactivation method for detecting sensitization in AISI 304 stainless steels. Corrosion 40:584–593
Cihal V, Stefec R (2001) On the development of the electrochemical potentiokinetic method. Electrochim. Acta. 46:3867–3877. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(01)00674-0
Doerr C, Kim JY, Singh P, Wall JJ, Jacobs LJ (2017) Evaluation of sensitization in stainless steel 304 and 304L using nonlinear Rayleigh waves. NDT E Int. 88:17–23
Jothilakshmi N, Nanekar PP, Kain V (2013) Assessment of intergranular corrosion attack in austenitic stainless steel using ultrasonic measurements. Corrosion 9312:388–395
Remillieux MC, Kaoumi D, Ohara Y, StuberGeesey MA, Xi L, Schoell R, Bryan CR, Enos DG, Summa DA, Ulrich TJ, Anderson BE, Shayer Z (2020) Detecting and imaging stress corrosion cracking in stainless steel, with application to inspecting storage canisters for spent nuclear fuel. NDT E Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2019.102180
Doerr C, Lakocy A, Kim JY, Singh PM, Wall JJ, Qu J, Jacobs LJ (2017) Evaluation of the heat-affected zone (HAZ) of a weld joint using nonlinear Rayleigh waves. Mater. Lett. 190:221–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.01.021
Shaikh H, Sivaibharasi N, Sasi B, Anita T, Amirthalingam R, Rao BPC, Jayakumar T, Khatak HS, Raj B (2006) Use of eddy current testing method in detection and evaluation of sensitisation and intergranular corrosion in austenitic stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 48:1462–1482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.05.017
Kelidari Y, Kashefi M, Mirjalili M, Seyedi M, Krause TW (2020) Eddy current technique as a nondestructive method for evaluating the degree of sensitization of 304 stainless steel. Corros Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108742
Tucker WC, Lockhart P, Guzas E (2019) Evaluating sensitized chromium steel alloys with induction infrared thermography. J Nondestruct Eval. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-019-0581-x
Roberts M, Wang K, Guzas E, Lockhart P, Tucker W (2021) Induction infrared thermography for non-destructive evaluation of alloy sensitization. J. Nondestruct. Eval 10(1063/1):5099848
Fregonese M, Idrissi H, Mazille H, Renaud L, Cetre Y (2001) Initiation and propagation steps in pitting corrosion of austenitic stainless steels: Monitoring by acoustic emission. Corros. Sci. 43:627–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(00)00099-8
Mazille H, Rothea R, Tronel C (1995) An acoustic emission technique for monitoring pitting corrosion of austenitic stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 37:1365–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-938X(95)00036-J
Mukhopadhyay CK, Jayakumar T, Haneef TK, Suresh Kumar S, Rao BPC, Goyal S, Gupta SK, Bhasin V, Vishnuvardhan S, Raghava G, Gandhi P (2014) Use of acoustic emission and ultrasonic techniques for monitoring crack initiation/growth during ratcheting studies on 304LN stainless steel straight pipe. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 116:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpvp.2014.01.005
Shaikh H, Amirthalingam R, Anita T, Sivaibharasi N, Jaykumar T, Manohar P, Khatak HS (2007) Evaluation of stress corrosion cracking phenomenon in an AISI type 316LN stainless steel using acoustic emission technique. Corros. Sci. 49:740–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2006.06.007
Mudali UK, Rao CB, Raj B (2006) Intergranular corrosion damage evaluation through laser scattering technique. Corros. Sci. 48:783–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2005.02.027
Jingpin J, Junjun S, Guanghai L, Bin W, Cunfu H (2015) NDT & E international evaluation of the intergranular corrosion in austenitic stainless steel using collinear wave mixing method. NDT E Int. 69:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2014.09.001
Knight SP, Salagaras M, Trueman AR (2011) The study of intergranular corrosion in aircraft aluminium alloys using X-ray tomography. Corros. Sci. 53:727–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.11.005
Ruiz A, Ortiz N, Medina A, Kim JY, Jacobs LJ (2013) Application of ultrasonic methods for early detection of thermal damage in 2205 duplex stainless steel. NDT E Int. 54:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2012.11.009
Li F, Slusarski K, Xiang D, Qin Y, Pond RB (2010) Measurements of degree of sensitization (DoS) in aluminum alloys using EMAT ultrasound. Ultrasonics 51:561–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2010.12.009
Stella J, Cerezo J, Rodríguez E (2009) Characterization of the sensitization degree in the AISI 304 stainless steel using spectral analysis and conventional ultrasonic techniques. NDT E Int. 42:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ndteint.2008.11.005
Ghanei S, Kashefi M, Mazinani M (2013) Eddy current nondestructive evaluation of dual phase steel. Mater. Des. 50:491–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.040
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivasan, N. Sensitization of Austenitic Stainless Steels: Current Developments, Trends, and Future Directions. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 10, 133–147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-021-00724-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-021-00724-y